Prerequisites
- OpenTofu CLI installed
- AWS CLI configured for LocalStack (or your AWS account)
- A project directory named
project-jade
1. Initialize the Project Directory
Open your terminal and navigate to theproject-jade folder:
2. Review the Existing Terraform Configuration
Below is the current HCL setup. It defines an AWS provider, global variables, and a set of EC2 instances:| Variable | Description | Example Default |
|---|---|---|
var.name | Set of EC2 instance names | ["jade-webserver","jade-lbr","..."] |
var.ami | AMI ID for all instances | "ami-0c9bfc21ac5bf10eb" |
var.instance_type | EC2 instance type | "t2.nano" |
var.key_name | SSH key pair name | "jade" |
3. Identify Unmanaged Resources
To list all resources tracked in state versus your code, run:Question: Which resource appears in the state but not in the configuration?
Answer: An EC2 instance (e.g.,
jade-agent) that wasn’t defined in code.
4. Provision the SSH Key Pair
OpenTofu did not create thejade key pair—it was generated via AWS CLI:
jade.pem.
Keep your private keys out of version control. Add
jade.pem to .gitignore.5. Locate the External EC2 Instance ID
Another EC2 instance named Jade-MW was created manually. Retrieve its Instance ID: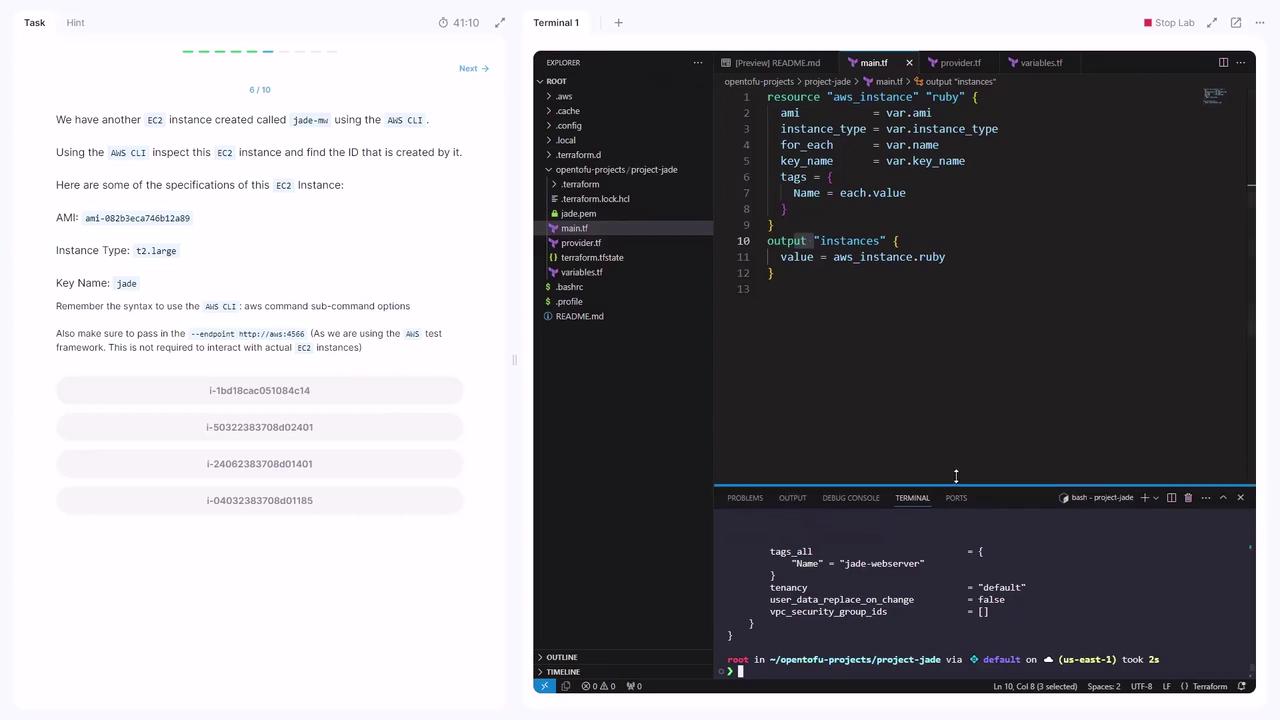
Instance ID: i-1bd18cac05184c14
6. Import the EC2 Instance into OpenTofu
-
Create an empty resource block in main.tf:
-
Import the existing EC2 resource:
7. Complete the Imported Resource Definition
After import, runningtofu apply will show missing arguments. Inspect the imported state:
You can always re-run
tofu show to confirm attribute names and values for any imported resource.8. Validate the Configuration
Run a plan to ensure no changes are pending: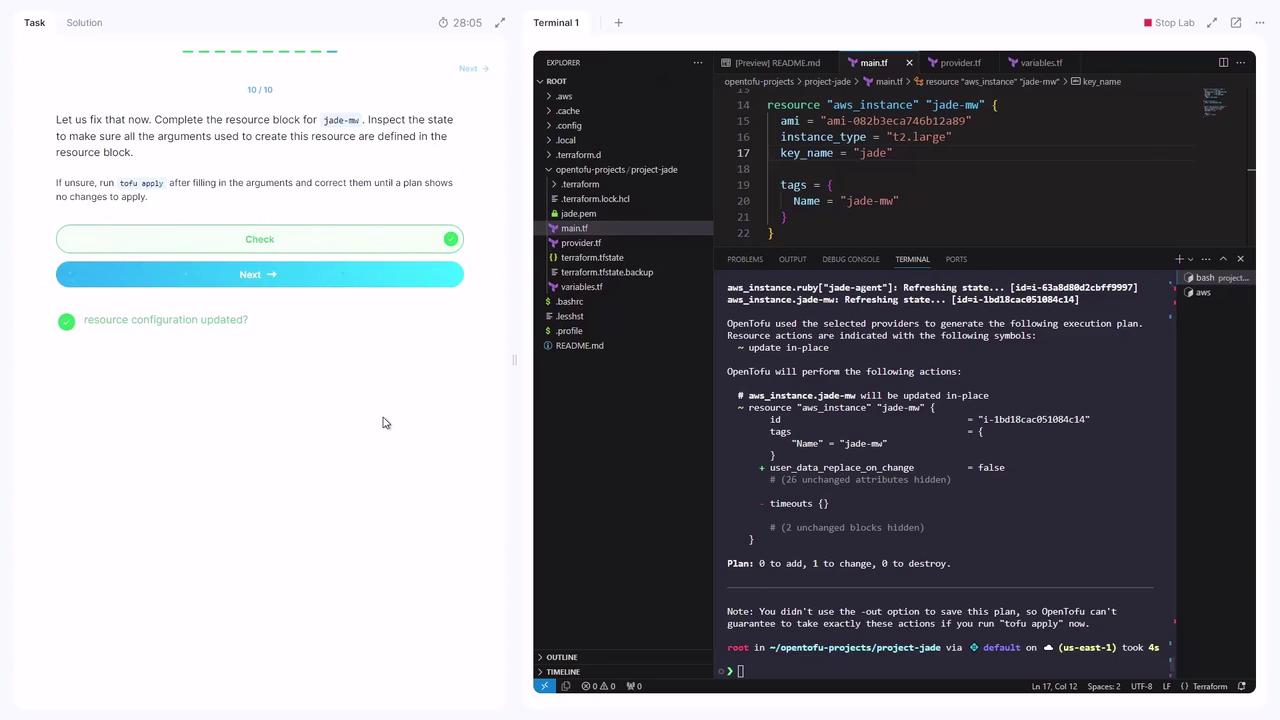
Congratulations! You’ve successfully imported and now manage an existing AWS EC2 instance with OpenTofu.