Traditional Programming vs. Machine Learning
In traditional programming, you explicitly write rules (business logic) that transform input data into output. For example, converting US dollars to another currency involves fetching the current exchange rate and applying it. Machine Learning flips this paradigm: it ingests historical exchange-rate data and learns the conversion pattern without you specifying the rule.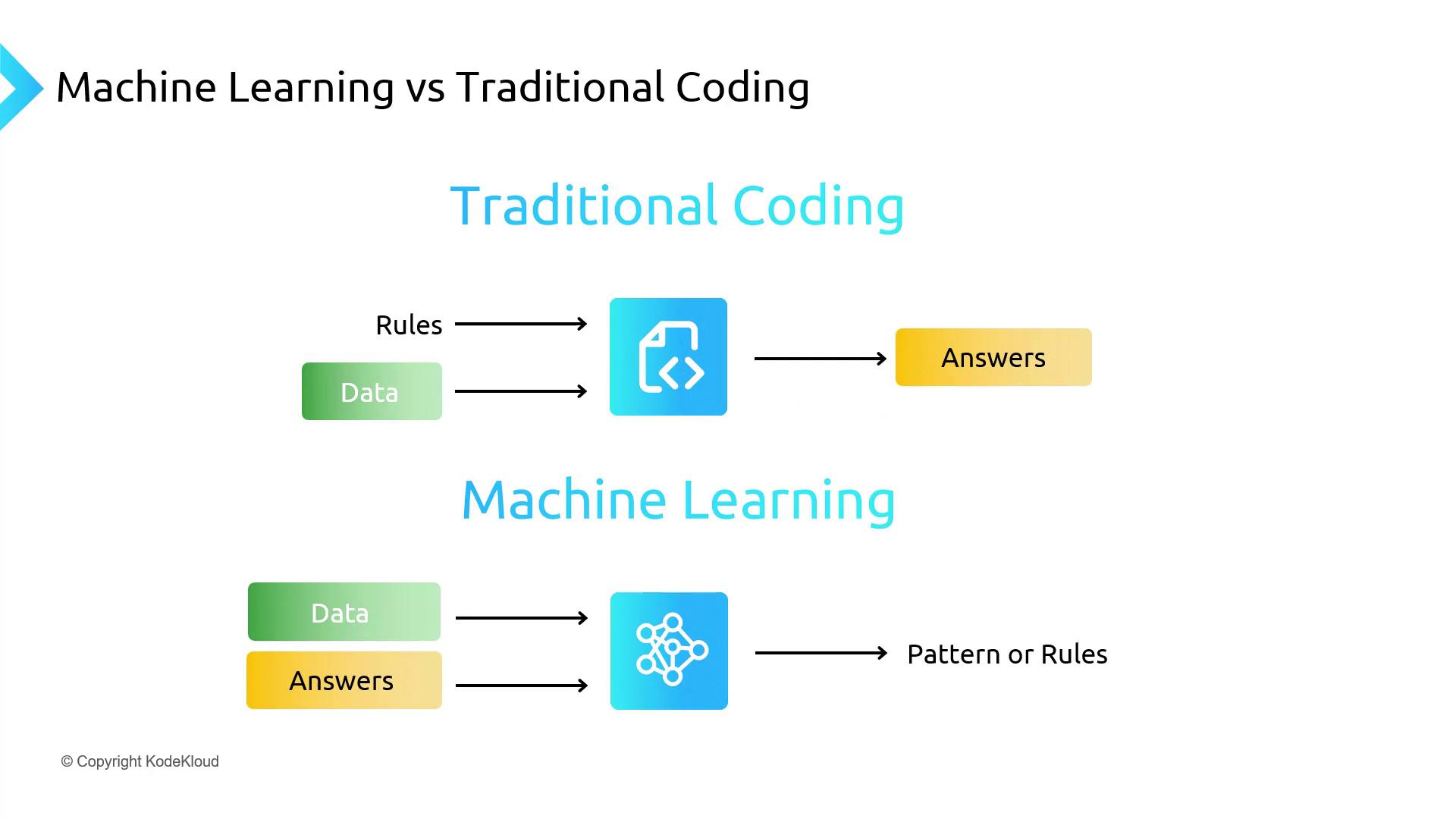
