Step 1: Deploying an EC2 Instance
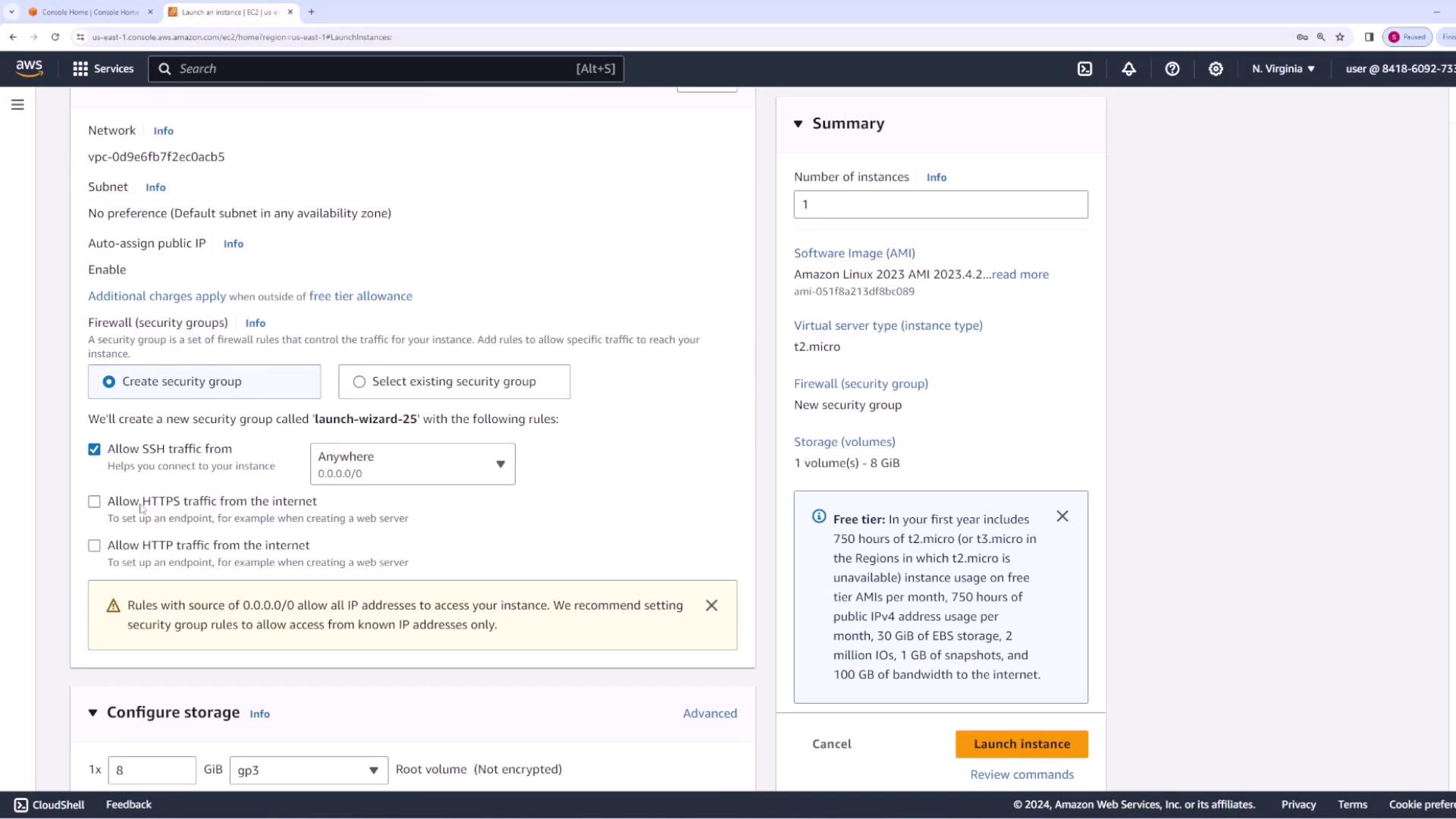
Start by launching an EC2 instance that will host your application. For this demo, we use the Amazon Linux 2023 AMI and deploy the instance in the default VPC. Name the instance “CodeDeploy EC2.” When configuring the instance, ensure you select a valid key pair and configure a security group that permits HTTP and HTTPS traffic, as these protocols are required to serve your web application.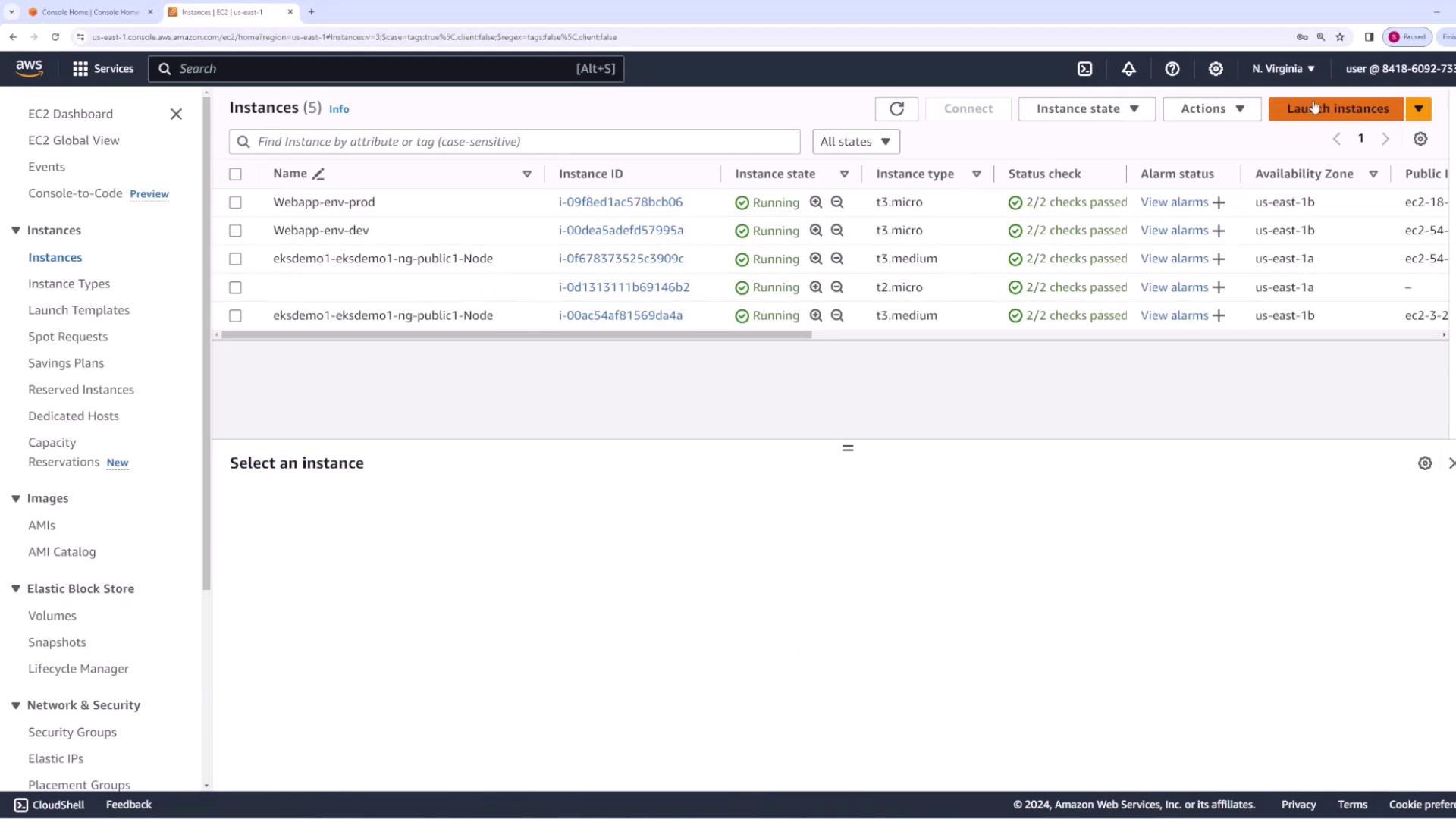
