AWS Certified SysOps Administrator - Associate
Domain 6 Cost and Performance Optimization
Cost Optimization Strategies Overview and Best Practices
Welcome to our comprehensive guide on cost optimization strategies for AWS. This article provides an in-depth look at various licensing options, key financial metrics such as ROI and TCO, and the billing tools that can help you manage and forecast your AWS spending. These insights are not only vital for cost control but also for preparing for AWS certification exams.
Licensing Options for AWS Services
Understanding the different licensing options for AWS services, particularly for Amazon EC2 instances, is fundamental to optimizing your cloud expenditure. Here are the primary pricing models:
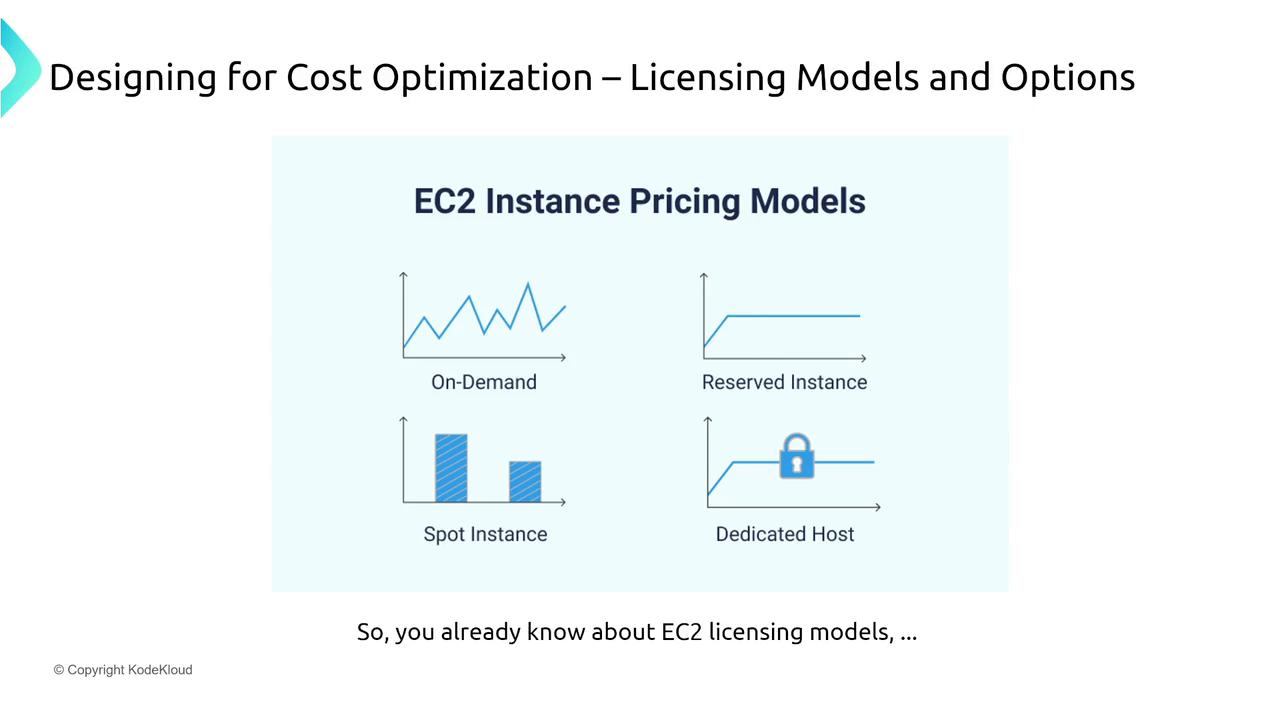
On-Demand Pricing
With on-demand pricing, you pay a fixed hourly rate (for example, $1 per hour) with no long-term commitment. This model provides maximum flexibility for variable workloads.Reserved Instances (RIs)
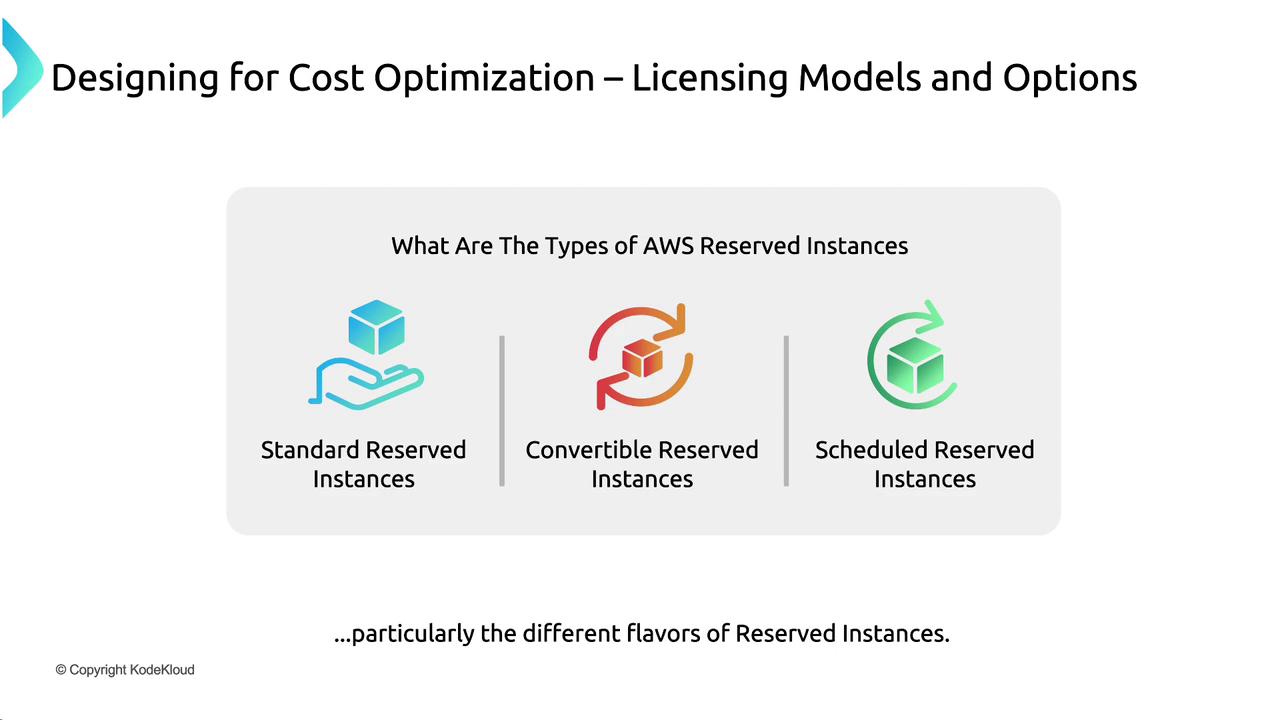
Reserved Instances require you to commit to a one- or three-year term, regardless of actual usage. In exchange for this commitment, you enjoy significant discounts (e.g., paying 70 cents per hour instead of $1). RIs come in several types:- Standard Reserved Instances: Offer the deepest discounts (up to 66% off) but require strict configuration commitments.
