[Updated] AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator
Administer Intersite Connectivity
Site to Site and Point to Site
This guide details how to establish both Site-to-Site and Point-to-Site VPN connections in Azure. It covers the required resources, configurations, and step-by-step procedures for securely linking your on-premises network or individual devices to an Azure Virtual Network.
Site-to-Site Connection
A Site-to-Site connection creates a secure VPN tunnel between your on-premises VPN device and an Azure VPN Gateway in your Virtual Network Gateway subnet. This setup enables seamless data transfer between your local environment and Azure as if they were part of the same network.
Key Components
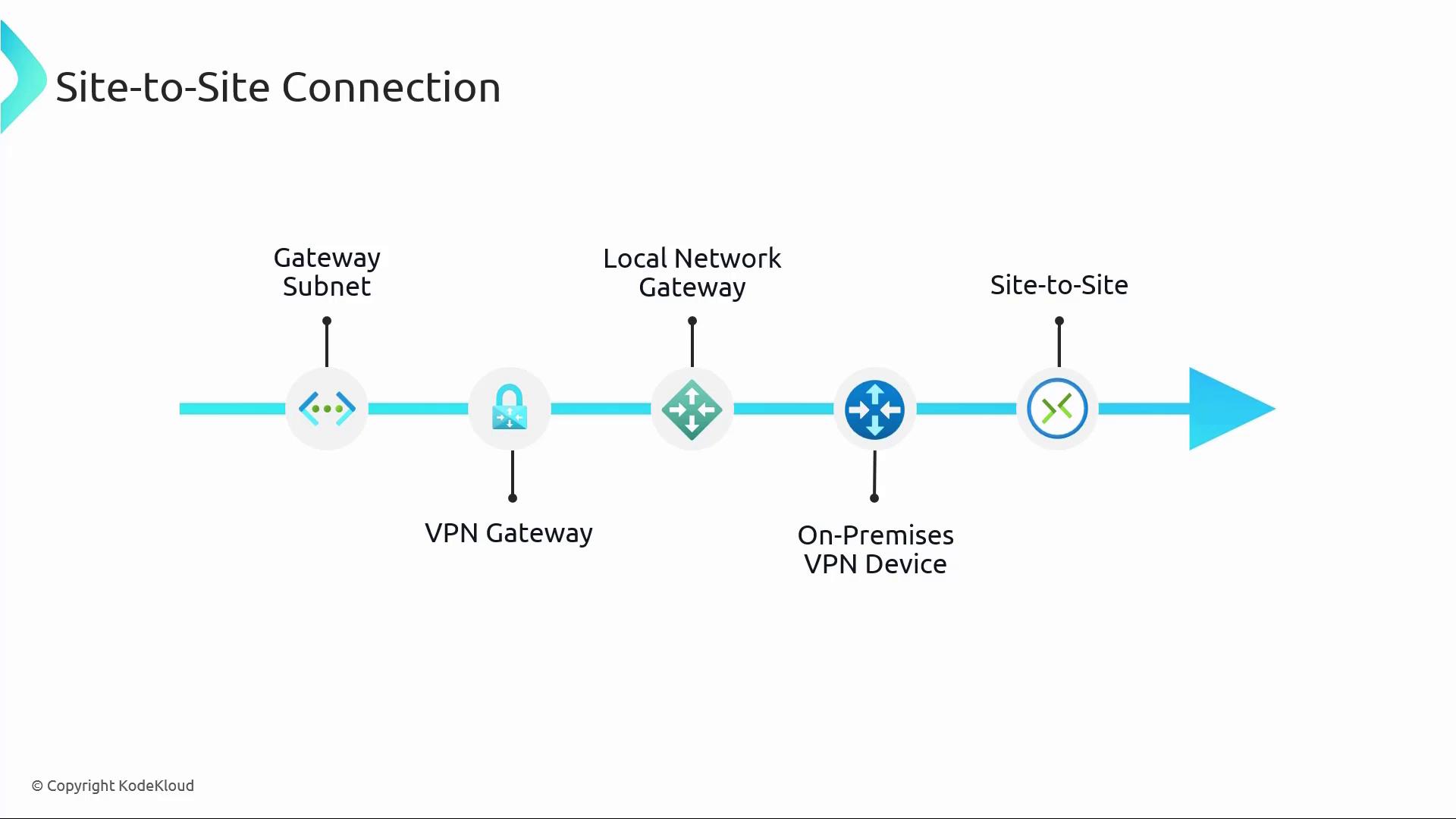
Gateway Subnet
Begin by creating a dedicated gateway subnet within your Virtual Network (VNet) in Azure. This subnet is exclusively reserved for the Azure Virtual Network Gateway.Virtual Network Gateway (VPN Gateway)
Deployed within the gateway subnet, the VPN Gateway encrypts and decrypts data, maintains the VPN tunnel, and manages the connectivity between Azure and on-premises resources.Local Network Gateway
This resource acts as a reference for your on-premises VPN device by storing its public IP address and address range. For example, if your on-premises device has an IP address of 13.12.11.11, configure the Local Network Gateway to reference this IP accordingly.On-Premises VPN Device
The VPN appliance (either physical or virtual) on your local network must be configured to align with the Azure VPN Gateway settings. Once the Site-to-Site connection is established, the Azure VPN Gateway and your on-premises VPN device communicate to form a secure tunnel.
