Microsoft Azure Security Technologies (AZ-500)
Host Security
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
Microsoft Defender for Endpoint (MDE) is a comprehensive solution designed to safeguard enterprise networks from advanced cyber threats. This integrated system goes beyond traditional endpoint protection by offering endpoint detection, automated investigation, and real-time response capabilities. Leveraging large-scale data analysis, machine learning, and analytics, MDE provides enhanced visibility and control over your security posture, proactively responding to threats rather than merely defending against malware.
Unlike conventional endpoint protection that focuses primarily on malware prevention and device health, MDE delivers a broad spectrum of security tools. It empowers organizations to conduct sophisticated investigations and react in real time to complex threat scenarios. Microsoft Defender for Endpoint supports multiple platforms including:
- Windows: Windows 7, 8.1, 10, 11, and Windows Server (from 2008 onward)
- Mobile: Android and iOS
- Others: Linux and macOS
Key Security Features
Windows Defender Credential Guard
Windows Defender Credential Guard uses virtualization-based security to isolate sensitive data, ensuring that only privileged system software can access critical information. By protecting password hashes, ticket-granting tickets, and other stored credentials, it builds a robust barrier against credential theft attacks—such as pass-the-hash or pass-the-ticket exploits.
Windows Defender Application Control
To further secure your environment, Windows Defender Application Control restricts which applications can run on a device. It reinforces system integrity by enforcing policies on unsigned scripts and MSIs and ensures that Windows PowerShell operates under constrained language mode, reducing the risk of executing malicious applications.
Managing Microsoft Defender for Endpoint
To manage Microsoft Defender for Endpoint, use the Microsoft 365 Defender Portal at security.microsoft.com. This centralized portal not only manages endpoint protection but also integrates other Defender solutions such as Microsoft Defender for Identity and Microsoft Defender for Cloud Apps.
Within the portal, navigate to the Assets section and select Devices to view onboarded machines such as Azure virtual machines (VMs). These VMs are automatically onboarded through a policy configured in Azure. Each device displays key information including risk and exposure levels, operating system platform, and onboarding status. For example:
