Step 1: Access the Cognito Service
Start by navigating to the AWS Cognito service page. Here, you can create user directories tailored for your application. Note that selecting “Grant access to AWS services” is intended for identity pools. In this demo, we will create a user pool. A separate lesson covers identity pool setup. Click on Create User Pool to start the process.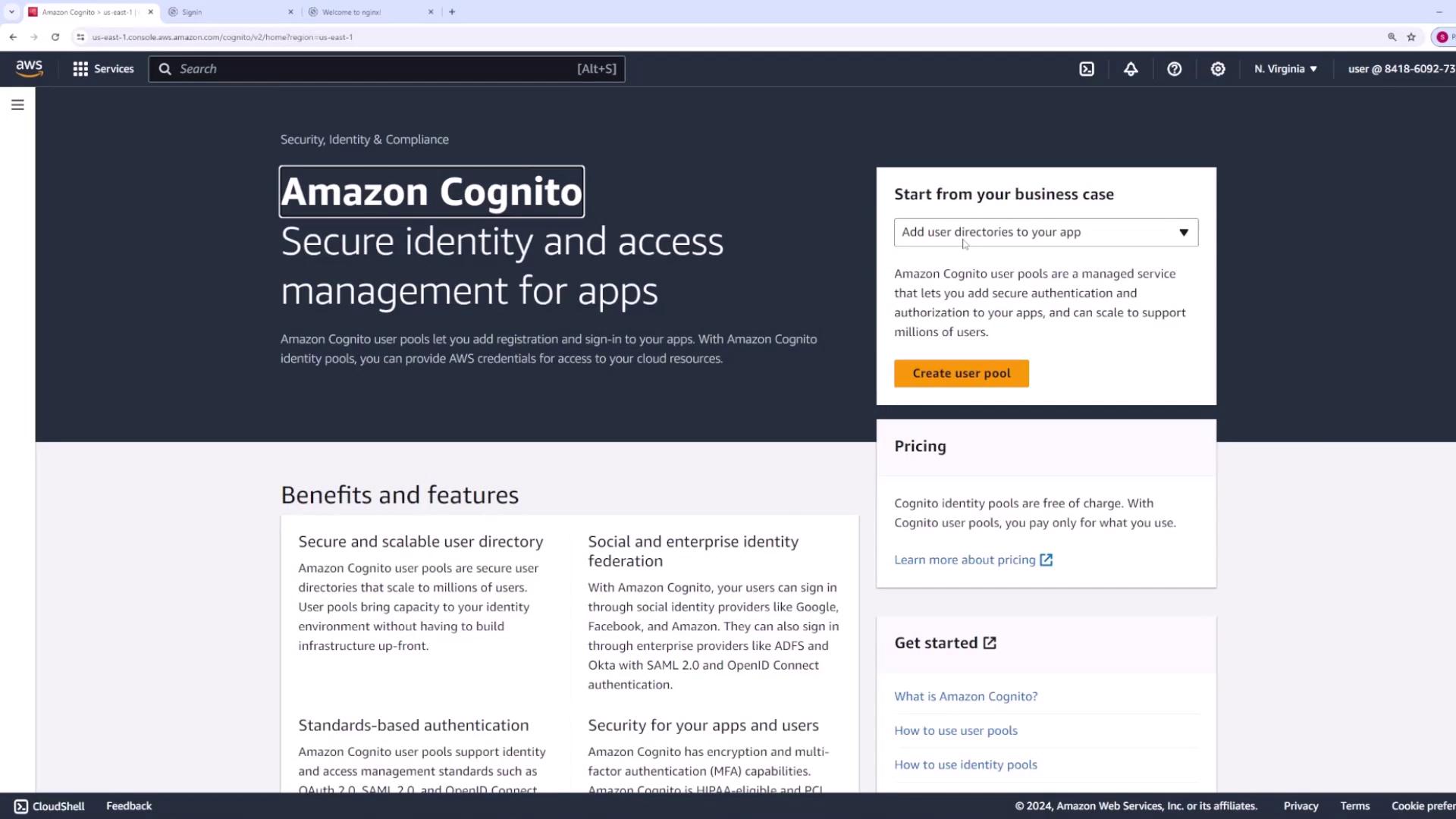
Step 2: Explore Cognito Authentication Capabilities
Amazon Cognito simplifies authentication by handling user registration, sign-in, sign-out, password recovery, and verification processes automatically. Under the “Provider Types” section, you will see that the Cognito user pool is pre-selected and grayed out, allowing sign-in using an email address, phone number, or username.