The diagram below illustrates the overall architecture of a Site-to-Site VPN connection, including the gateway subnet, VPN gateway, local network gateway, and the on-premises VPN device:
Setting Up a Site-to-Site Connection
Configure the Virtual Network Gateway:
In the Azure portal, navigate to your Virtual Network Gateway. Although the creation process for the Virtual Network Gateway is outside the scope of this guide, reviewing its configuration can help you understand the overall setup.Add a Connection:
Under the "Connections" section of the Virtual Network Gateway, click on "Add connection." You can choose between a VNet-to-VNet connection (for connecting to another VNet) or a Site-to-Site connection. For this guide, select Site-to-Site and assign a suitable name (e.g., "Demo Site-to-Site East US").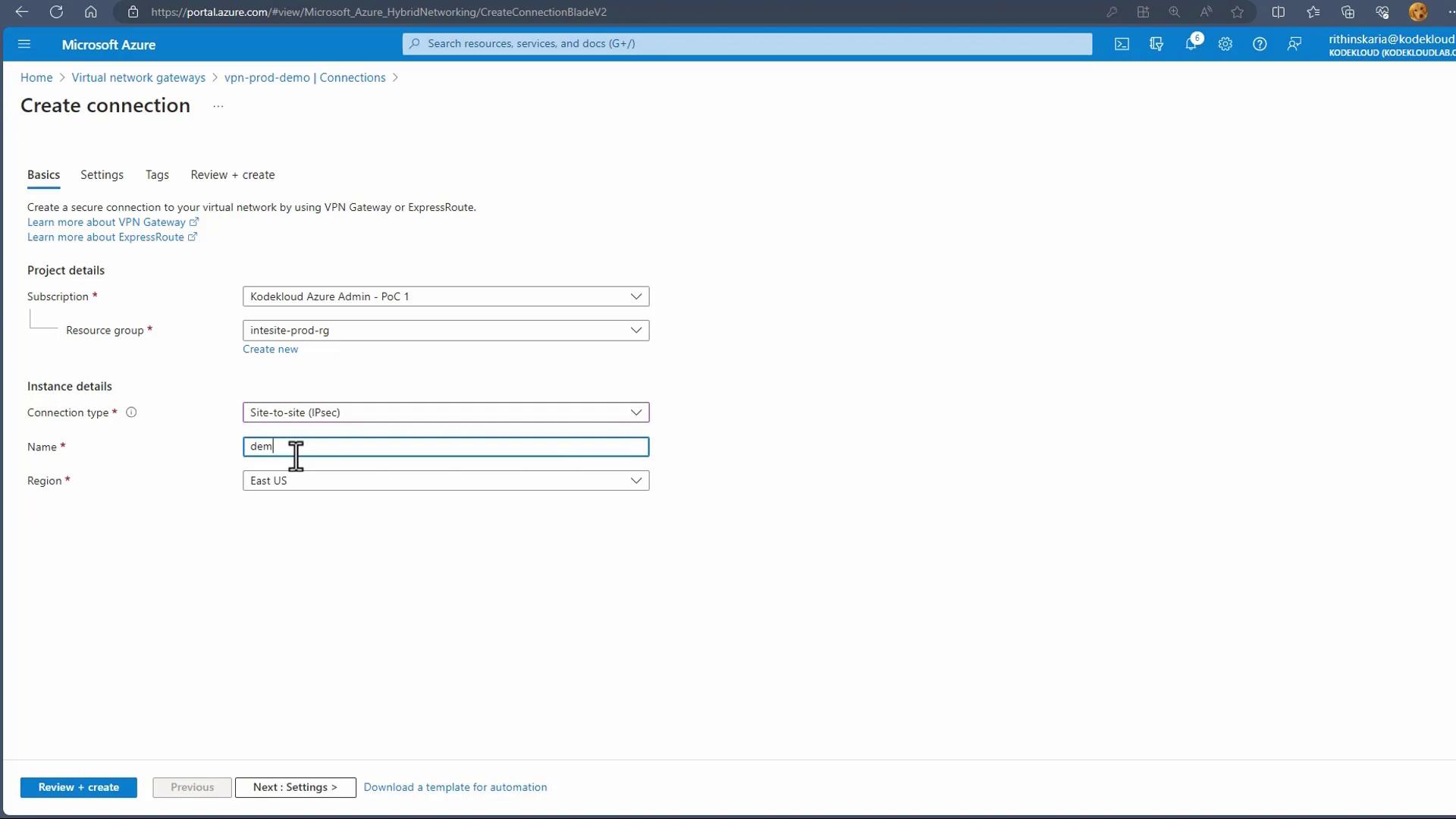
Configure Connection Settings:
In the next step, select the appropriate Virtual Network Gateway and reference the Local Network Gateway. Provide details such as the public IP address (or FQDN) of your on-premises VPN device and its served address range.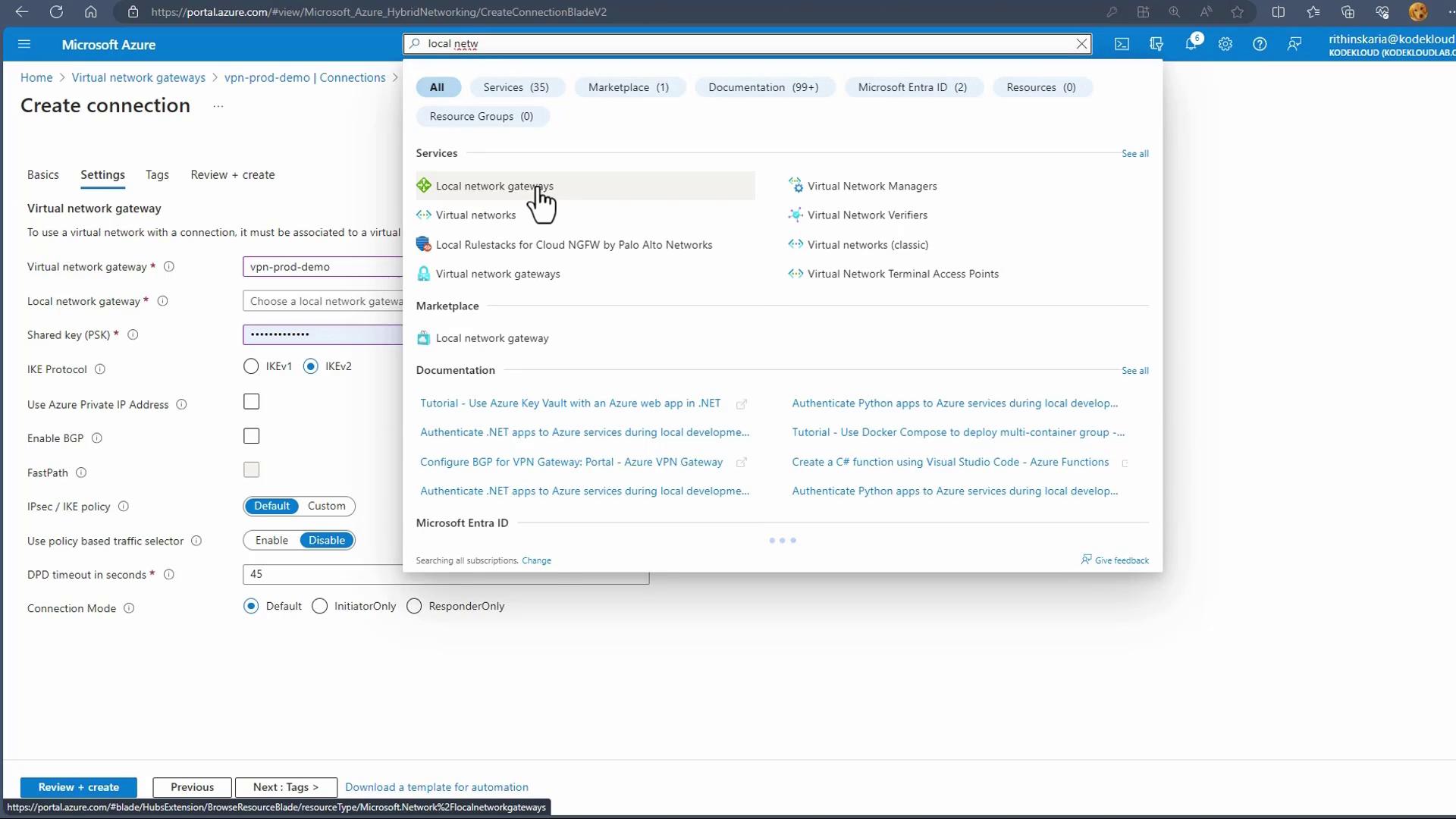