- Convertible Reserved Instances: Provide the flexibility to change instance type, size, or operating system during the term.
- Scheduled Reserved Instances: Allow you to reserve capacity for specific time windows, ideal for predictable usage periods such as weekday business hours.
Dedicated Hosts
If physical isolation is a priority, Dedicated Hosts offer that option, though they come at a premium cost (e.g., around $20 per hour).Spot Instances
Use Spot Instances to access AWS’s unused capacity at a significant discount (for instance, 50% less than on-demand pricing). Keep in mind, though, that these instances can be reclaimed by AWS with only a two-minute warning, making them suitable for interruptible workloads like batch processing or reporting.
AWS has further enhanced its pricing flexibility by introducing Savings Plans. Compute Savings Plans cover a variety of services—including Virtual Machines, Fargate under ECS/EKS, and AWS Lambda. For example, committing a fixed dollar amount (e.g., $10,000) over one or three years can unlock effective discounts across these services.
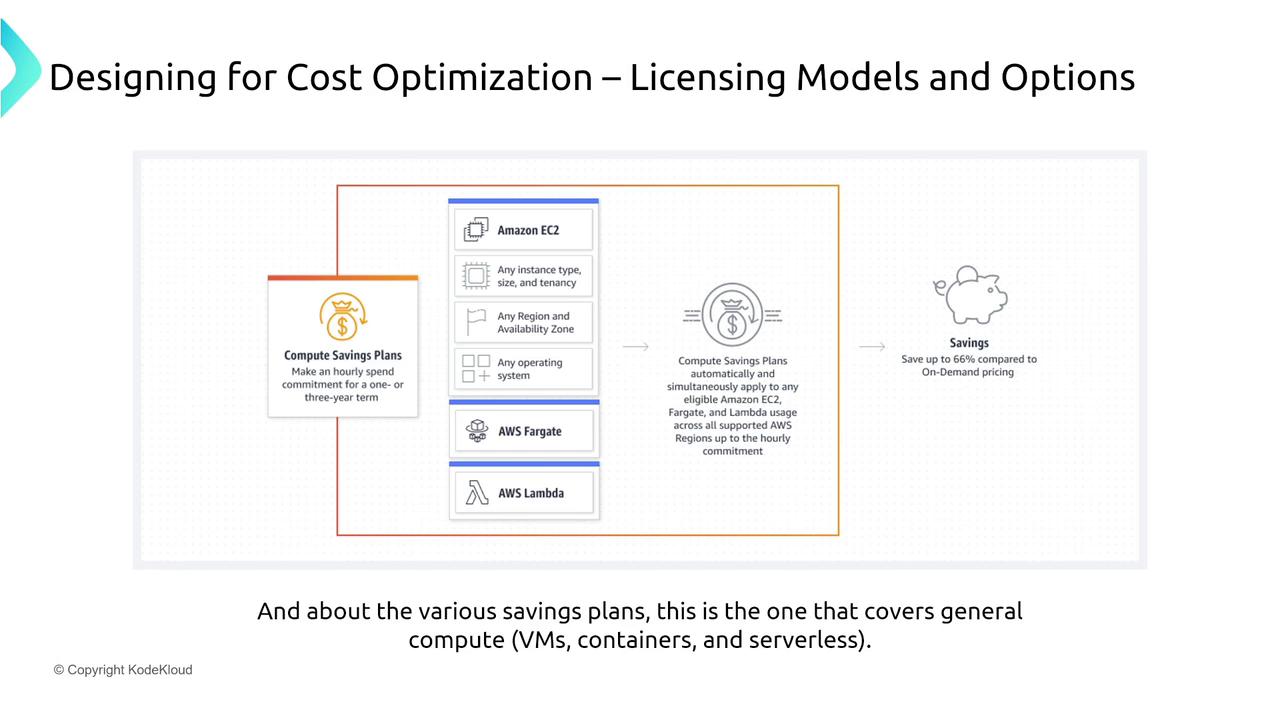
Different Savings Plans include:
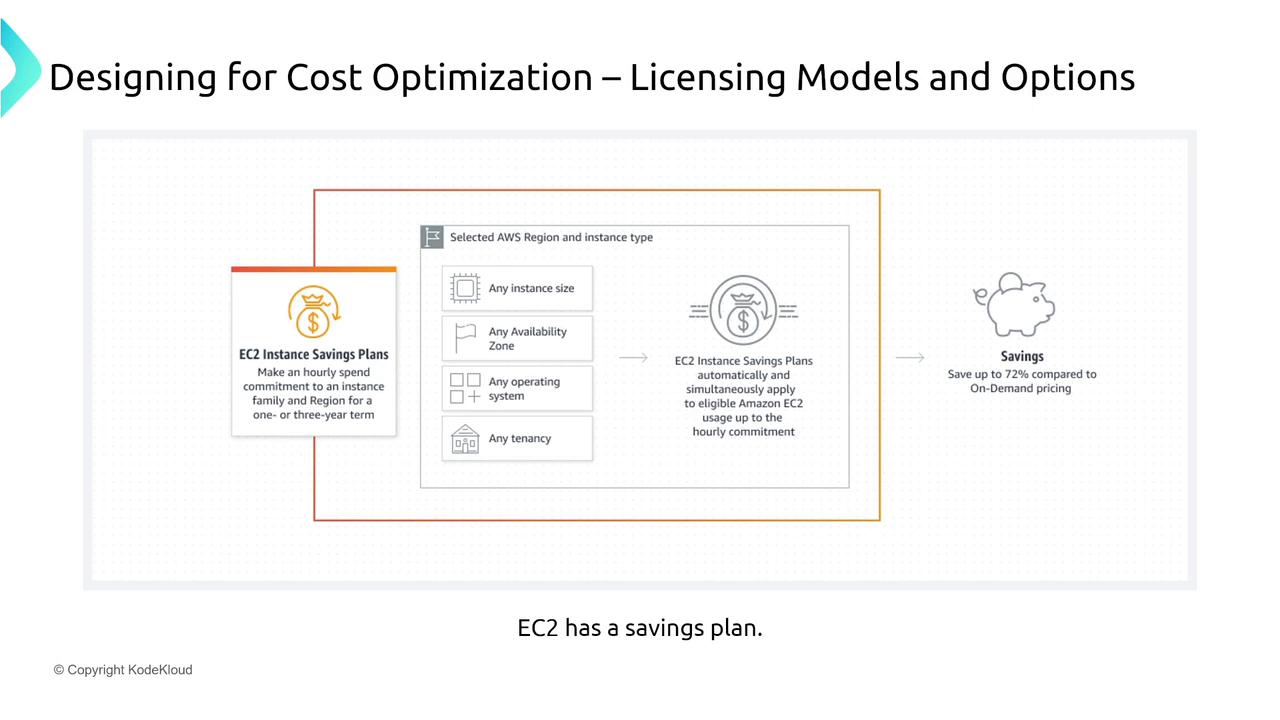
- EC2 Instance Savings Plans: Specific to Virtual Machines with potential savings of up to 72% with a three-year commitment.