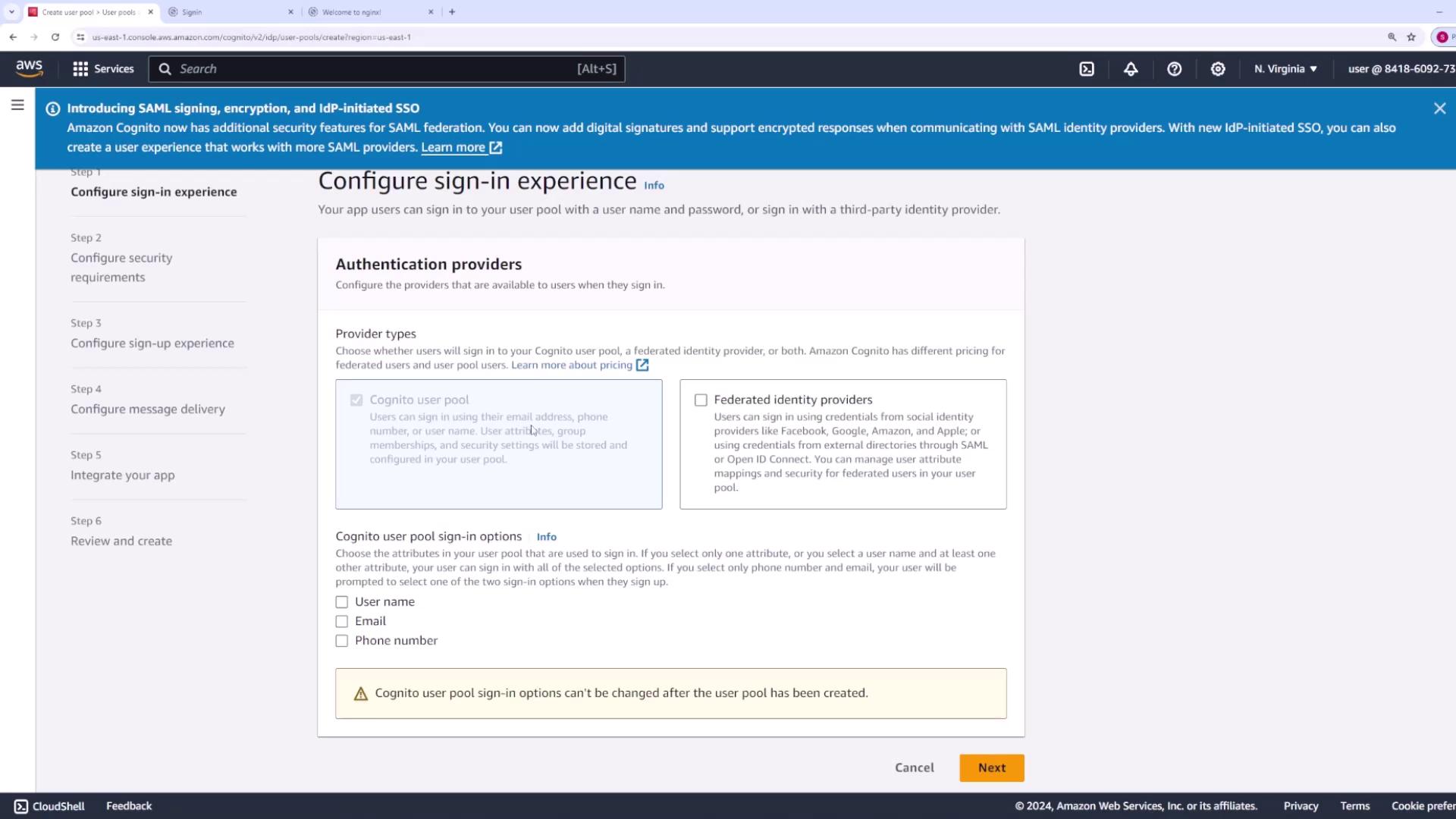
Step 3: Configure Password Policy and Security Settings
Set your password policy by modifying the default settings. Typically, passwords must be at least eight characters and meet specific complexity requirements. Customize these settings as needed for your organization’s security standards.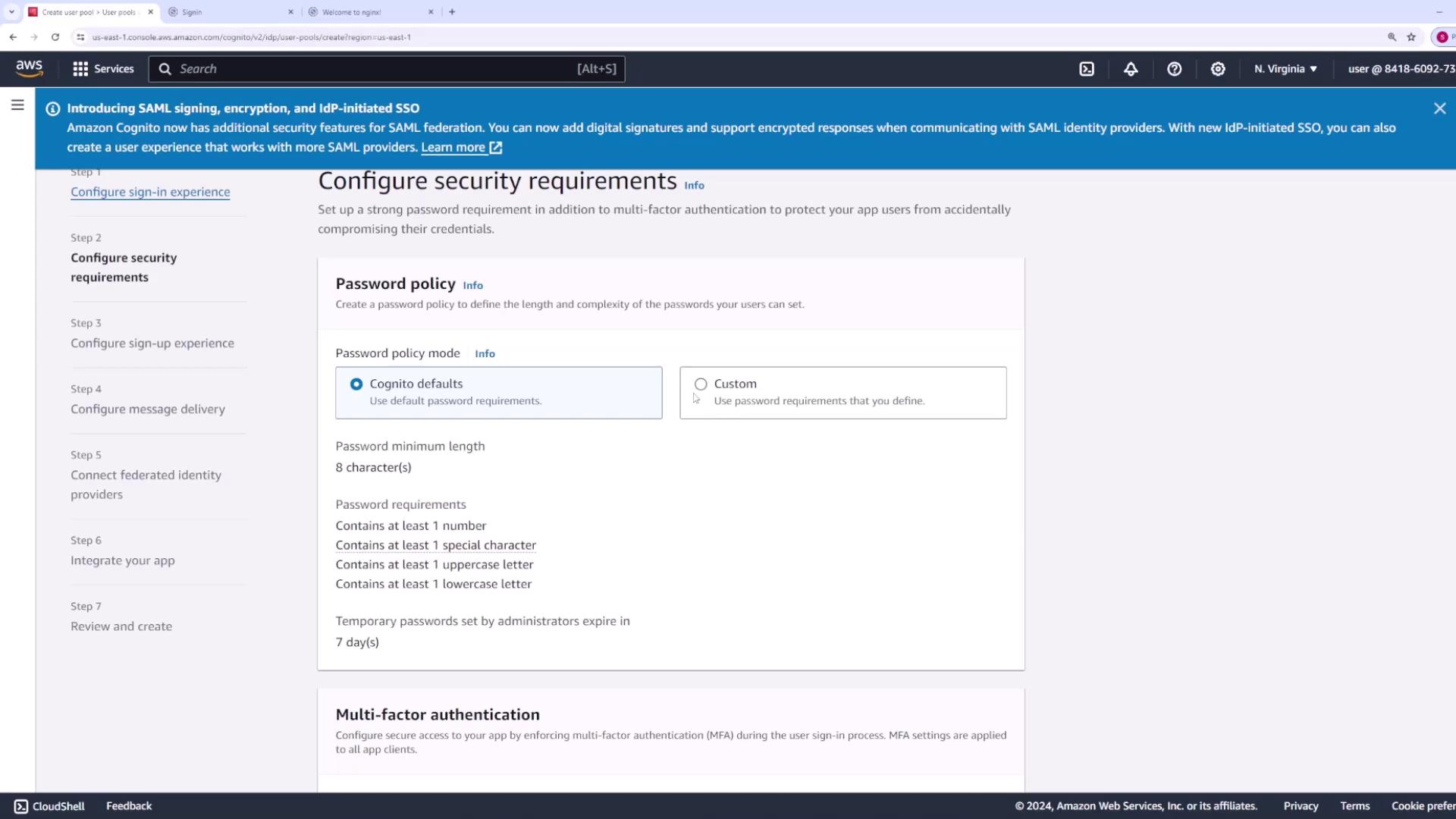
For this demo, MFA is disabled. However, you can enforce or optionally enable MFA (using SMS or an authenticator app) based on your security requirements.
Step 4: Verify Account Attributes