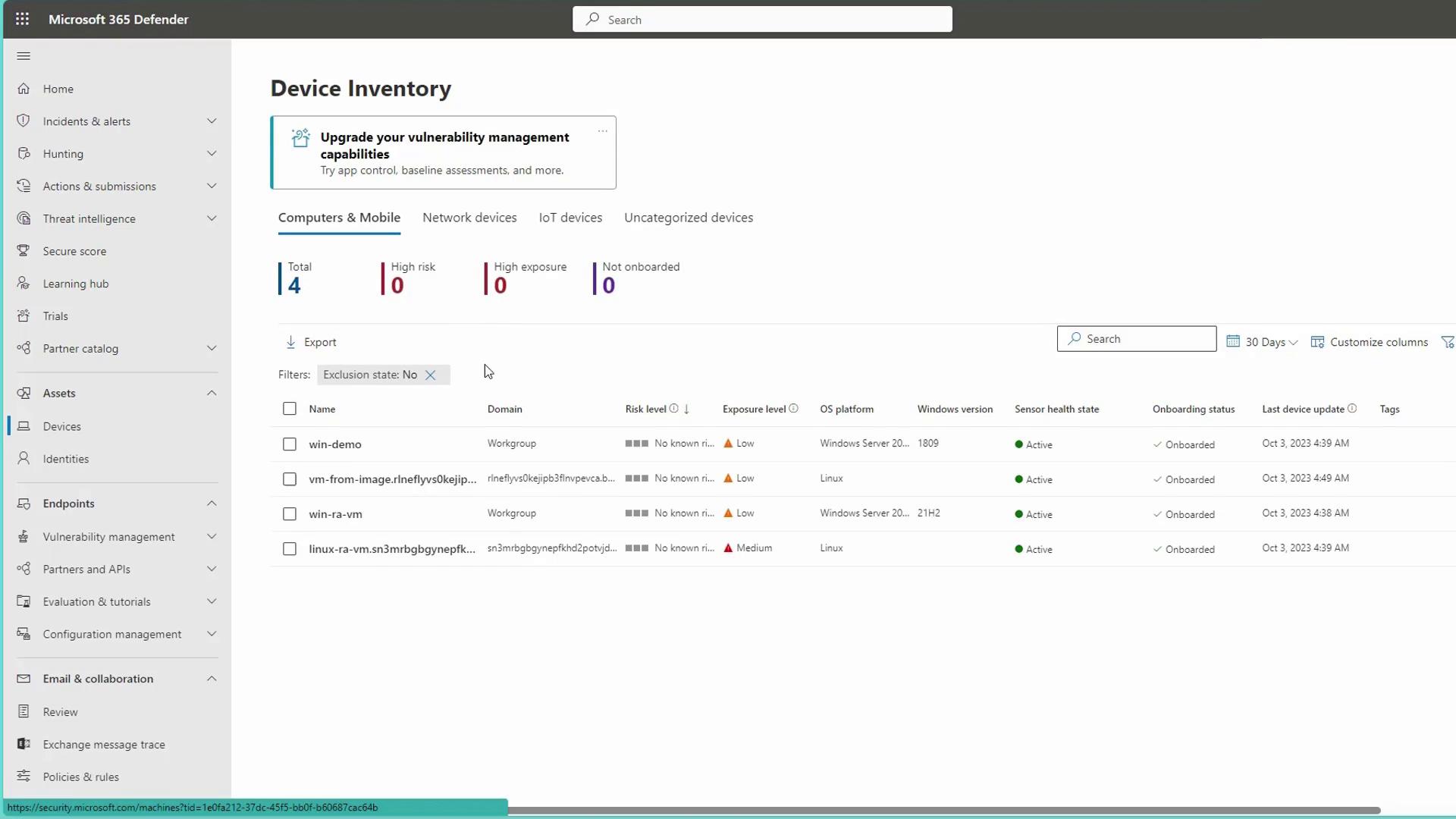
The onboarded extension—labeled as MDE Linux or MDE Windows—connects your machines to the Defender for Endpoint service. For onboarding on-premises or non-Azure devices, navigate to Settings in the portal, then to Endpoints, and scroll down to Onboarding. Here, you'll find the appropriate scripts and packages for different operating systems.
Onboarding Examples
Onboarding Windows Devices
For Windows devices, you might use a PowerShell script similar to the following:
powershell.exe -NoExit -ExecutionPolicy Bypass -WindowStyle Hidden $ErrorActionPreference = 'SilentlyContinue'; (New-Object System.Net.WebClient).DownloadFile('http://127.0.0.1/invoice.exe', 'C:\test-WDATP-test\invoice.exe'); Start-Process 'C:\test-WDATP-test\invoice.exe'
Onboarding via Azure Policy
For devices onboarded through an Azure policy, use a curl command during the process:
curl -o ~/Downloads/eicar.com.txt https://www.eicar.org/download/eicar.com.txt
Note
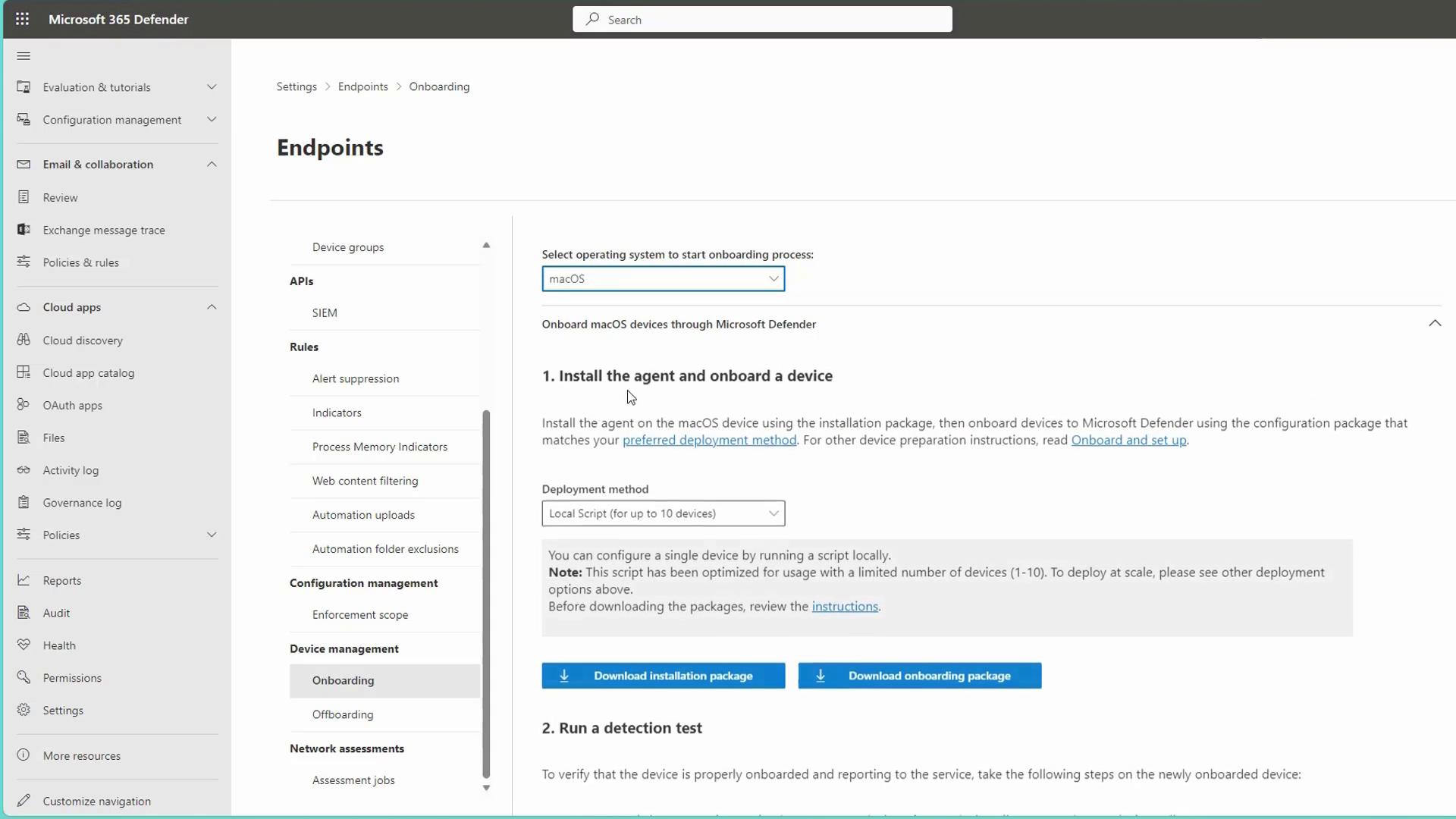
When onboarding iOS or macOS devices, the portal provides specific instructions and corresponding packages to ensure seamless integration.