Step 2: Installing the CodeDeploy Agent on EC2
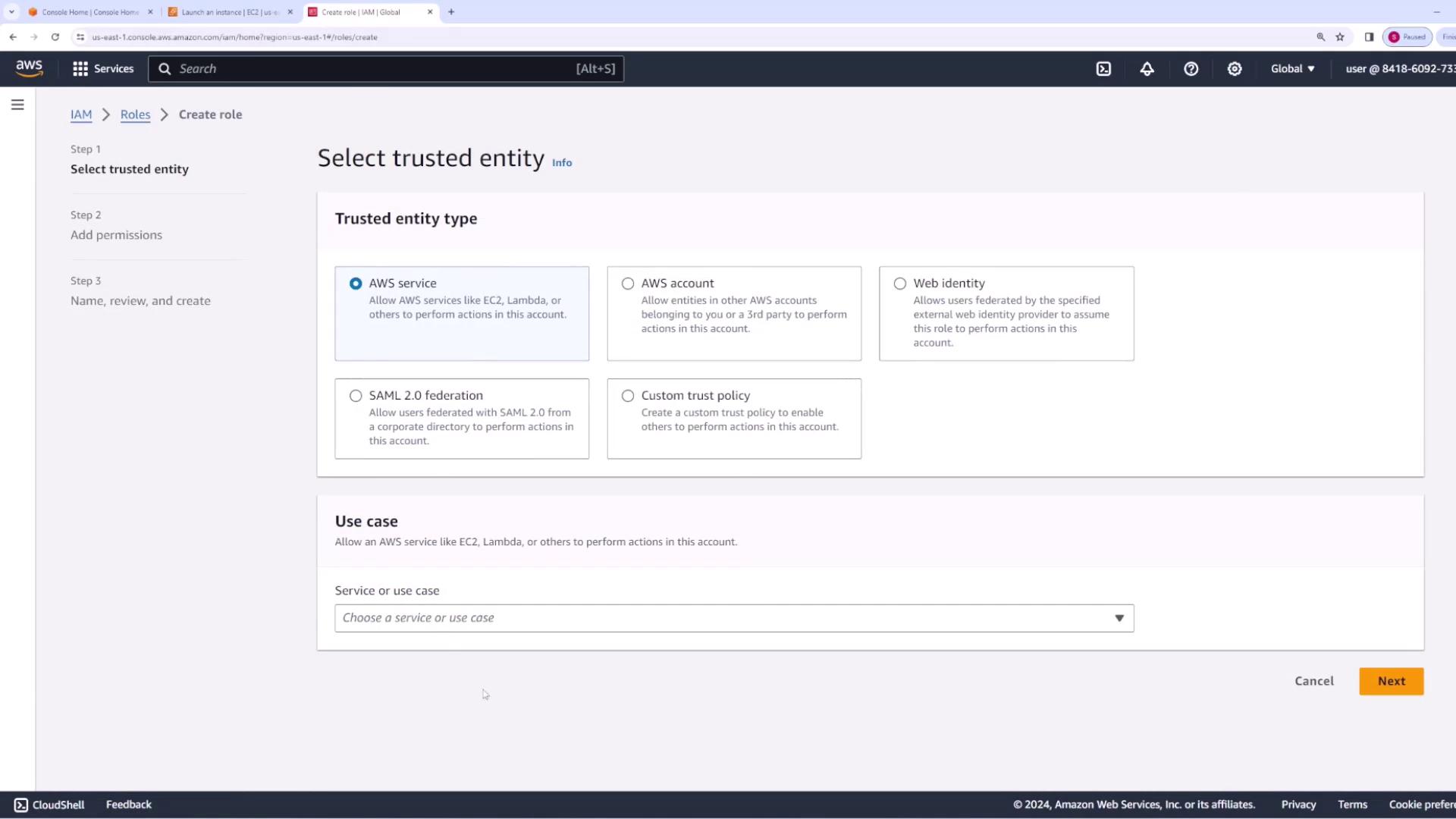
For CodeDeploy to manage EC2 instances, the CodeDeploy agent must be installed. Although you can install it manually or via Systems Manager, this demo uses the manual installation method. Before proceeding, ensure your EC2 instance is assigned an IAM role with permission to access S3, so the agent can download your application’s source bundle.Creating an IAM Role for EC2