Amazon Cognito automates the process of sending verification messages via SMS or email to confirm ownership of the provided email addresses or phone numbers. During registration, specify which attributes (e.g., email, phone number, birthdate, or custom attributes) are required.
Step 5: Configure Email and SMS Message Delivery
Decide whether to use Amazon SES (Simple Email Service) or the default Cognito email service for message delivery. The default service is suitable for development (up to 50 emails per day), while SES is recommended for production environments with higher throughput. Configure your “From” email address accordingly.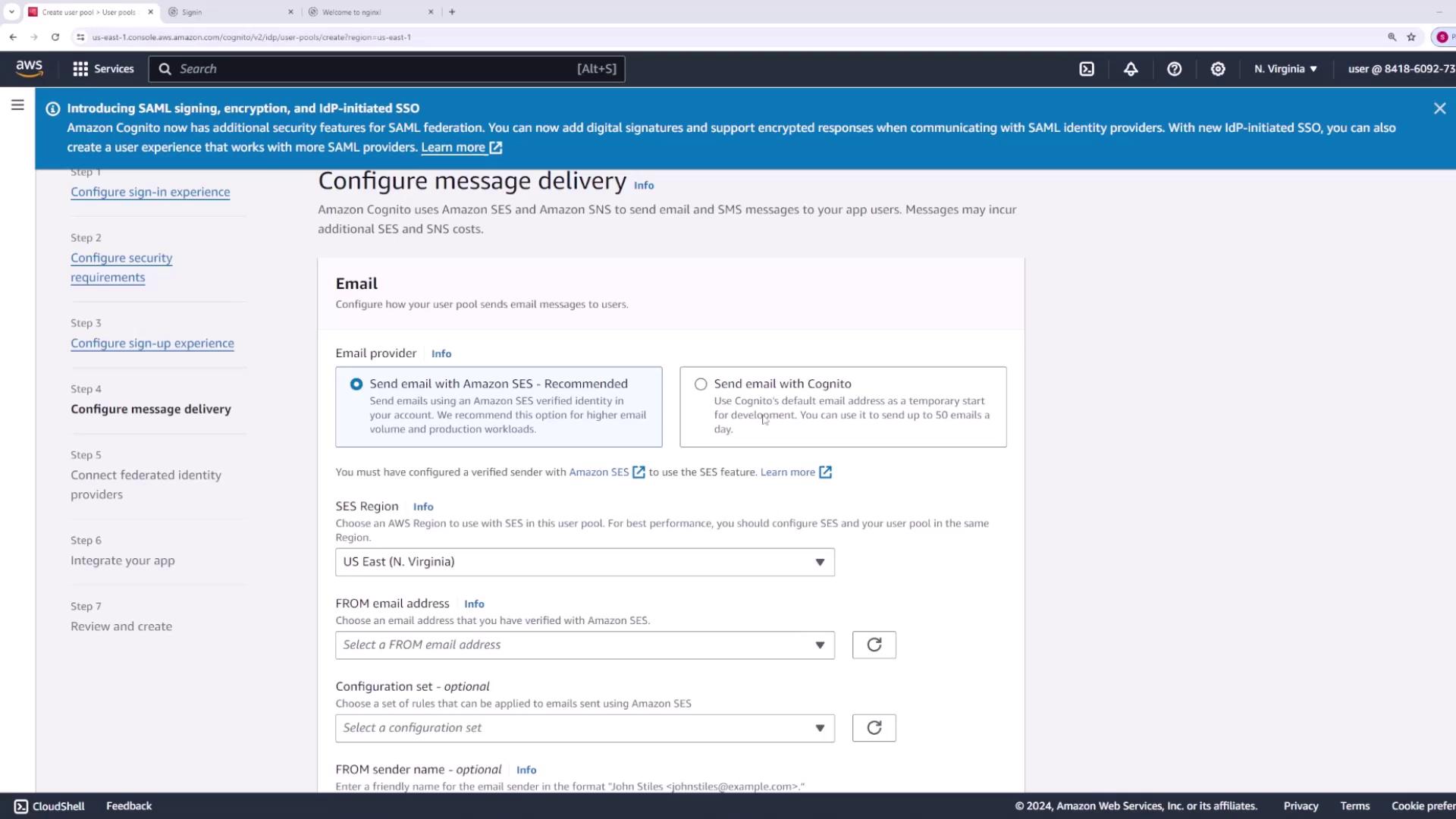
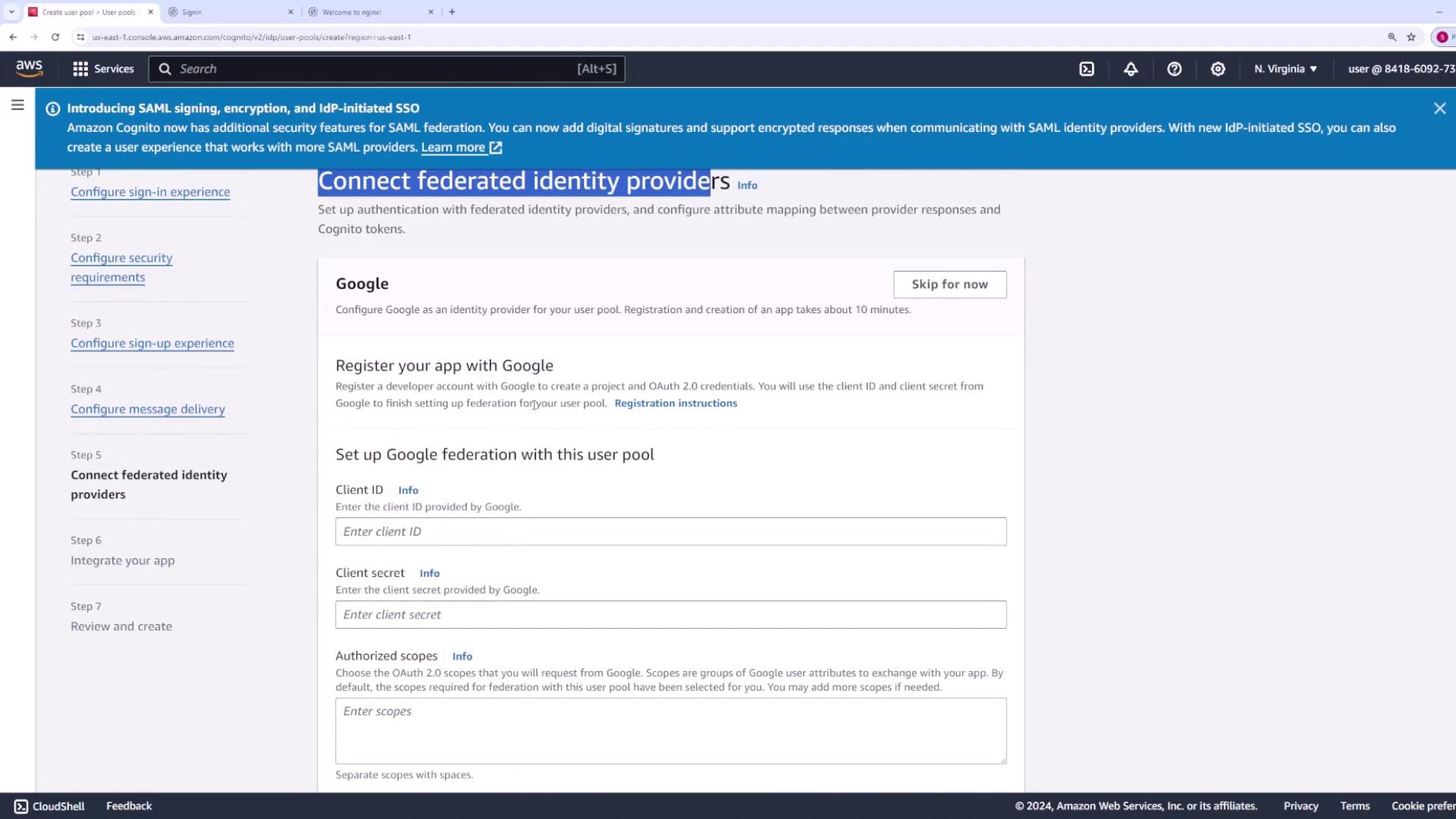
Step 6: Set Up SMS Role and Federated Identity Providers