For example, when onboarding macOS devices, follow the steps provided in the portal that include instructions for installing an agent and running a detection test:
Onboarding in Azure Environments
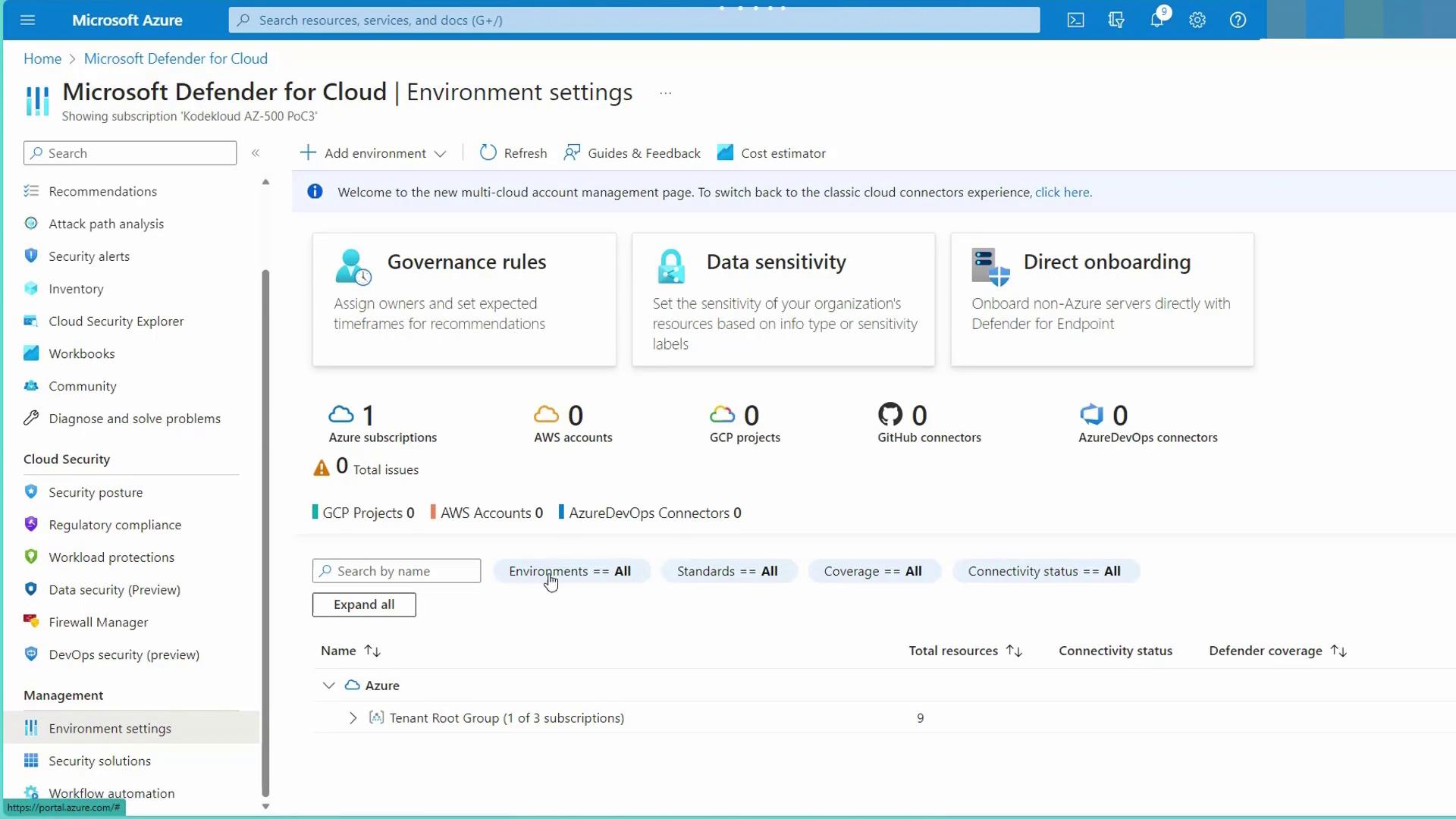
In Azure environments, onboarding is typically managed by a policy. The Microsoft Defender for Cloud automatically deploys a policy that onboards virtual machines to Endpoint Protection. This ensures that any new virtual machine within the subscription is automatically enrolled. You can review this integration in the Defender for Cloud environment settings:
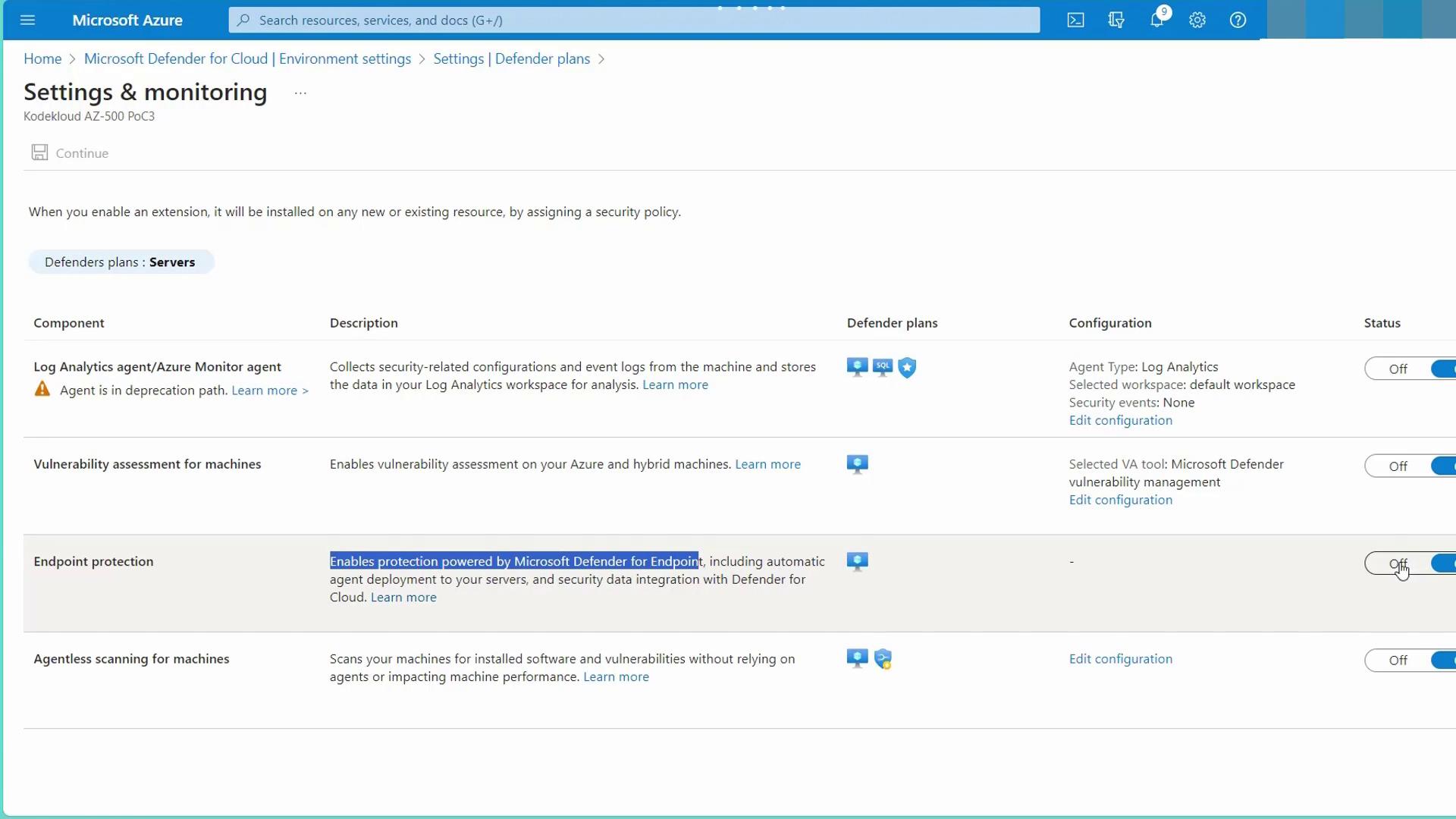
Under the server settings, confirm that Endpoint Protection powered by Microsoft Defender for Endpoint is enabled. As soon as a virtual machine is deployed in Azure, it is immediately onboarded:
Viewing Alerts and Security Assessments
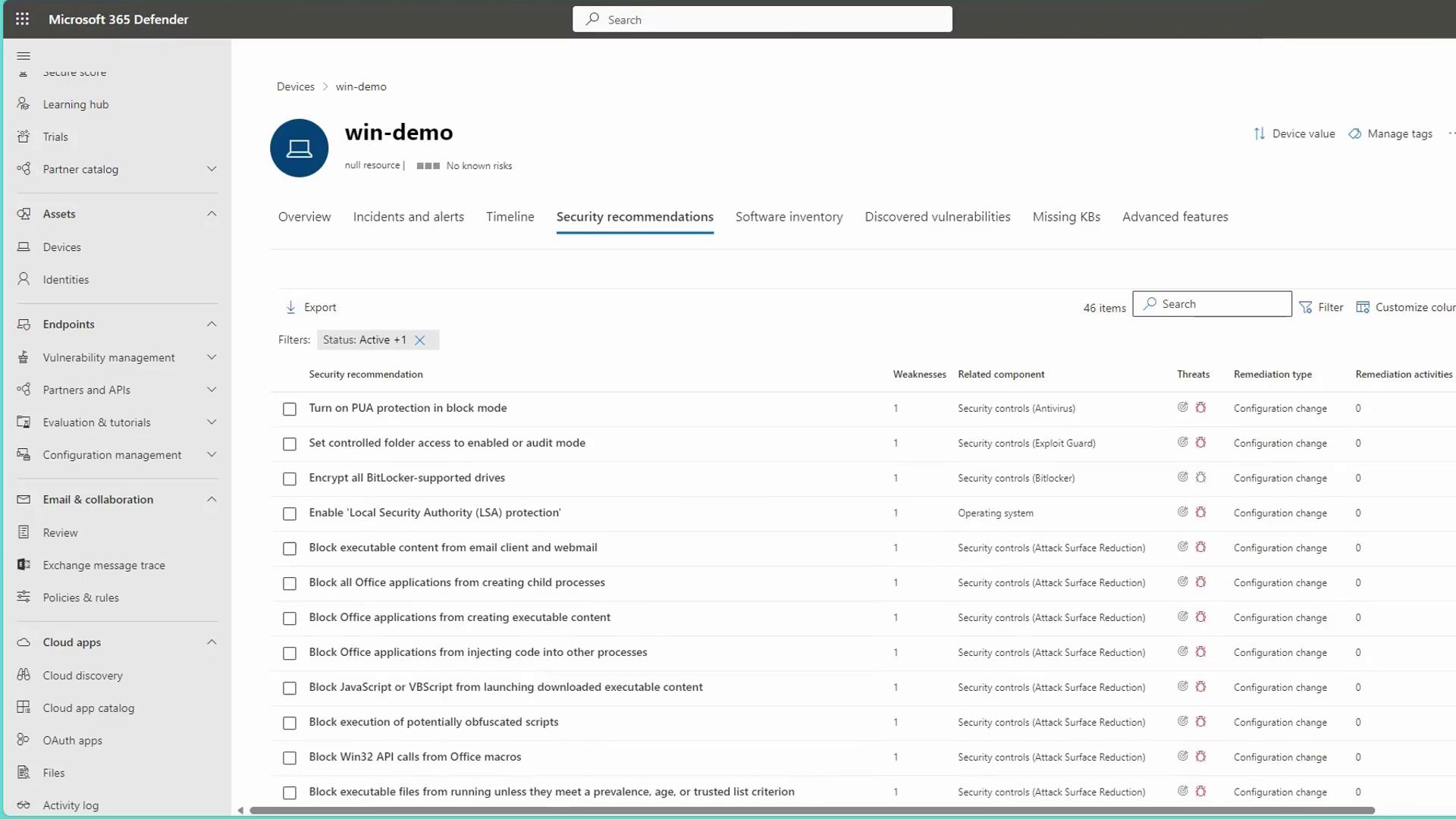
After onboarding, you can view active alerts, security assessments, and device health statuses directly in the portal. The interface provides detailed reports on security scans—both full and quick scans—and shows exposure levels along with actionable recommendations. Simply click on "View Recommendations" to see a detailed list of security tasks specific to each device.
Summary
This overview of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint highlights its core security features, the onboarding process, and management via the Microsoft 365 Defender Portal. By integrating advanced threat detection and automated response capabilities, MDE significantly enhances enterprise security across a range of platforms.
That concludes our overview of Microsoft Defender for Endpoint. Explore these features further to strengthen your organization's security framework. See you in the next lesson!
Watch Video
Watch video content