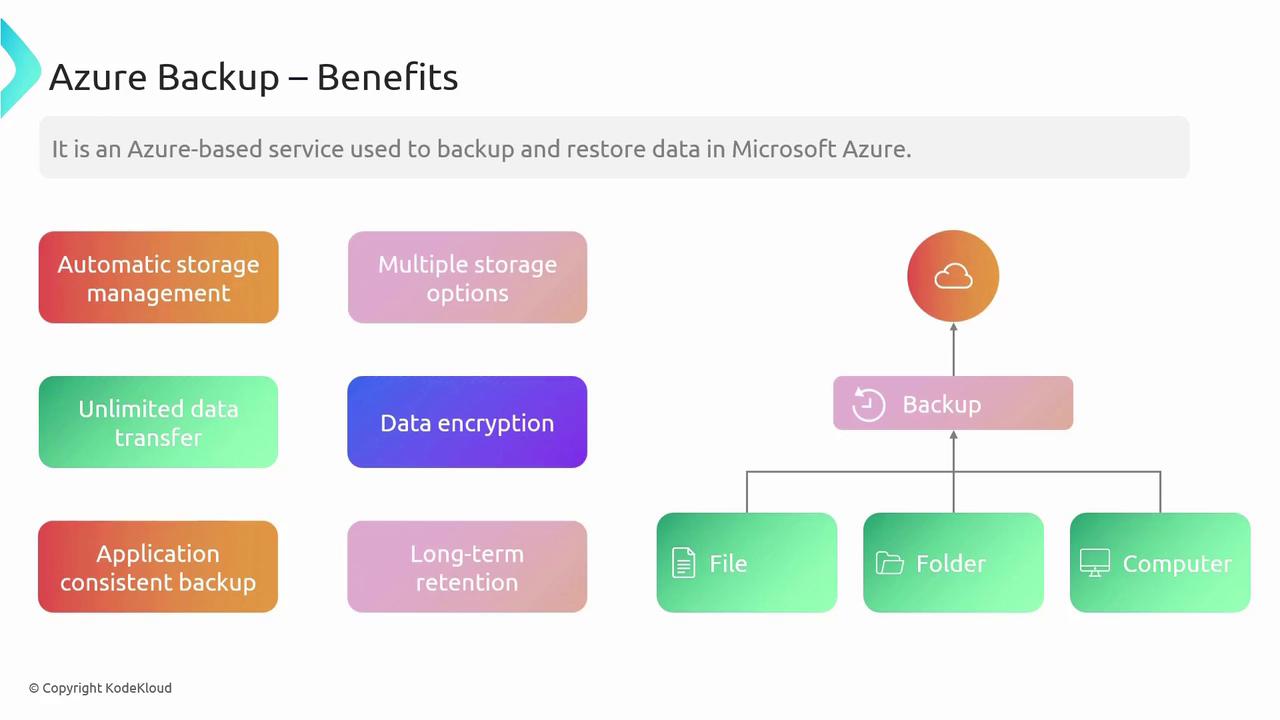
Data security is a top priority. Azure Backup encrypts data both in transit and at rest and supports application-consistent backups. This ensures that even running applications remain uninterrupted during the backup process while preserving data integrity. Additionally, configurable retention policies let you store backups for as long as needed to satisfy regulatory and organizational demands.
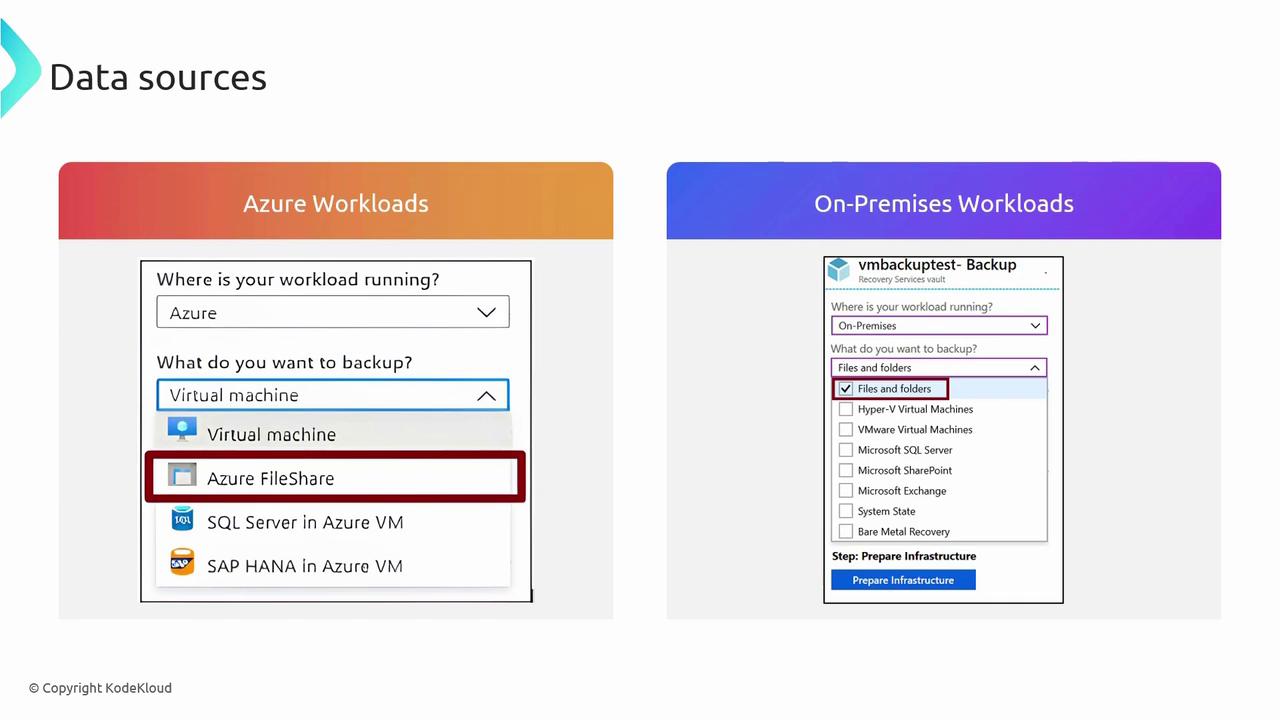
Data Sources
Azure Backup is capable of handling a wide range of data sources. Here’s a breakdown of supported workloads:Azure Workloads
- Virtual Machines: Protect your Azure VMs.
- Azure Files Shares: Back up file shares stored on Azure.
- SQL VMs: Ensure the integrity of your SQL Virtual Machines.
- SAP HANA on Azure VMs: Secure your SAP HANA environments.
On-Premises and Other Environments
- Files and Folders: Safeguard critical documents and directories.
- Hyper-V Virtual Machines: Manage backups for Hyper-V VMs.
- VMware Virtual Machines: Integrate VMware environment backups.
- SQL Server: Protect your SQL Server databases.
- SharePoint: Ensure SharePoint data consistency.
- Exchange: Back up your Exchange server data.
- System State: Preserve essential system configuration.
- Bare Metal Recovery: Support comprehensive system restores.
Before proceeding, ensure that your backup policies align with your organization’s compliance and retention requirements. This proactive check can help prevent potential data governance issues later on.