Specify the IAM role that Amazon Cognito uses to send SMS messages through Amazon SNS. If you do not have an existing role, create one (e.g., “Cognito User Pool Role”).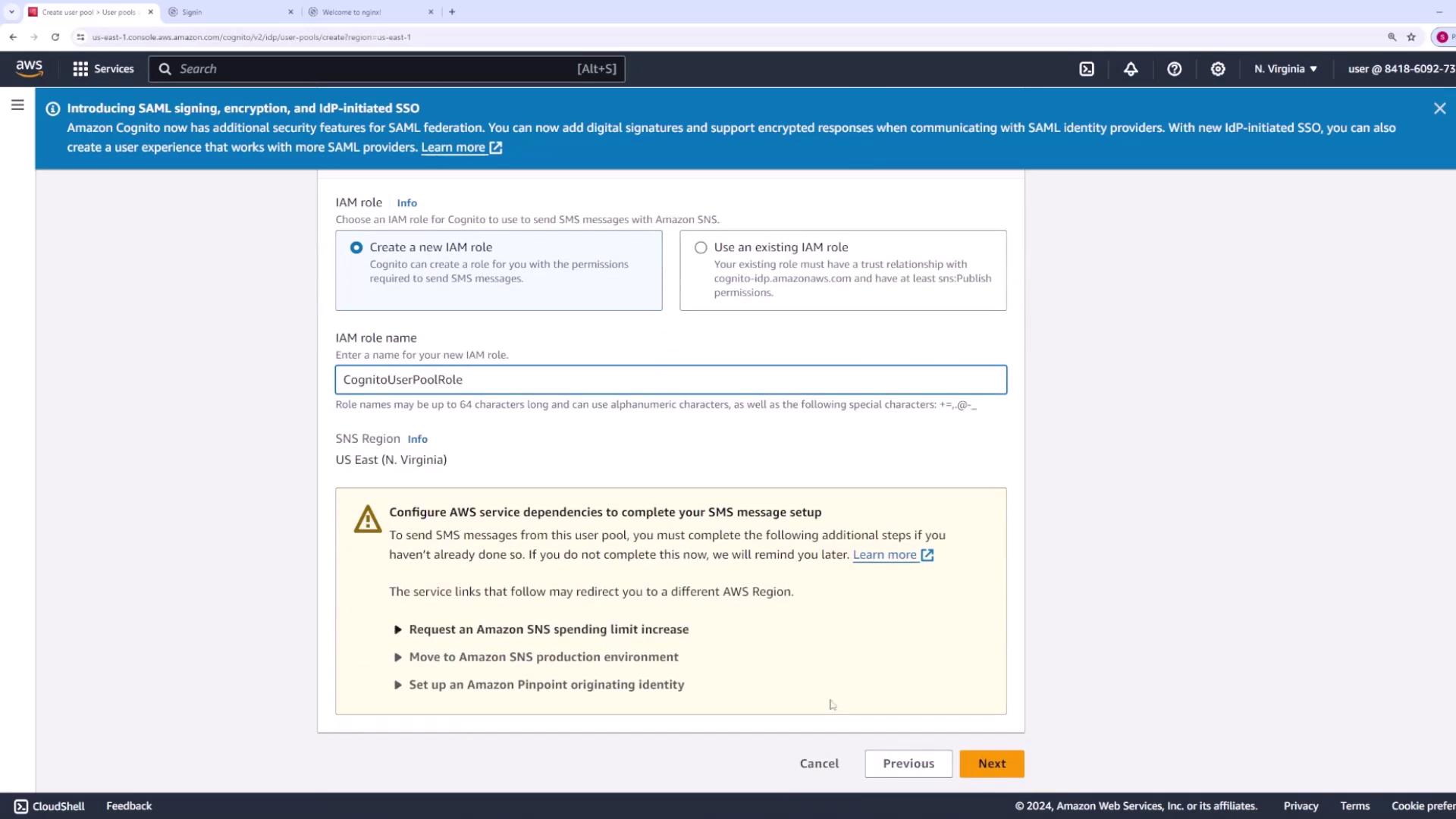
Step 7: Name Your User Pool and Configure the Domain
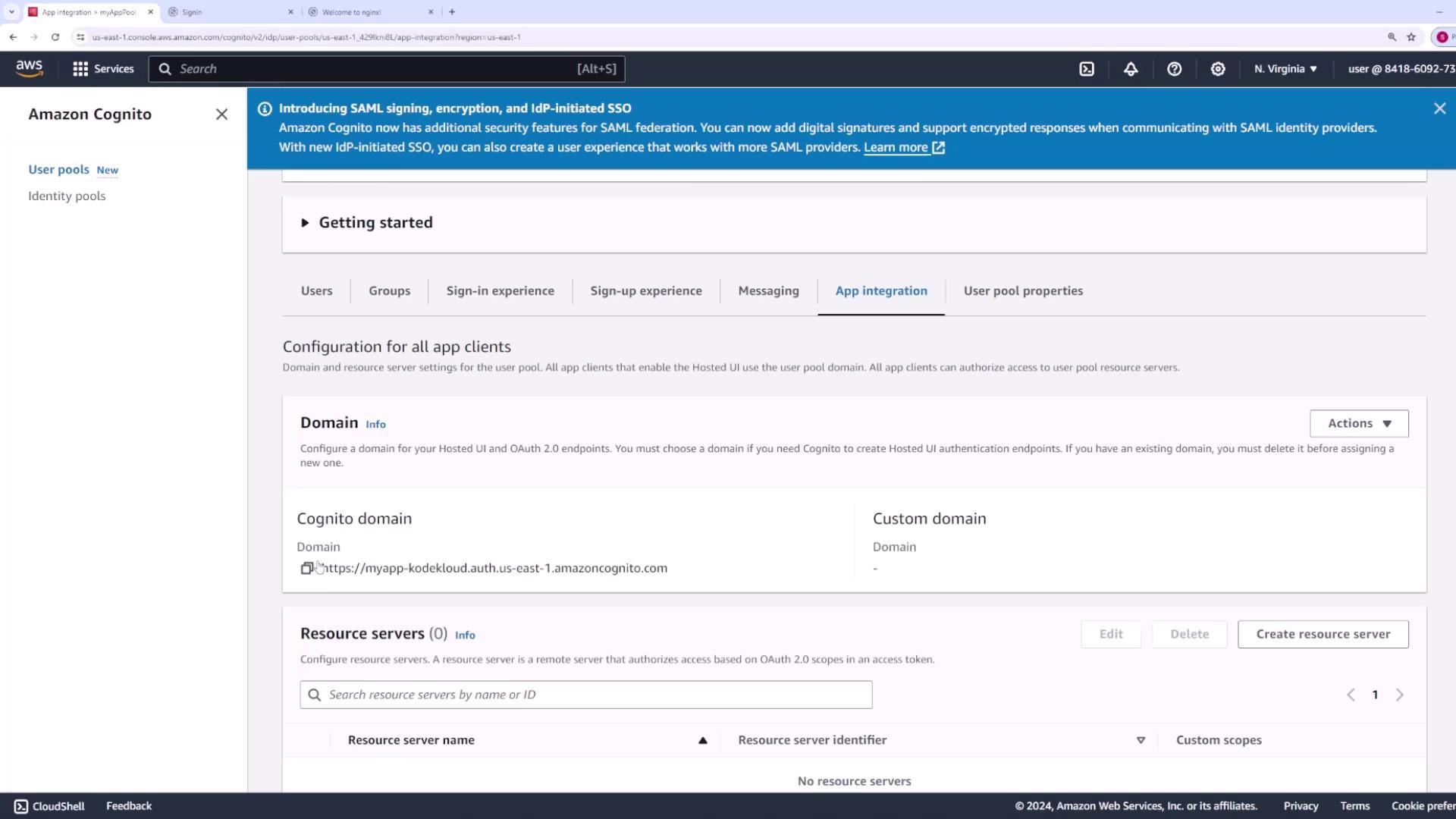
Assign a descriptive name to your user pool (e.g., “myAppPool”). Your application will also receive a domain name for the Cognito-hosted UI. You can either use a built-in Cognito domain with a unique prefix (e.g., “myapp-codecloud-”) or set up a custom domain if you have certificates from ACM.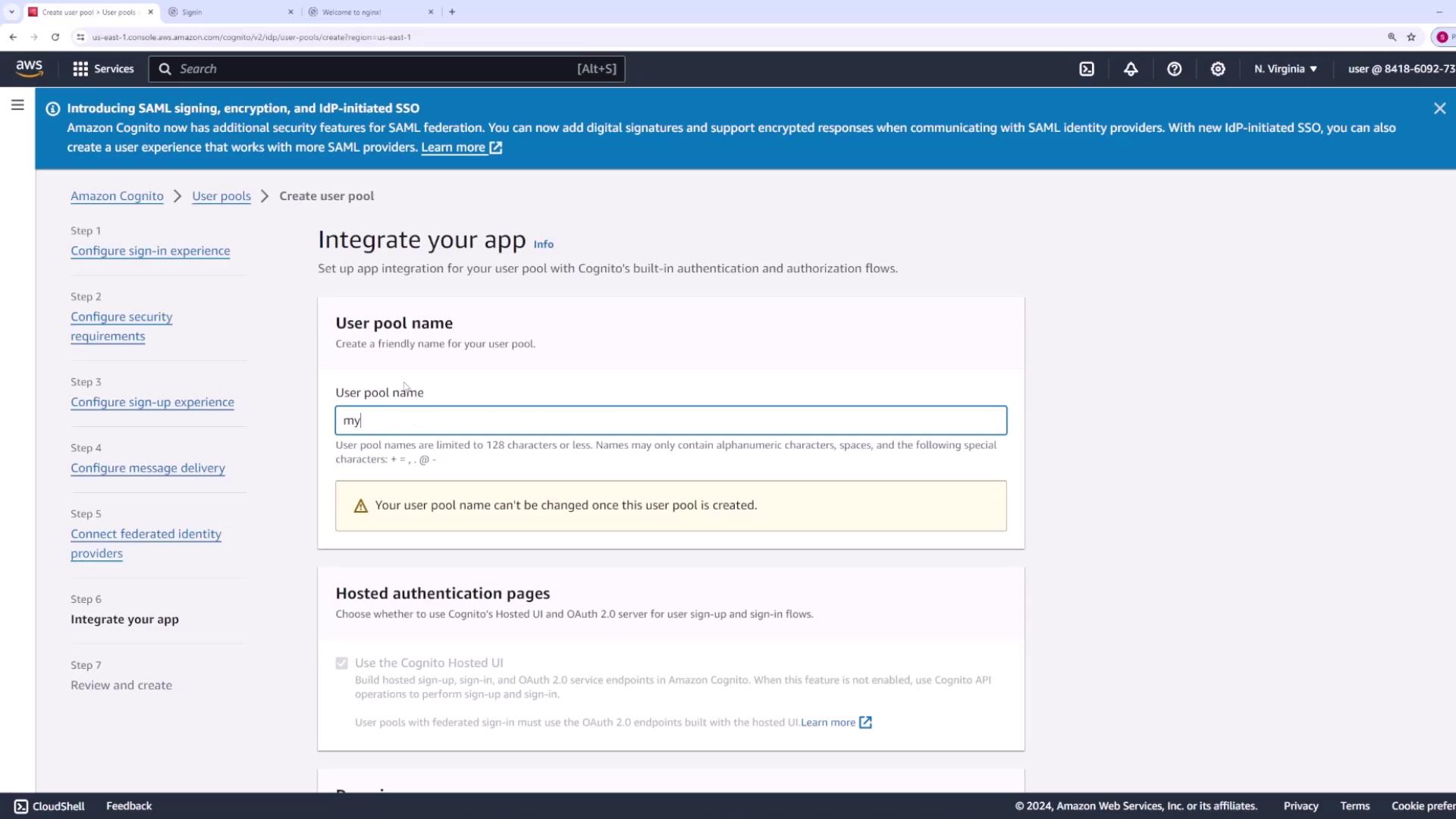
Step 8: Create an App Client
