One distinct advantage of the NLB is that it assigns a fixed IP address (static or Elastic IP), which is critical for both exam requirements and real-world configurations.
Advantages of the Network Load Balancer
The NLB offers several notable benefits:-
Retains the Client’s Source IP Address:
Unlike the Application Load Balancer (ALB) that substitutes the client’s IP with a specific header, the NLB preserves the original IP address. This is particularly useful for applications that require accurate source IP visibility. -
High Performance and Low Latency:
Designed for high throughput, the NLB minimizes latency making it suitable for performance-critical applications. -
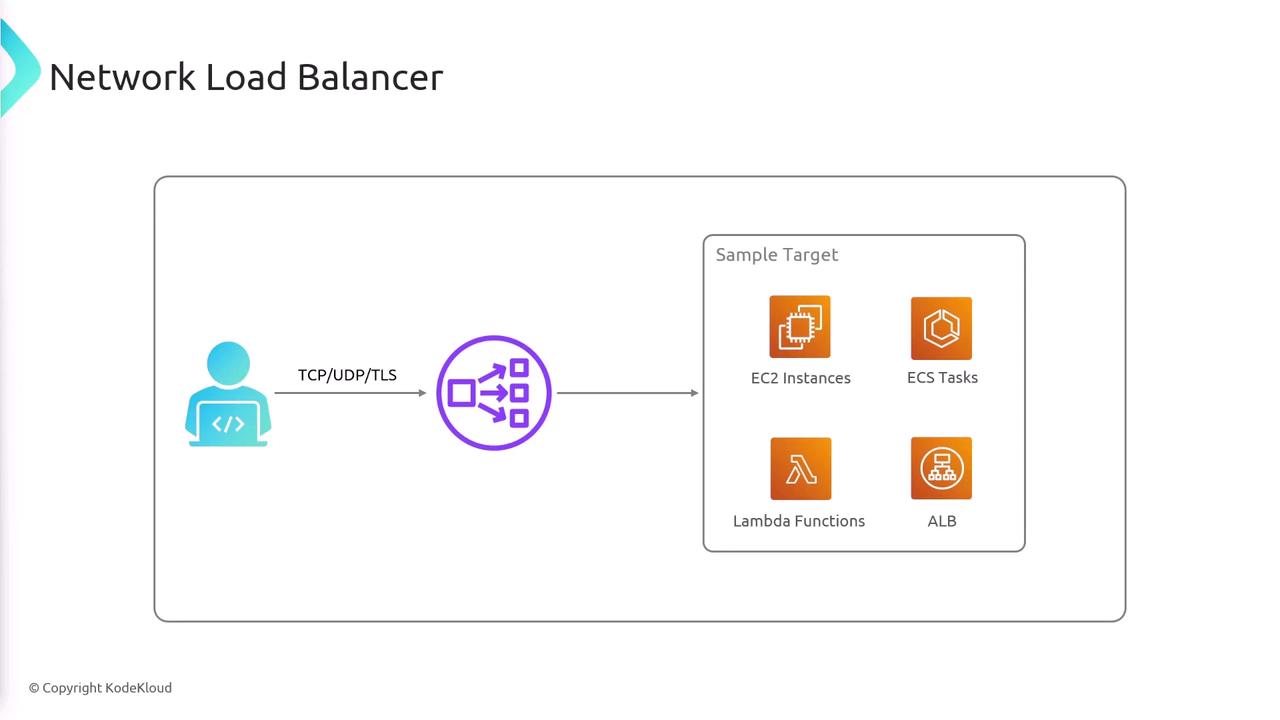
Robust Target Support:
The NLB can forward incoming traffic to various backend targets, including:Target Type Example EC2 Instances EC2 Instances ECS Tasks ECS Tasks Lambda Functions Lambda Functions Application Load Balancer ALB for additional routing capabilities
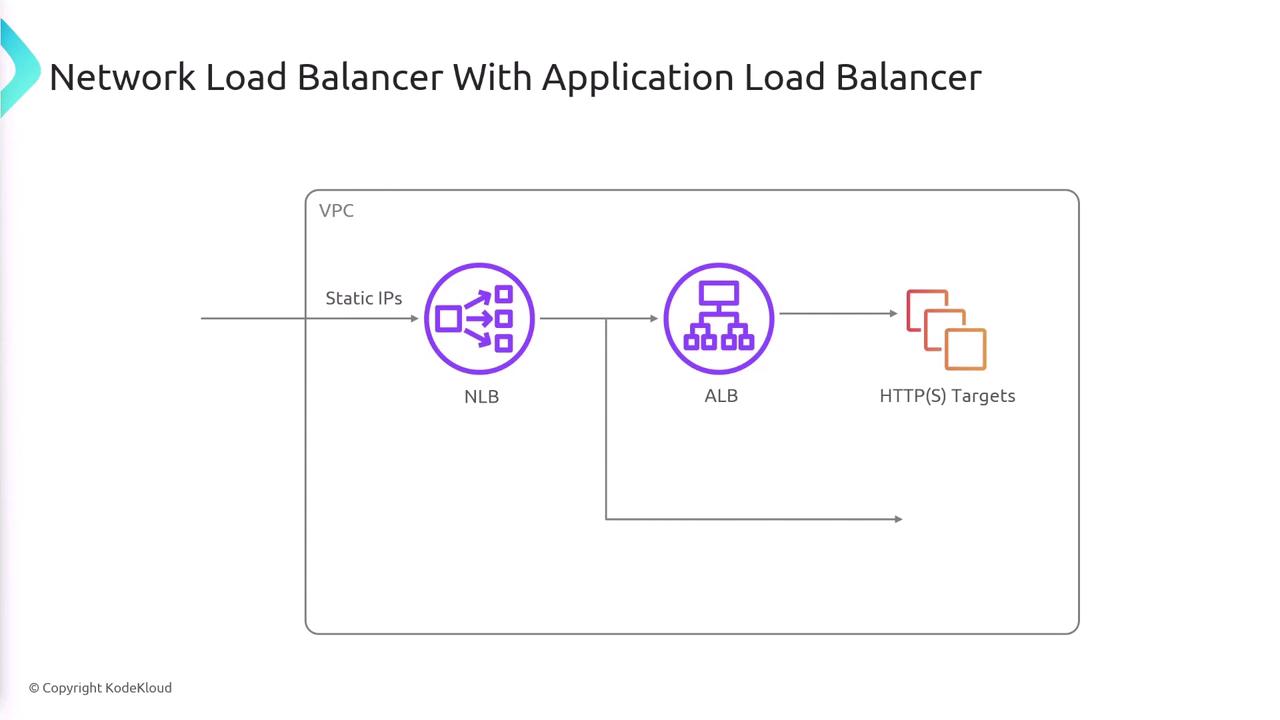
Routing Traffic to an Application Load Balancer
One of the unique capabilities of the NLB is its ability to forward traffic to an Application Load Balancer. This feature is not available with ALBs, as they cannot route traffic to other load balancers. The workflow for routing traffic is as follows:- Traffic is sent to the Network Load Balancer.
- The NLB’s static (or fixed) IP can be integrated into DNS settings or firewall configurations.
- The NLB forwards the incoming traffic to an Application Load Balancer.
- The ALB then routes the traffic to its designated backend targets.
Summary
The Network Load Balancer:- Operates at Layer 4 of the OSI model using TCP/UDP protocols.
- Retains the client’s original source IP address.
- Provides high performance with low latency.
- Offers a static IP address essential for secure DNS and firewall configurations.
- Supports routing to various backend targets, including the capability to integrate with Application Load Balancers.
For more insights on load balancing strategies in cloud environments, explore AWS Load Balancers and other cloud networking resources.