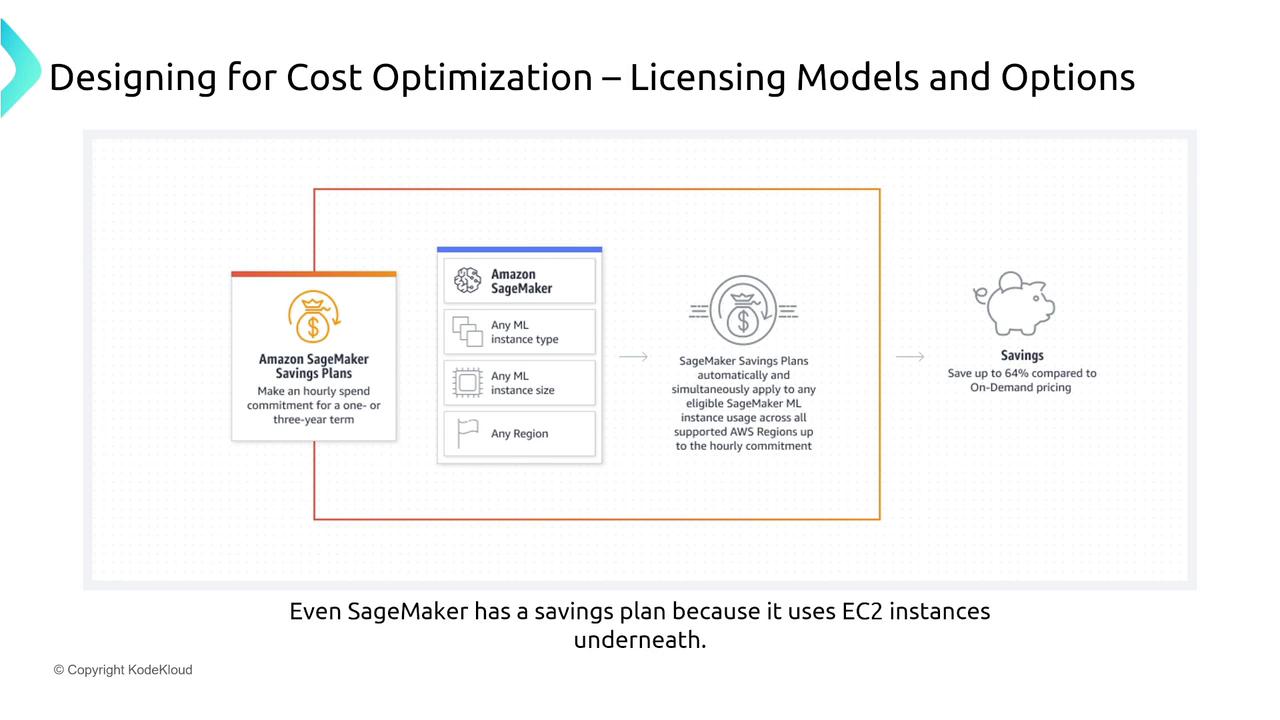
- SageMaker Savings Plans: Tailored for machine learning workloads on SageMaker, offering discounts up to 64%.
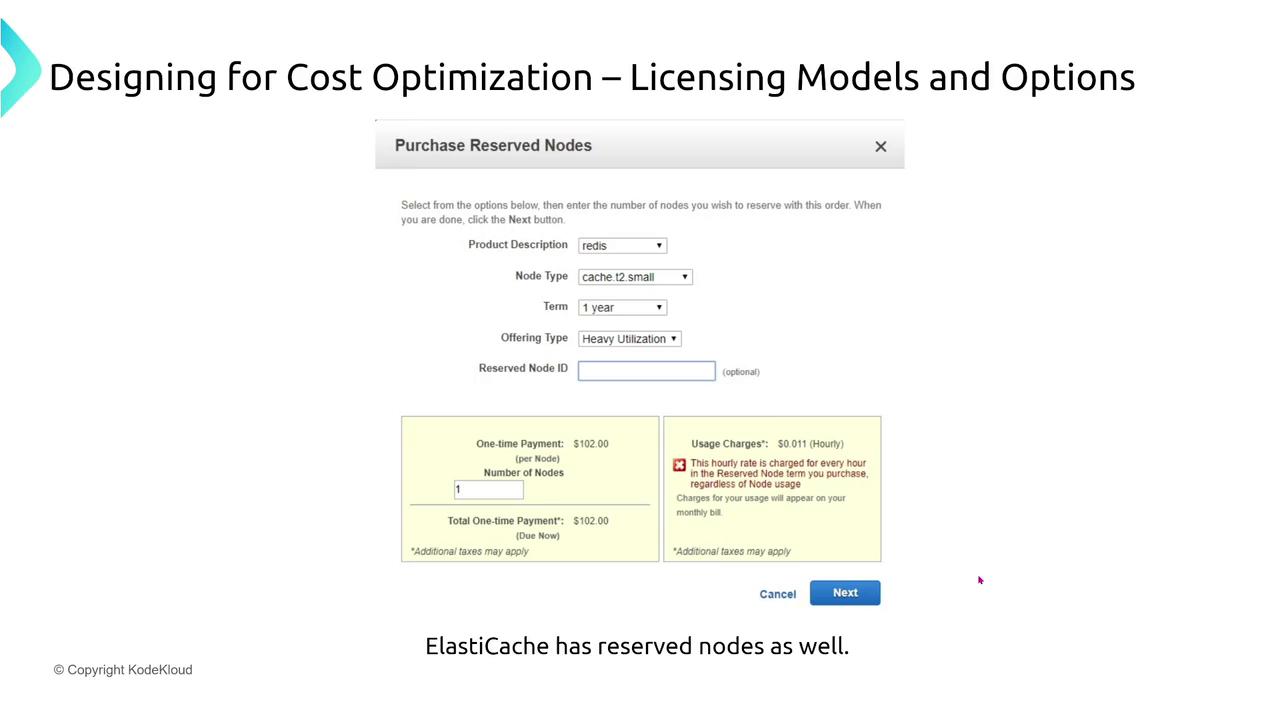
Cost reservations are also available for other AWS services such as RDS, ElastiCache, OpenSearch, Redshift, and even DynamoDB (for reserved capacity on read/write units). For instance, reserving a MySQL instance on RDS or a T2 small node in ElastiCache for one or three years can yield substantial savings.
