Key Phases of Azure Blueprints
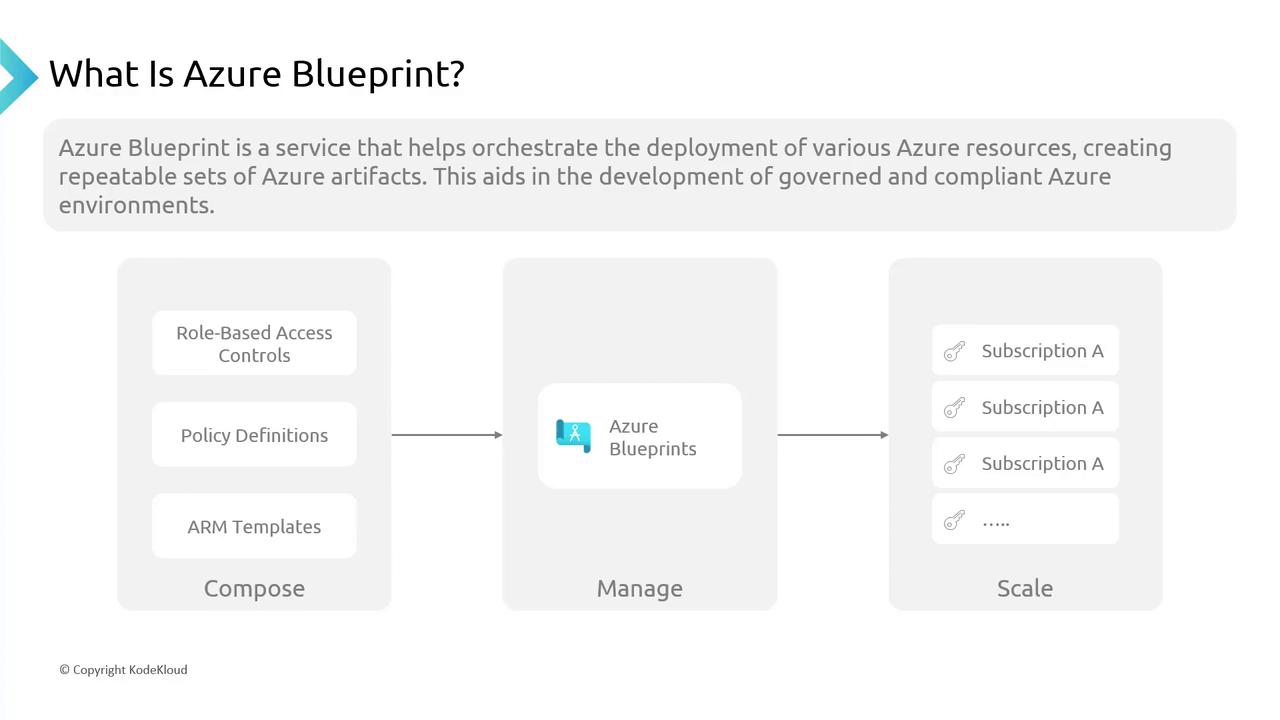
Azure Blueprints operate through three essential phases: Compose, Manage, and Scale.Compose
During the compose phase, you create a blueprint by integrating three vital components:- RBAC: Defines access control by specifying who can manage which resources. For example, you can restrict network configuration changes to network administrators only.
- Policy Definitions: Establish the guardrails for resource deployments by enforcing conditions such as limiting virtual machine locations to approved regions.
- ARM Templates: Serve as the architectural framework, enabling the deployment of resources like multi-tier applications, virtual machines, and databases.
Manage
Once your blueprint is composed, apply it to an Azure environment—whether it’s a single subscription or multiple subscriptions under various management groups. For instance, after creating a blueprint for a secure web application environment, you can deploy it consistently across different subscriptions, ensuring uniform policies and configurations. This phase is comparable to utilizing a building blueprint across multiple construction sites, ensuring every structure maintains the same design integrity.Scale
As your organization evolves, the need to adjust your blueprint may arise. Scaling involves updating your blueprint to accommodate changes, similar to modifying a building plan to include additional floors or new facilities. With simple updates and re-assignments, you can ensure that new deployments remain both compliant and secure.Remember that scaling a blueprint is a continuous process that ensures your infrastructure adapts to new business needs while maintaining compliance.