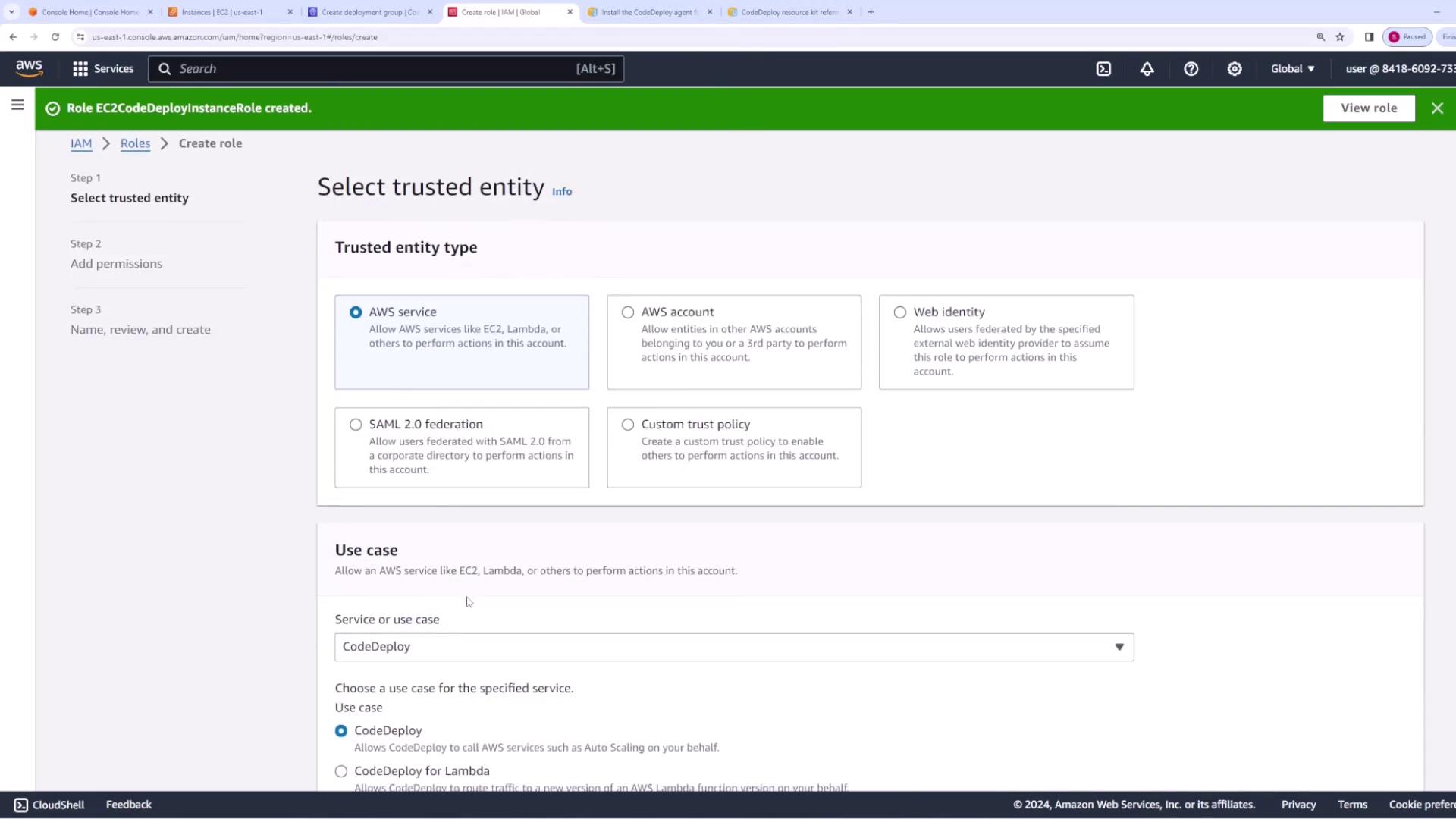
- Open the IAM console and create a new role for the AWS service EC2.
- Attach the AmazonS3ReadOnlyAccess policy to allow the instance to read objects from S3.
- Name the role “EC2 CodeDeploy instance role.”
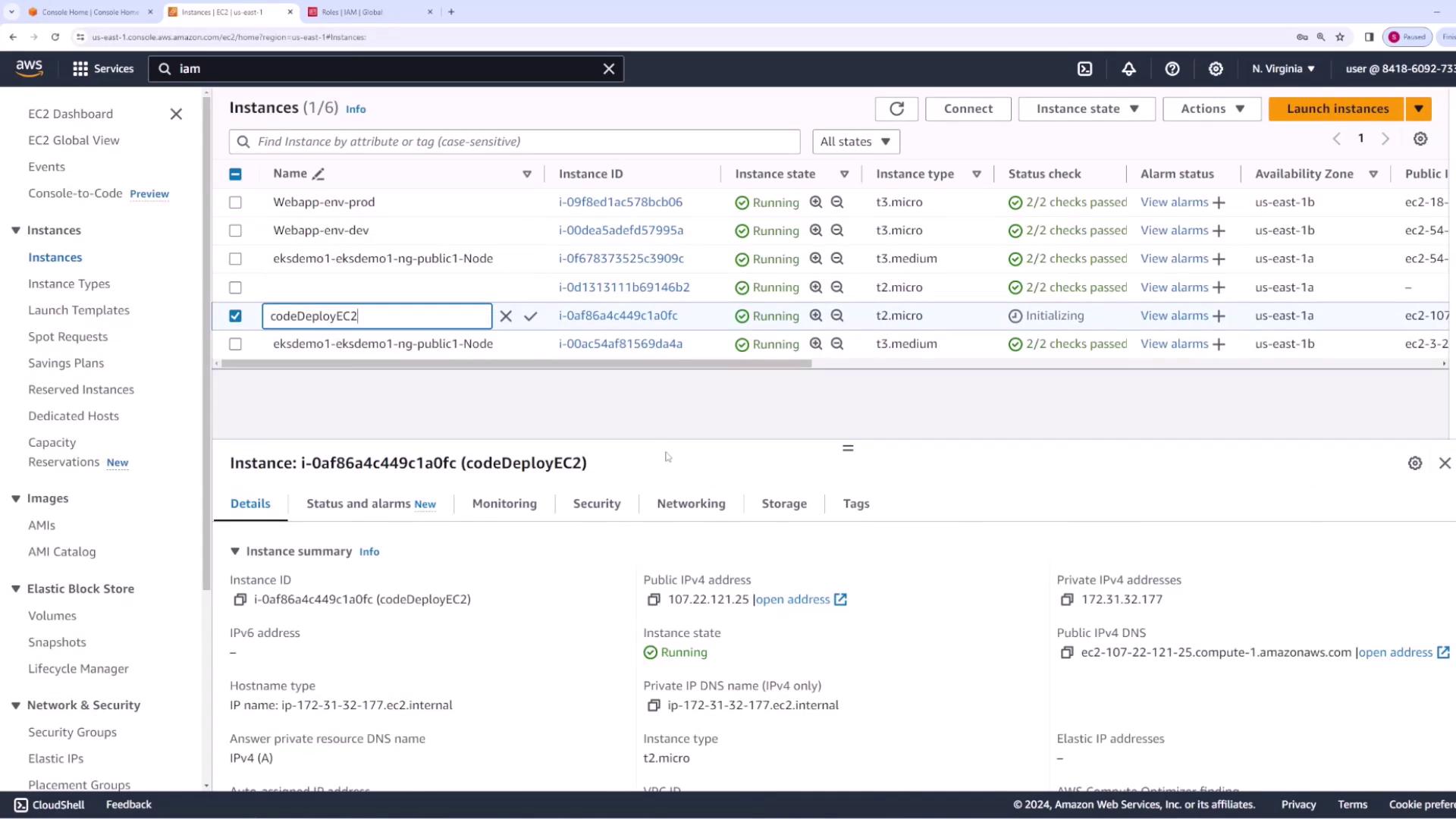
- In the EC2 console, select your instance (e.g., CodeDeploy EC2), navigate to Actions → Security → Modify IAM Role, and assign the newly created role.