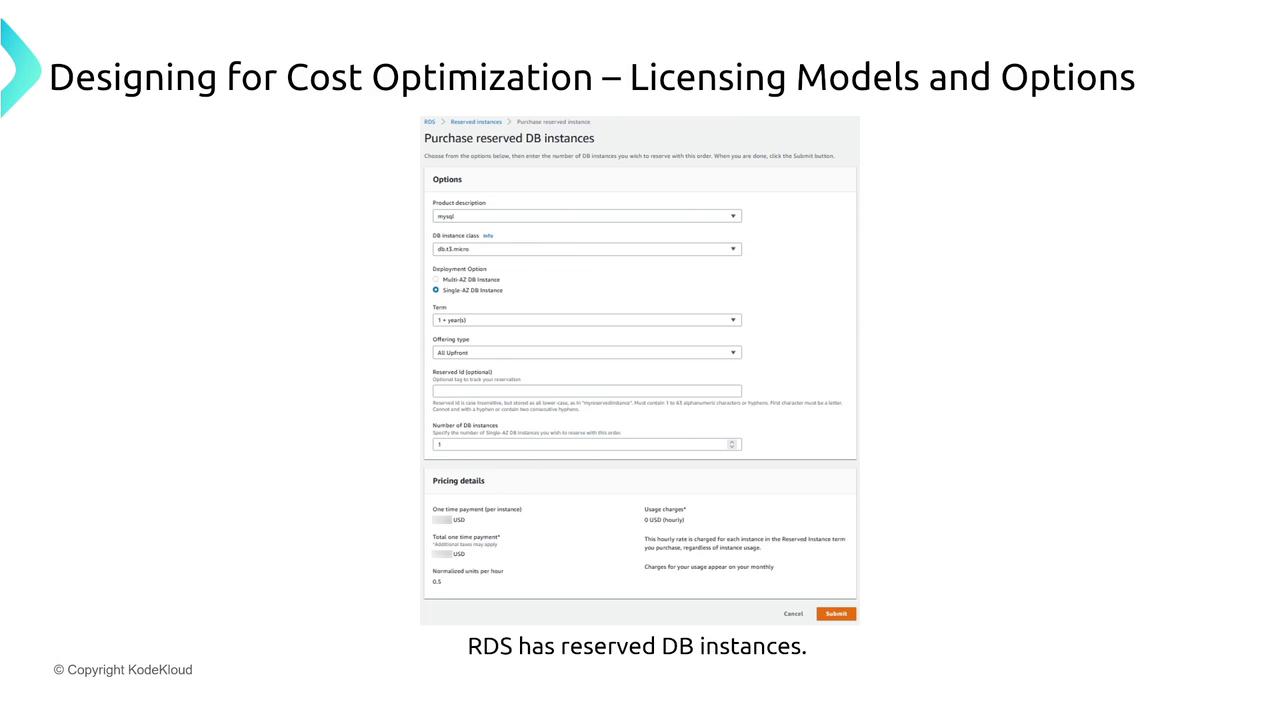
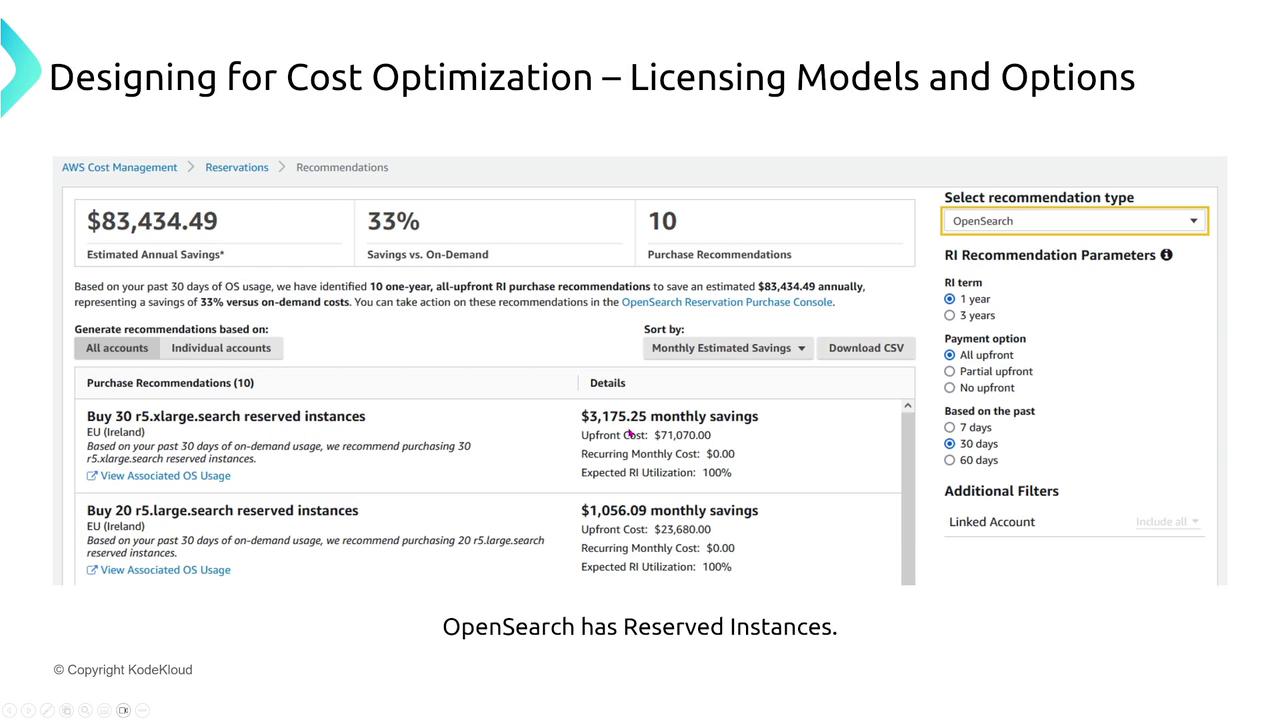
For services like OpenSearch and Redshift, AWS provides recommendations on reserved instance purchases through its cost management system. These recommendations help you compare on-demand pricing with reserved options for more informed decision-making.

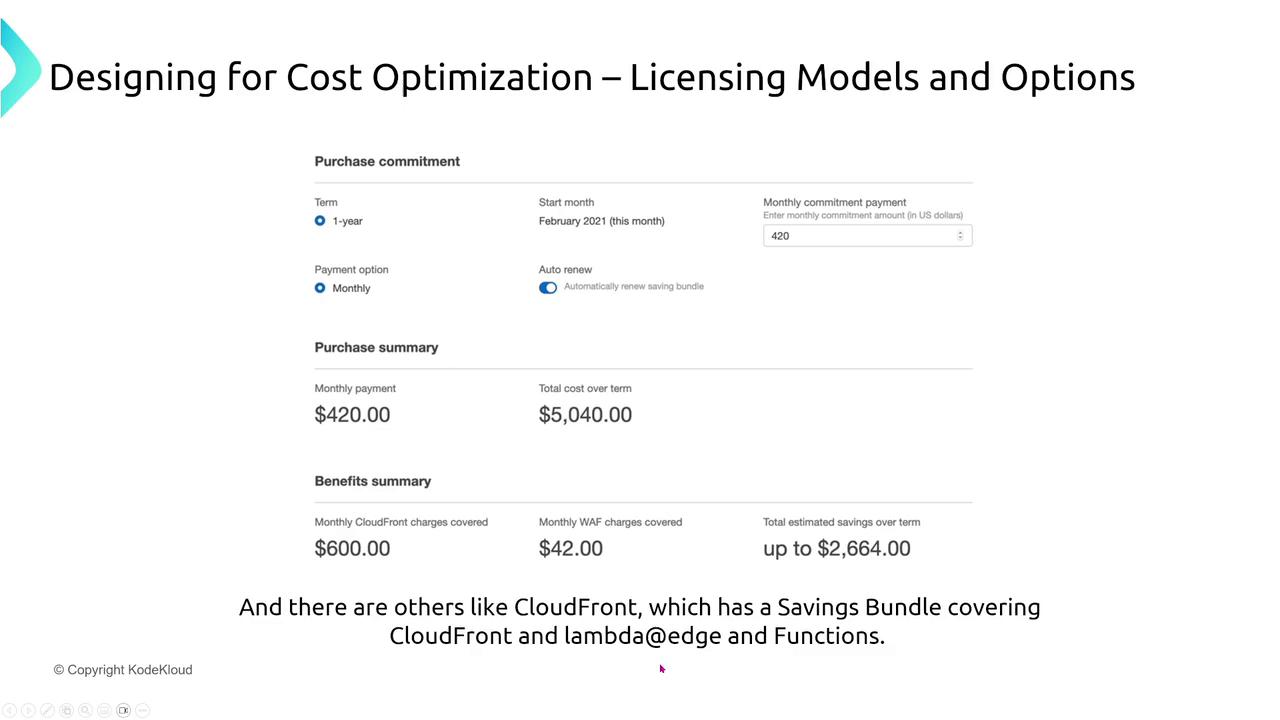
Additionally, reservation options are available for serverless services like DynamoDB and CloudFront, allowing you to manage costs even when infrastructure is abstracted.