Blueprint Analogy for Better Understanding
Imagine a building blueprint that guides architects and builders with clear, detailed construction instructions. Azure Blueprints function similarly for IT architects by providing a master plan for Azure service deployment.- Compose: Like drafting an architectural plan with room layouts and essential utilities.
- Manage: Similar to executing the blueprint at multiple construction sites, ensuring consistency.
- Scale: Adjusting the blueprint for expansion, much like planning for additional buildings as demand increases.
Key Features of Azure Blueprints
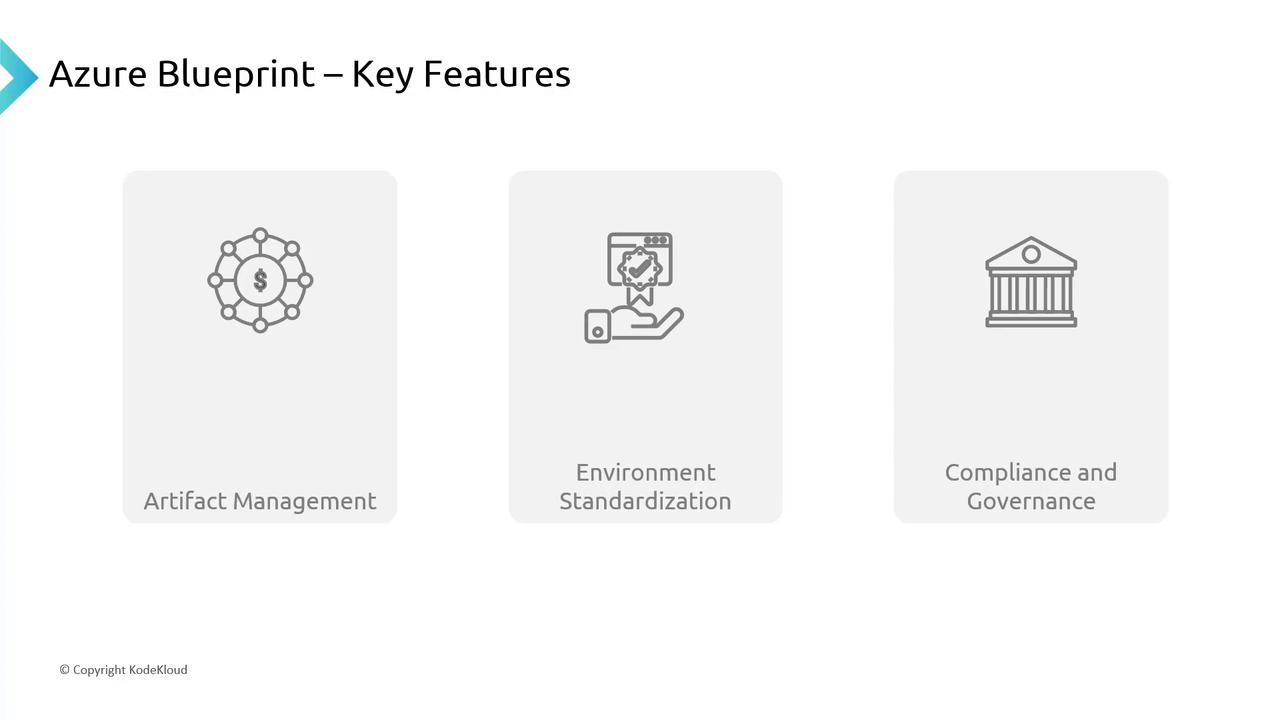
Azure Blueprints offer an integrated approach to manage your cloud infrastructure through:Artifact Management
Deploy a variety of components seamlessly. For example, when setting up a digital storefront, you can:- Deploy separate resource groups for distinct store components.
- Assign RBAC roles such that only authorized teams (e.g., the finance team) have access to sensitive databases.
- Enforce regional deployment policies.
- Utilize ARM templates to automatically provision virtual machine instances.