After creating the user pool, configure an app client to control how users interact with your application. Public clients are suitable for web or mobile applications, while confidential clients work best for server-side applications. For this demo, we will use a public client. Enter an app client name (e.g., “AppOne”) and optionally generate a client secret. Also, specify a callback URL (for testing, you might use “test.com”) to redirect users after signing in.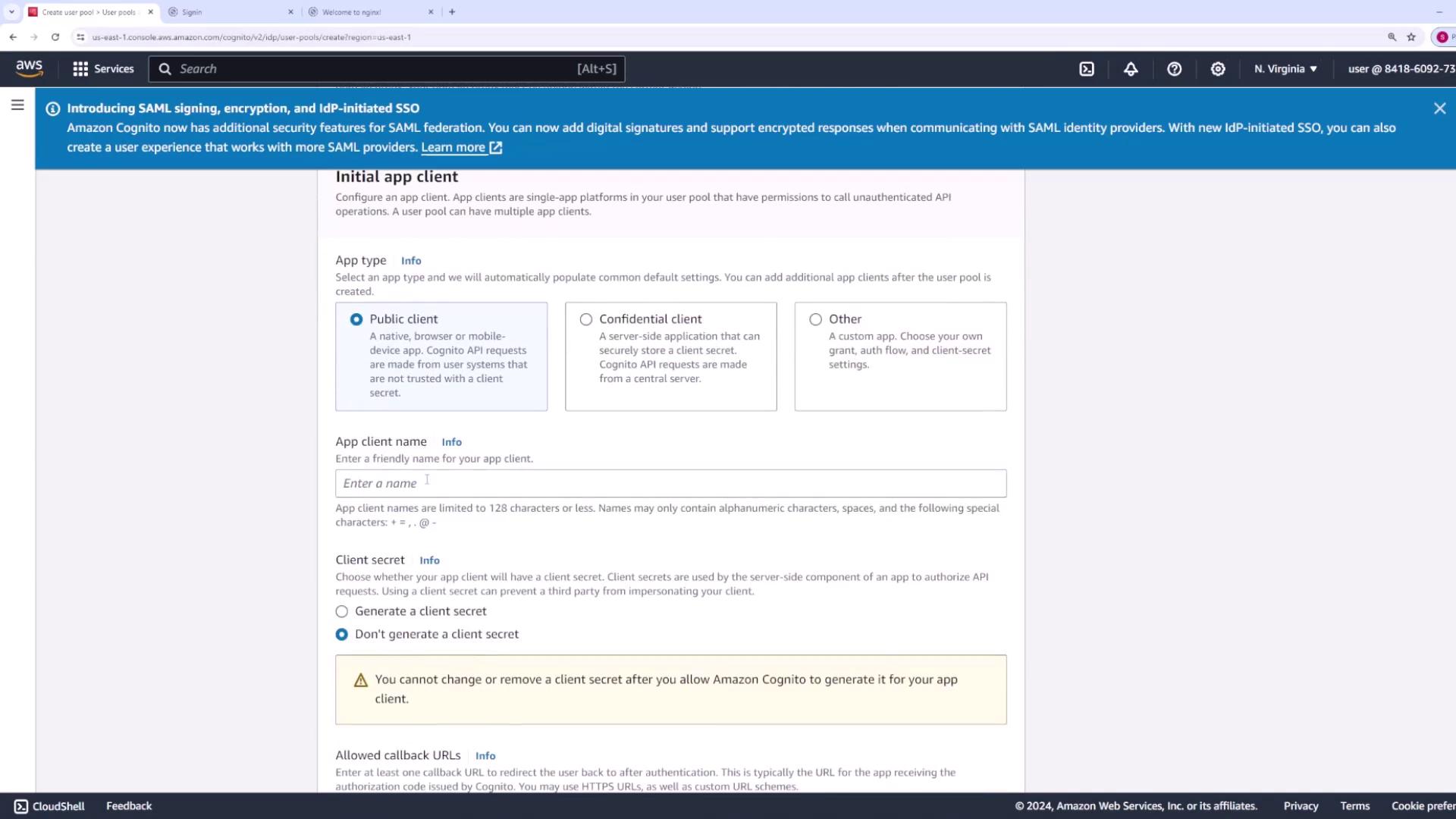
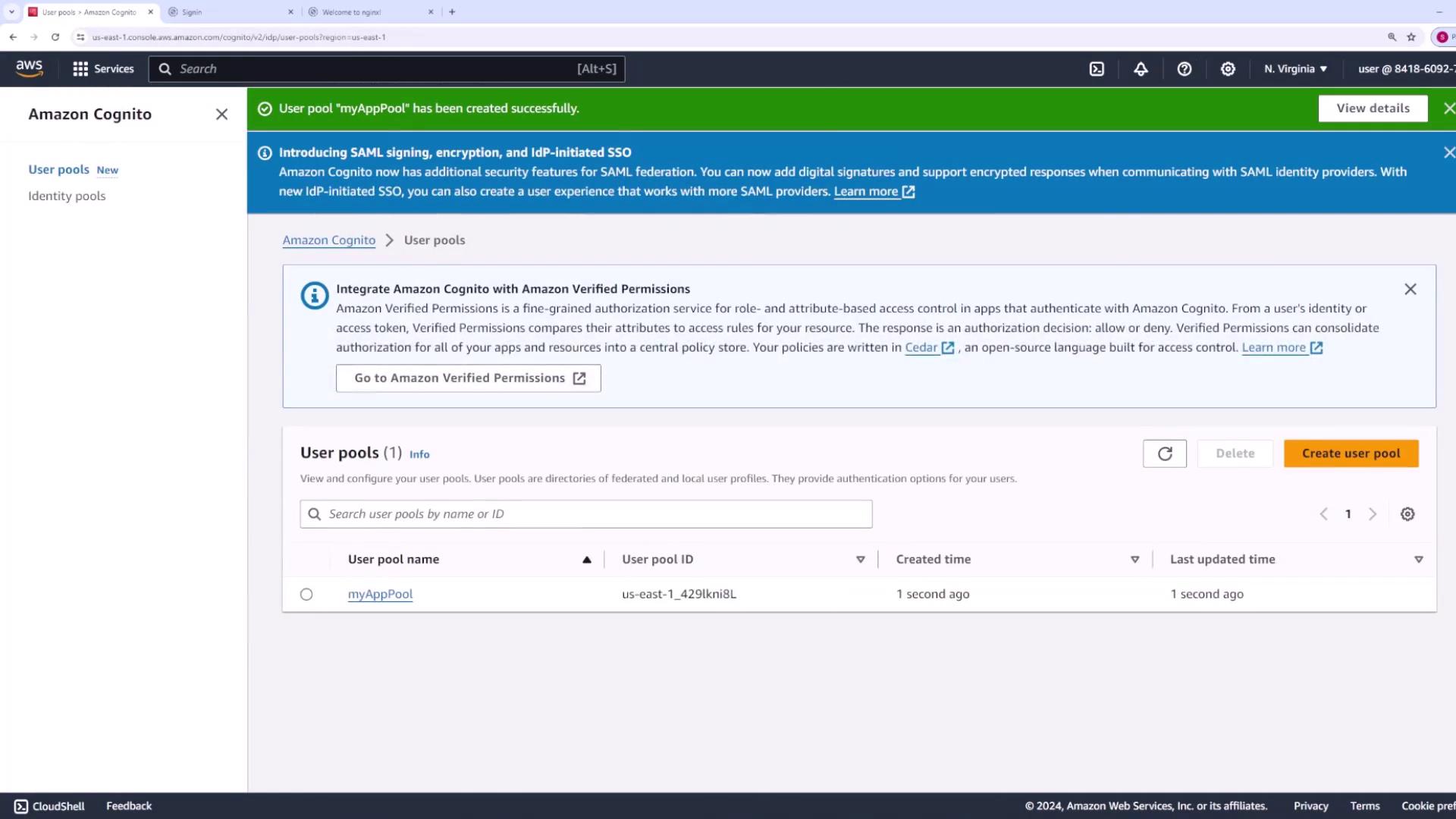
Step 9: Review the User Pool Configuration
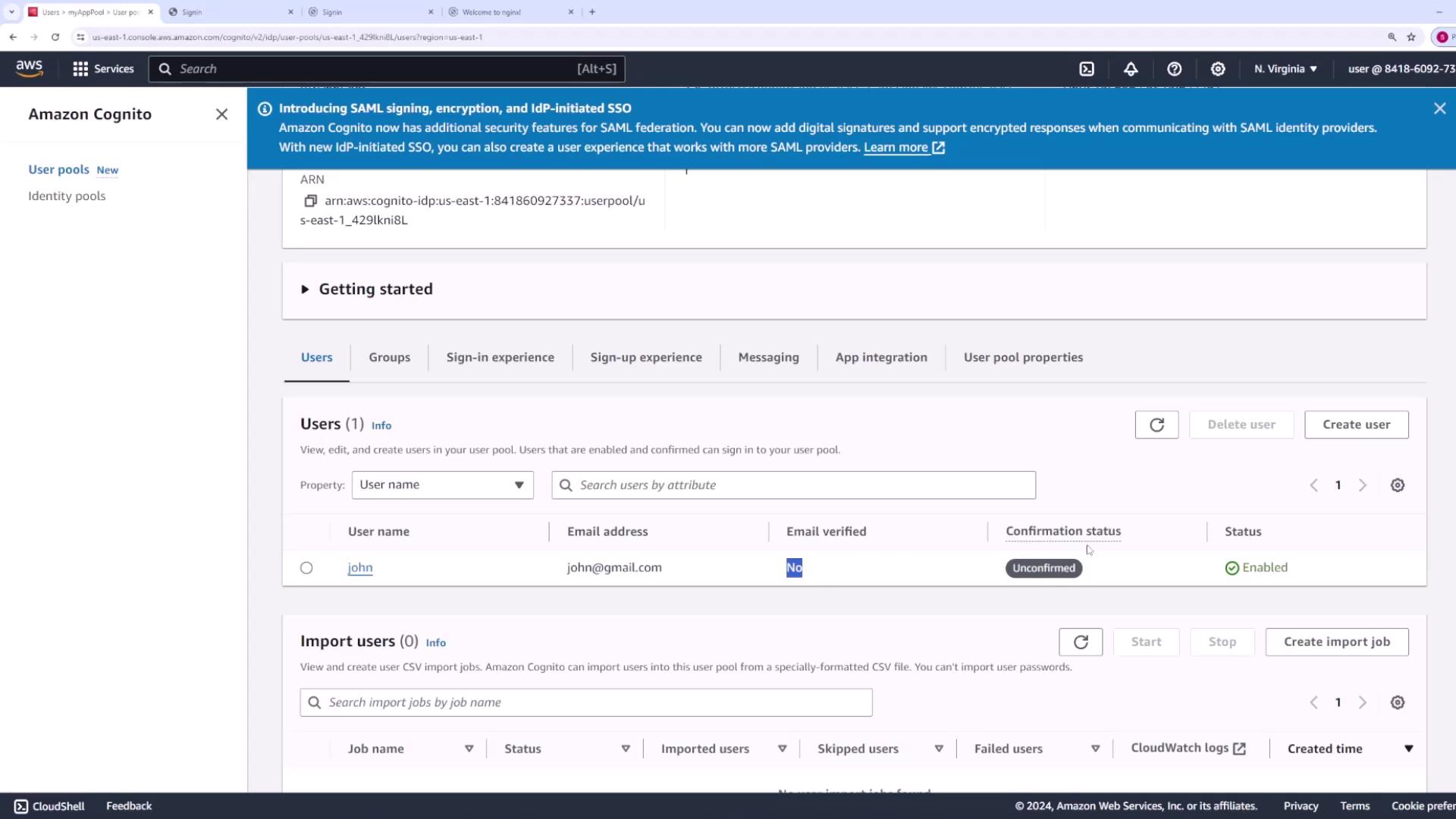
Once the user pool is created, review and manage its various sections:- Users: View and manage the list of registered users.