Return on Investment (ROI) and Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
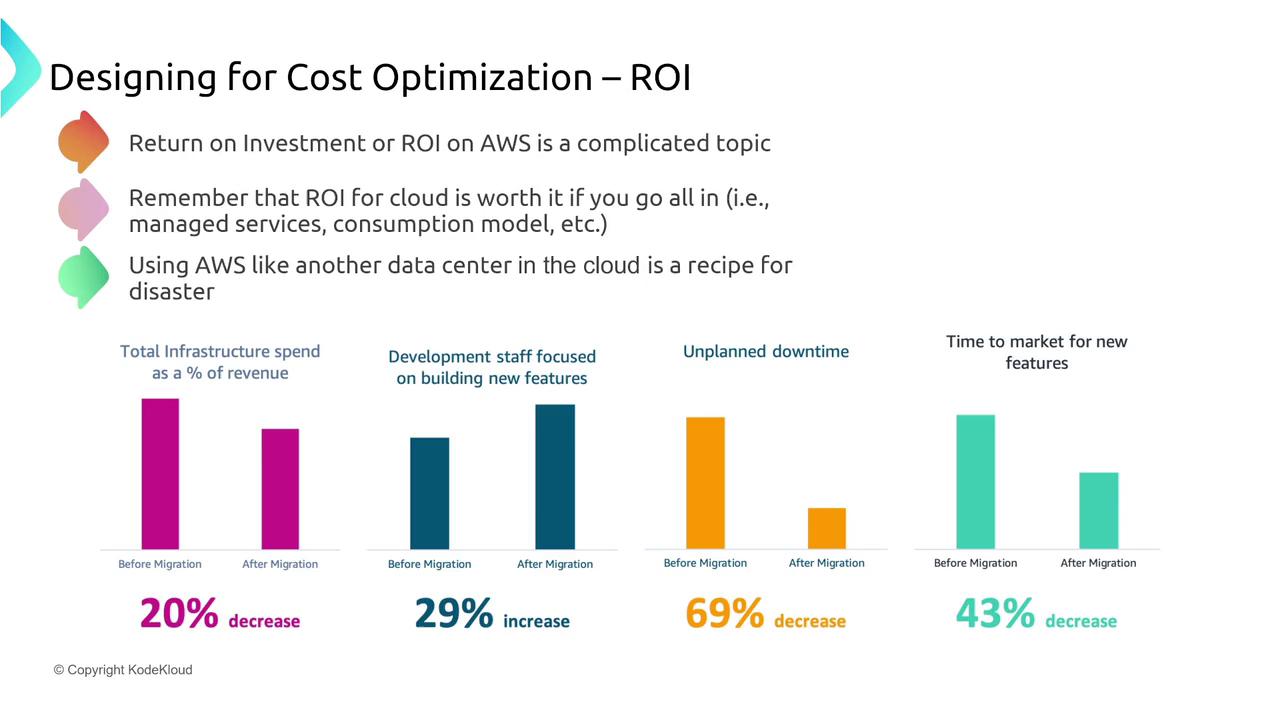
Evaluating cost optimization strategies requires a clear understanding of financial metrics. Two critical measures to consider are ROI and TCO.
Return on Investment (ROI)
ROI assesses the value generated relative to your investment. In a cloud context, a positive ROI is achieved by leveraging managed services and a consumption-based model. Benefits include:
- Reduced downtime and accelerated time to market for new features.
- Decreased overall infrastructure spending as a percentage of revenue following migration.
- A refocused effort on application development rather than maintaining physical data centers.
Note
Legacy, monolithic applications might not fully benefit from cloud economics, resulting in a less pronounced ROI.

Total Cost of Ownership (TCO)
TCO looks beyond direct costs to include “soft” costs such as labor, maintenance, and unplanned disruptions. Factors to weigh include:
- Eliminating initial capital expenditures associated with on-premises data centers.
- Reduced operational expenses, including ongoing maintenance costs.
- Lower labor costs due to increased uptime and reduced disruptions.
- Considerations for energy efficiency, compliance, and security that impact overall costs.
When comparing AWS to traditional on-premises systems, the lower operational overhead and improved uptime of AWS often make it the more cost-effective choice—even if the monthly direct costs seem comparable.


AWS Billing Tools and Considerations
Keeping a close eye on your AWS billing is essential for proactive cost management. AWS provides robust tools to monitor, analyze, and forecast spending.