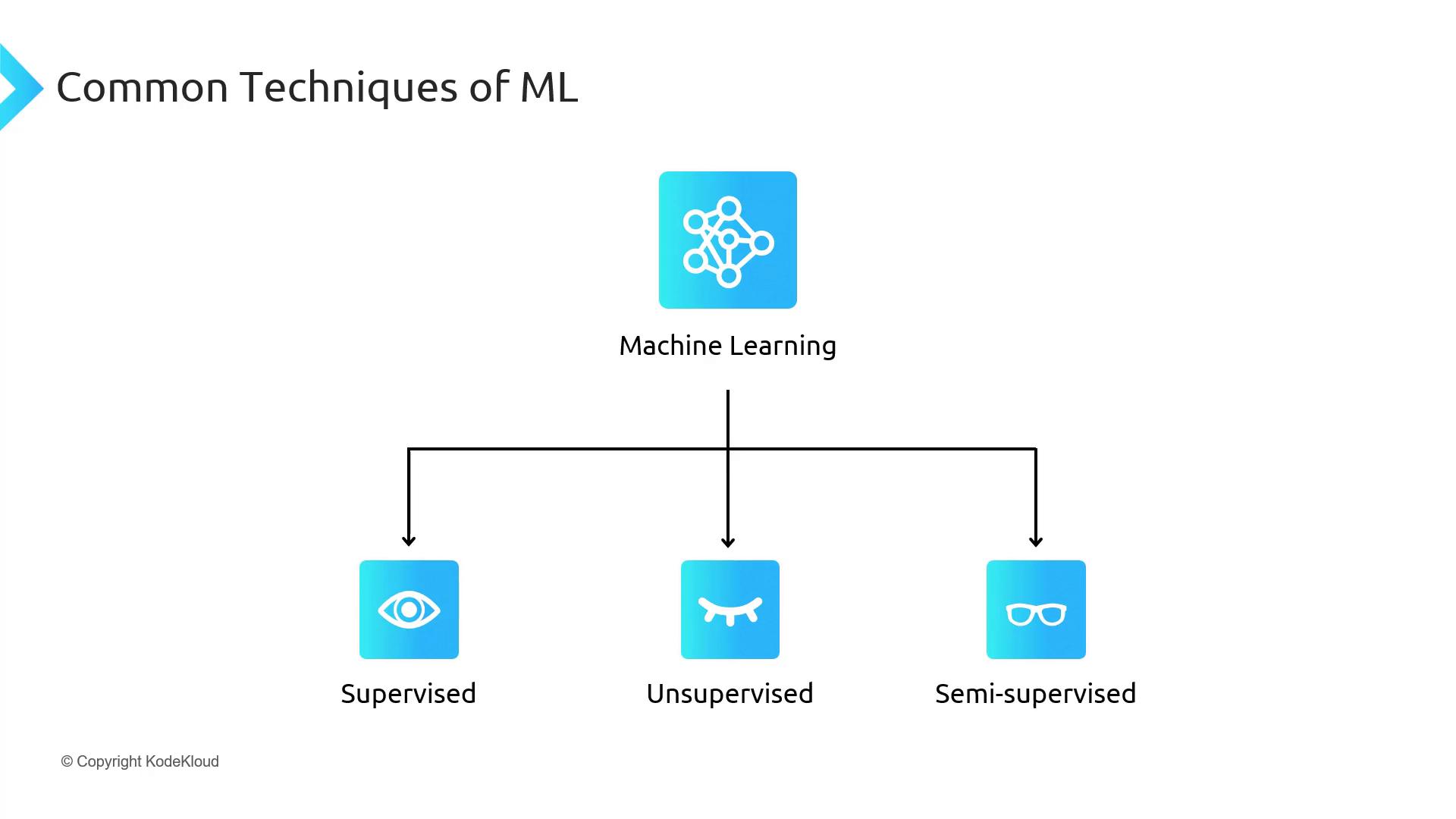
Common Machine Learning Techniques
Machine Learning algorithms typically fall into three categories:| Technique | Data Type | Goal |
|---|---|---|
| Supervised Learning | Labeled data | Predict labels for new inputs |
| Unsupervised Learning | Unlabeled data | Discover patterns or clusters in the dataset |
