How It Works
For a server to interact with AWS Systems Manager, it must have the SSM agent installed. This agent facilitates secure communication between the server and Systems Manager, enabling remote command execution and configuration changes seamlessly.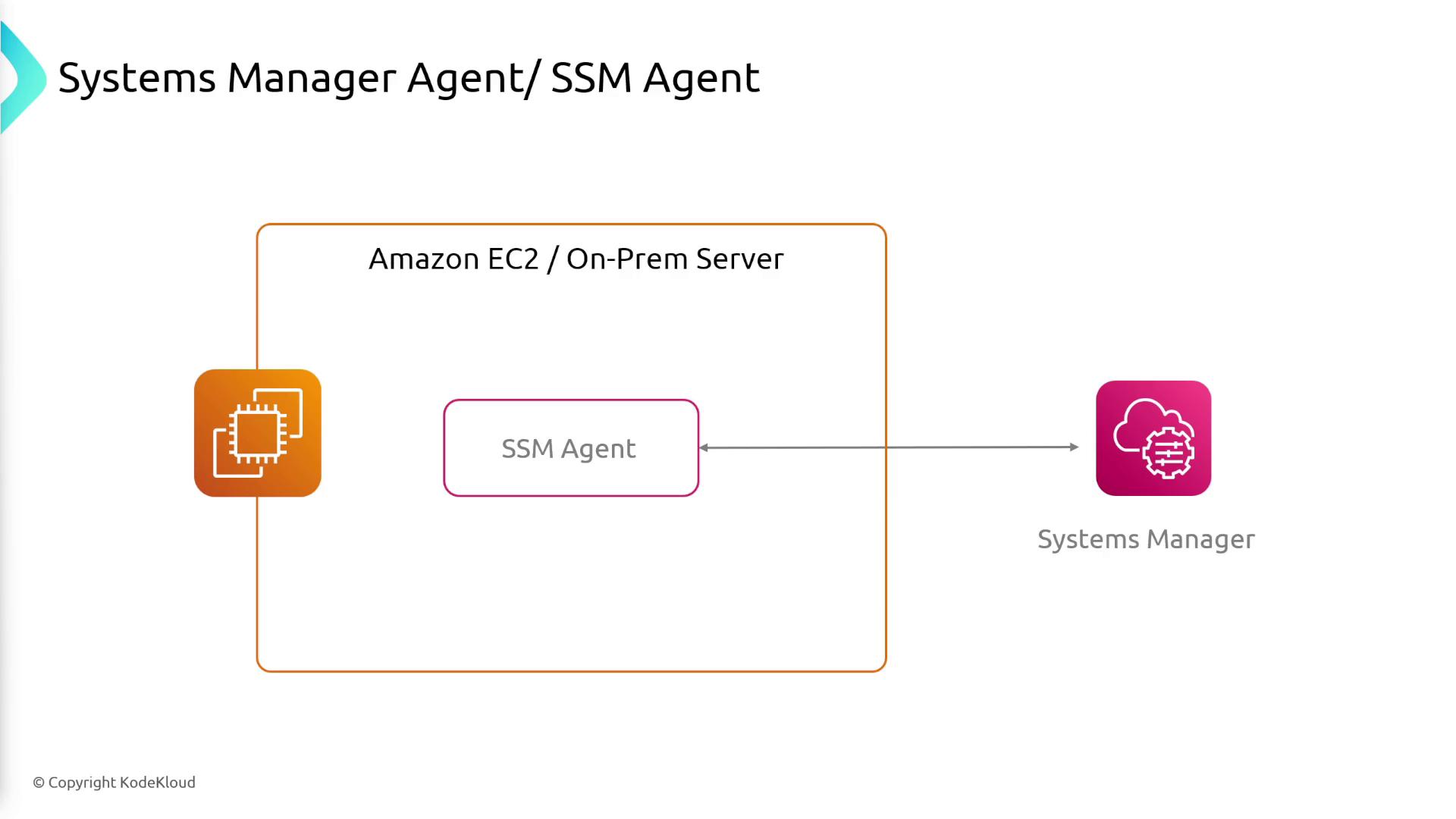
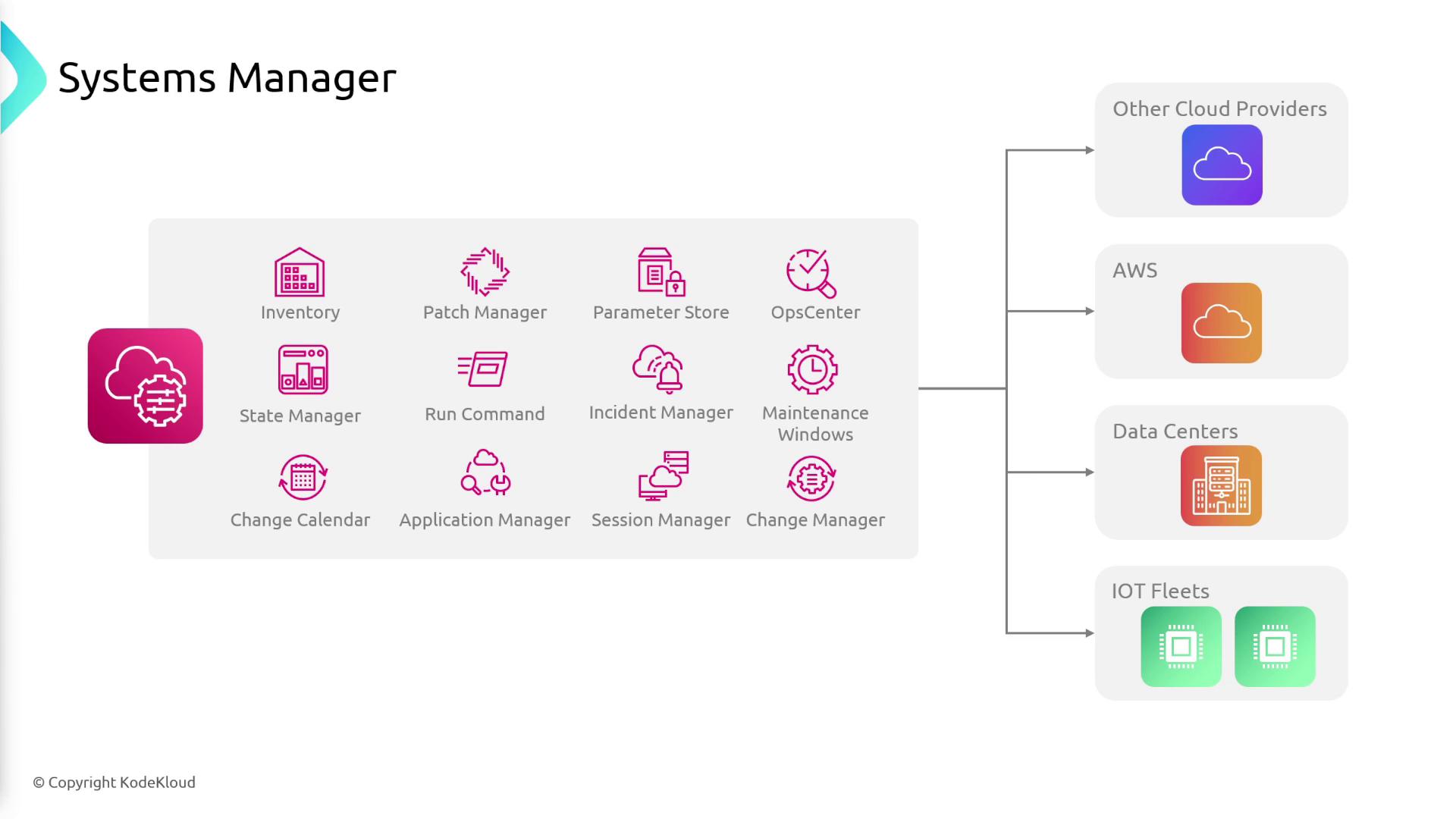
Key Features and Capabilities
AWS Systems Manager offers a unified interface to monitor operational data and automate tasks across your resources. Its core features include:- Centralized Management: Group and manage your resources based on applications, workloads, or environments.
- Automation: Automate routine IT operations and maintenance tasks safely.
- Patch Manager: Ensure automated deployment of OS and security patches across managed instances.
- Operational Insights: Gain detailed insights into the health and status of your infrastructure.
- Parameter Store: Securely store configuration data and secrets using a hierarchical structure.
- Remote Management: Access and manage instances via a browser-based shell or AWS CLI without the need to open inbound ports or handle SSH keys.
- Compliance and Inventory: Continuously monitor patch compliance, configuration consistency, and collect metadata from instances.
- Hybrid Management: Seamlessly manage both cloud-based and on-premises resources.
AWS Systems Manager centralizes management tasks, enabling greater operational efficiency and reducing the risk associated with manual interventions.
