VPC Pricing Overview
When you create a VPC, AWS does not charge for the VPC itself or its fundamental components. Many services run within your virtual network without incurring extra base charges. However, there are specific details and exceptions worth noting.Base Billing Charges
The following VPC components are free of charge:- Subnets
- Security groups
- Network ACLs (NACLs)
- IP address ranges
Data Transfer Charges
Understanding data transfer fees is crucial when designing your AWS infrastructure.General Rule
- Inbound data: Transferred into AWS is free.
- Outbound data: Transferred out of AWS is charged.
Inbound Data
Data transferred into an AWS region, VPC, or Availability Zone (AZ) comes at no cost. AWS encourages data ingress to maximize performance within its infrastructure.Outbound Data
Charges are applied when data exits an AWS environment, whatever the connection method (e.g., dedicated cable, VPN, or the Internet). Consider the following scenarios:Within the Same Region but Different AZs
Even if the data transfer occurs within a single region, if it crosses between different data centers (AZs), you might face charges—especially if the traffic is routed using a public IP address.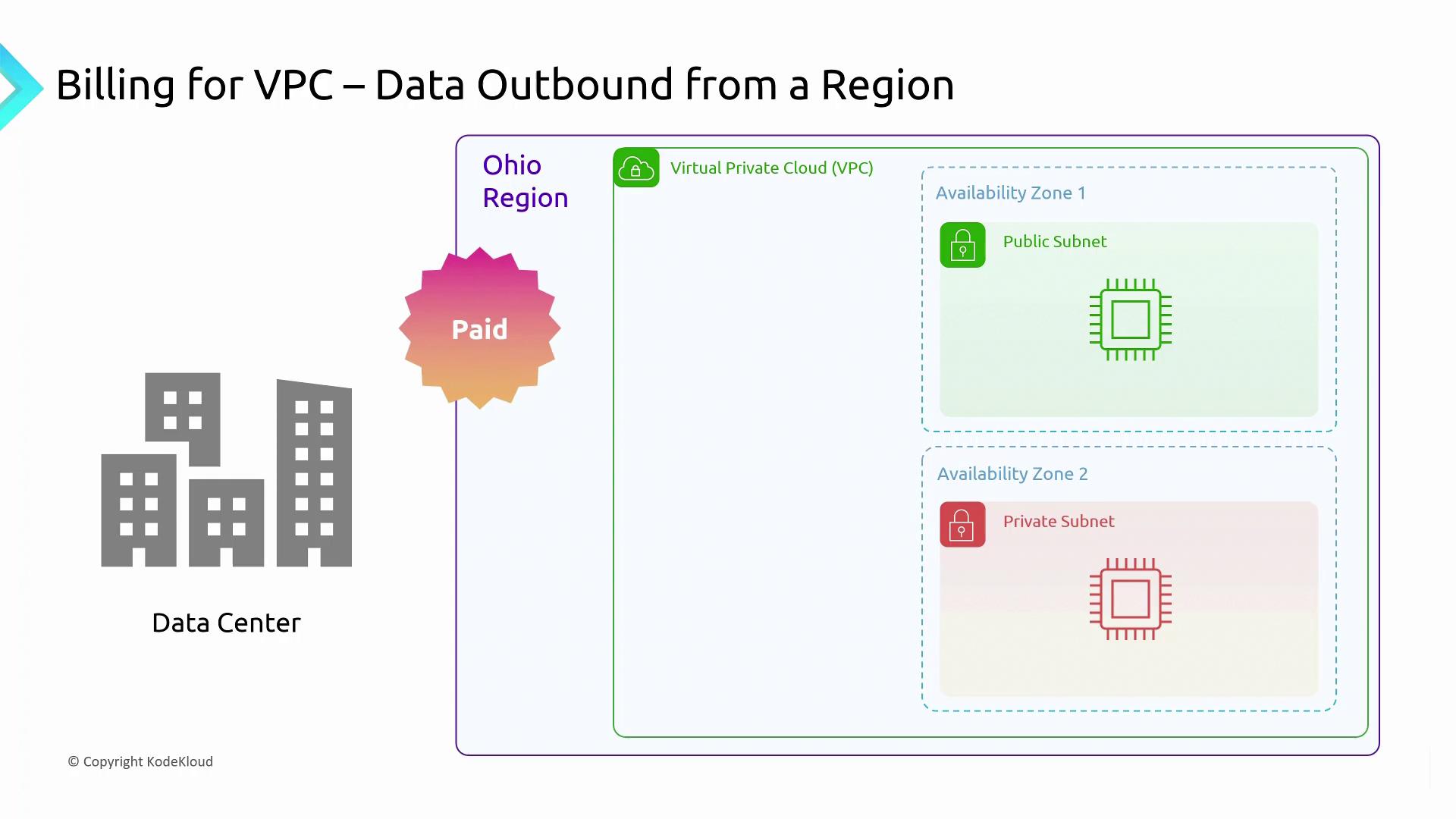
Between Regions
If you transfer data from one region (e.g., Ohio) to another (e.g., Virginia), AWS charges for data leaving the source region (Ohio). Data entering the destination region (Virginia) remains free.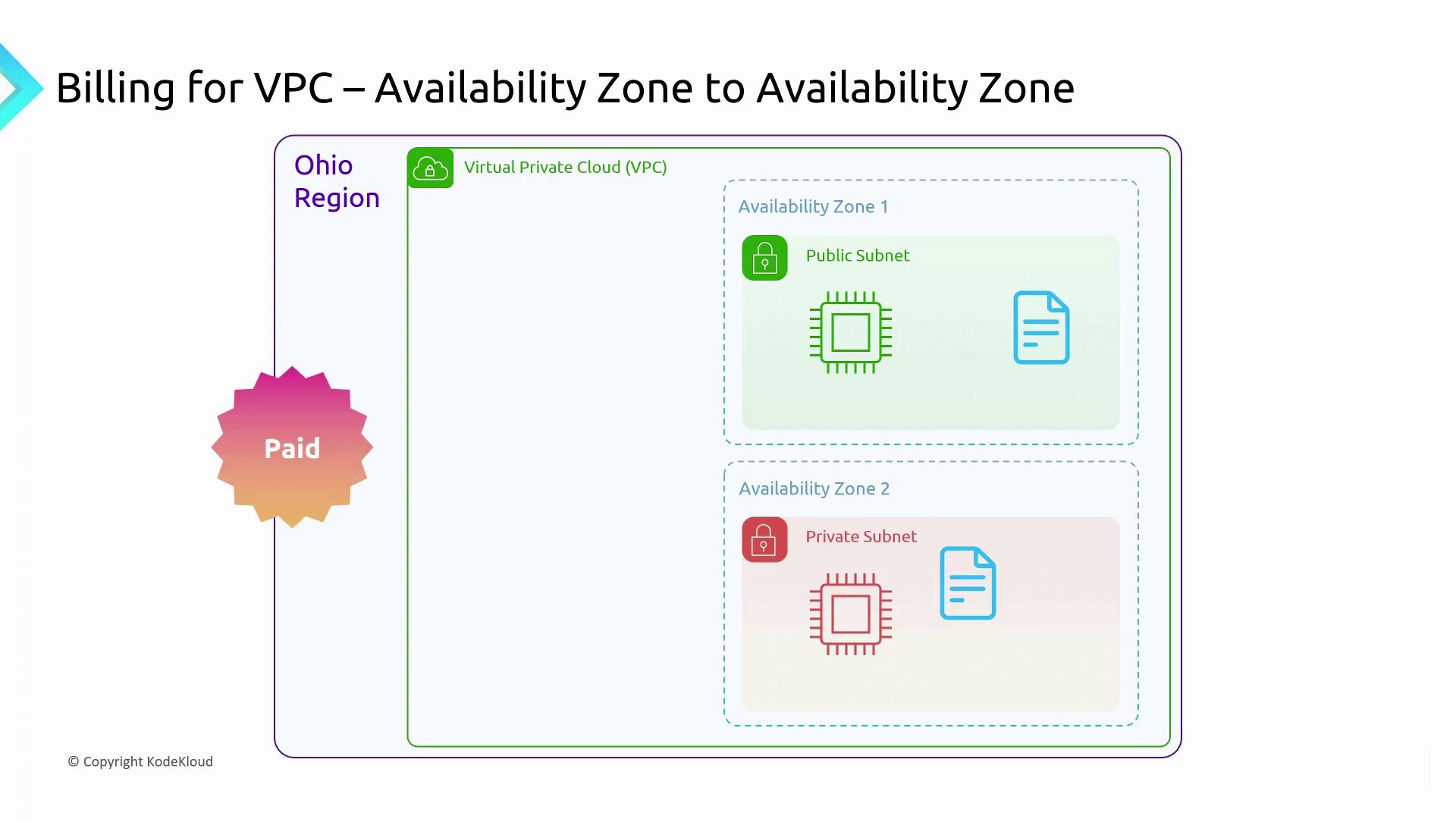