| Semi-Supervised | Mixed data | Combine a small labeled set with large unlabeled data |
Supervised Learning
Supervised learning trains models on labeled datasets, teaching them to map inputs to known outputs. Once trained, the model generalizes to classify or predict labels on unseen data.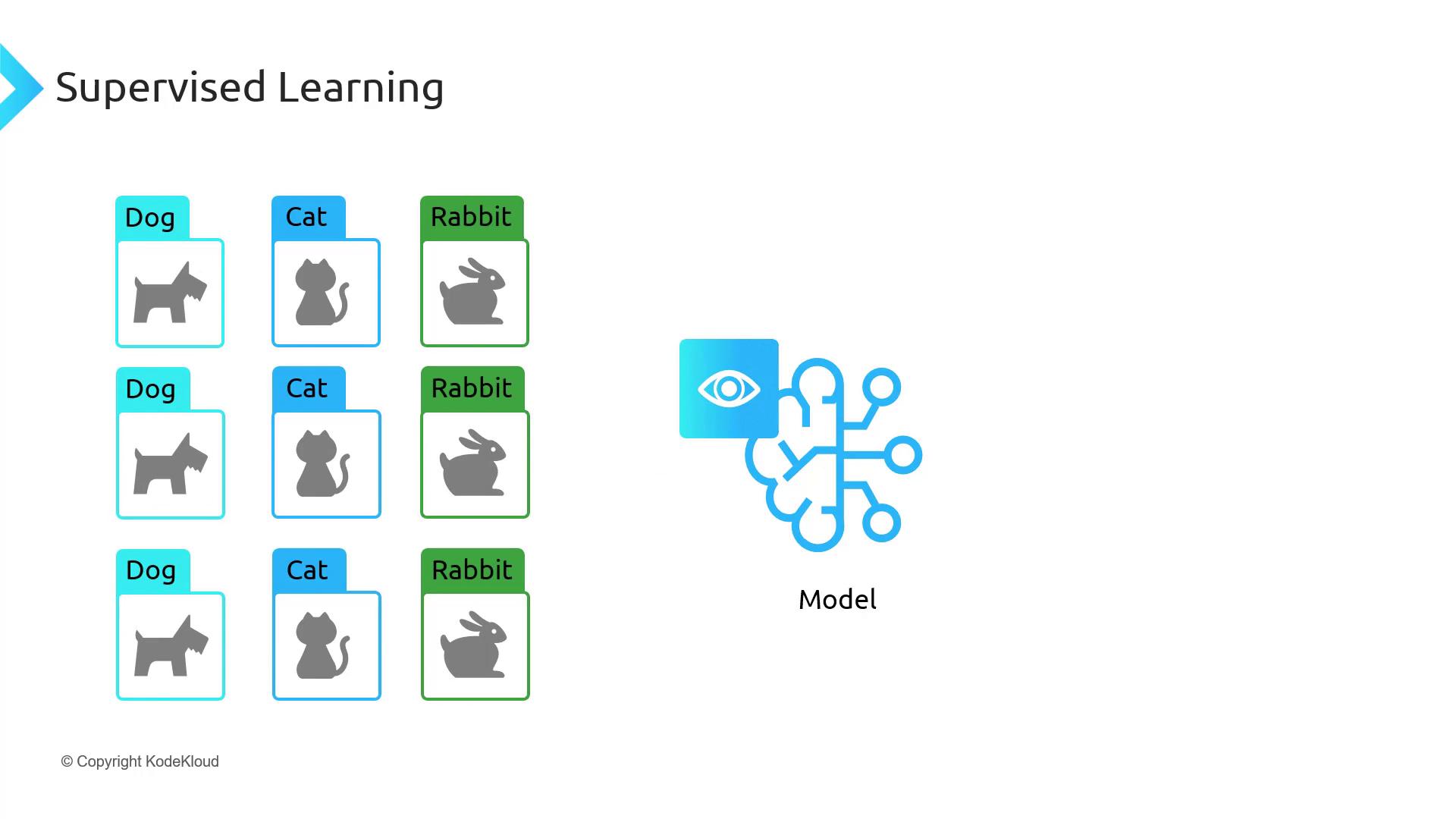
Ensure your labeled dataset covers diverse examples to avoid bias and improve model accuracy.