Step 3: Manually Installing the CodeDeploy Agent
- SSH into your EC2 instance.
- Execute the following commands to update packages, install dependencies (Ruby and wget), download the CodeDeploy agent installer, and run it. (Note: The installer URL is for the us-east-1 region; update it if you are using another region.)
Step 4: Setting Up CodeDeploy in AWS
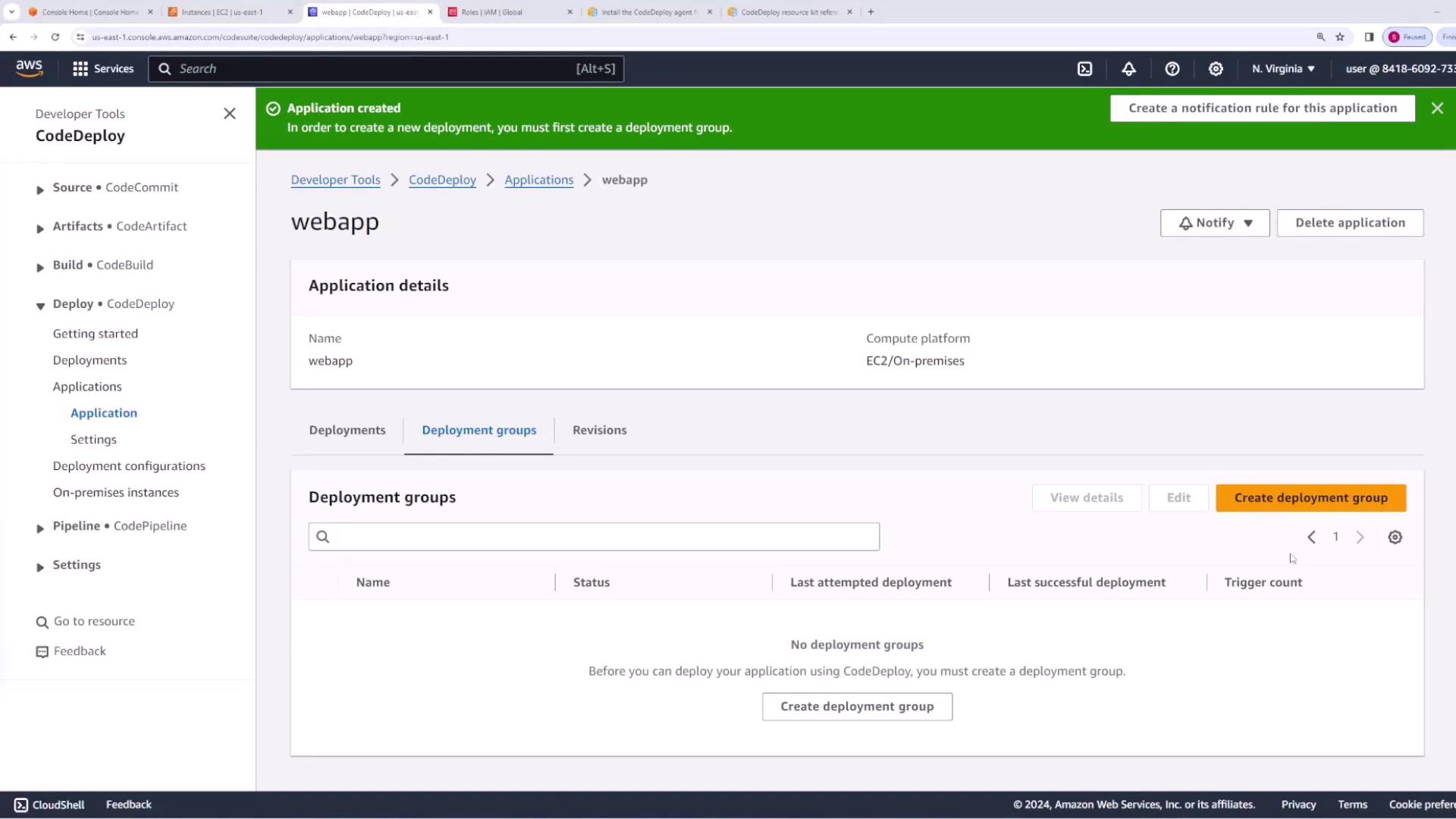
Creating an Application and Deployment Group
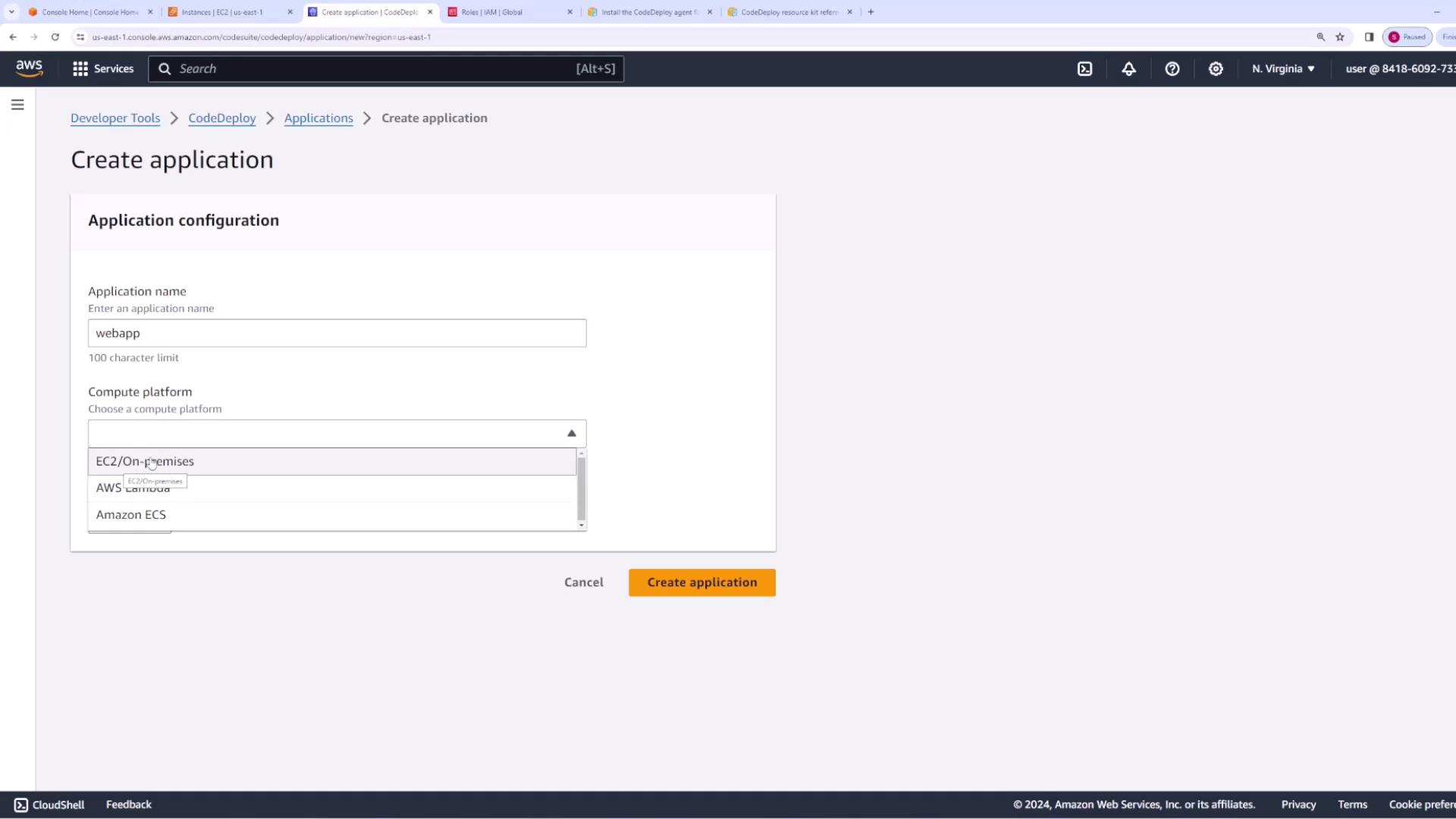
- Open the CodeDeploy console and navigate to Applications.
