Instance Store
Instance Store provides ephemeral storage that is directly hosted on the physical hardware supporting your EC2 instances. It is ideal for storing temporary data where high I/O performance is critical. However, keep in mind that data stored using Instance Store is lost if the instance is stopped, terminated, or migrated to another physical server. Key advantages of Instance Store include:- Data is stored on the physical host, ensuring high performance and low latency.
- It is suited for temporary storage scenarios where speed is paramount.
- If an instance is shut down, terminated, or moved, the data will not persist.
- Storage media may vary (SSD or HDD) based on the instance type selected.
- Many instance types offer Instance Store volumes at no additional cost beyond the EC2 instance fee.
Instance Store is best used for scratch data or caching where data persistence is not required.
Elastic Block Store (EBS)
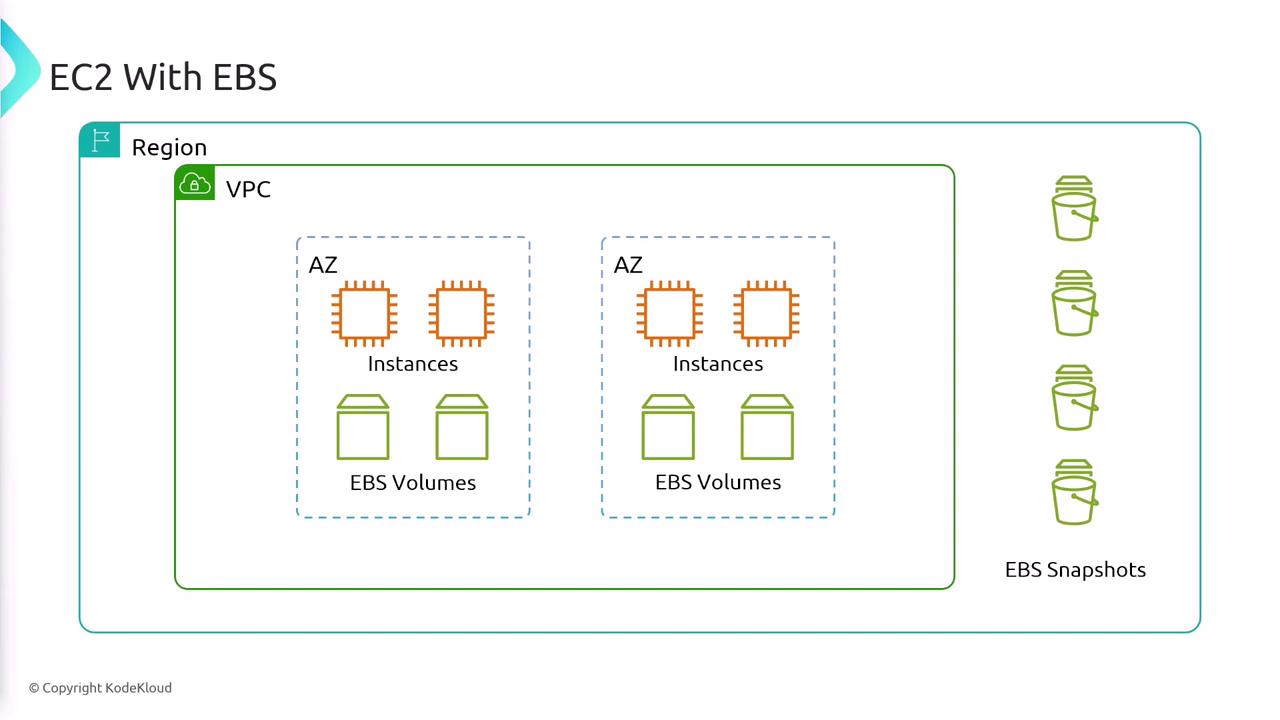
Elastic Block Store (EBS) offers scalable, persistent block storage designed for EC2 instances. It is an excellent choice for storing operating systems, databases, and critical applications that require reliable storage. Notable features of EBS include:- Ability to attach EBS volumes to EC2 instances, including using them as boot volumes.
- EBS snapshots provide point-in-time backups that incrementally save your data in Amazon S3, capturing the entire state of the volume.
