Linux Professional Institute LPIC-1 Exam 101
GNU and Unix Commands
Process Text Streams Using Filters
In Linux, nearly every interaction—SSH sessions, command outputs, system logs, and configuration files—is plain text. Mastering text filters allows you to view, transform, and compare these streams efficiently at the command line.
Viewing Files with cat, tac, head, and tail
Displaying Entire and Reversed Files
Use cat for quick, on-screen dumps of small files:
cat /home/users.txt
# Output:
# user1
# user2
# user3
# user4
# user5
# user6
To flip the order (last line first), pipe through tac:
tac /home/users.txt
# Output:
# user6
# user5
# user4
# user3
# user2
# user1
Inspecting the Start or End of Large Logs
Log files can grow huge. Quickly grab the first or last N lines:
Last 10 lines (default):
tail /var/log/dnf.logLast 20 lines:
tail -n 20 /var/log/dnf.logFirst 20 lines:
head -n 20 /var/log/dnf.log
These let you preview recent errors or initial startup messages without opening the full file.
Automating In-File Replacements with sed
The stream editor sed excels at find-and-replace tasks:
- Preview changes (no file modified):
sed 's/canda/canada/g' userinfo.txt - Apply in-place (
-i) substitutions:sed -i 's/canda/canada/g' userinfo.txt cat userinfo.txt
s/pattern/replacement/greplaces all occurrences on each line.- The
-iflag edits the file directly.
Warning
Always preview your sed commands without -i first. To keep a backup, use -i.bak (e.g., sed -i.bak 's/old/new/g' file).
Extracting Fields with cut
When working with delimited data (spaces, commas, or tabs), cut slices out columns:
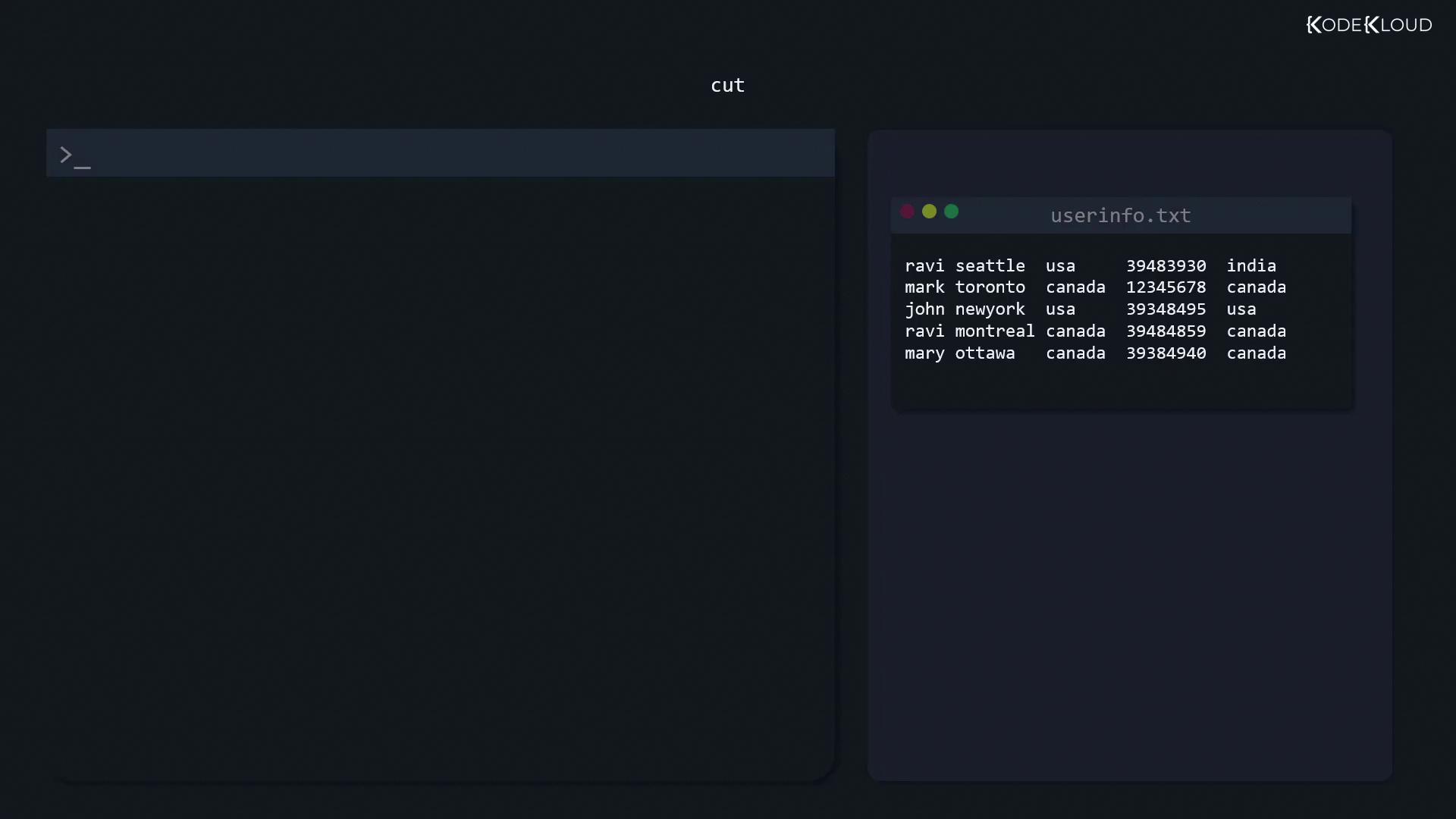
- By space delimiter: extract the first field (name)
cut -d ' ' -f 1 userinfo.txt - By comma delimiter: extract the third field (country) and save
cut -d ',' -f 3 userinfo.txt > countries.txt
Listing Unique Entries with sort and uniq
The uniq filter only removes adjacent duplicates—sort first to catch all duplicates:
sort countries.txt | uniq
Note
If your file isn’t sorted, uniq may leave non-adjacent duplicates. Always sort before uniq for a full cleanse.
Comparing Files with diff
Spot differences between configuration files using:
- Basic side-by-side:
diff file1 file2 - Unified context (
-c):diff -c file1 file2 - Two-column view (
-y):diff -y file1 file2
This helps pinpoint changes before editing or deploying configurations.
Quick Reference: Linux Text Filters
| Command | Purpose | Basic Usage |
|---|---|---|
cat | Dump entire file | cat file.txt |
tac | Reverse file order | tac file.txt |
head | Show first N lines | head -n 20 file.log |
tail | Show last N lines | tail -n 20 file.log |
sed | Stream editor (find & replace) | sed -i 's/old/new/g' file.txt |
cut | Extract columns from delimited streams | cut -d',' -f3 file.csv |
sort | Sort lines alphabetically or numerically | sort file.txt |
uniq | Remove adjacent duplicates | sort file.txt | uniq |
diff | Compare files line by line | diff -y file1 file2 |
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content