- Create a new application (e.g., “web app”) and choose the EC2/On-premise compute platform.
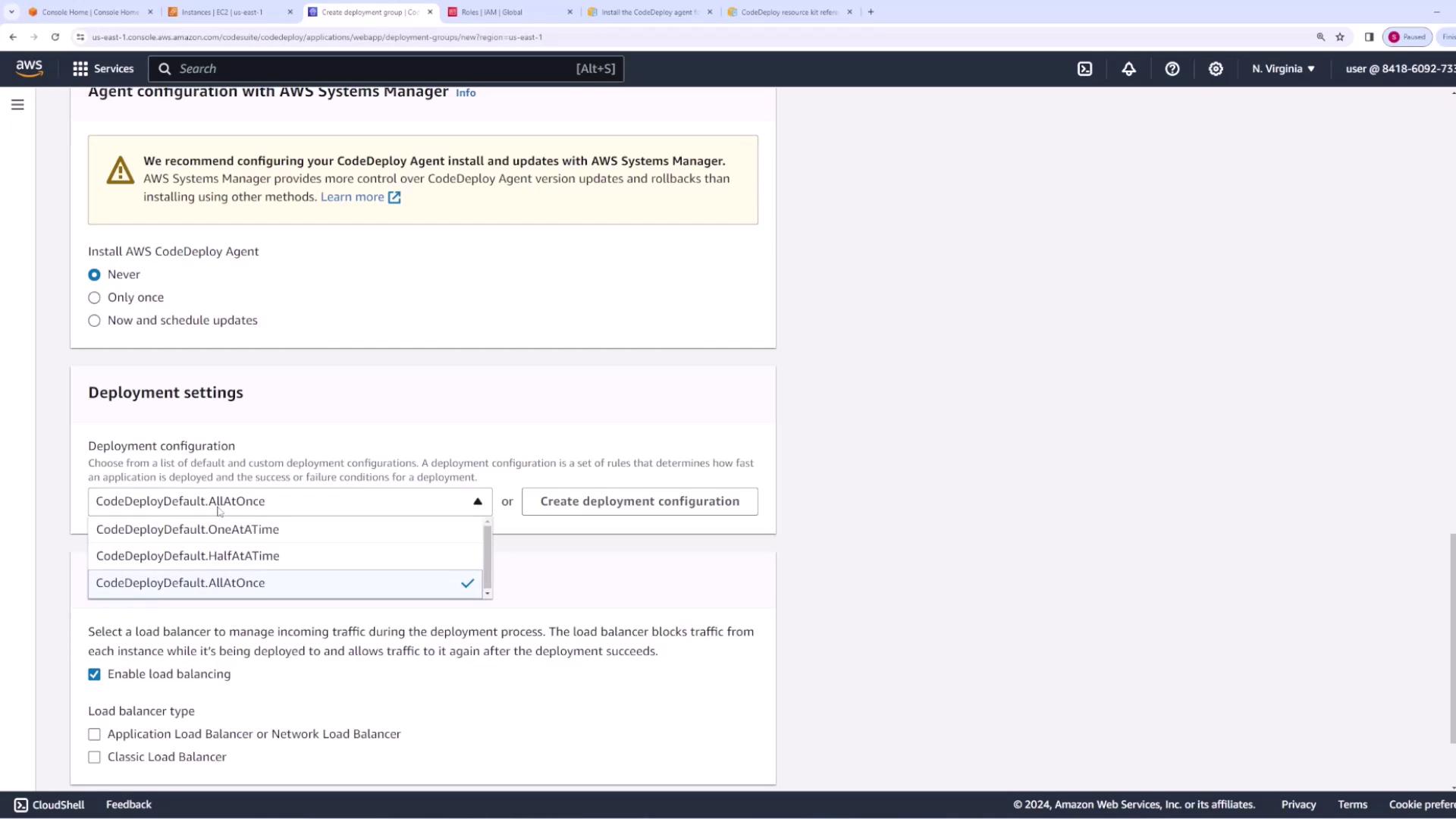
- Create a deployment group named “web app deployment group.” The deployment group requires a service role with permissions for Auto Scaling, EC2, CloudWatch, and load balancing. To create this role:
- Go to the IAM console and create a new role for the AWS service CodeDeploy.
- Attach the necessary policies.
- Name it “CodeDeploy service role.”

If you are not using AWS Systems Manager, set the CodeDeploy agent management option to “Never.”
Creating the CodeDeploy Service Role
If your deployment group does not automatically detect your previously created CodeDeploy service role, refresh the console after role creation. An example trust relationship for the CodeDeploy role is shown below:
Step 5: Preparing Your Application Revision
Our web application is a simple HTML page served by Nginx. Initially, the application consists of anindex.html file displaying version one of the application. Nginx is used as the web server to serve this content.
Below is the content of the index.html file (version one):
appspec.yaml file. This file instructs CodeDeploy where to place files and defines lifecycle event hooks to execute at different stages of the deployment. Below is our sample appspec.yaml:
Hook Scripts
-
BeforeInstall (scripts/install.sh): Installs Nginx.
-
ApplicationStart (scripts/start.sh): Starts the Nginx service.
-
ApplicationStop (scripts/stop.sh): Stops Nginx if it is running.
appspec.yaml file directs CodeDeploy to copy index.html into Nginx’s default directory (/usr/share/nginx/html) and execute the defined hook scripts during deployment.