Directing Data to a Public IP Address
Traffic directed to a public IP address is usually charged since it generally exits the AWS network and travels over the Internet.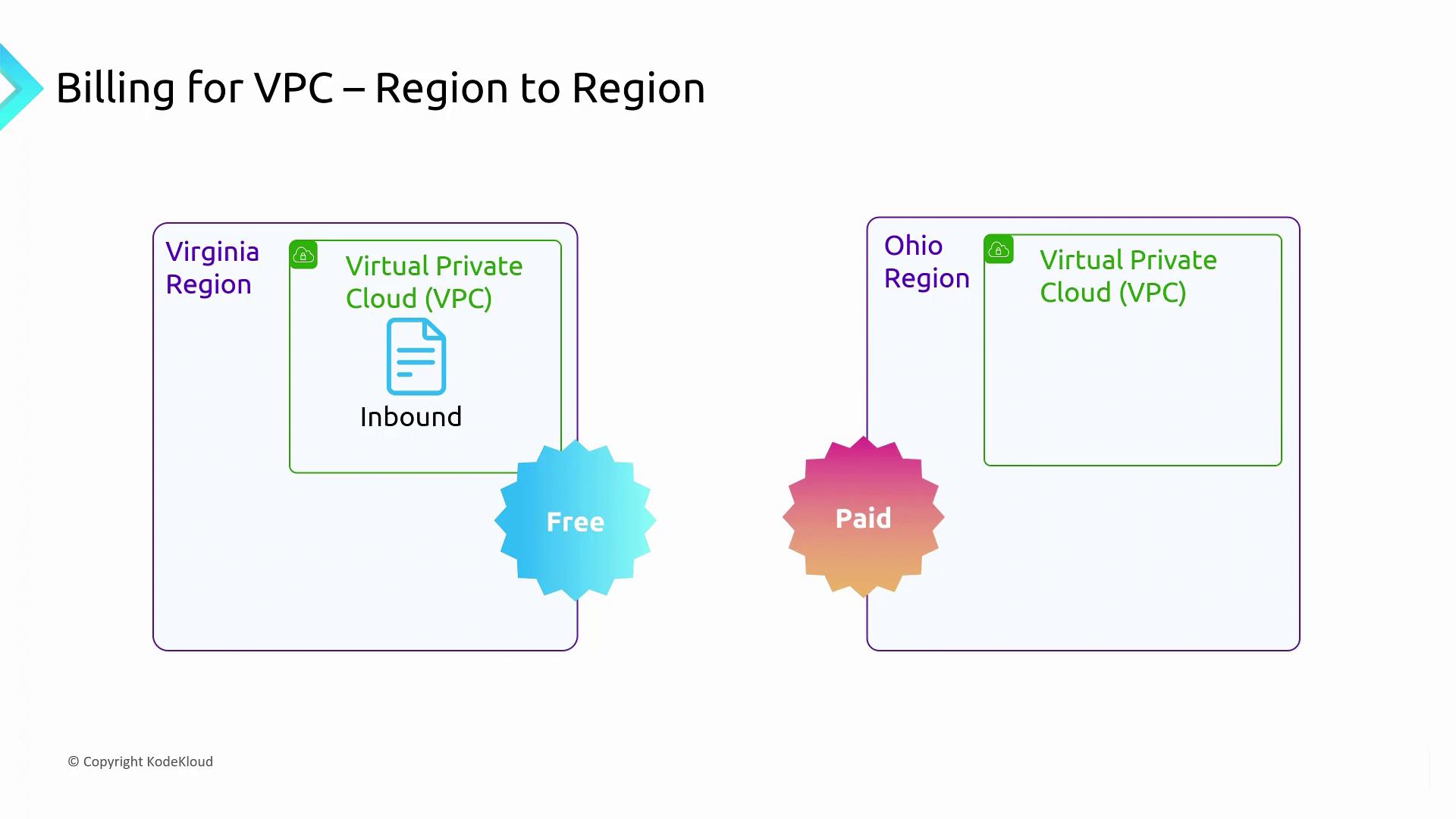
Intra-Region Transfers
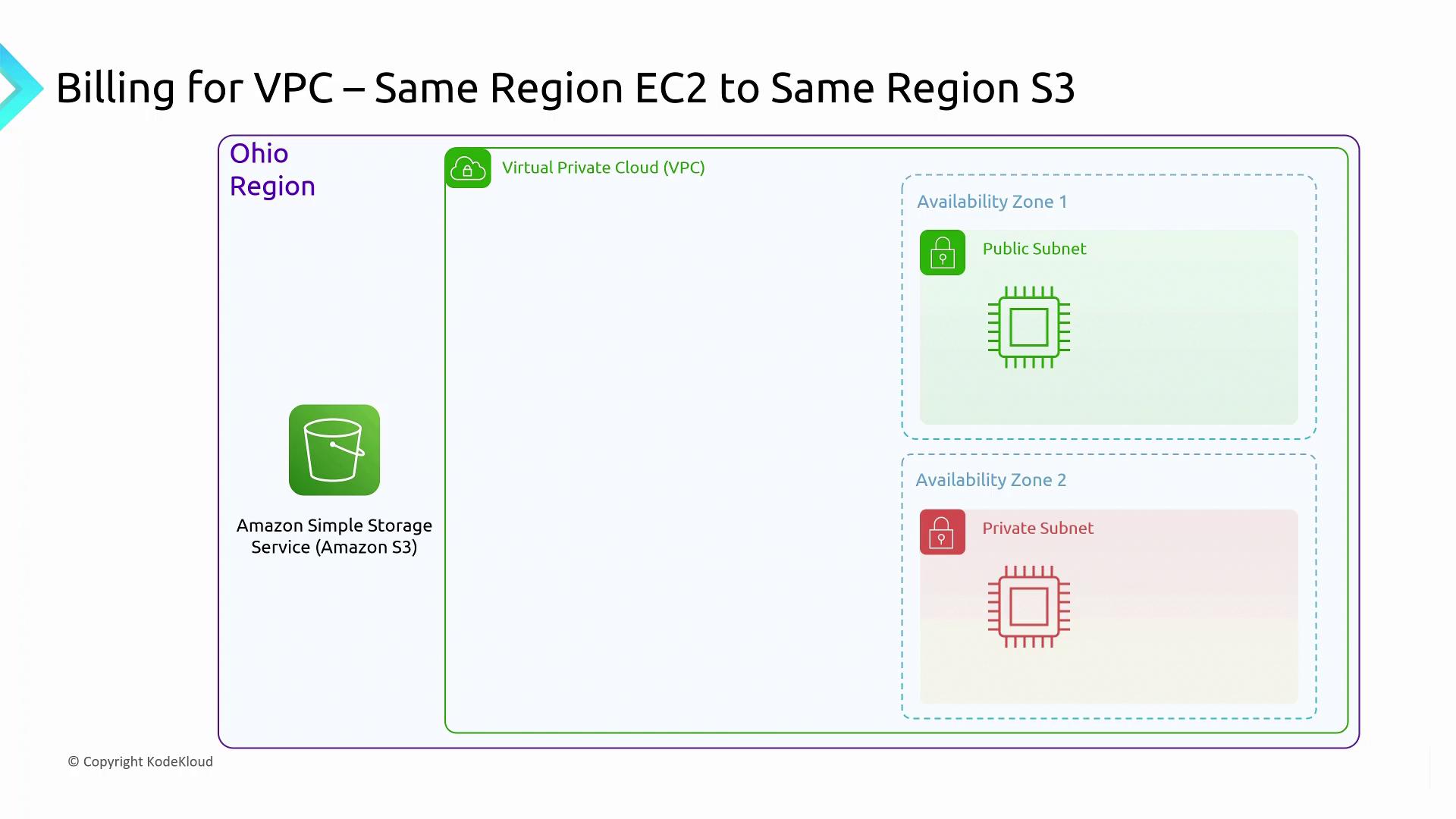
Transfers within the same region might be free in specific cases:- Data transfer between an EC2 instance and an S3 bucket in the same region is free.
- Services like CloudFront, when used within the same region, also incur no transfer charges.
