Terraform Basics Training Course
Working with Terraform
Datasources
In this lesson, we explore how Terraform utilizes data sources to read information from resources that are managed externally. Terraform leverages configuration files and a state file to provision infrastructure resources, but it can also interact with resources that are created manually, by other tools (such as Puppet, CloudFormation, SaltStack, Ansible, etc.), ad-hoc scripts, or even resources provisioned by another Terraform configuration.
For instance, consider a database instance that was manually provisioned in the AWS cloud. Even though Terraform does not manage this resource, it can still read attributes—such as the database name, host address, or DB user details—and use that information to provision an application resource managed by Terraform.
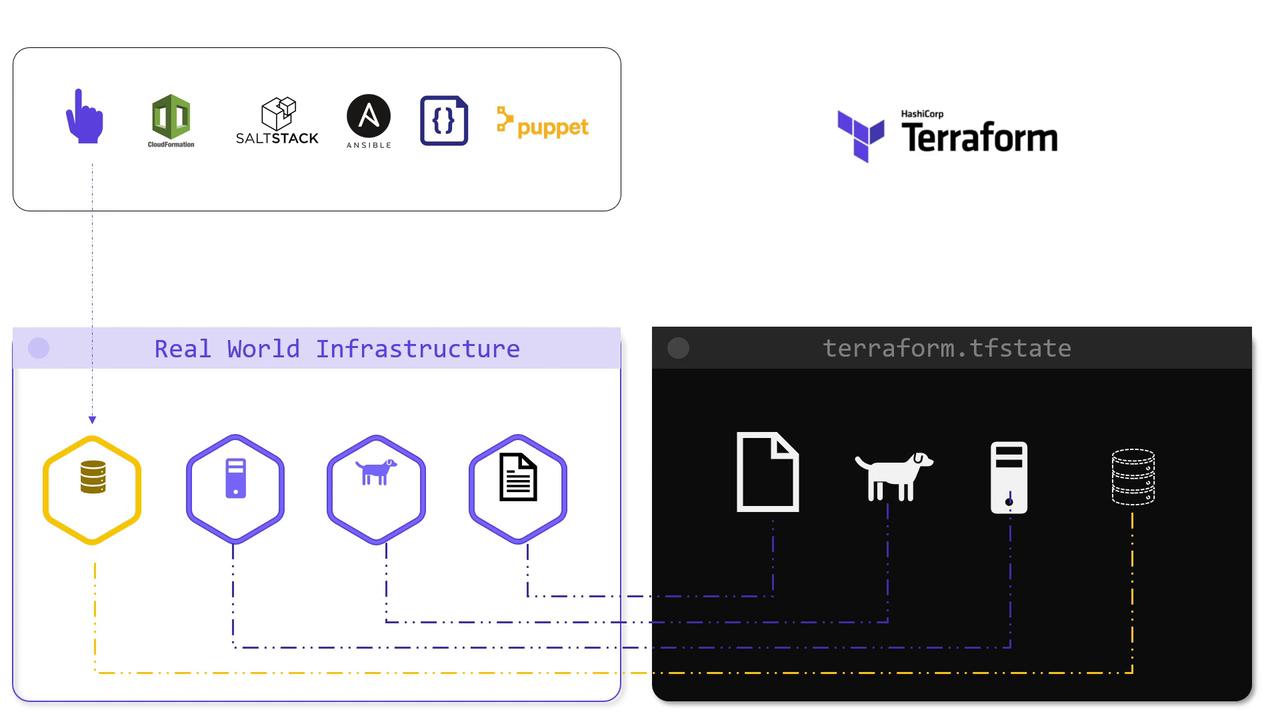
Now, consider a simpler scenario with a local file resource named "pet" containing the text "We love pets!" When Terraform creates this resource, it generates the file /root/pets.txt and stores its information in the state file. Meanwhile, another file—created by an external shell script—is located at /root/dog.txt and contains "Dogs are awesome!" Because dog.txt is not managed by Terraform, we can use it as a data source to supply content for our managed resource pets.txt.
Understanding Data Sources
Data sources in Terraform enable you to use attributes from external resources, integrating them into your Terraform-managed infrastructure.