Finalize the Connection:
Specify additional parameters such as BGP (if needed), private IP addressing, policy settings, and connection modes. Make sure these settings are mirrored on your on-premises VPN device. After reviewing and confirming all settings, the Site-to-Site VPN connection will be established.
Point-to-Site Connection
A Point-to-Site connection is designed for individual devices to securely connect to an Azure VNet, creating a virtual experience that mimics being physically present within an Azure data center. This connection is ideal for remote workers, developers, and IT professionals requiring on-demand access to Azure resources.
Overview of the Setup Process
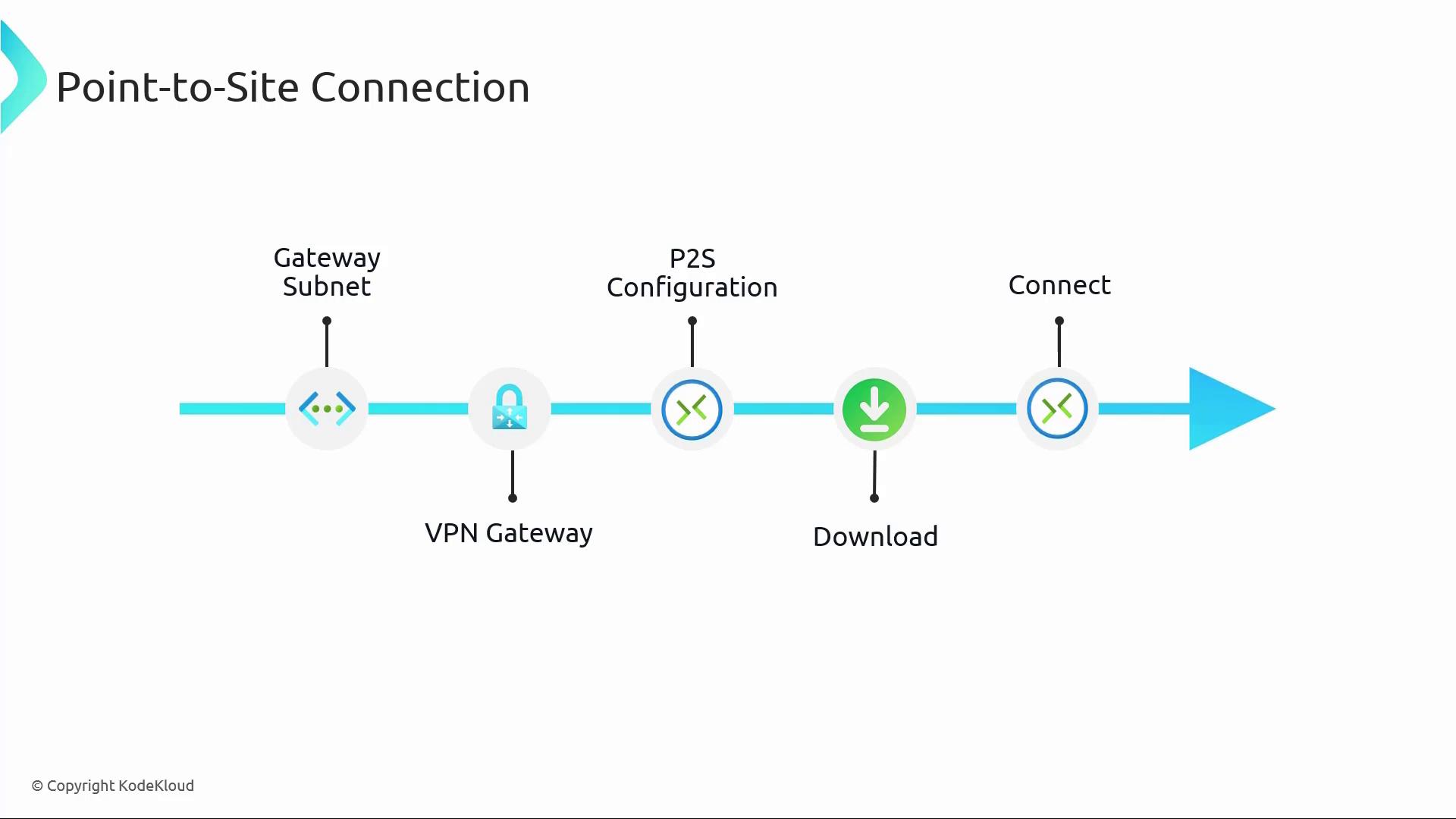
Gateway Subnet and VPN Gateway:
Like the Site-to-Site setup, a Point-to-Site connection requires an existing gateway subnet and Virtual Network Gateway.Point-to-Site VPN Configuration:
Within the Azure portal, configure the VPN client settings by specifying an address pool for VPN clients, choosing a tunnel type (such as IKEv2, OpenVPN, or SSTP), and selecting an authentication method. Supported authentication methods include Azure Certificate Authentication, RADIUS Authentication, and Azure Active Directory integration. If you opt for Azure Active Directory, provide the tenant ID, audience, and issuer details as outlined in the official documentation.Download and Install the VPN Client:
After finalizing the Point-to-Site configuration, download the VPN client package from the Azure portal. Windows users can opt for the "Azure VPN" app available in the Windows Store. Once installed, import the configuration details and connect to the Azure VNet securely.
The flowchart below outlines the key steps involved in establishing a Point-to-Site VPN connection:
Demonstration in the Azure Portal
Access Point-to-Site Configuration:
In the Virtual Network Gateway settings of the Azure portal, navigate to the "Point-to-Site configuration" tab (instead of "Connections"). Click on "Configure now" to begin setting up the connection.Set Up VPN Client Settings:
Enter the necessary details, such as the address pool for connected clients, preferred tunnel type, and selected authentication method. After saving these settings, download the VPN client configuration.Connect to Azure:
Install and launch the VPN client on your device. Use the provided settings to establish a secure connection to your Azure Virtual Network. Once connected, you can access Azure virtual machines and other resources as if they were part of your local network.
Note
For enhanced security, ensure that the configurations on your on-premises VPN device precisely match the settings in the Azure portal.
Gateway Transit
Both Site-to-Site and Point-to-Site VPN connections leverage Gateway Transit. This feature allows on-premises networks and remote clients to extend the secure connection established by the Azure VPN Gateway. Implementing Gateway Transit ensures that all connected devices benefit from robust, secure connectivity.
Happy networking!
For further reading on Azure VPN solutions, consider reviewing the Azure VPN Gateway documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content