Environment Standardization
Just as franchise outlets maintain a consistent brand experience, Azure Blueprints ensure your cloud environments have a uniform setup. This consistency is particularly valuable when deploying similar environments for multiple clients, eliminating configuration discrepancies.Compliance and Governance
Ensuring regulatory compliance is critical, especially in sectors like healthcare. Azure Blueprints enforce strict policies—such as data encryption for data at rest and in transit—ensuring each deployment meets necessary standards. This robust approach minimizes human error and enhances security.ARM Templates vs. Azure Blueprints
ARM templates are JSON files that detail specific Azure resources and their configurations, such as a virtual machine along with its network settings. In contrast, Azure Blueprints provide a high-level solution by bundling ARM templates with governance components like RBAC assignments and policy definitions. Consider ARM templates as the detailed plans for constructing individual houses, whereas Azure Blueprints represent the master plan for an entire housing complex, including roads, parks, and community guidelines.Working with Azure Blueprints in the Azure Portal
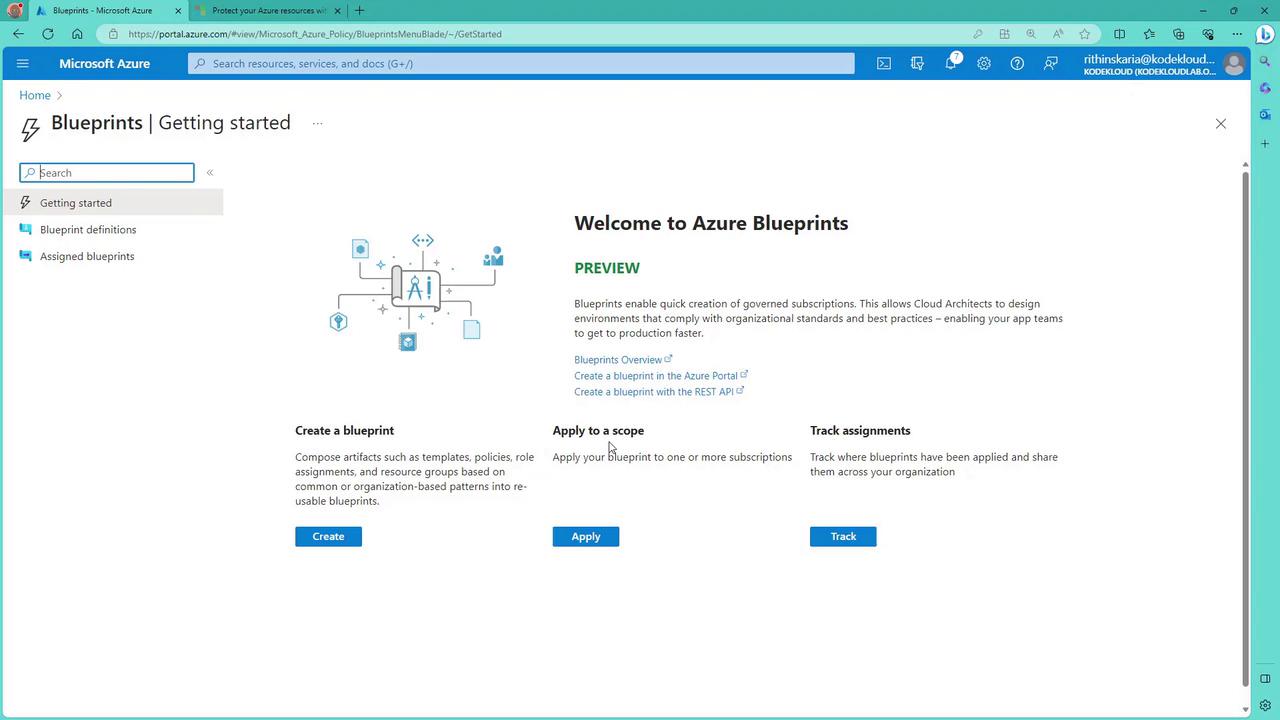
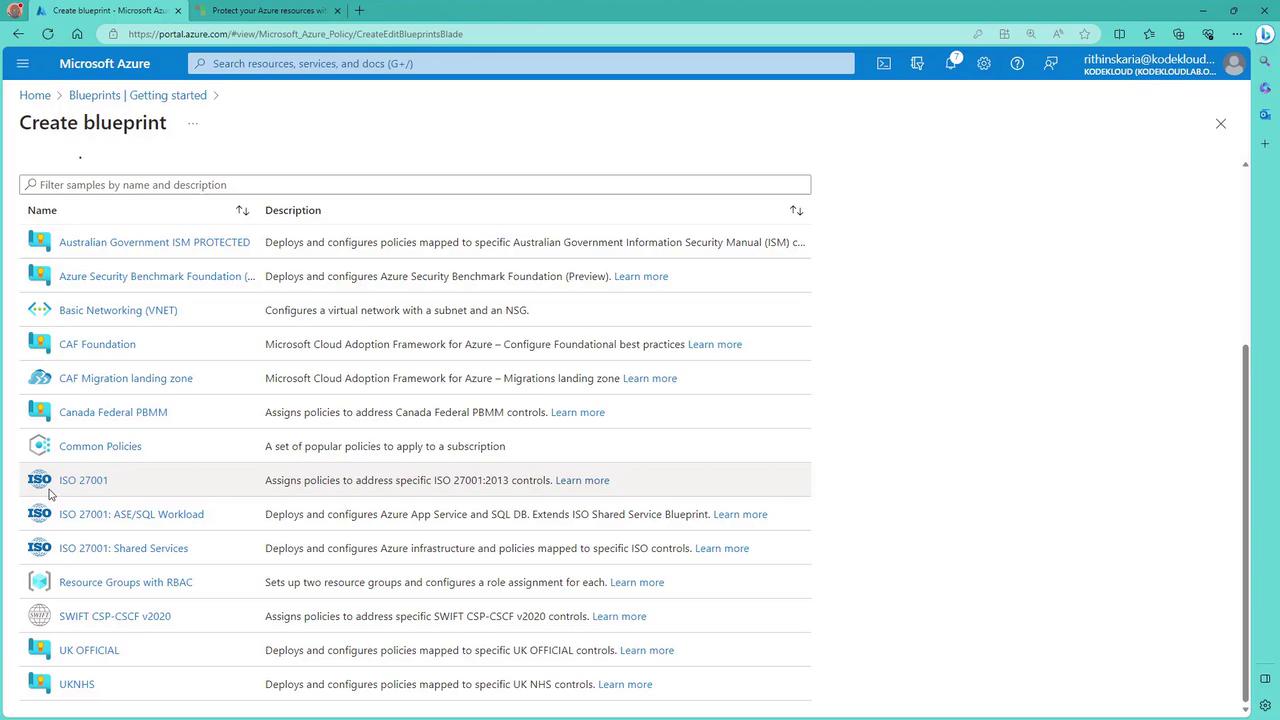
Follow these steps to get started with Azure Blueprints in the Azure Portal:- Create a Blueprint:
Begin by creating a blueprint that includes artifacts such as ARM templates, policy definitions, role assignments, and resource groups.
-
Save and Publish:
Once the blueprint is configured, save your draft and publish it (e.g., version 1.0). -
Assign the Blueprint:
Assign the blueprint to your chosen scope (subscription or management group). During this process, any dynamic values (like resource group names or locations) will be prompted for input while static values remain unchanged.
-
Add Artifacts:
Within the scope, add artifacts such as resource groups, policy assignments, role assignments, and ARM templates. For example, to deploy a storage account using an ARM template, you can use the JSON snippet below:This ARM template provisions a standard storage account.