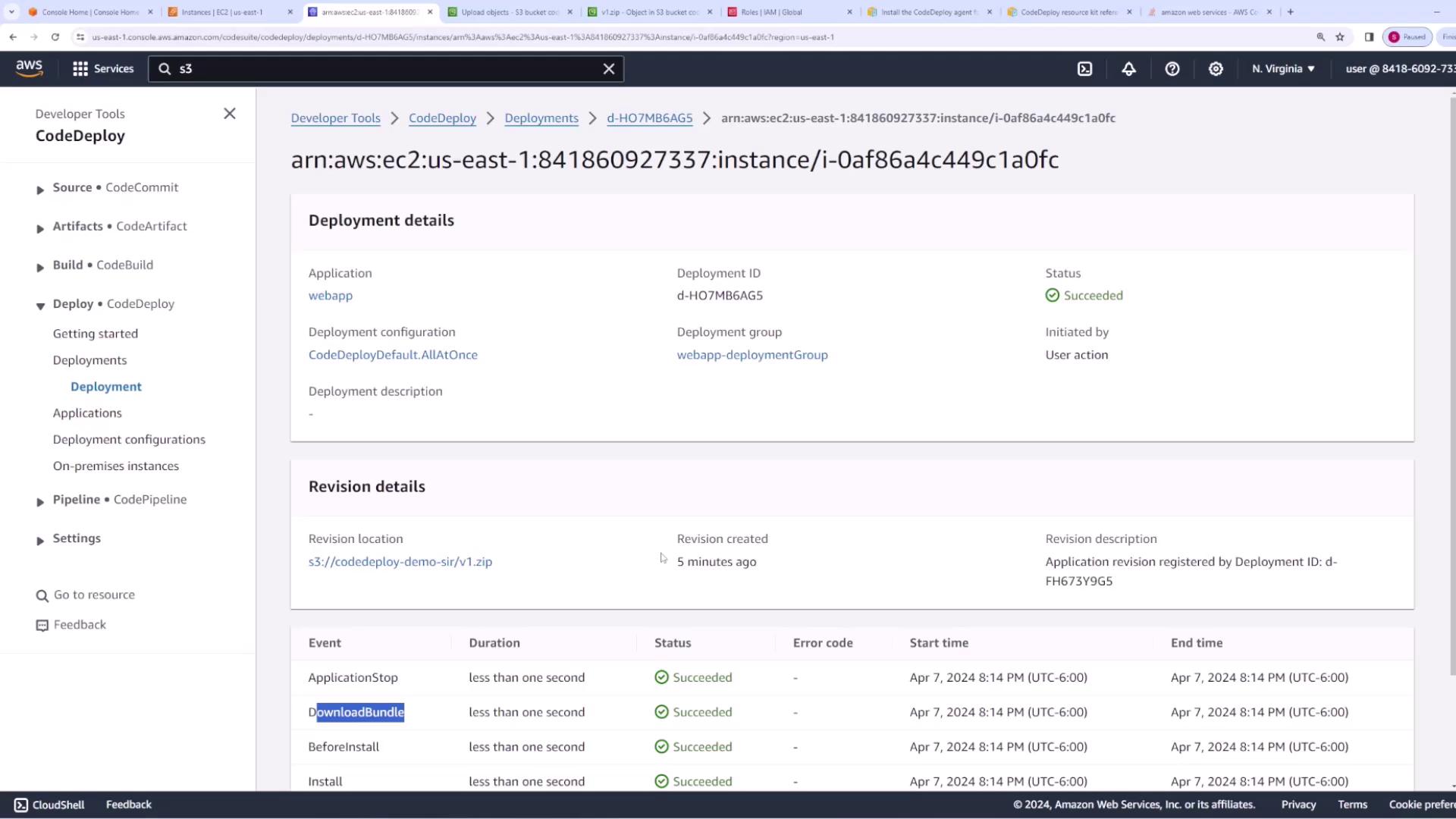
Step 6: Creating and Deploying the Application Revision
To deploy a new revision of your application, follow these steps:- Package your application files (including
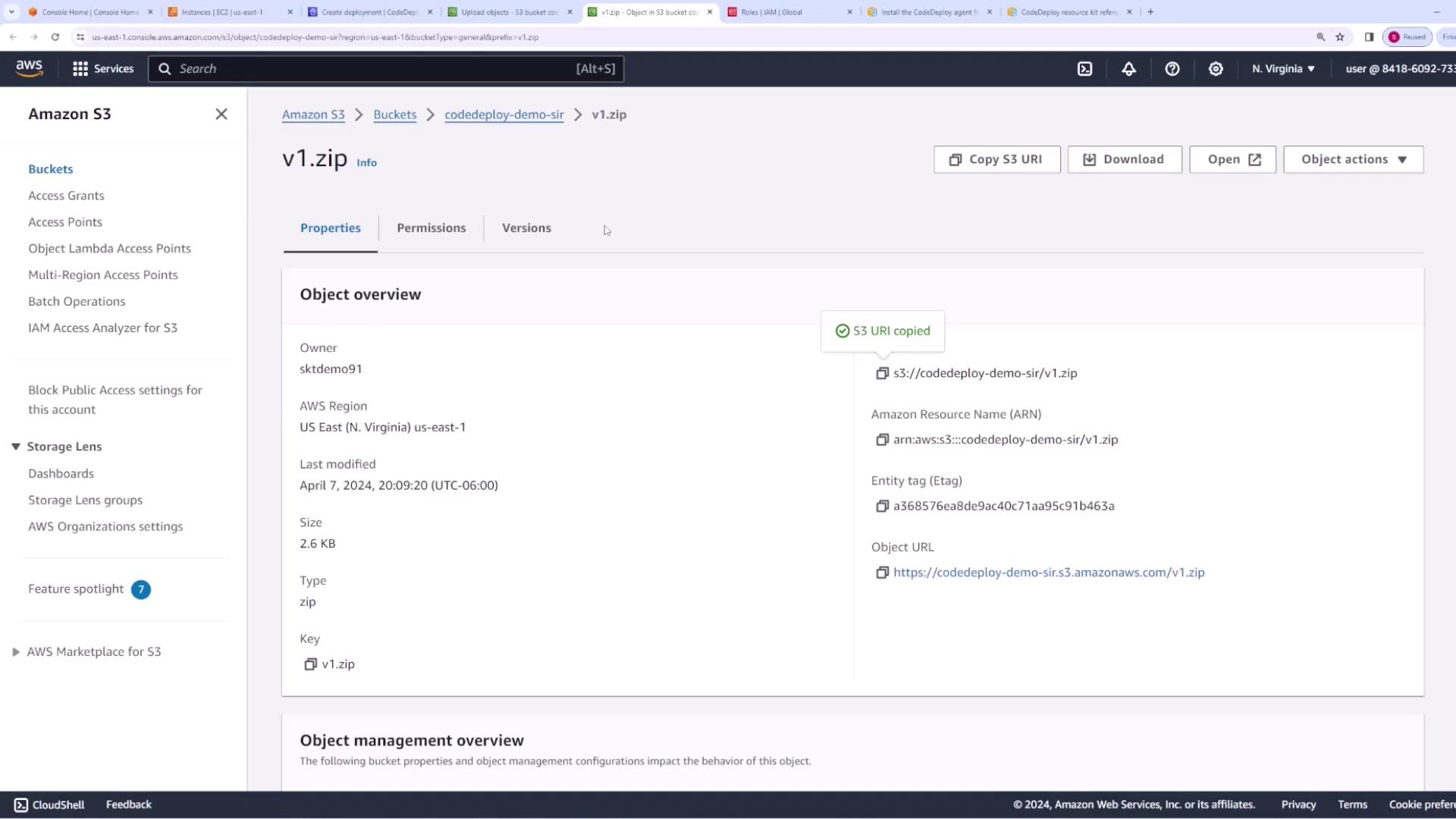
index.html, theappspec.yaml, and thescriptsfolder) into a ZIP file (e.g., v1.zip). - Upload the ZIP file to an S3 bucket configured for CodeDeploy.
