Advanced Routing Capabilities
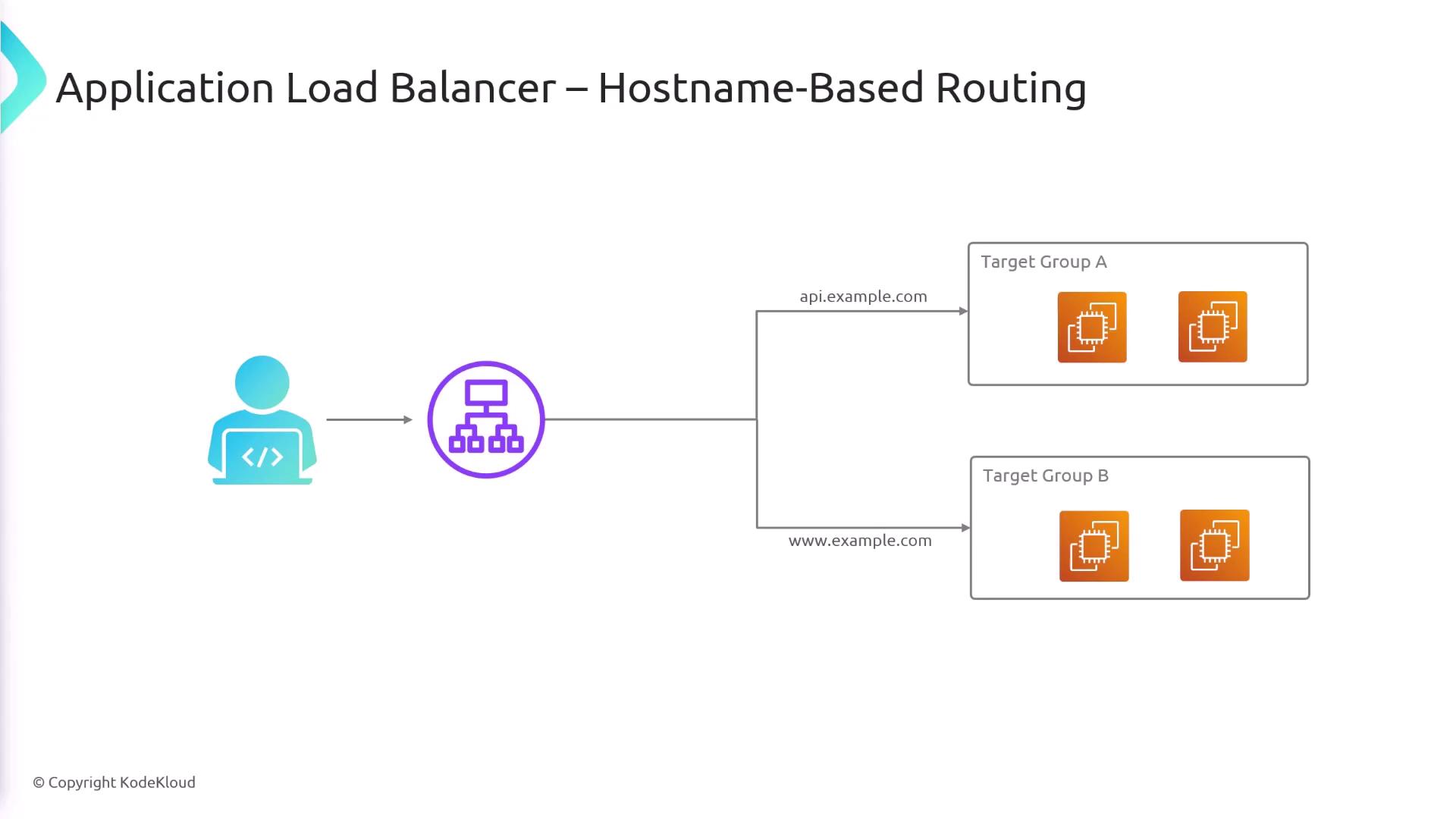
Since the ALB understands HTTP protocols, it routes requests based on numerous HTTP packet attributes. The common routing methods include:Hostname-Based Routing
The ALB can direct traffic based on the hostname in the HTTP header. For instance, if a request contains the hostnameapi.example.com, you can configure a rule to forward this traffic to a designated target group. Other hostnames can be routed to different target groups, allowing you to host multiple applications under unique domain names.