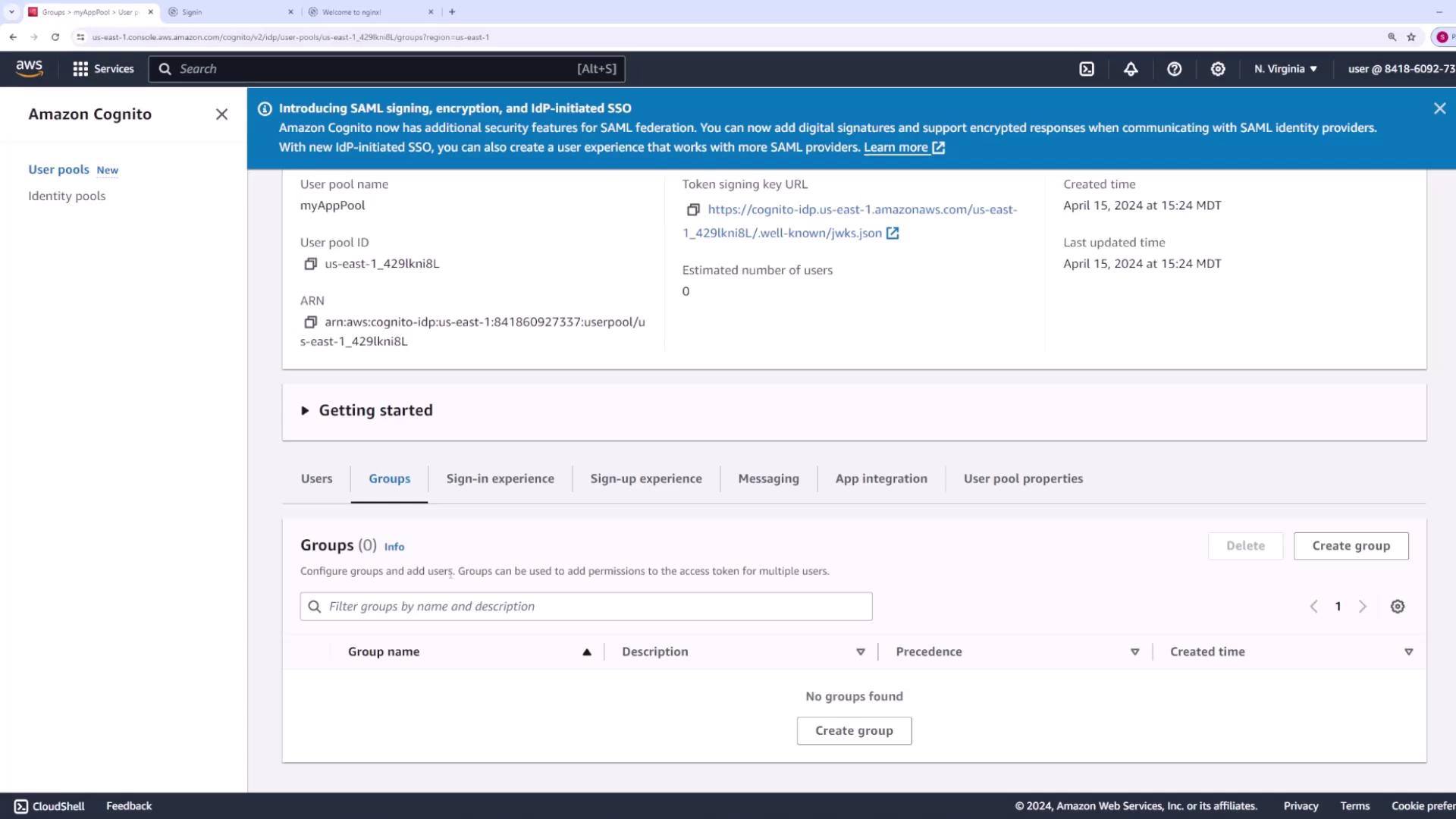
- Groups: Create and manage groups to assign roles and permissions (e.g., administrators, end users).
- Sign-In Experience: Customize sign-in methods, including federated identity provider settings and password policies.
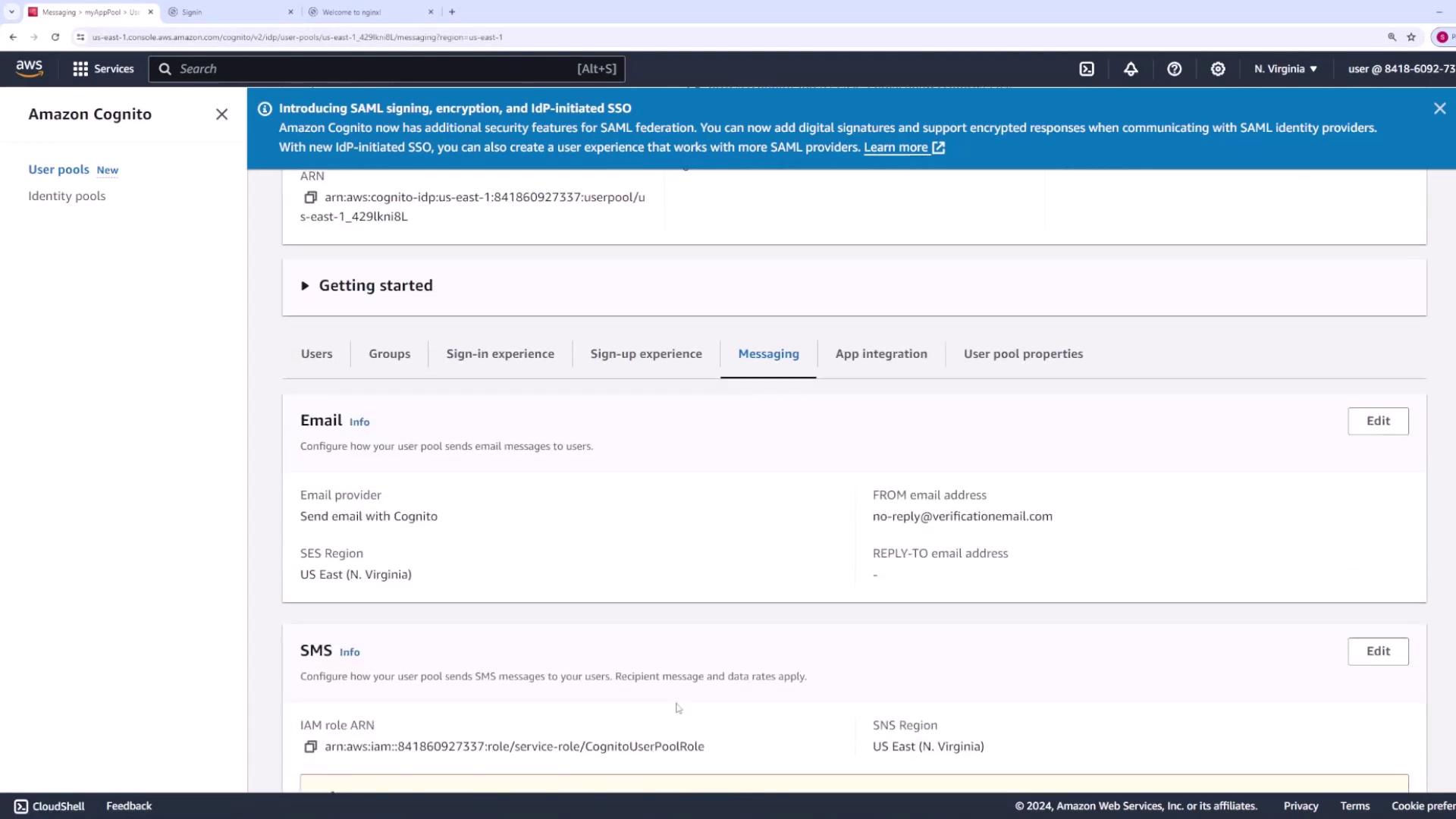
- Messaging: Customize email and SMS templates for communications.