- Open your application and select the deployment group.
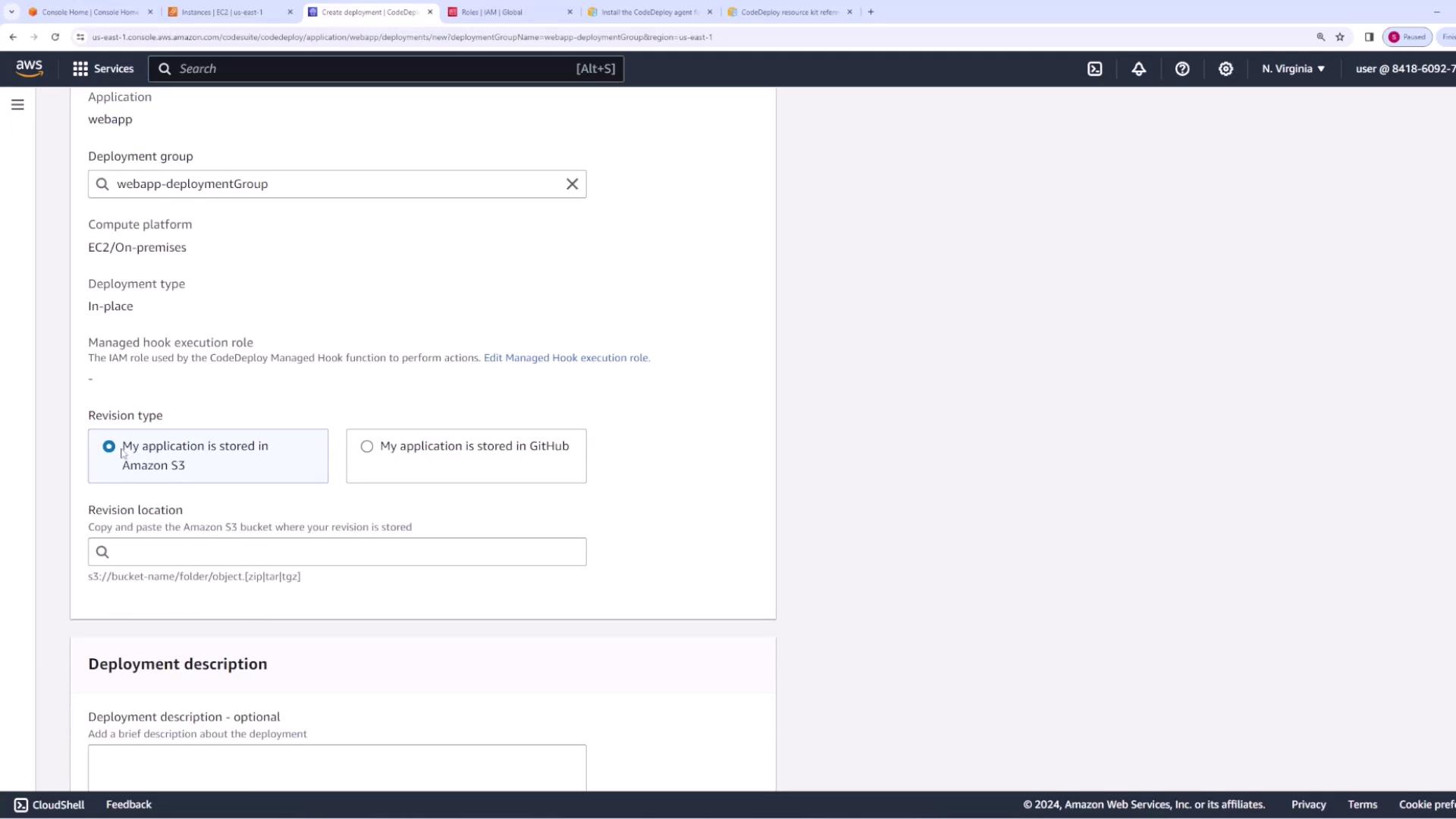
- Create a new deployment.
- Under Revision Location, paste the S3 URI and make sure the file type is set to ZIP.
- Select the option to overwrite existing file content so the new revision replaces the old one.
- Provide a clear deployment description, such as “Deployment of version 1,” and create the deployment.
