Installing Rust with Rustup
The recommended method to install Rust is by using Rustup, the official toolchain installer. This tool manages the installation, update, and uninstallation of Rust components.-
Open your terminal and run the following command to start the installation:
This command launches the installation process and prompts you to choose your installation options. Proceed with the standard installation.
-
Once installed, verify the installation by checking the versions of the Rust compiler (
rustc) and the package manager (cargo). Run:You should see output similar to: -
Update your Rust toolchain to the latest stable version:
The terminal will display updates for the Rust compiler, Cargo, and Rustup itself. For example:
-
To access the comprehensive local Rust documentation via your default web browser, run:
Alternatively, you can open the Cargo-generated documentation with:
Setting Up Your Integrated Development Environment (IDE)
An efficient IDE boosts your productivity when working with Rust. We recommend Visual Studio Code (VS Code) in combination with the Rust Analyzer extension.- Download and install VS Code from its official website.
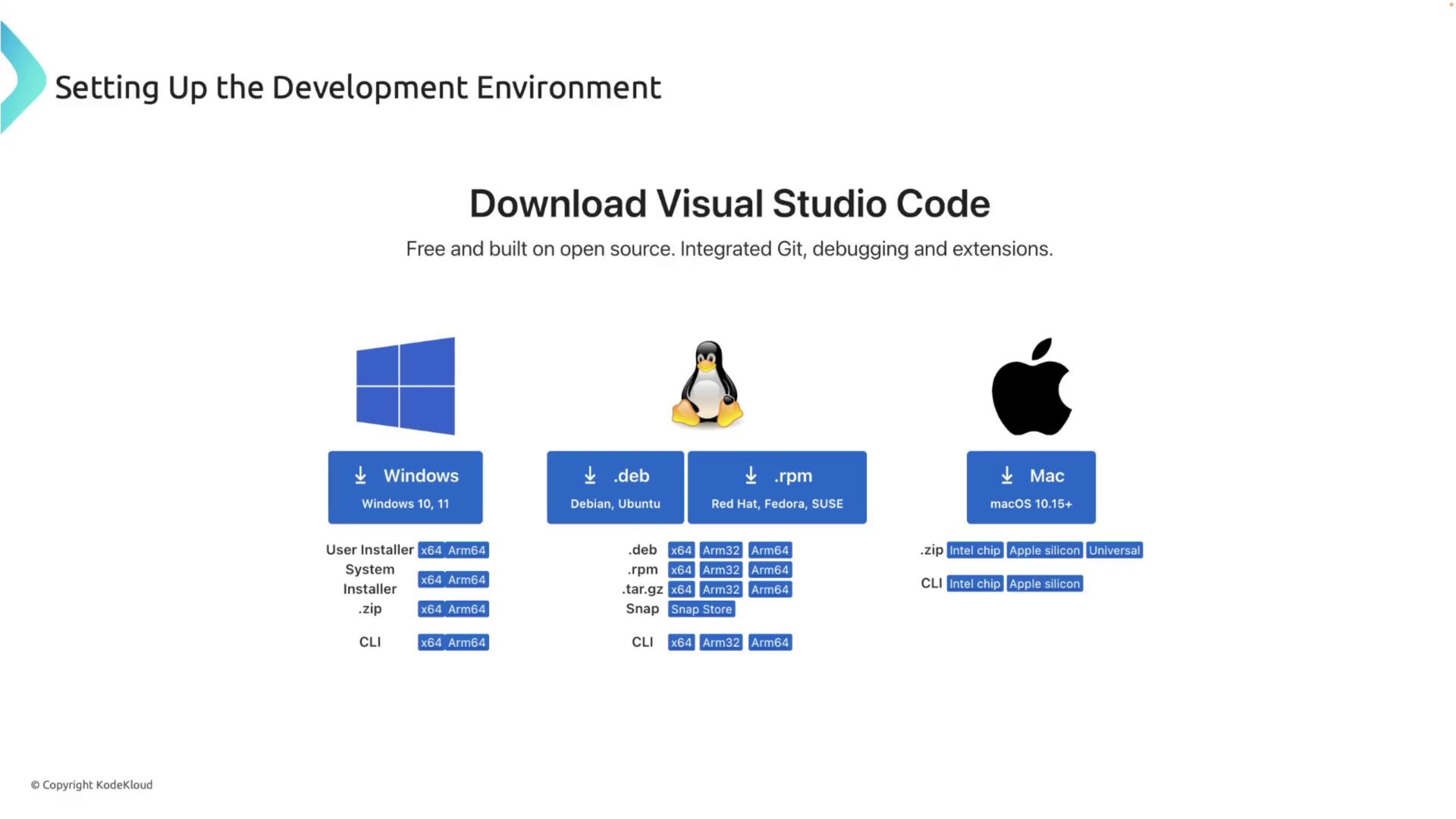
- Open VS Code, navigate to the extensions view by clicking the extensions icon, and search for “Rust Analyzer.” Install the extension provided by the Rust team.