- Persistent volumes remain intact even when the associated EC2 instance is terminated, and can be reattached to new instances.
- Consistent, low-latency performance supports various volume types optimized for either throughput or IOPS.
- Volumes can be resized dynamically, allowing adjustments as your application demands evolve.
- Automatic replication within the Availability Zone ensures high durability and protection against hardware failures.
Elastic File System (EFS)
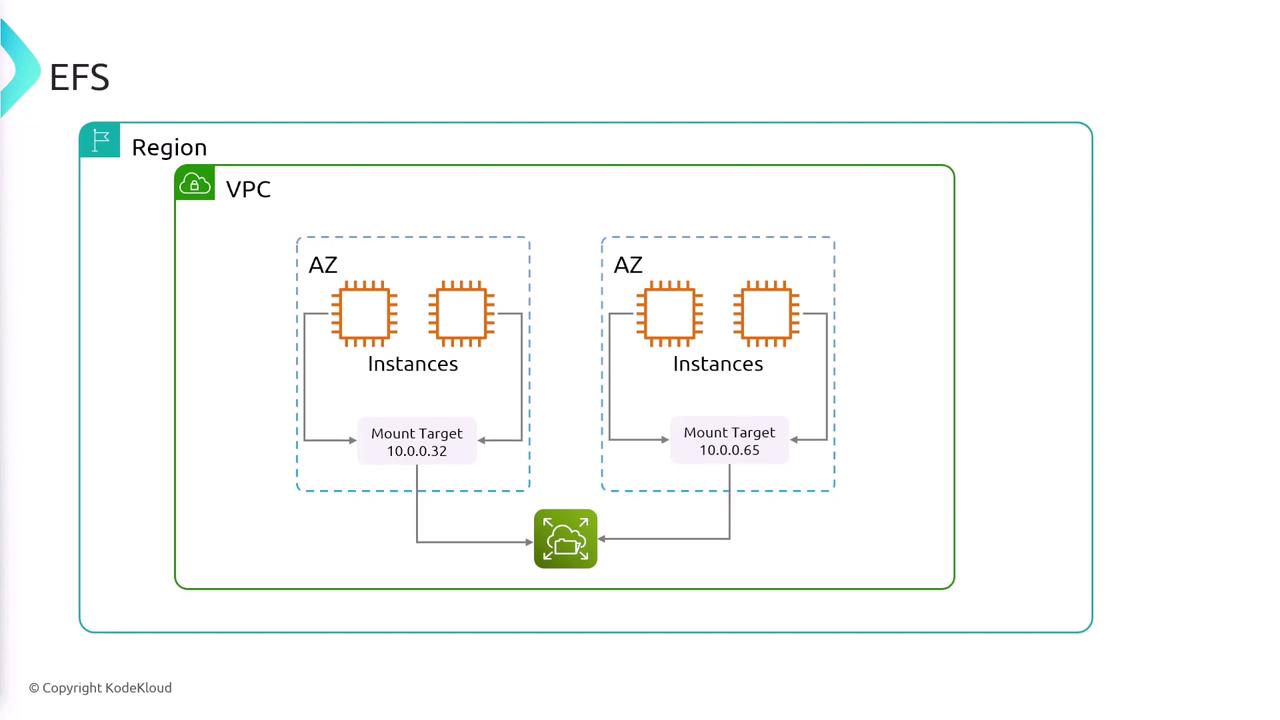
Amazon Elastic File System (EFS) is a managed, cloud-based file storage service that provides scalable and elastic NFS storage for your AWS services and on-premise resources. EFS is particularly beneficial for applications that require a shared file system accessible by multiple EC2 instances concurrently. Key characteristics of EFS include:- Easy mounting of a remote file system over the network from various EC2 instances simultaneously.
- Simplified deployment and maintenance of file storage infrastructure, as the service automatically scales to meet your needs.
- Pay-as-you-go pricing ensures that you only pay for the storage you consume.
- Automatic scaling adjusts storage capacity as data is added or removed, accommodating workloads from small datasets to petabyte-scale storage.