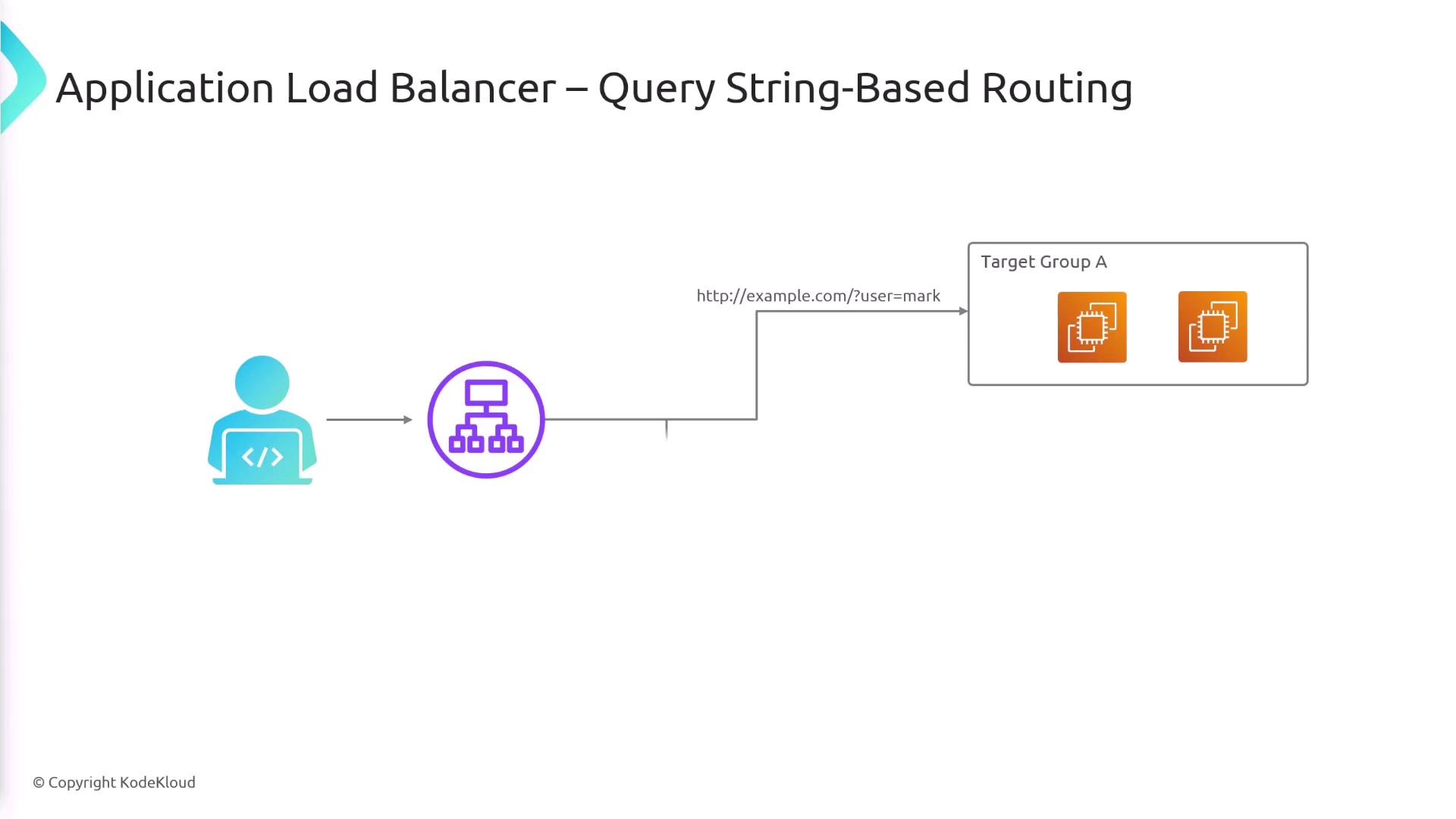
Query String-Based Routing
The ALB is also capable of routing based on query string parameters. For example, a request toexample.com with the query parameter user=mark might be forwarded to Target Group A, while a query string containing action=edit could be routed to another target group.