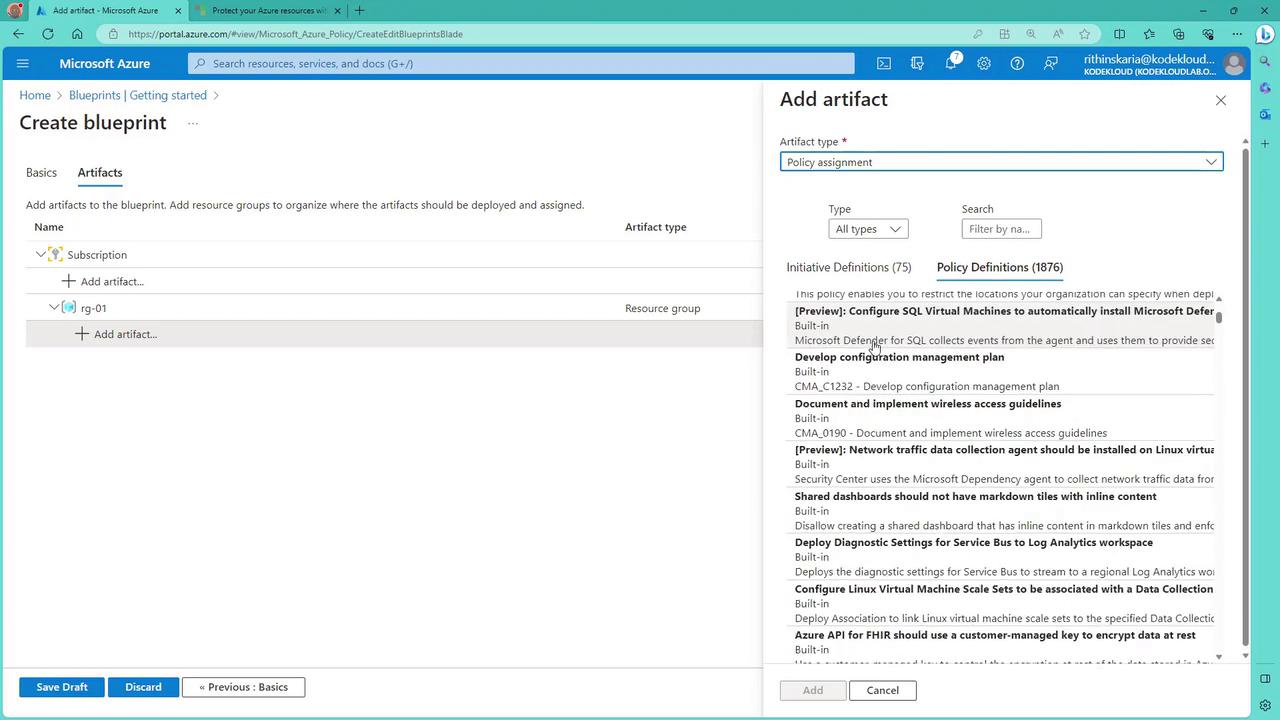
- Configure Role Assignments and Additional Artifacts:
Add further artifacts such as role assignments. For instance, assign a Reader role to a specific group for monitoring purposes.
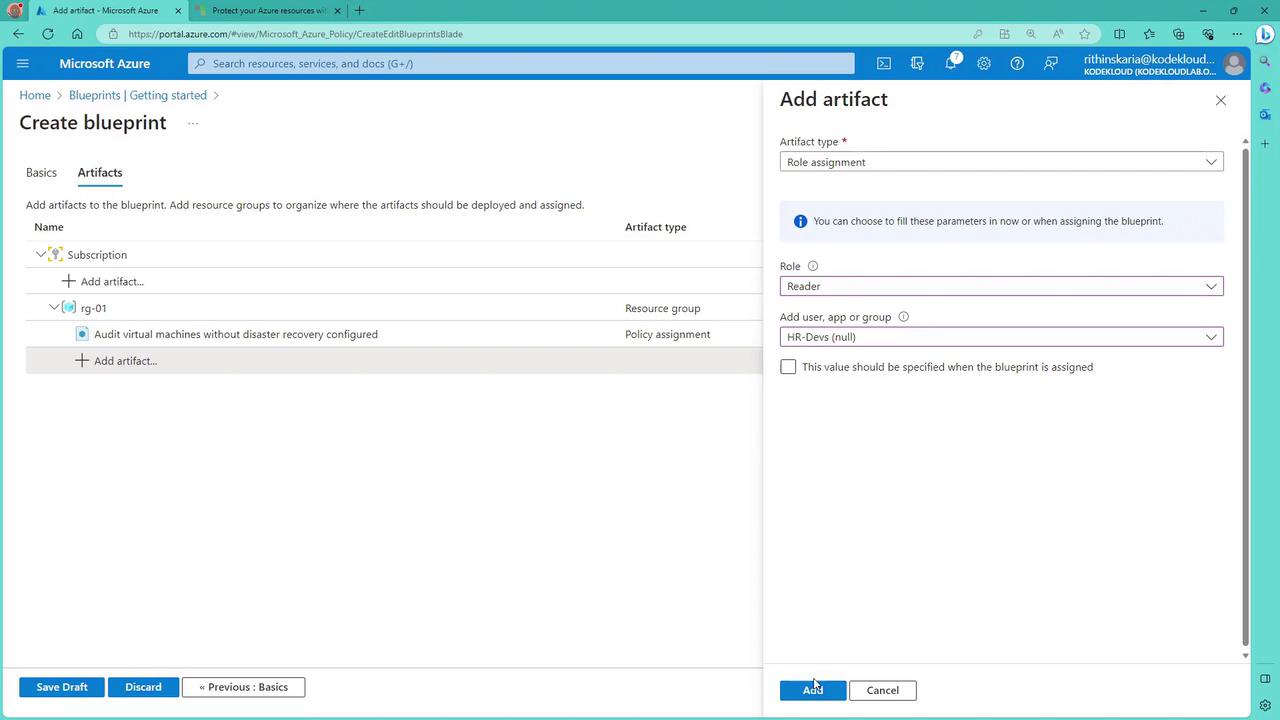