- Designed to deliver high durability and availability through multi-AZ replication.
- Supports NFS version 4, allowing multiple instances to access and operate on the same file system concurrently.

Storage Options Comparison
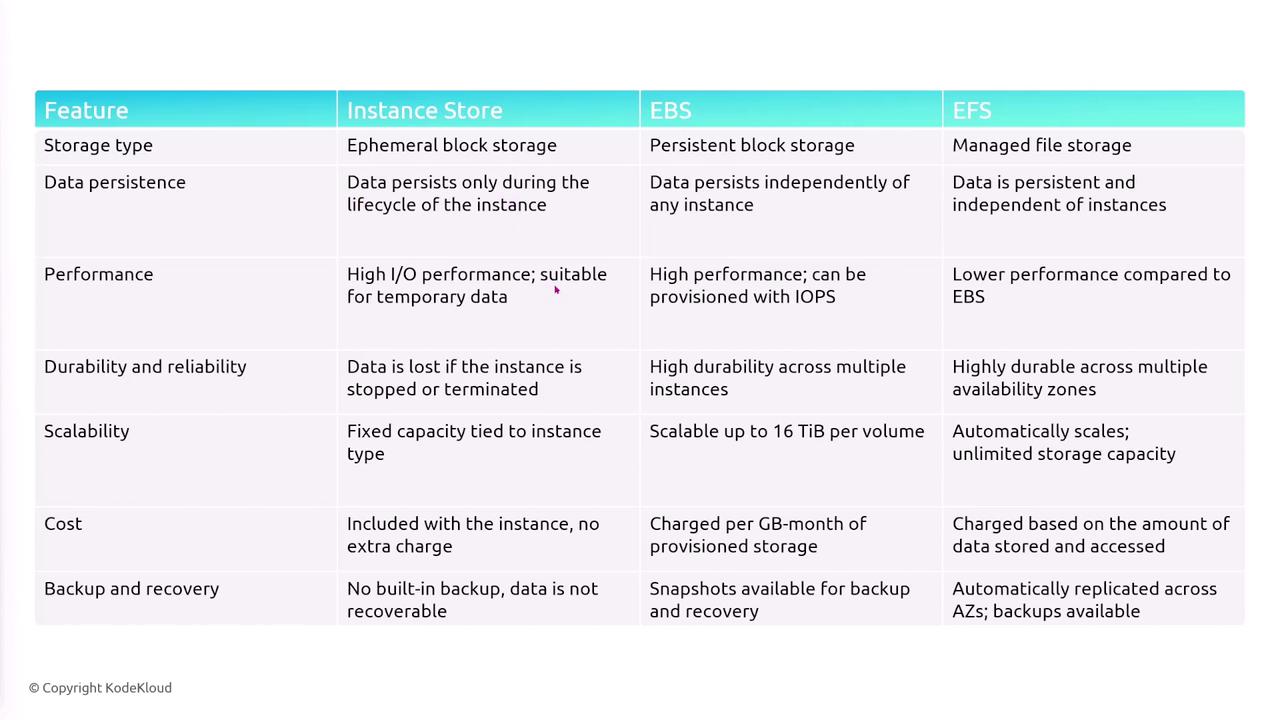
Below is a summary comparing the three primary EC2 storage options:| Feature | Instance Store | Elastic Block Store (EBS) | Elastic File System (EFS) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Storage Type | Ephemeral | Persistent block storage | Managed NFS file storage |
| Data Persistence | Data is lost on stop/termination | Data persists even if the instance is terminated | Data persists with multi-AZ replication |
| Performance | High performance with low latency | Consistent low-latency with configurable IOPS or throughput options | Appropriate for file storage with elastic scalability |
| Use Cases | Temporary data, caching, high I/O tasks | Boot volumes, databases, applications needing reliable, persistent storage | Shared file system for multiple instances |
| Flexibility & Scaling | Fixed capacity tied to instance type | Can be dynamically resized and supports snapshot backups | Automatically scales up and down based on the storage demand |
| Cost Considerations | Included with your EC2 instance cost (varies) | Charged based on provisioned capacity and IOPS | Pay-as-you-go pricing model |