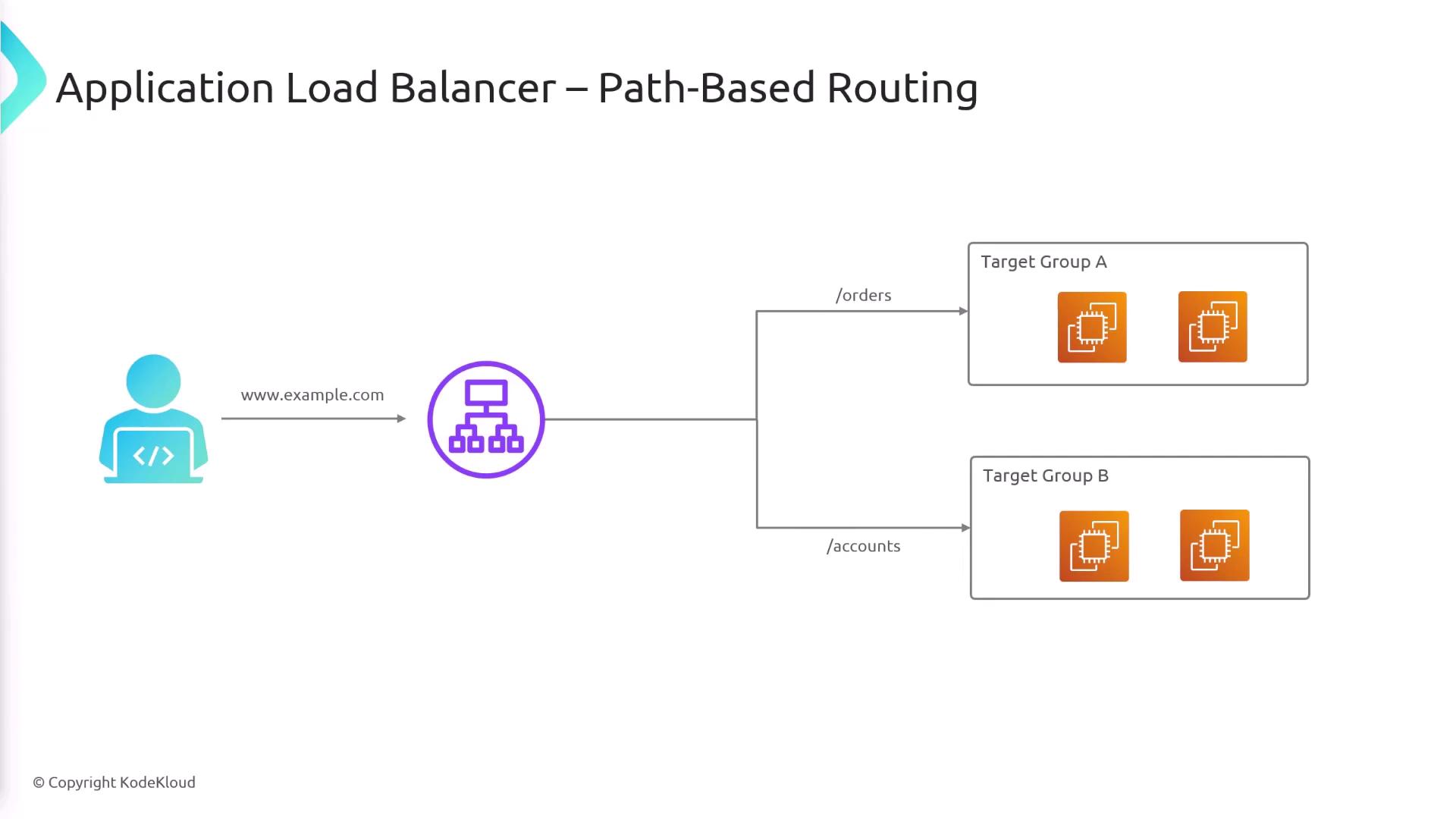
Path-Based Routing
Path-based routing allows traffic to be distributed according to the URL path. For example, requests toexample.com/orders can be directed to one target group, while requests to example.com/accounts can be sent to a different target group.
Preserving Client IP Information
When client requests pass through an ALB, the original client IP address is preserved in theX-Forwarded-For header. This header ensures that your application can access the true client IP address.
