AWS Certified Developer - Associate
Serverless
Lambda Versions Aliases
AWS Lambda provides powerful features for managing your functions through versions and aliases. In this guide, we’ll explore how Lambda function versions and aliases work and how you can leverage them to streamline your development and deployment processes.
Understanding Lambda Versions
When you create a Lambda function, you can publish different versions of your function. Each published version is an immutable snapshot of your code and configuration at the time of publication. For example, the first published version is labeled as v1, the next v2, and so on. This mechanism allows you to manage different environments -- API Gateway, for instance, can route traffic to v1 for a development environment and to v2 for a production environment.
Note
The version labeled as "latest" is mutable and represents your working copy during development. Once you decide to publish these changes, a new immutable version is generated.

When updates are needed, simply modify the "latest" version and publish it again to create another snapshot (e.g., v3). Remember, once a version is published, its configuration cannot be altered.
Exploring Lambda Aliases
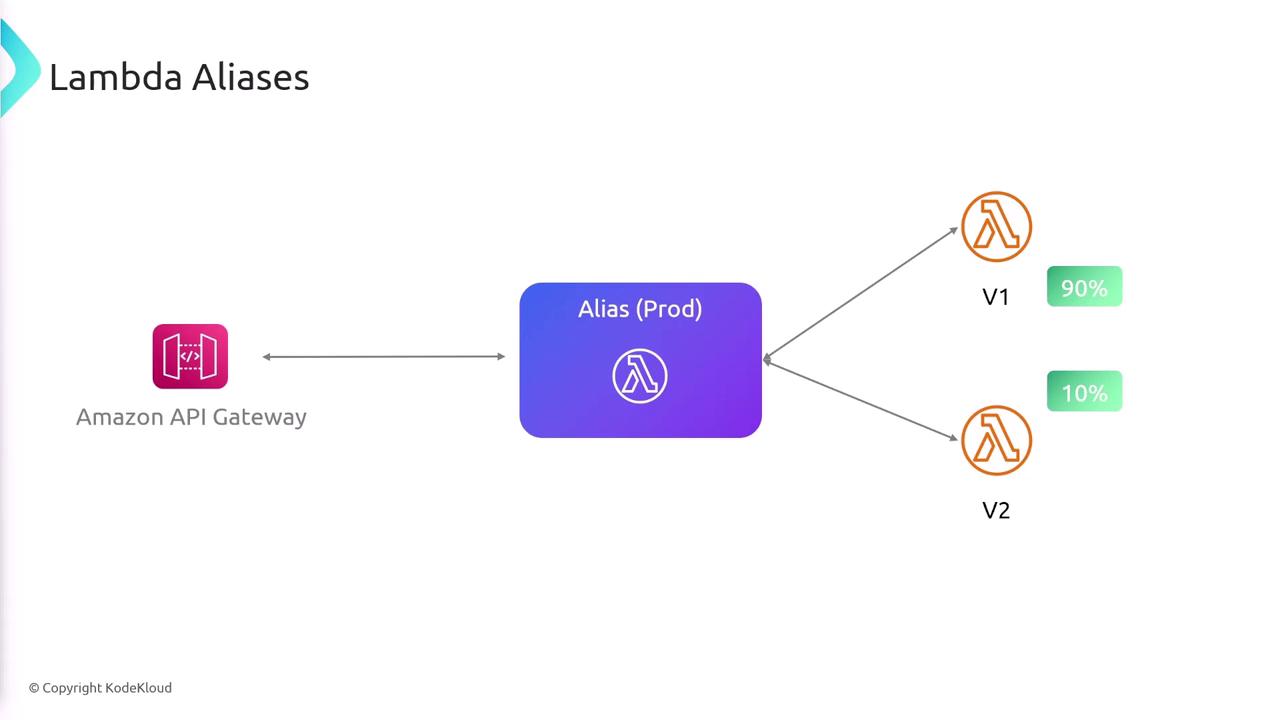
Lambda aliases act as named pointers to specific Lambda versions. This allows you to abstract version details away and refer to your function with user-friendly names like "prod" for production or "dev" for development.
Beyond simple version mapping, aliases can manage traffic routing between multiple versions. For instance, you can configure an alias to route 90% of incoming traffic to v1 and the remaining 10% to v2. This feature is particularly useful for scenarios such as canary testing or gradually rolling out new updates.
Key Takeaways
- Versions provide immutable snapshots of your Lambda function at a given time.
- The "latest" version is mutable, representing your active development state.
- Aliases act as fixed pointers to a specific version and can also facilitate traffic splitting between versions.
Summary Note
Leveraging Lambda versions and aliases allows for controlled deployments and smoother transitions between different versions of your function. This is essential for maintaining stability while implementing new features or fixes.

Watch Video
Watch video content