Step 7: Updating the Application
To update your application (for example, to version two), modify theindex.html file as needed. Below is an updated version of index.html for version two:
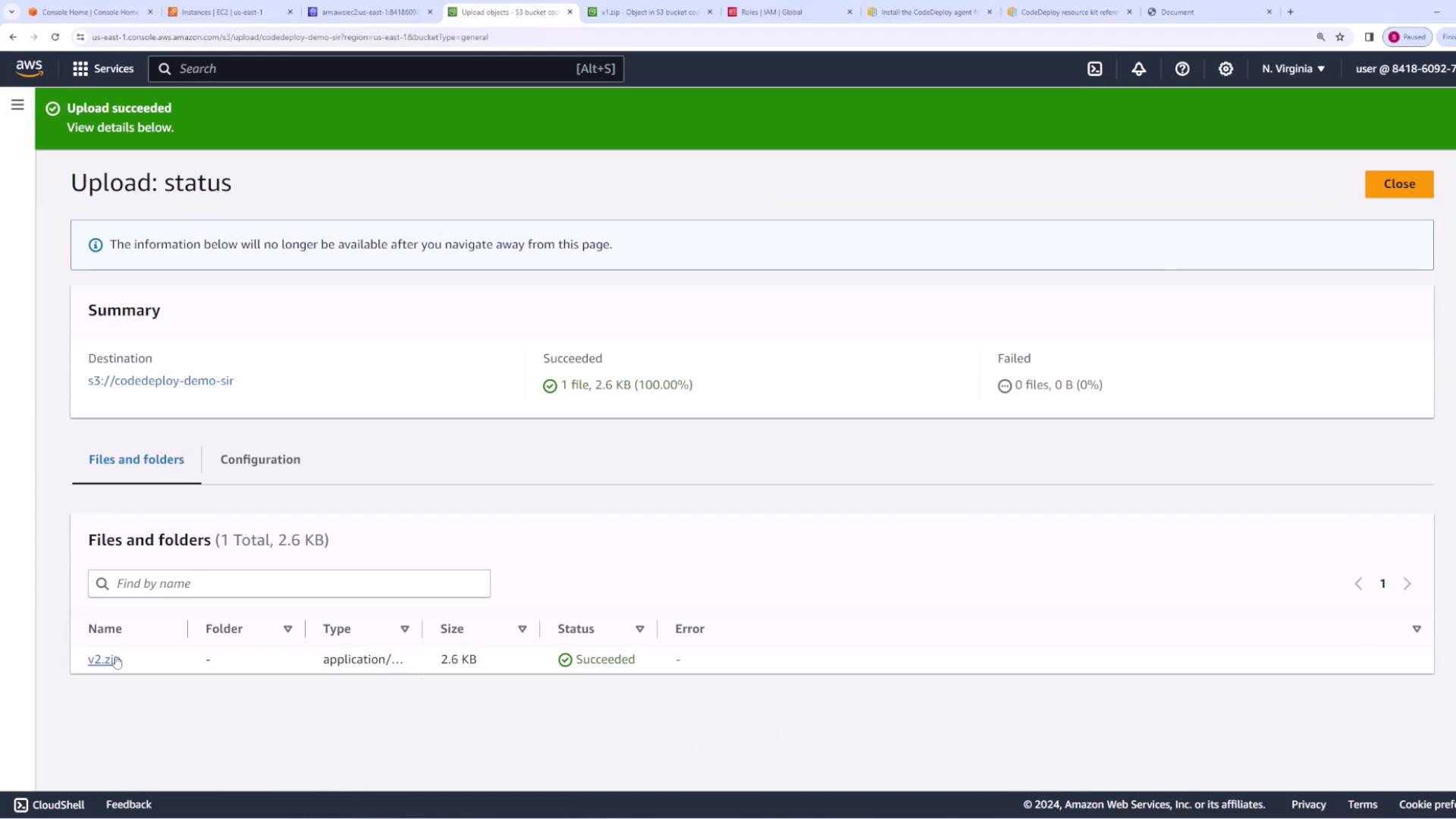
- Repackage the revised application files into a new ZIP file (e.g., v2.zip).
- Upload the new ZIP file to your S3 bucket.
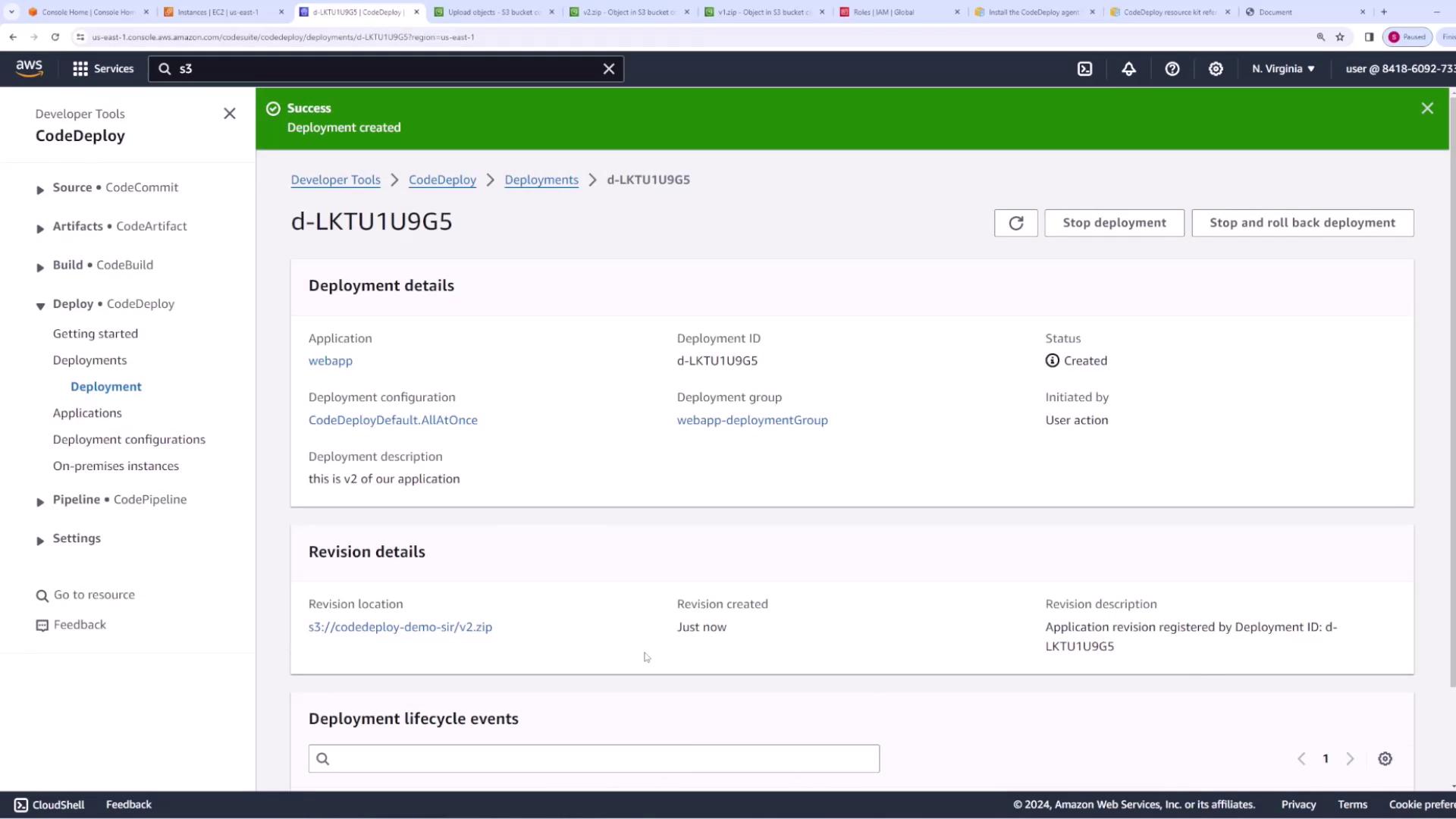
- Copy the updated S3 URI and create a new deployment in the CodeDeploy console, ensuring you select the option to overwrite the existing files.
Conclusion
This lesson covered the basics of AWS CodeDeploy, including:- Deploying an EC2 instance with the appropriate IAM role.
- Manually installing the CodeDeploy agent.
- Creating and configuring the necessary IAM roles and deployment groups.
- Configuring the deployment using an
appspec.yamlfile and lifecycle hook scripts. - Creating and updating application revisions with CodeDeploy.