Summary of Data Transfer
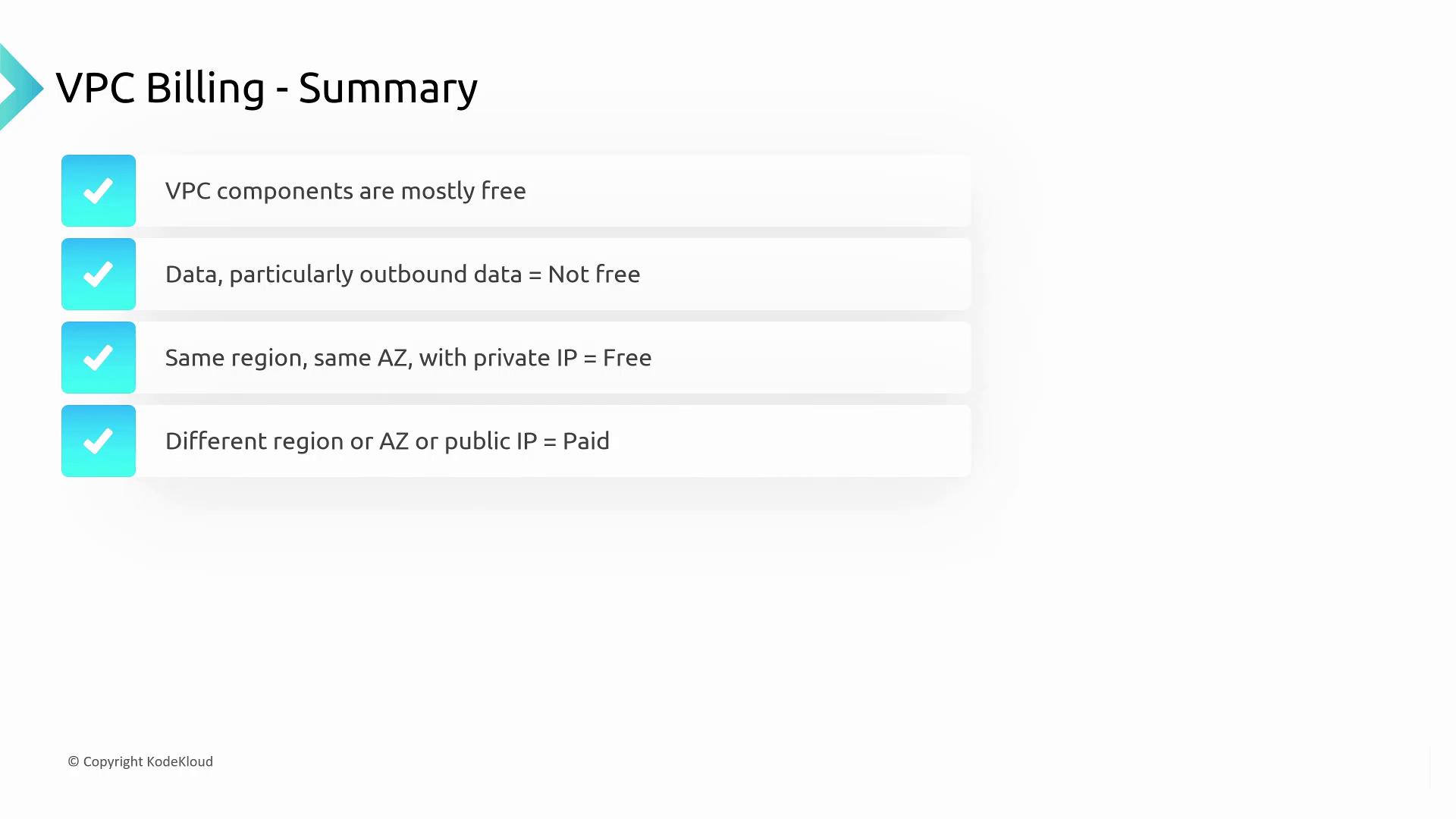
Key takeaways include:- Inbound data is always free.
- Outbound data is charged, except when transferred to another AWS service within the same region.
- Data transfers on private IP addresses within the same AZ are free.