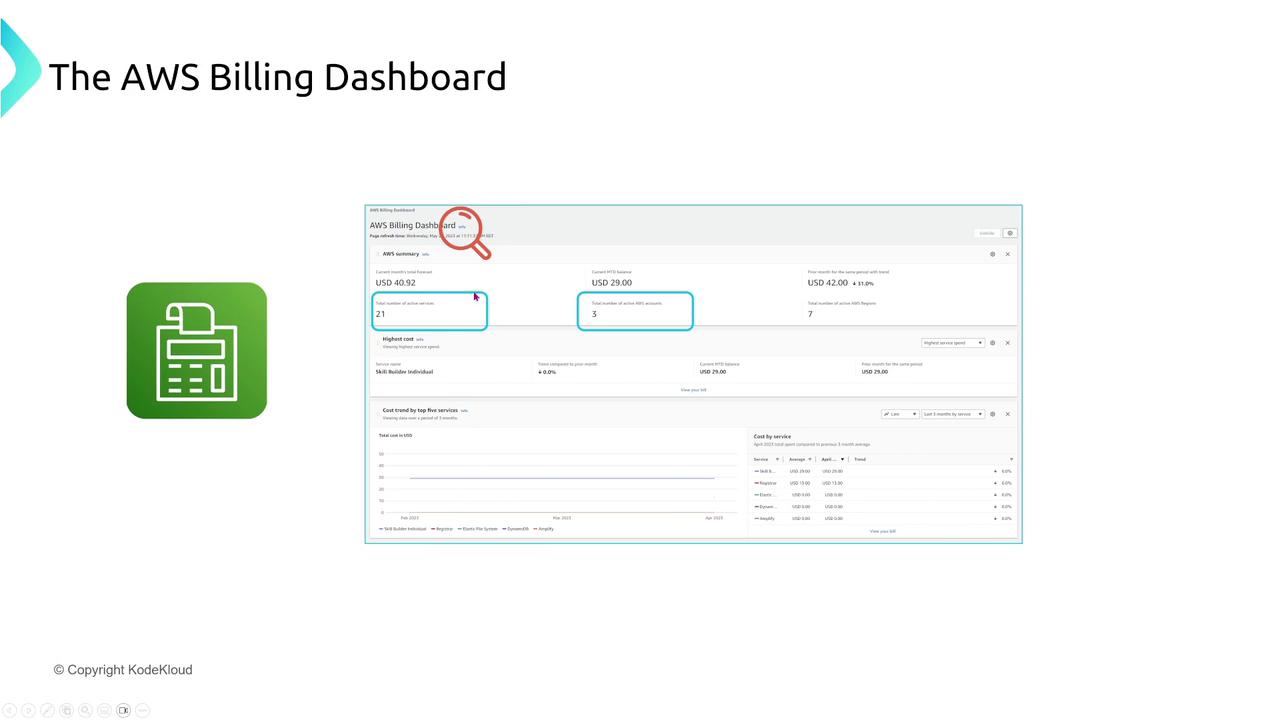
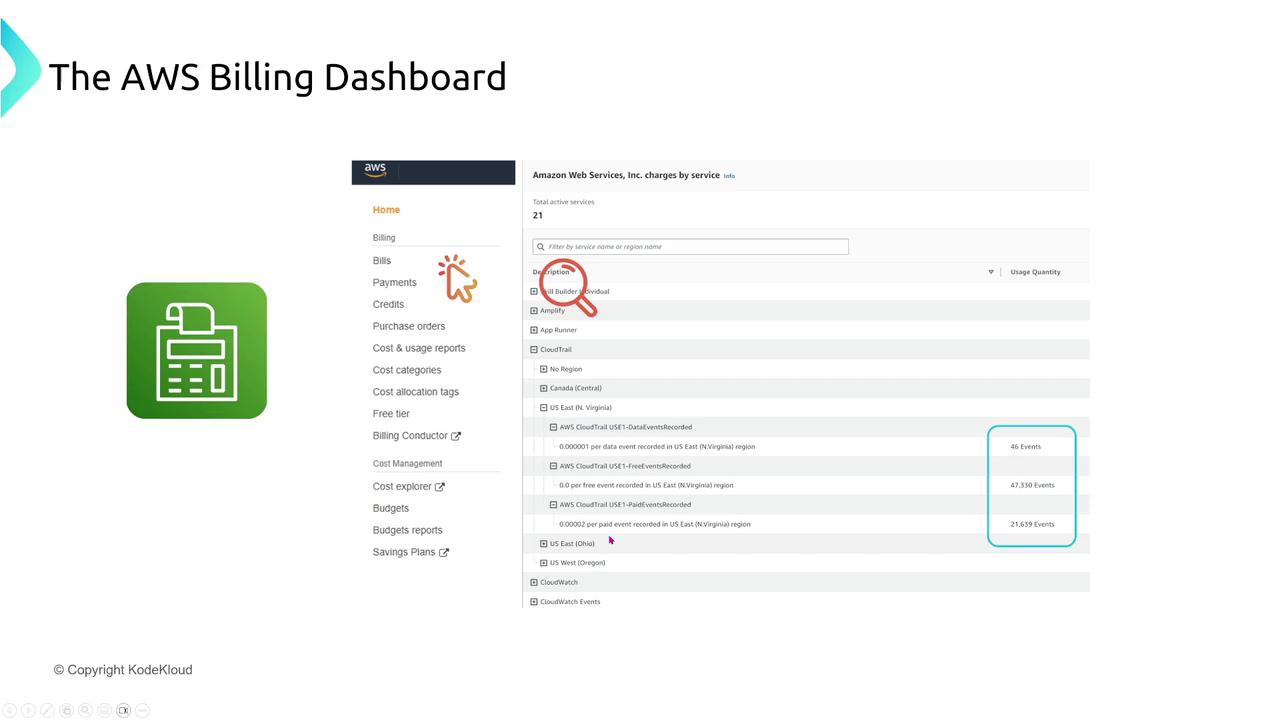
Billing Dashboard
The AWS Billing Dashboard offers an interactive view of your cost data, breaking down expenses by service, region, and usage. This dashboard is ideal for a quick overview without the need for deep dive analysis.
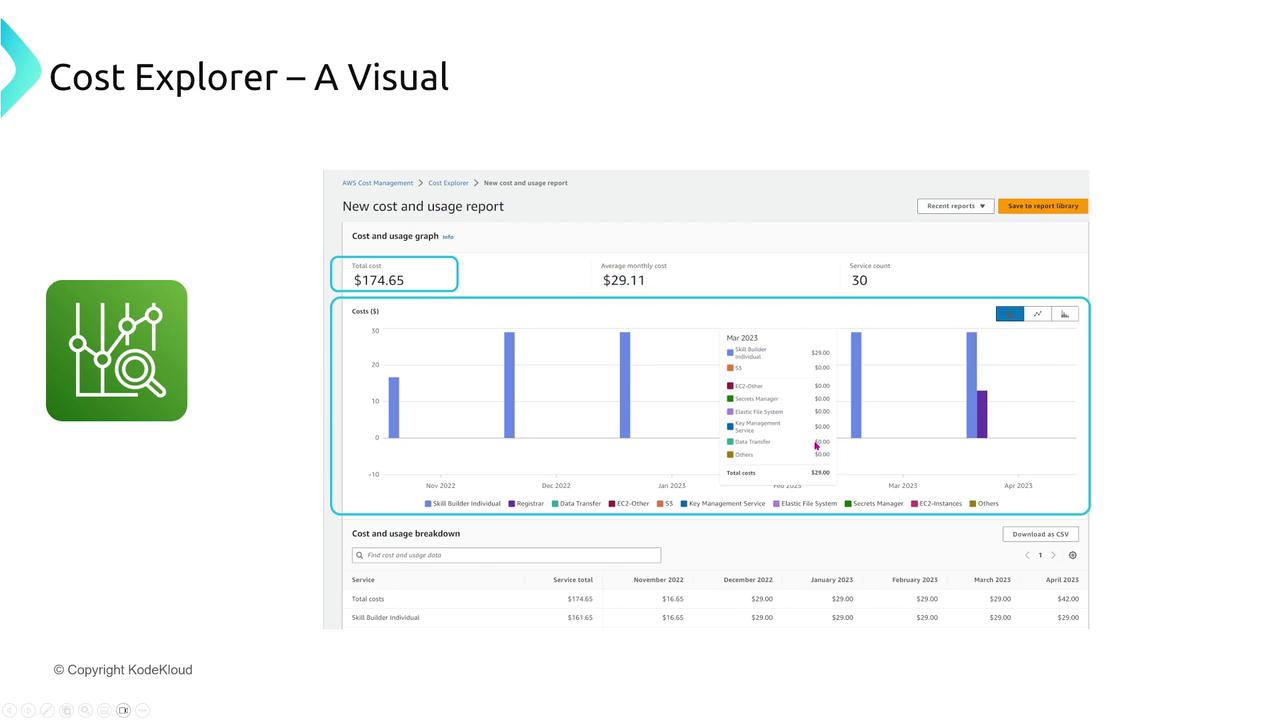
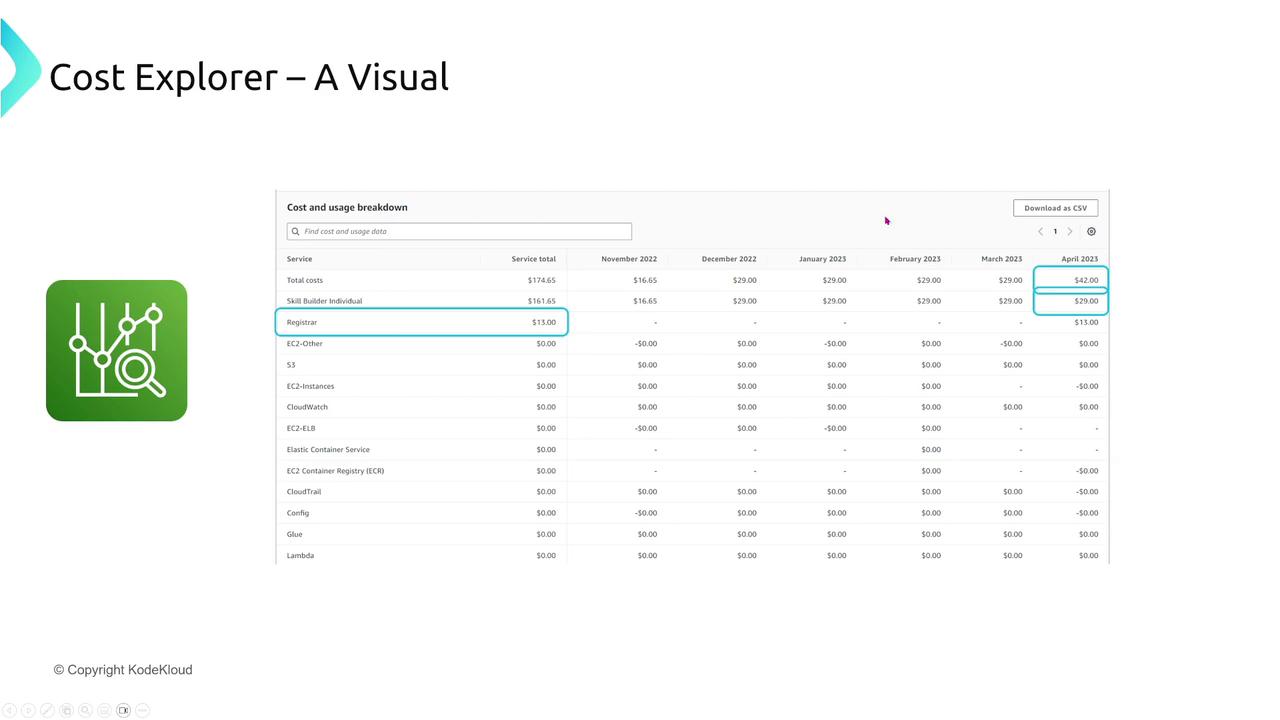
Cost Explorer
For deeper insights, AWS Cost Explorer presents interactive charts and graphs that help you visualize cost and usage trends. Key features include:
- Filtering by usage types, service, region, and linked accounts.
- Exporting detailed reports as CSV files.
- Analyzing minute expenses that often aggregate into significant costs over time.
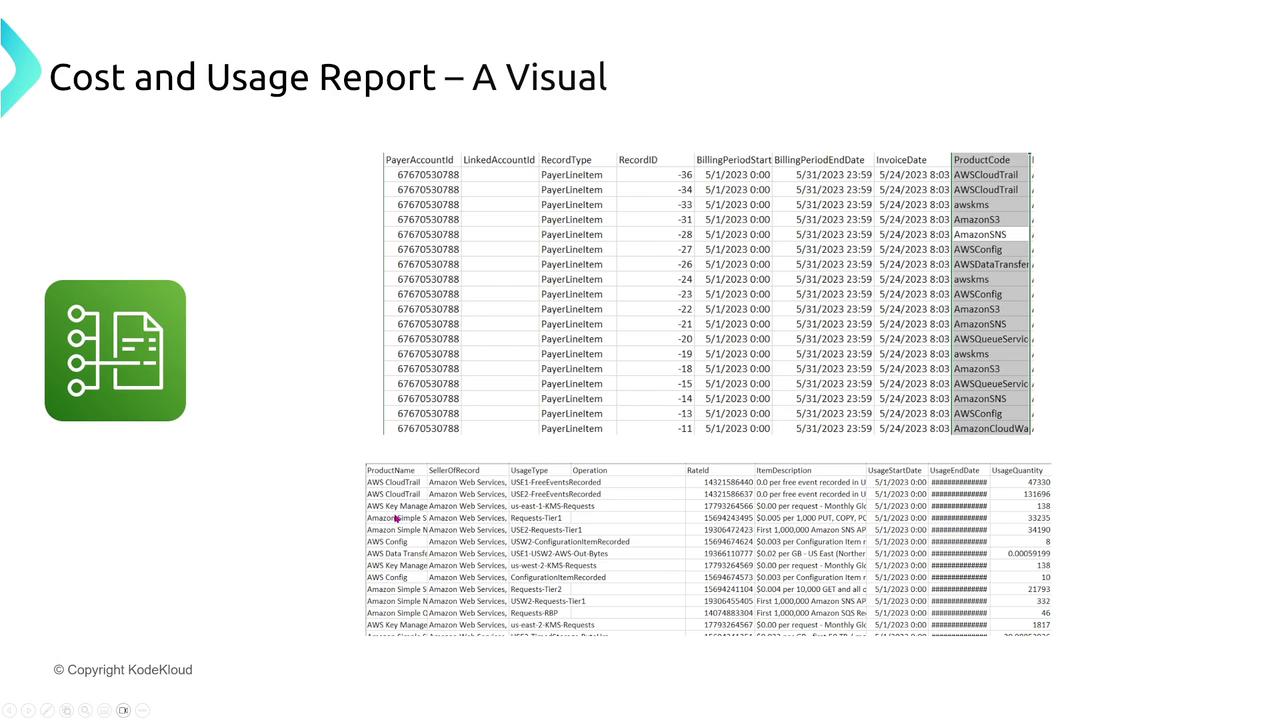
Cost and Usage Report
For granular reporting, the AWS Cost and Usage Report delivers hourly data in CSV format to an S3 bucket. This information can be integrated with tools like Athena or QuickSight for detailed analysis.