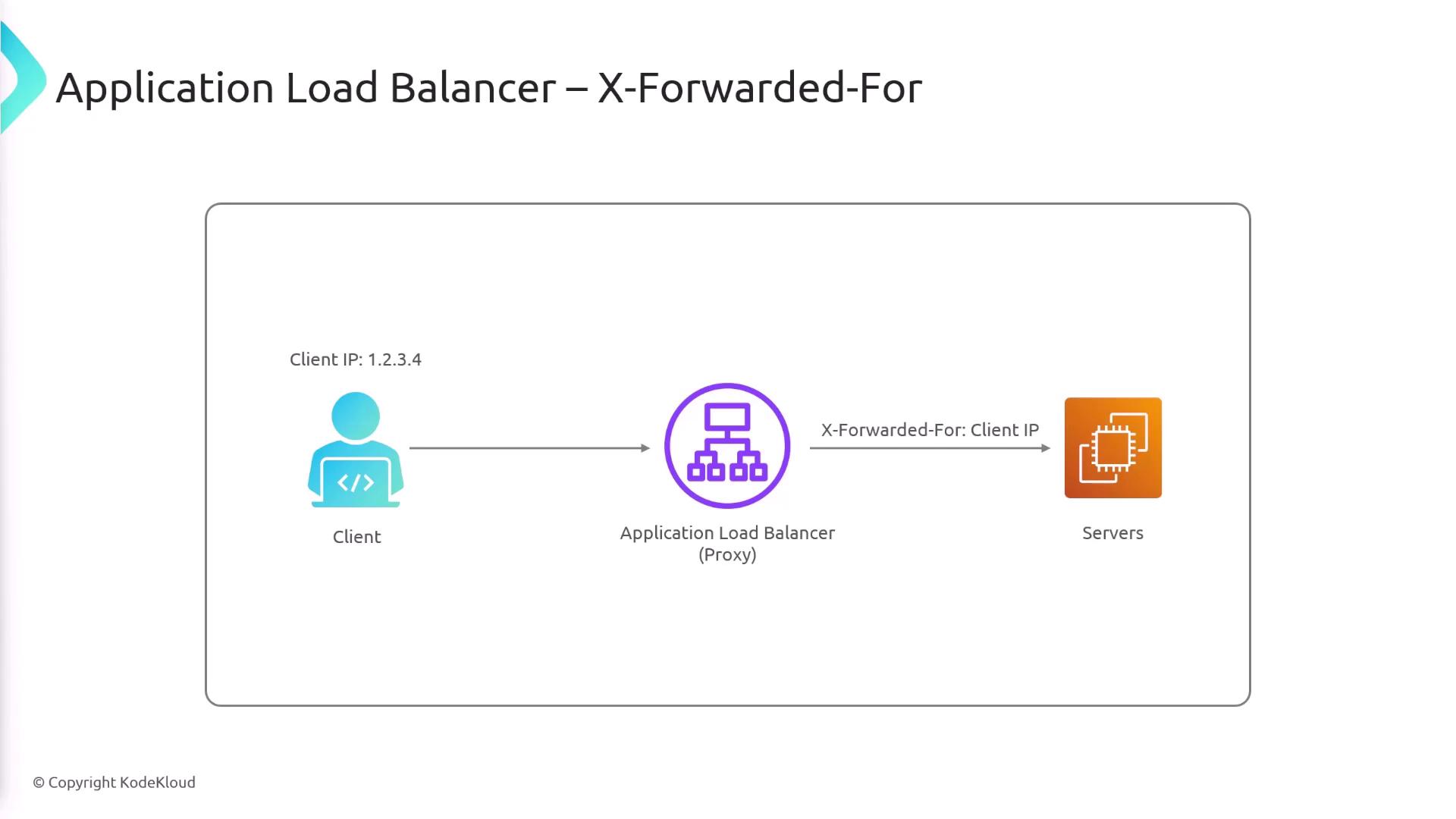
Utilizing the
X-Forwarded-For header is essential for accurate client tracking and logging, ensuring that your application has access to the original client IP.SSL Termination
One of the key benefits of using an ALB is its ability to terminate SSL/TLS connections. A typical SSL termination flow is as follows:- The client sends HTTPS traffic to the ALB.
- The ALB terminates the SSL connection and converts the request to HTTP before forwarding it to your web server.
- The web server processes the request over HTTP, and the ALB can re-encrypt the response when sending it back to the client.
SSL termination reduces the processing burden on your web servers, allowing them to focus on delivering content rather than handling encryption tasks.
Summary
The Application Load Balancer functions at the application layer (Layer 7) and supports HTTP, HTTPS, and WebSocket protocols. Its capabilities include hostname-based, query string-based, and path-based routing, as well as SSL termination. These features enable you to efficiently distribute traffic and design scalable, robust architectures.