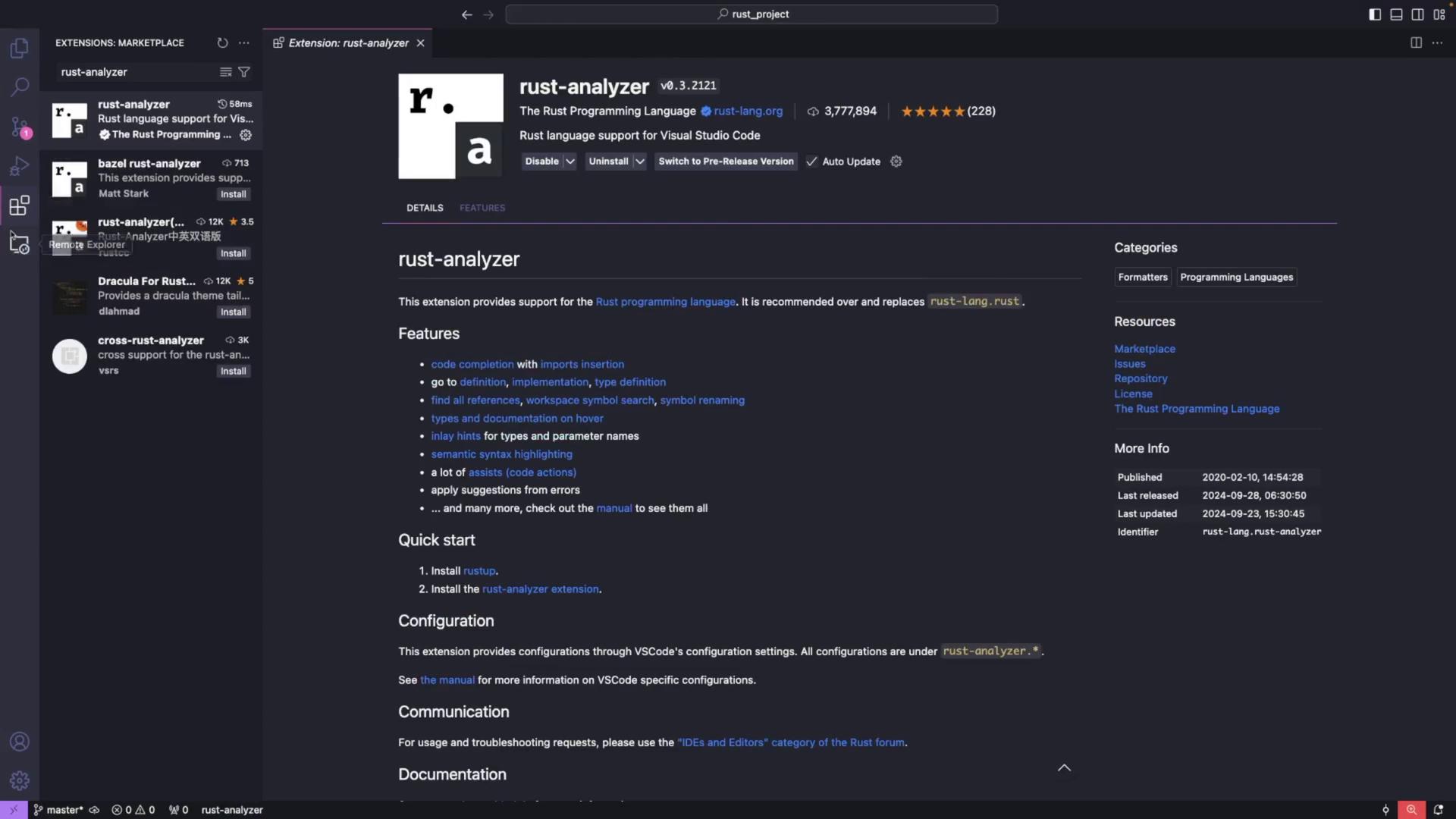
Creating and Running a Rust Project
After setting up Rust and your IDE, it’s important to test the setup by creating a simple Rust project.Step 1: Create Your Project Directory
Open your terminal and navigate to your preferred projects directory. For example, to create a directory named “projects” in your home directory:Step 2: Create the Source File
Open the project directory in VS Code. Then, using the integrated terminal, create a new file namedmain.rs:
Step 3: Write a “Hello, world!” Program
Editmain.rs and add the following Rust code:
Step 4: Compile and Run Your Program
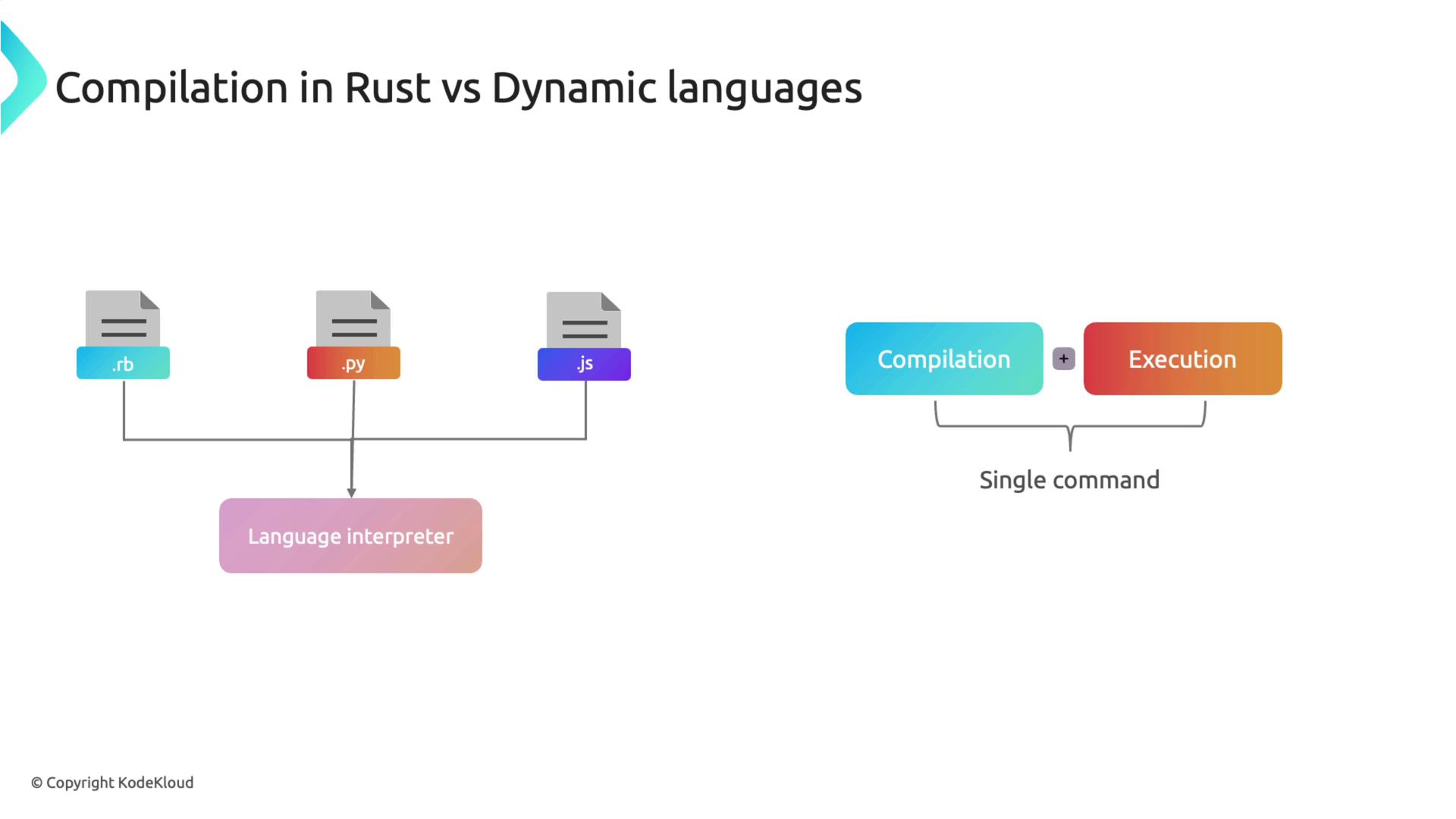
Compile your program using the Rust compiler:Unlike dynamic languages such as Ruby, Python, or JavaScript, which are interpreted on the fly, Rust requires ahead-of-time compilation. The Rust compiler (
rustc) converts your source code into an executable, enabling it to run on any compatible system without needing Rust installed.Managing Projects with Cargo
For small programs, compiling withrustc is sufficient. However, as your projects grow, managing dependencies and builds manually can become challenging. Cargo, Rust’s package manager and build system, simplifies this process by managing project dependencies, compiling code, and generating documentation.
Integrate Cargo into your workflow early, as it not only manages dependencies but also simplifies tasks such as testing, building, and documentation generation.