Unsupervised Learning
With no labels, unsupervised algorithms uncover inherent structures—such as clusters or hidden features—by analyzing the input data alone. This is useful for customer segmentation, anomaly detection, and feature extraction.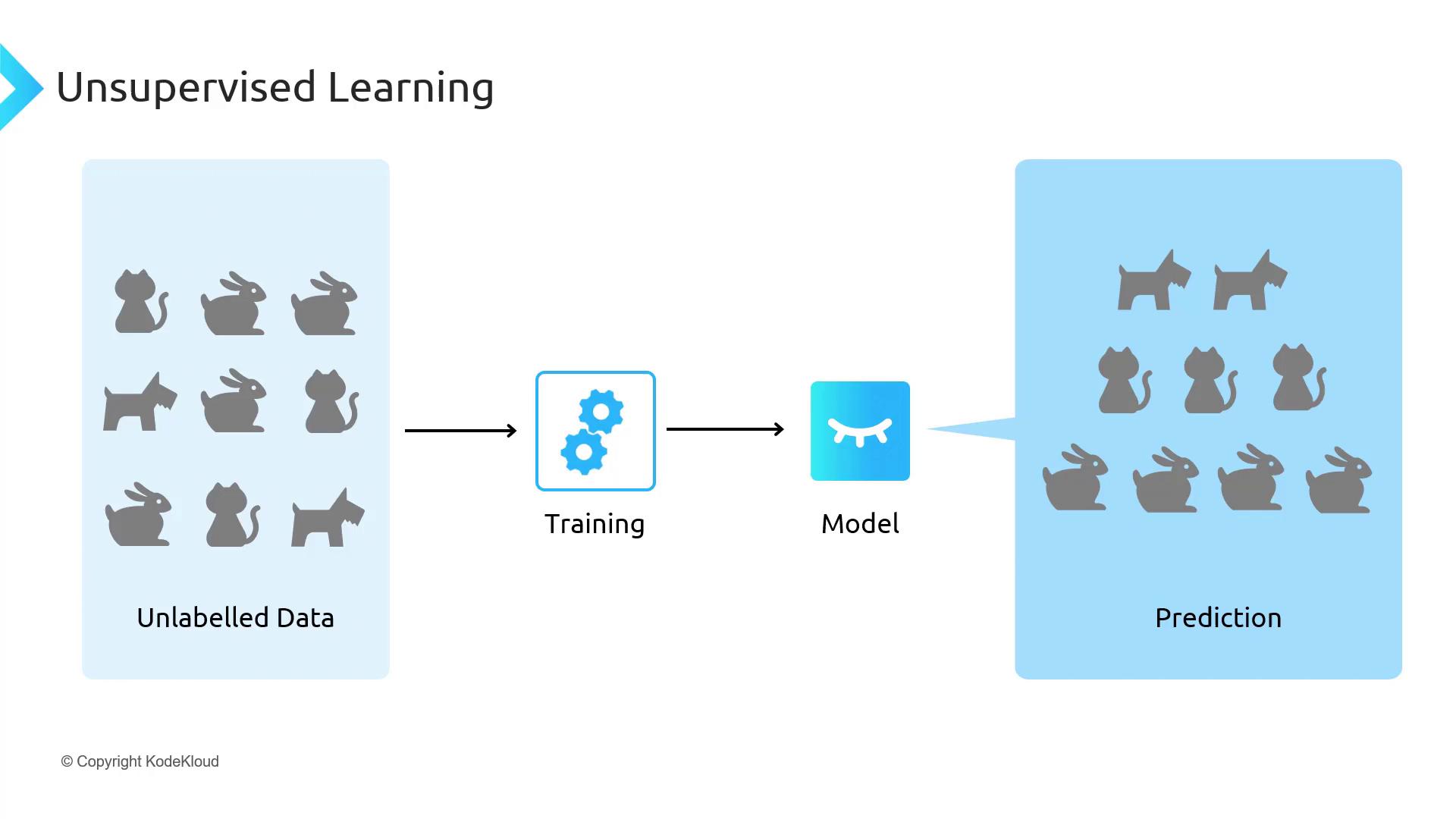
Semi-Supervised Learning
Semi-supervised learning bridges supervised and unsupervised methods by pairing a small amount of labeled data with a large pool of unlabeled data. This approach often yields high accuracy while reducing labeling costs.Quality of unlabeled data affects performance. Preprocess and clean data to avoid propagating errors.