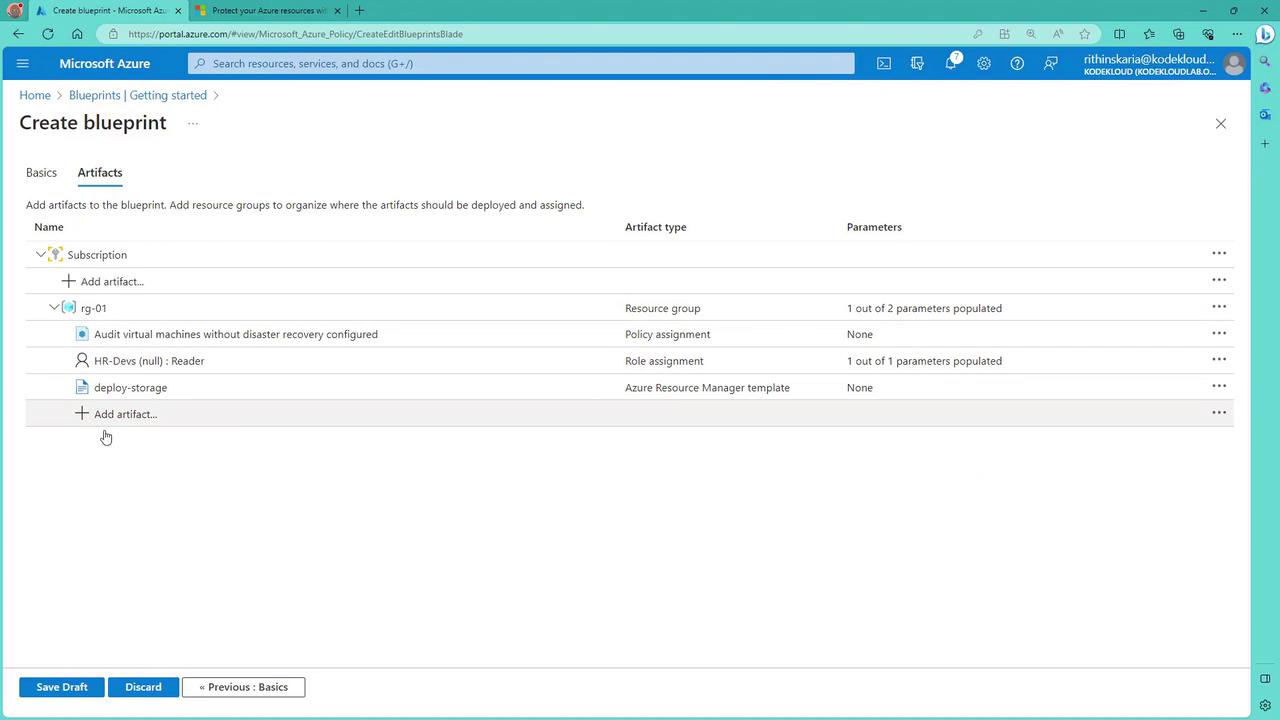
- Finalize and Track Deployments:
After adding all artifacts and publishing the blueprint, assign it to deploy the resources. You can then track the blueprint assignment status via the Azure portal.
