In this lesson, we’ll authenticate into a temporary AWS lab account, inspect our Terragrunt configuration, and deploy a VPC module. Follow along to learn how to initialize, plan, apply, and clean up with Terragrunt.
1. Authenticate to the AWS Lab Account When the lab starts, you’ll receive a URL and temporary credentials:
Open the provided URL in your browser.
Log in with the displayed username and password.
If you lose your credentials, run:
This lab account has limited AWS permissions. Only perform the tasks outlined in this lesson to avoid permission errors.
SSH into the AWS client server and verify your toolchain:
Tool Check Version Sample Output Terraform terraform versionTerraform v1.8.3Your version is out of date! Terragrunt terragrunt --versionterragrunt version v0.58.8
Terraform v1.8.3 on linux_amd64 Your version of Terraform is out of date! The latest version is 1.8.5. Download: https://www.terraform.io/downloads.html
terragrunt version v0.58.8
3. Inspect the VPC Module Navigate to the aws-stack/vpc directory where the VPC module lives:
Open terragrunt.hcl to review:
terraform { source = "git::https://github.com/terraform-aws-modules/terraform-aws-vpc.git//?ref=v5.8.1" } locals { vpc_cidr = "10.0.0.0/16" } include "root" { path = find_in_parent_folders () expose = true } inputs = { name = " ${ include . root . locals . project } -vpc" cidr = local.vpc_cidr azs = [ " ${ include . root . locals . aws_region } a" , " ${ include . root . locals . aws_region } b" , " ${ include . root . locals . aws_region } c" ] public_subnets = [ "10.101.0.0/24" , "10.102.0.0/24" , "10.103.0.0/24" ] }
Provider Version Override To ensure compatibility, this module locks the AWS provider to major version 5:
generate "provider_version" { path = "provider_version_override.tf" if_exists = "overwrite" contents = << EOF terraform { required_providers { aws = { source = "hashicorp/aws" version = "~> 5.0" } } } EOF }
Locking the AWS provider version prevents unexpected breaking changes when Terraform and modules update.
4. Initialize the Terragrunt Project Initialize the backend and download provider plugins:
You should see:
Initializing the backend... Initializing provider plugins... Terraform has been successfully initialized!
5. Plan the VPC Deployment Generate and review the execution plan:
Look for the summary at the end:
Plan: 13 to add, 0 to change, 0 to destroy.
6. Apply the Configuration Create the VPC resources:
Type yes when prompted. After completion:
Apply complete! Resources: 13 added, 0 changed, 0 destroyed.
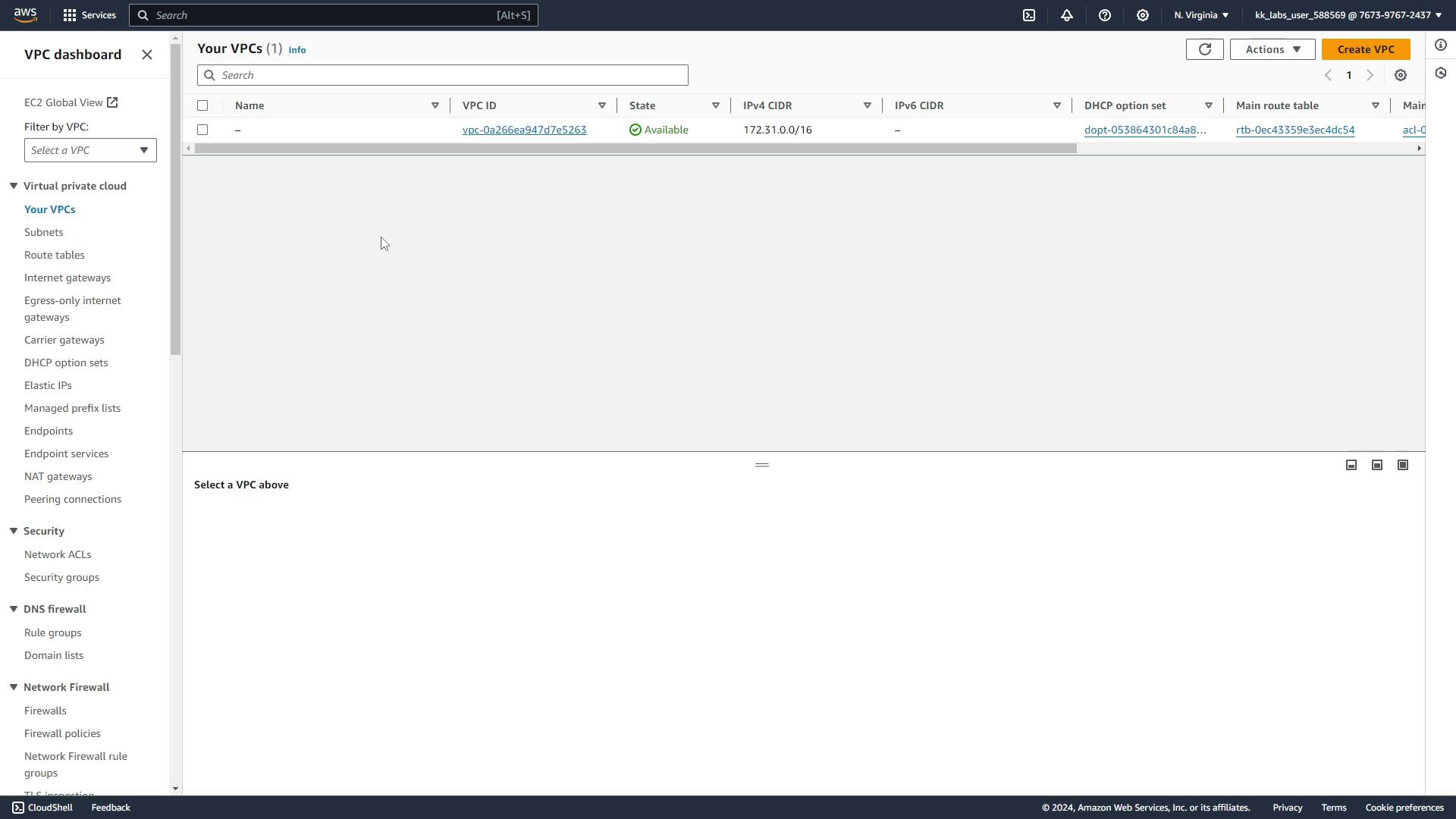
In the AWS console (US East 1), verify your VPC:
7. Clean Up: Destroy the VPC Remove all created resources to avoid incurring costs:
Confirm with yes. You’ll see:
Destroy complete! Resources: 13 destroyed.
The AWS console will now only list the default VPC.
References