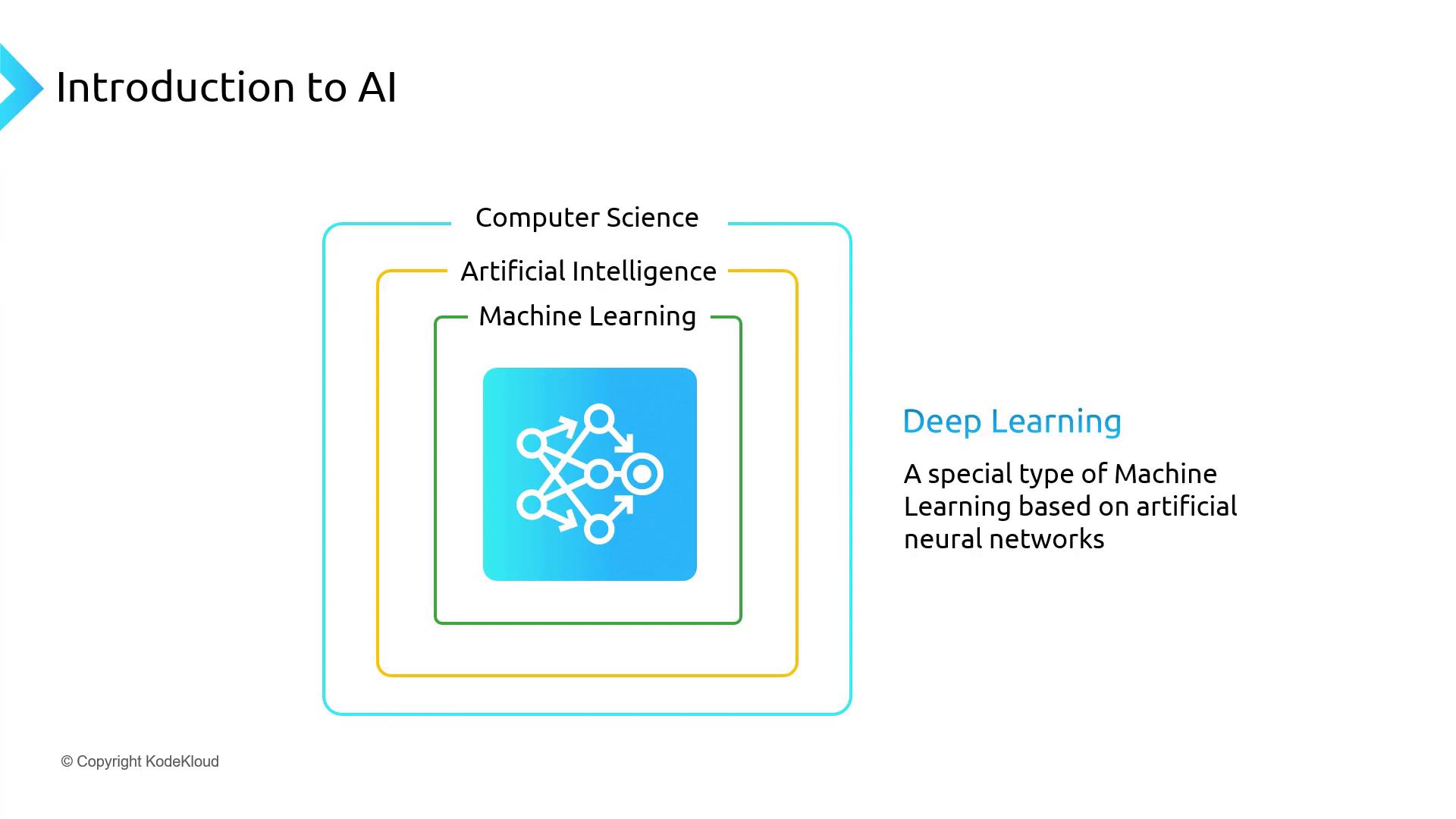
Deep Learning
Deep Learning models consist of multiple layers of interconnected neurons, inspired by the human brain. These neural networks can learn complex representations across supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised tasks, making them highly versatile for image recognition, natural language processing, and more.Summary
- AI: Broad field that imbues machines with human-like intelligence.
- Machine Learning: Subset of AI focused on learning patterns from data.
- Deep Learning: Advanced ML using neural networks; excels with unstructured data and demands powerful hardware.