Data sources are defined using the data block in your configuration. Although these blocks resemble resource blocks, they start with the keyword data instead of resource. Below is an example configuration that demonstrates this process:
$ cat /root/dog.txt
Dogs are awesome!
resource "local_file" "pet" {
filename = "/root/pets.txt"
content = data.local_file.dog.content
}
data "local_file" "dog" {
filename = "/root/dog.txt"
}
In the configuration above:
- The resource block creates a file called
/root/pets.txtwith its content dynamically populated using data fromdog.txt. - The data block reads from the local file located at
/root/dog.txtand makes its content available via the expressiondata.local_file.dog.content.
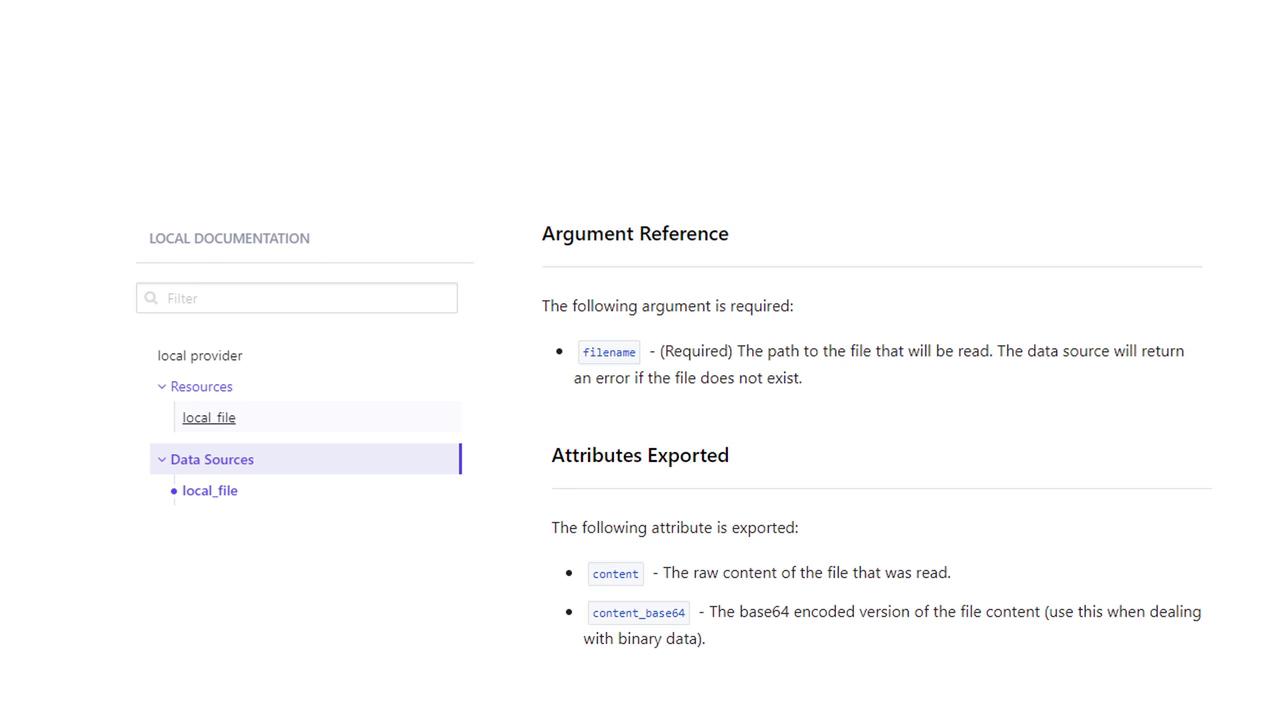
According to the Terraform documentation on the Terraform Registry, the local file data source exports two attributes:
- The raw content of the file.
- The base64-encoded version of the file's content.
This feature allows you to easily integrate external data into your Terraform configurations.
To clearly distinguish between resources and data sources in Terraform:
| Type | Purpose | Management by Terraform |
|---|---|---|
| Resource | Create, update, and destroy infrastructure elements | Managed; stored in the state file |
| Data Source | Read and reference information from unmanaged resources | Not managed; used for reference within Terraform |
This distinction is further illustrated in the following comparison diagram:

That concludes this article on data sources in Terraform. For further information on utilizing Terraform with external resources, refer to the official Terraform Documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content
Practice Lab
Practice lab