Table: Hard Link vs. Symbolic Link
| Link Type | Definition | Use Case | Limitation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Hard Link | Direct reference to the same inode | Duplicate names for the same data | Cannot span filesystems |
| Symbolic Link | Special file containing target’s pathname | Flexible alias or shortcut | Broken if the target path changes |
1. Create a Symbolic Link
Use theln utility with the -s (or --symbolic) flag:
<path_to_target>: File or directory you want to reference.<path_to_link>: Name (and optional path) for the symlink.
You can use absolute or relative paths. Relative links remain valid if you move the containing directory, as long as the relative structure doesn’t change.
2. Verify a Symlink
List files with detailed info:- Leading
ldenotes a symlink. - Arrow (
->) shows the target path.
3. Permissions and Access
Symbolic links always display full permissions (rwxrwxrwx), but actual access is governed by the target’s permissions:
Even though the symlink appears writable, you’re blocked because the real file (
/etc/fstab) isn’t writable by your user.4. Absolute vs. Relative Paths
Absolute paths may break if you rename or move parent directories:/home/alex as long as the relative tree is preserved.
5. Linking Directories & Cross-Filesystem
Since symlinks store paths, you can reference directories and even across different filesystems: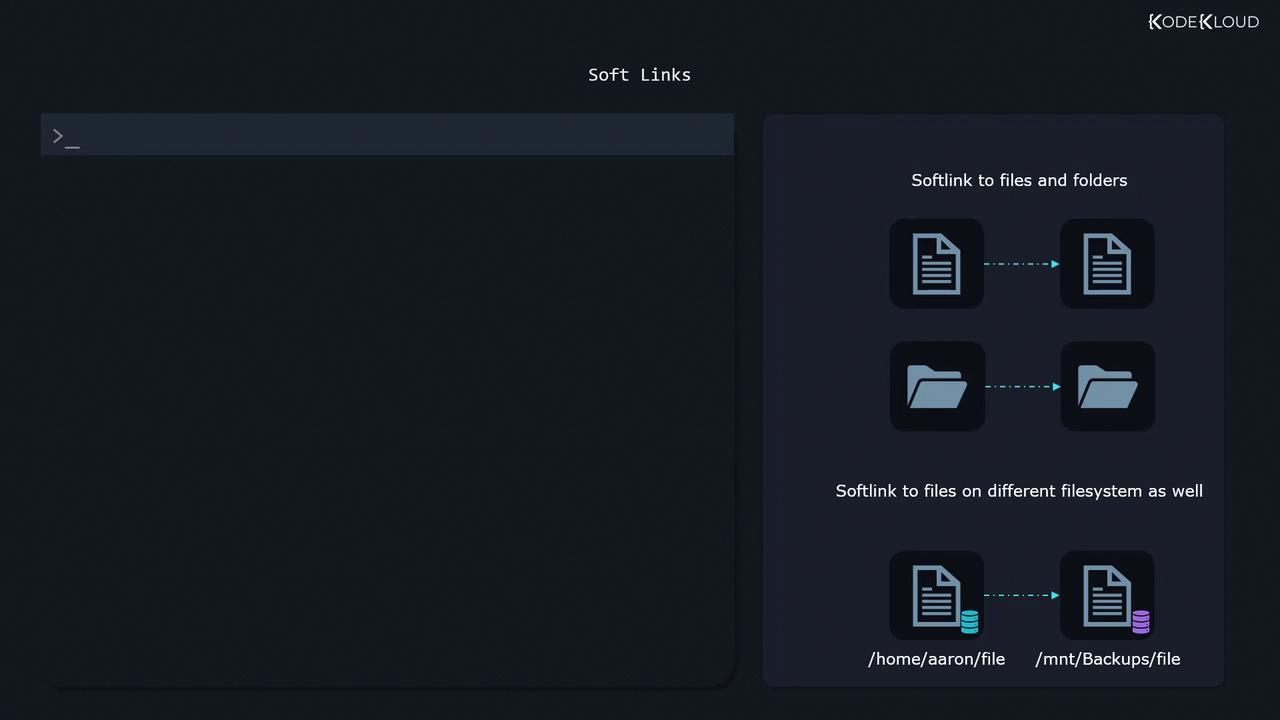
Further Reading
- GNU ln manual
- readlink(1) Manual Page
- Linux Filesystem Hierarchy: Filesystem layout