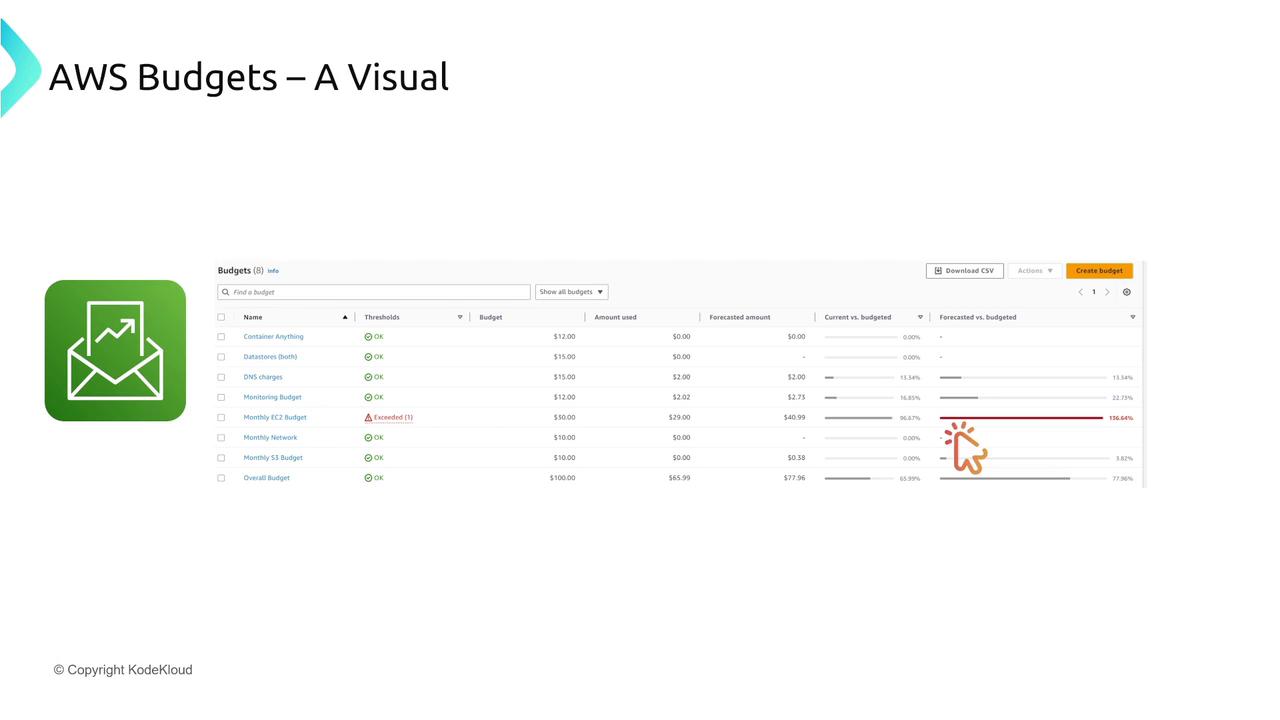
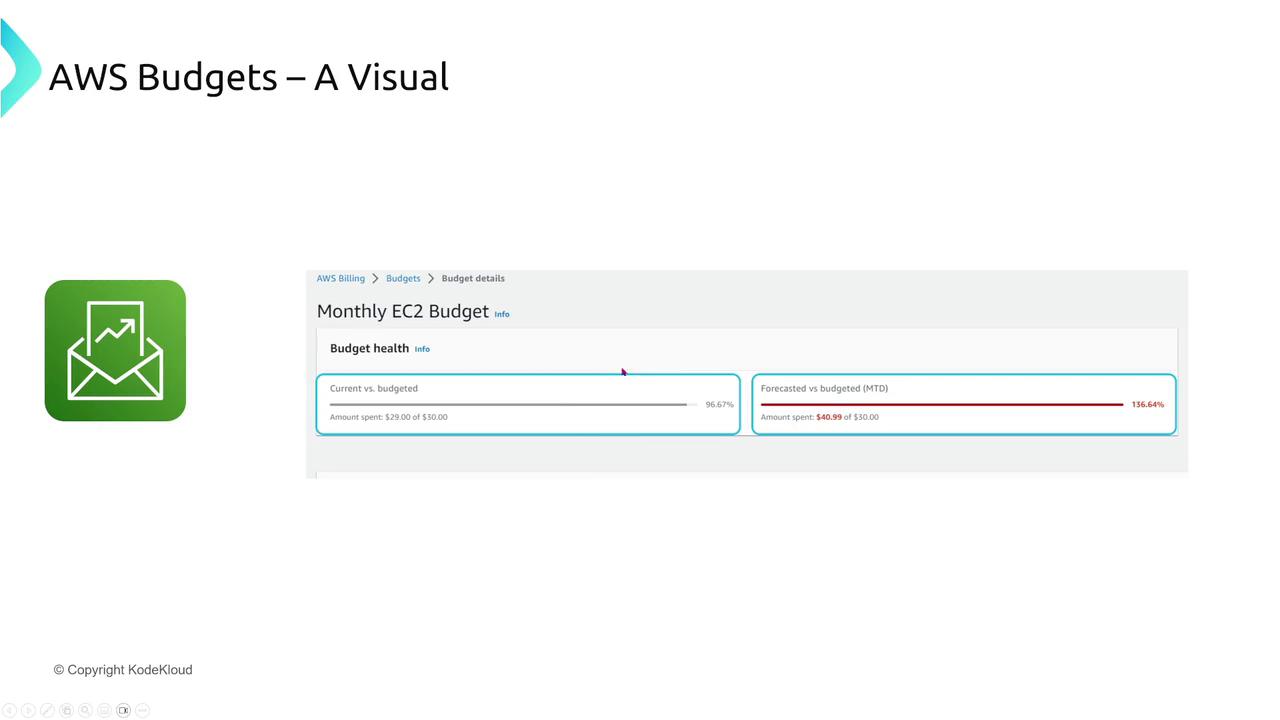
AWS Budgets
AWS Budgets empowers you with proactive cost management by setting spending limits and triggering alert notifications when thresholds are exceeded. You can establish budgets for overall spending, specific services, or even individual accounts. These notifications can lead to automated actions, such as restricting new resource launches when spending gets too high.
Conclusion
To summarize, effective cost optimization on AWS involves:
Licensing Models:
Gain a comprehensive understanding of pricing options—from on-demand and reserved instances to spot instances and dedicated hosts. Leverage Savings Plans to capitalize on discounts across various services including compute, container, and serverless technologies.ROI and TCO:
Assess your cloud investments by carefully considering both the Return on Investment and the Total Cost of Ownership, which include both direct expenses and hidden operational costs.Billing Tools:
Utilize tools such as the Billing Dashboard, Cost Explorer, detailed Cost and Usage Reports, and AWS Budgets to monitor spending, conduct forecasts, and enforce cost controls.
These strategies are foundational not only for managing AWS costs effectively but also for acing certification exams focused on cost management and optimization.
For any questions or further discussions, please reach out via the forums or contact [email protected].
Happy optimizing!
Watch Video
Watch video content