Application Manager
The Application Manager feature enables you to troubleshoot issues in AWS resources by visualizing them within the context of applications and clusters. For instance, if an application reliant on an EC2 instance, an RDS instance, and Lambda functions experiences increased error rates, the Application Manager will provide a detailed architecture view. This visualization aids in quickly identifying anomalies, such as a misbehaving EC2 instance, by presenting in-depth metrics, logs, and configuration details.Parameter Store
Parameter Store is a secure repository for storing configuration data and secrets. This tool ensures that applications can retrieve necessary settings and credentials at runtime in a secure and centralized manner.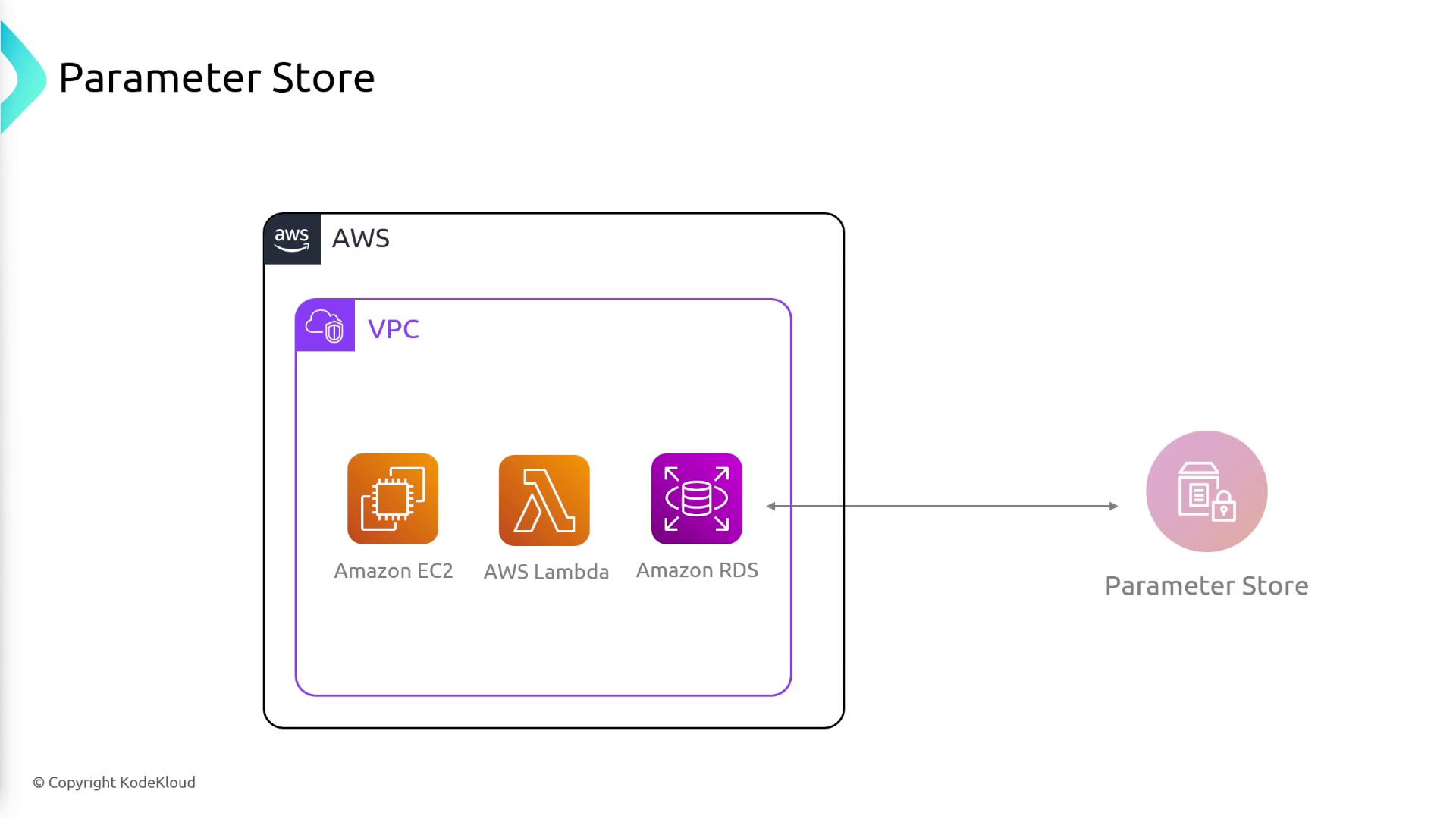
Change Management Components
AWS Systems Manager includes several features to support controlled and auditable operational changes:- Change Manager: Establish a structured workflow for critical changes—such as upgrading databases—that require pre-approval before implementation.
- Automation: Automatically execute pre-defined tasks (e.g., applying security configurations or assigning IAM roles) when launching new EC2 instances to ensure compliance.
- Change Calendar: Schedule blackout periods (like high-traffic holidays) during which operational changes are not permitted.
- Maintenance Windows: Plan tasks during off-peak hours, like late night or early morning, to reduce user impact when performing updates or patches.
Node Management
Within node management, Systems Manager provides a range of functionalities designed to maintain and secure your servers:- Compliance and Inventory: Continuously scan your server fleet for patch compliance and configuration consistency while collecting detailed metadata.
- Session Manager: Securely access and manage instances via an auditable session without requiring open inbound ports.
- Run Command: Execute commands remotely on multiple servers simultaneously.
- State Manager: Ensure that instances adhere to a desired state automatically.
- Patch Manager: Automate the deployment of operating system patches.
- Distributor: Facilitate the distribution of software packages across your instances.
- Incident Manager: Quickly respond to incidents such as website downtime by detecting outages via CloudWatch alarms, notifying on-call engineers, and executing a pre-defined response plan.
- Ops Center: Consolidate alerts from various AWS services into a centralized dashboard to manage operational issues effectively.
Conclusion
In summary, AWS Systems Manager simplifies the management of both EC2 and on-premises servers by providing a single, powerful interface for configuration, automation, patch management, and operational insights. For successful integration, ensure that the SSM agent is installed and properly configured on each server. By leveraging the rich features of Systems Manager, you can achieve robust, secure, and efficient infrastructure management across your entire environment.