- Crossing between AZs or regions (or using a public IP address) will typically result in charges.
| Data Transfer Scenario | Charge |
|---|---|
| Inbound Data | Free |
| Outbound Data (Same AZ, same region) | Free |
| Outbound Data (Different AZ or public IP) | Charged |
| Outbound Data (Between Regions) | Charged |
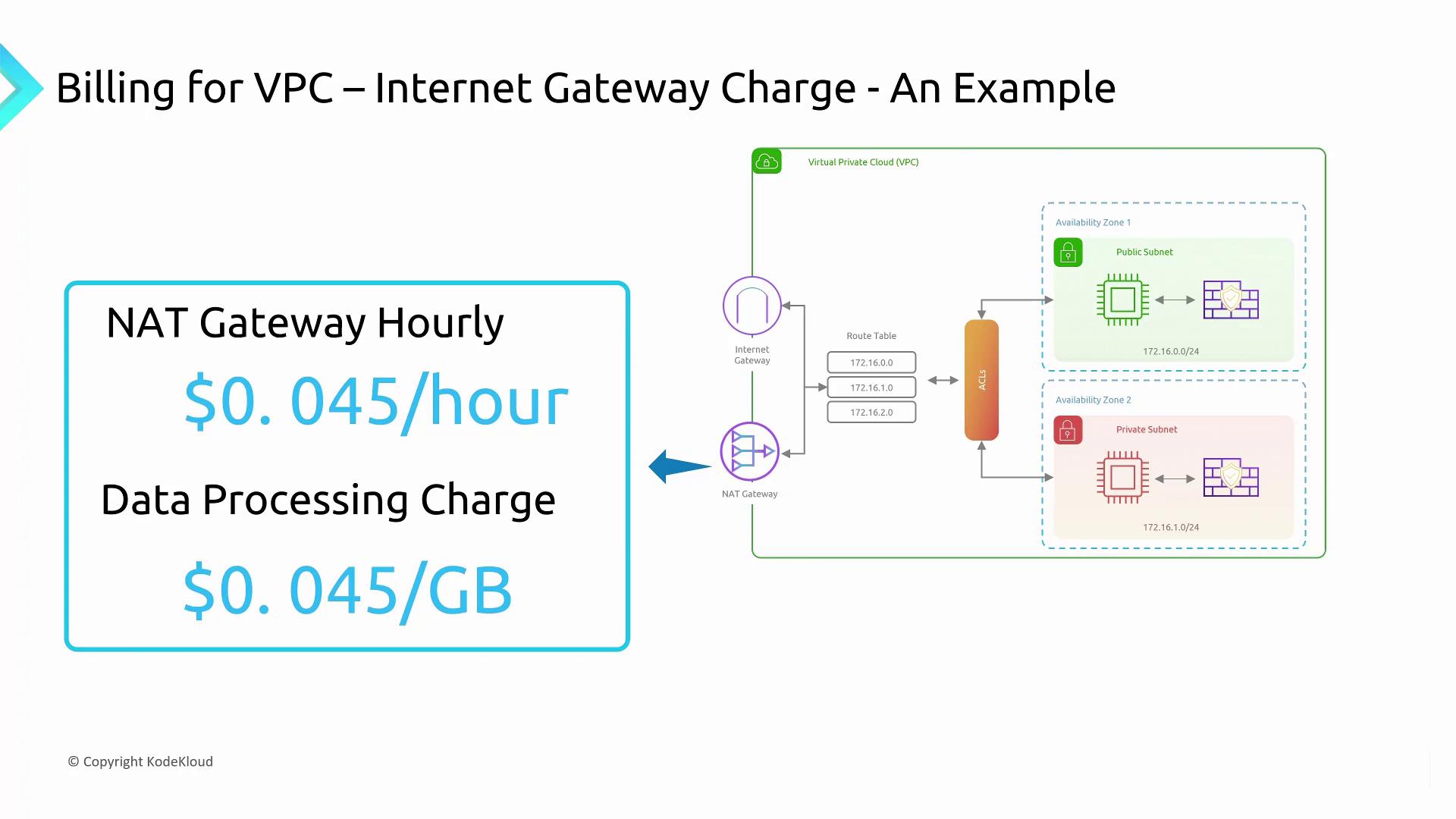
Additional Components: NAT Gateways
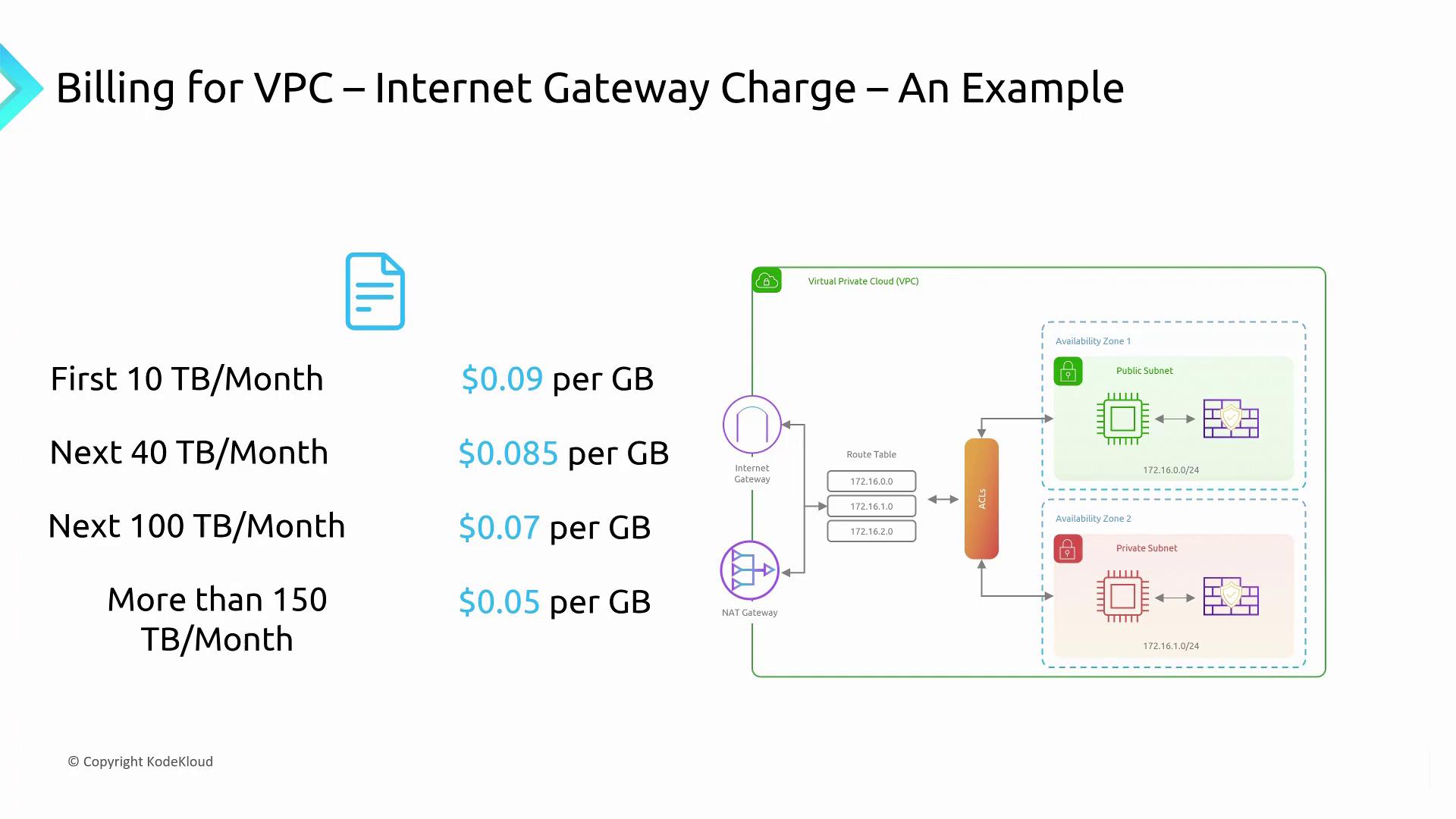
NAT gateways are another aspect that can drive up your costs:- NAT gateways use the Internet gateway to provide outbound Internet access.
- They incur an hourly charge, along with a per-gigabyte fee for data processed (approximately $0.045 per hour, though rates may vary).

Keep in mind that AWS billing practices can change, so always refer to the official AWS pricing page to get the most up-to-date information.
Final Thoughts
While most components within a VPC—such as subnets, firewalls, routing tables, and security groups—are free, it’s essential to be aware of the following:- Inbound data transfers are free.
- Outbound transfers incur charges, especially if they cross AZs, regions, or use public IP addresses.
- Additional services, such as NAT gateways, add further costs.