- App Integration: Access the hosted UI endpoint and other integration settings.
Step 10: Test the Hosted UI
To see the hosted UI in action, navigate to the app client list and select your app. Choose “View Hosted UI” to access the Cognito sign-in page. The page includes fields for username and password and an option for new users to sign up.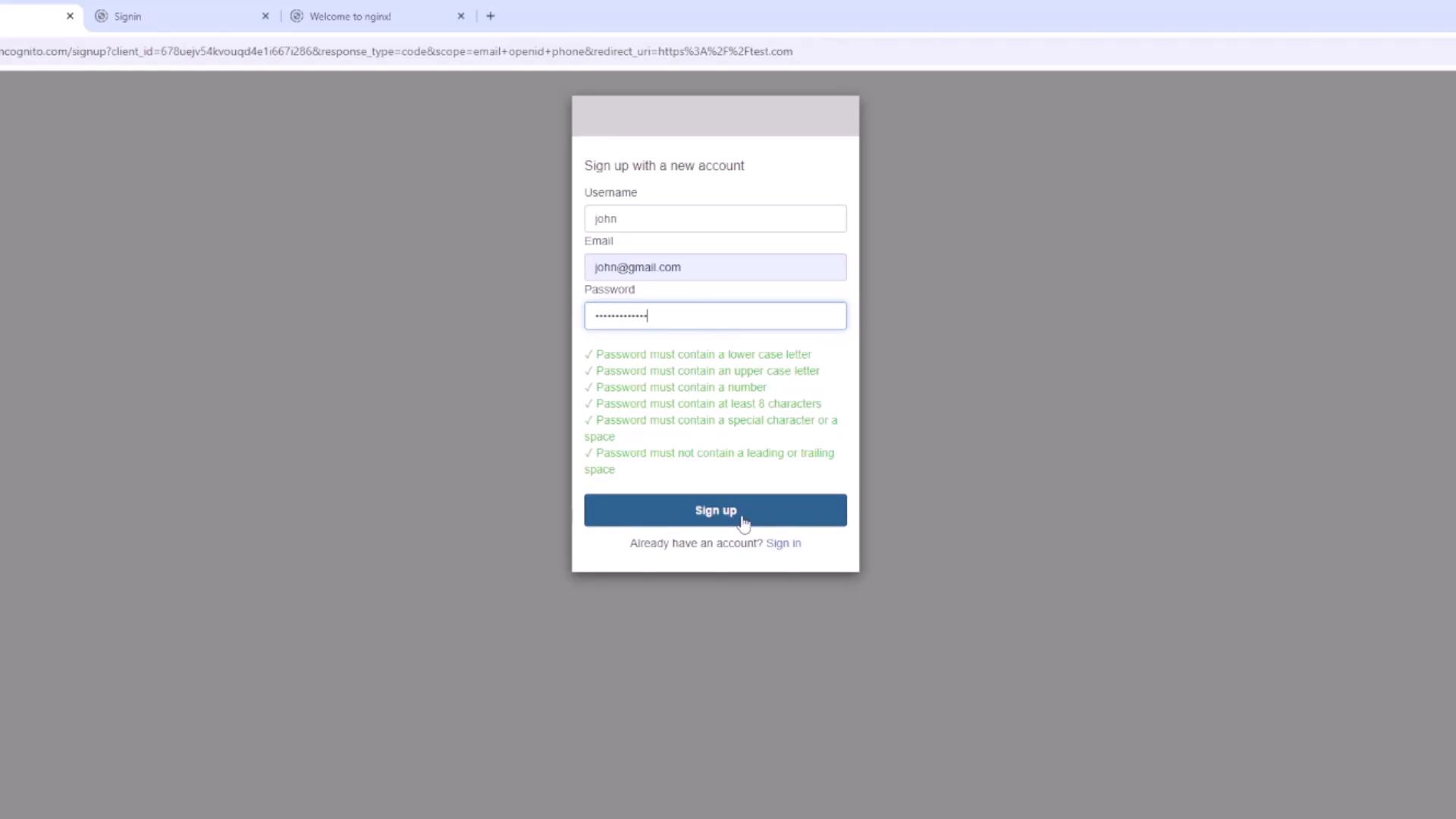
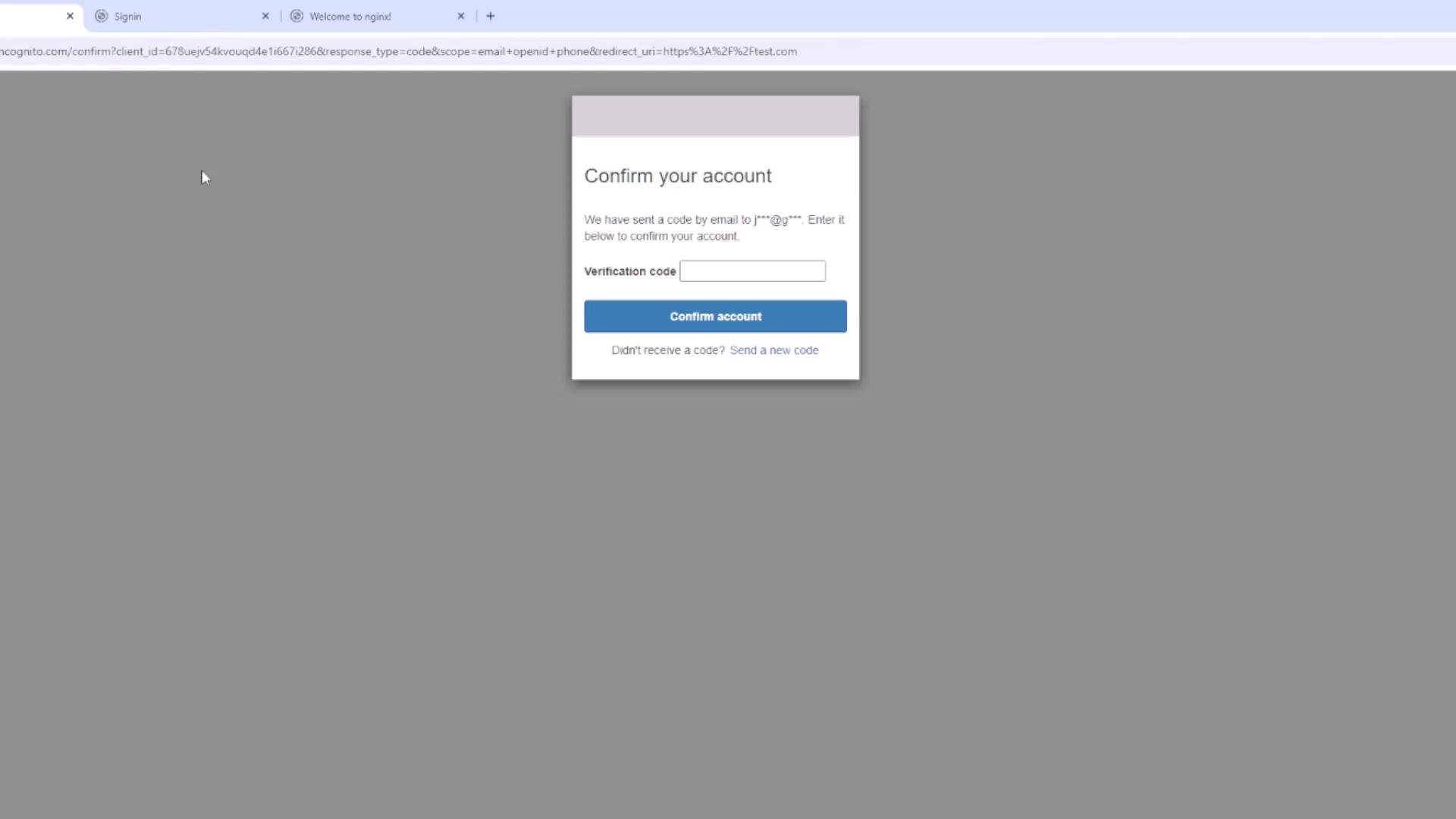
Step 11: Advanced Settings and Lambda Triggers
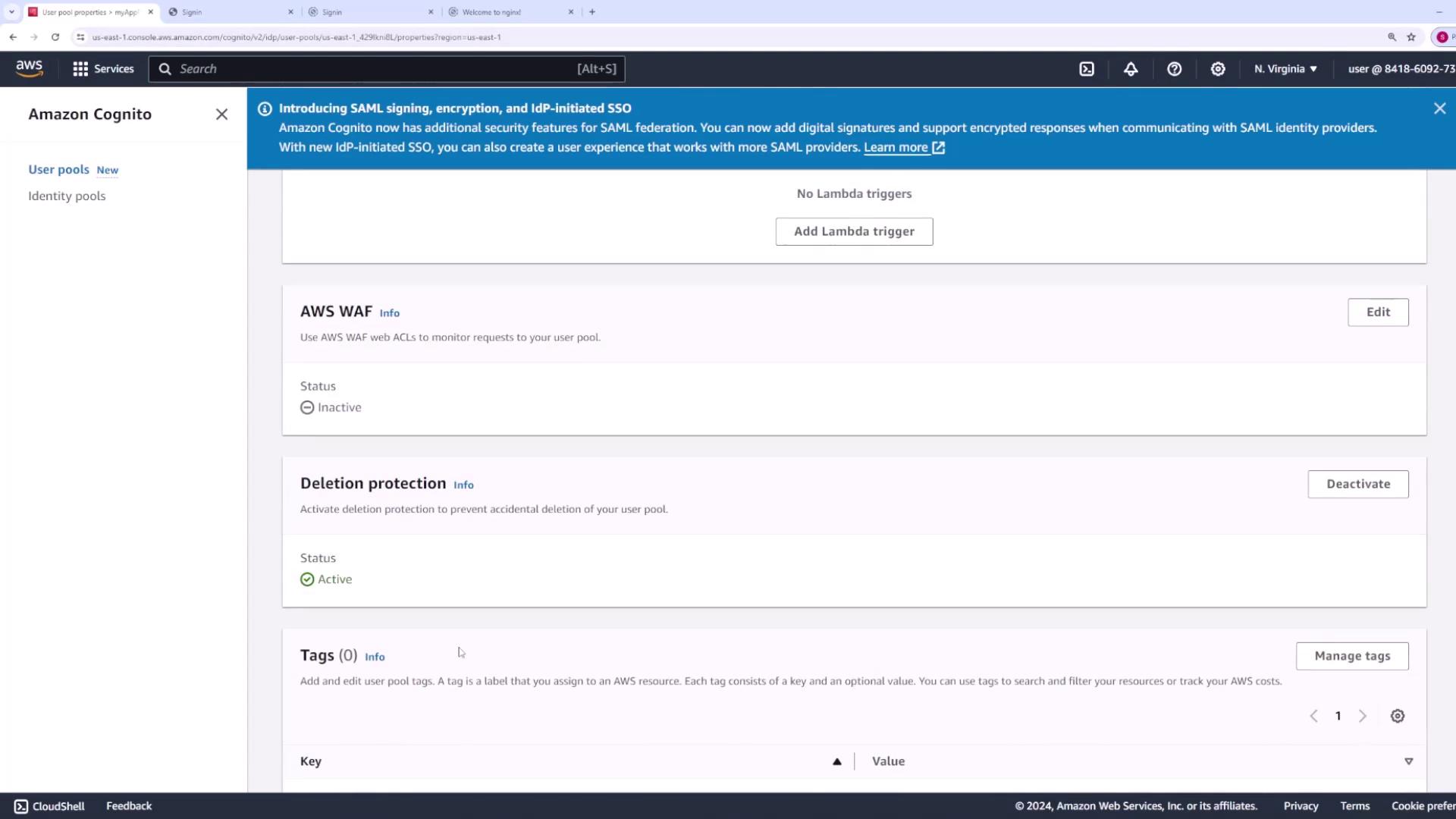
After exploring the core configuration, review additional settings available in your user pool:- AWS WAF: Configure web ACLs to protect your endpoints.
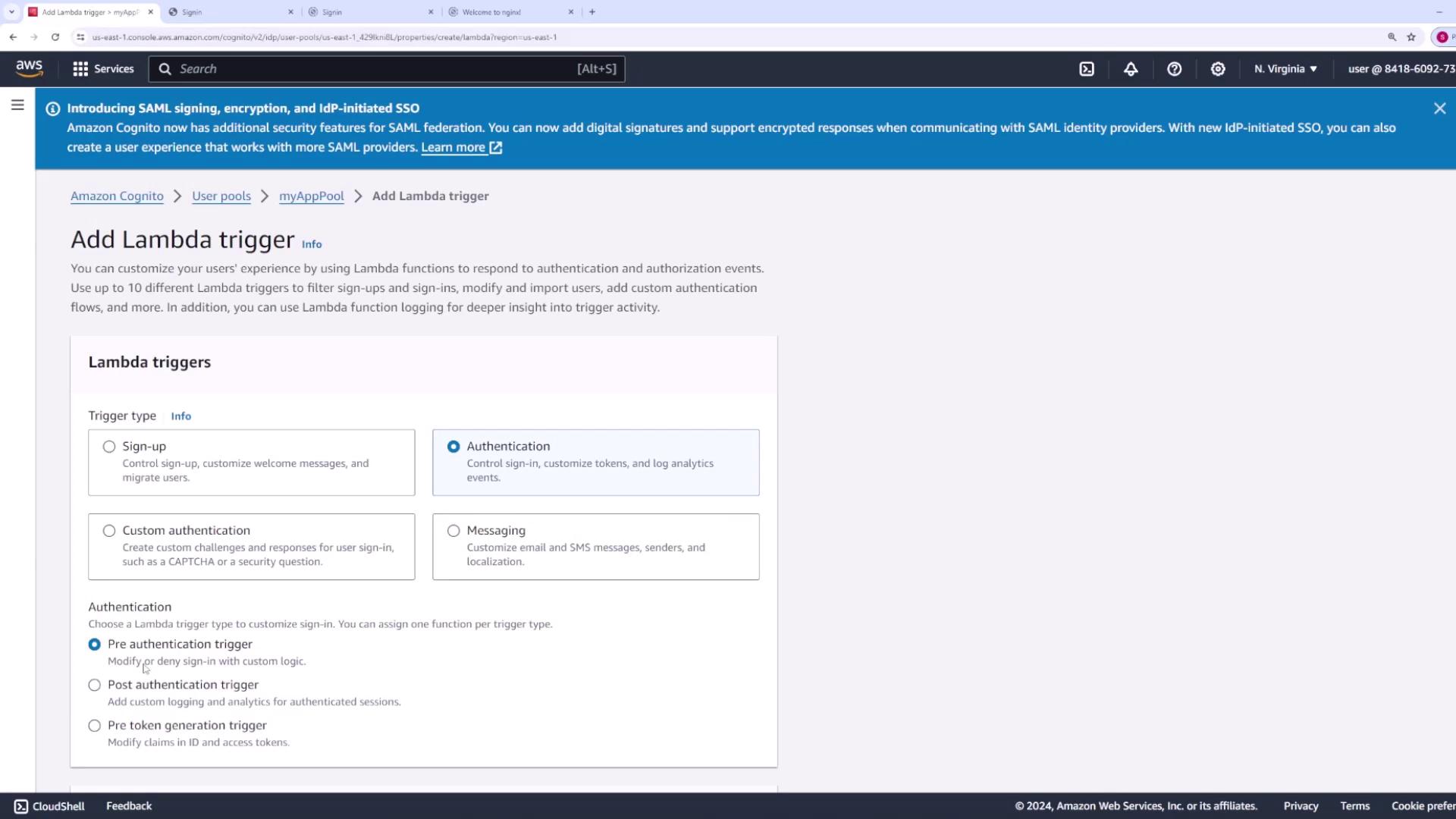
- Lambda Triggers: Integrate AWS Lambda functions to run custom code during various authentication stages, such as before sign-up, after confirmation, during messaging customization, before sign-in, or before token generation.
Conclusion
This lesson provided a detailed walkthrough of configuring an AWS Cognito user pool. You learned how to set up authentication methods, configure password policies and MFA, manage email and SMS messaging, integrate federated identity providers, and utilize advanced settings like IAM roles and Lambda triggers. Adjust these configurations to fit your application’s requirements and enhance your security strategy. Enjoy building secure and scalable applications with AWS Cognito! For further information, please visit the AWS Cognito Documentation.Explore additional AWS services and features to further enhance your application’s security and scalability.