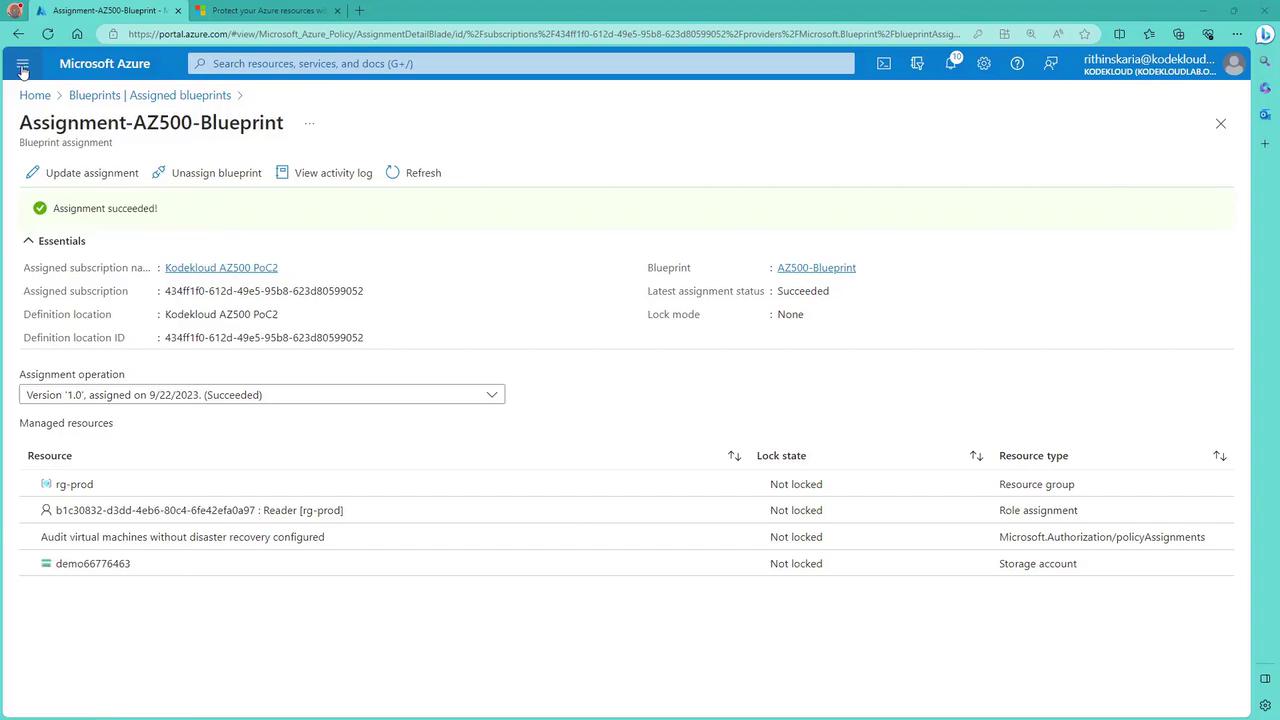
For more detailed guidance on Azure Blueprints, visit the Azure Documentation for best practices and advanced configuration options.
Blueprint and Security
Azure Blueprints simplify the enforcement of consistent role assignments, policy compliance, and governance across your Azure environments. This ensures that your deployments conform to strict security standards and regulatory requirements—similar to adhering to established building codes.
Summary
Azure Blueprints provide a robust solution for:- Artifact Management
- Environment Standardization
- Compliance and Governance