AWS Cloud Practitioner CLF-C02
Cloud Computing
Benefits of Cloud
Welcome back, Cloud Practitioner students! In this lesson, we explore the key benefits of cloud computing as defined by industry standards and Amazon Web Services (AWS). Understanding these advantages is not only essential for practical implementation but also forms part of the exam objectives. Let’s examine the six core benefits in detail.
1. Converting Capital Expenditure (CAPEX) into Operating Expense (OPEX)
One of the major advantages of utilizing AWS is the ability to transform substantial upfront hardware investments into manageable monthly operating expenses. Rather than investing heavily in physical servers and infrastructure, you can use AWS to acquire virtual machines on a pay-as-you-go basis. This means you’re billed only for the resources you actually use and can efficiently scale down when those resources are no longer required.
2. Moving Away from Data Center Dependence
A significant benefit of AWS is that it alleviates the need to manage your own data centers. For many organizations, such as insurance companies, running a data center is not a core competency. By shifting these responsibilities to AWS, you can concentrate on your primary business objectives, such as customer service and innovative application development.
3. Enhanced Scalability on Demand
Traditional data centers are often constrained by fixed hardware capacities and limited vendor supply, forcing companies to anticipate future requirements. AWS offers dynamic scalability, allowing you to rapidly adjust your virtual machines or database resources as demand fluctuates. This flexibility reduces risks associated with over- or under-provisioning.

Note
When using AWS platform services, you pay solely for the actual capacity consumed, avoiding the sunk cost of unused hardware in traditional setups.
4. Leveraging Economies of Scale
AWS capitalizes on massive economies of scale, meaning that as your consumption of cloud services increases, the cost per unit decreases. For instance, while the initial cost per gigabyte might be higher, high-volume usage can lead to significantly reduced rates. AWS’s continual push to lower prices on services like Amazon S3 further enhances cost savings and budget predictability.
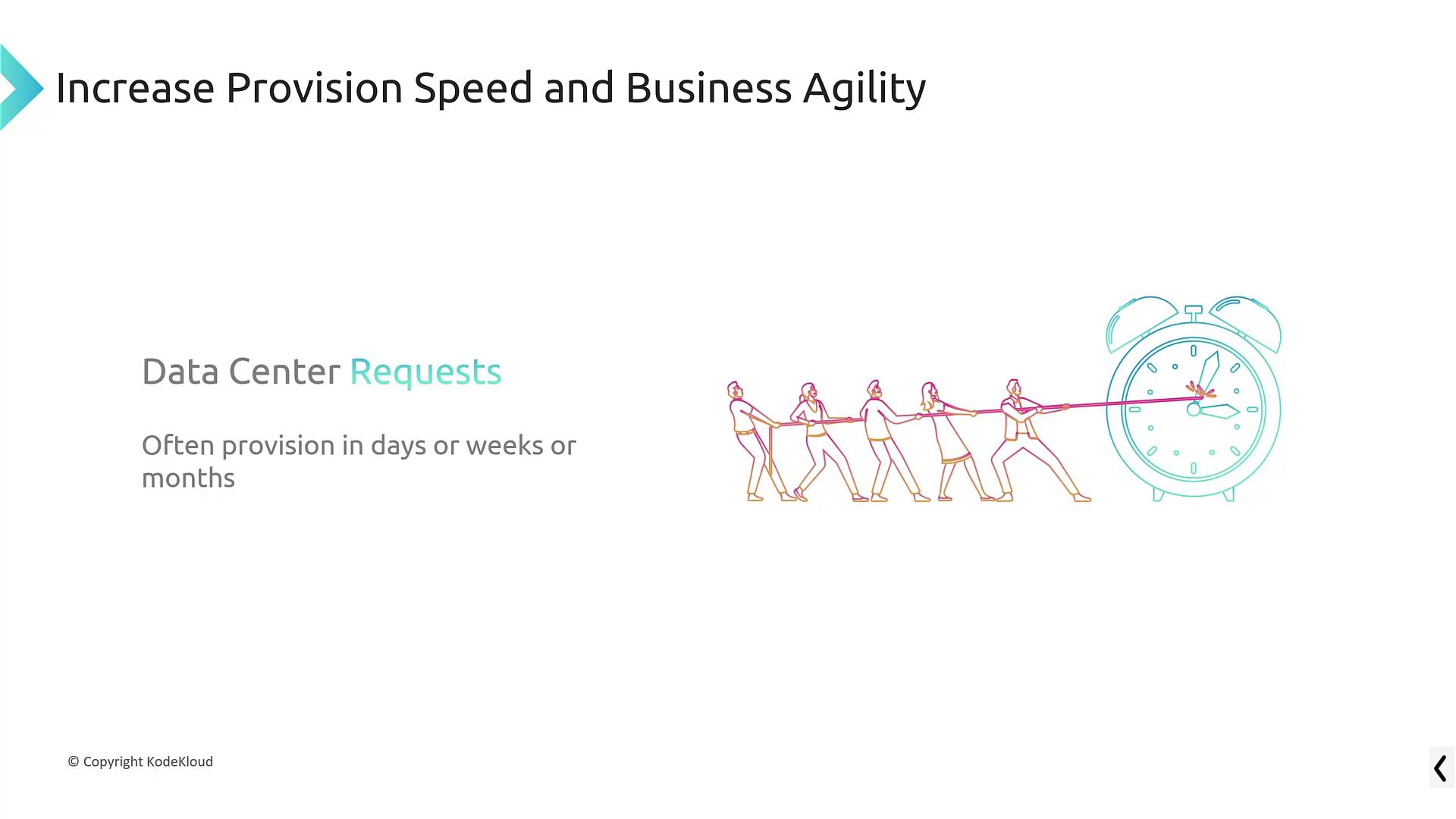
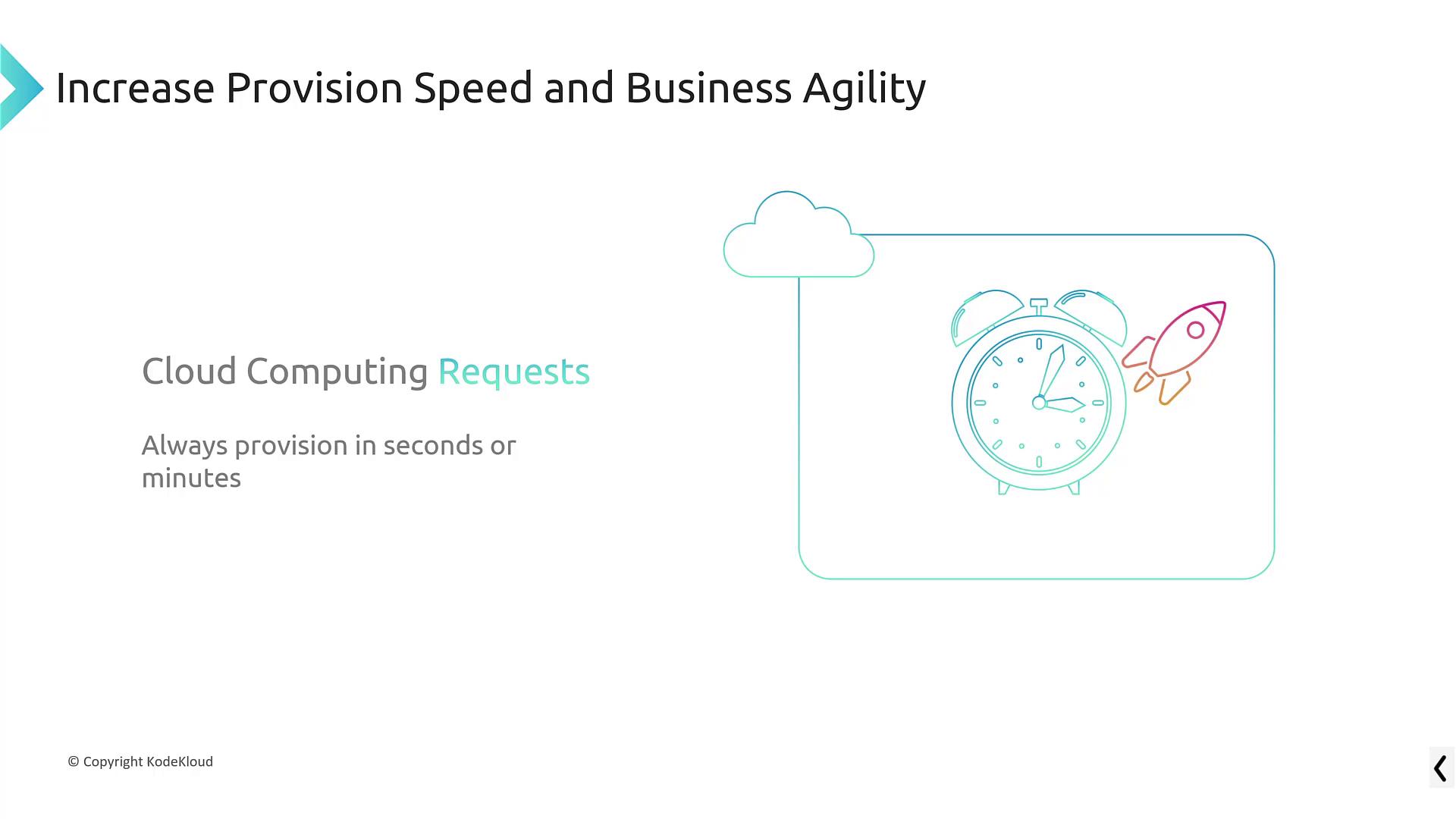
5. Rapid Provisioning and Increased Business Agility
Provisioning hardware in a conventional data center often involves lengthy delays, sometimes taking days, weeks, or even months. In contrast, AWS enables you to launch resources in a matter of seconds or minutes. For example, a basic Linux instance can be up and running in as little as 45 seconds. This speedy provisioning not only accelerates the deployment of new projects but also provides the agility needed to experiment and innovate quickly.
6. Global Reach with Versatile Deployment Options
Unlike traditional data centers, which are limited to specific geographical locations, AWS boasts a vast network of 31 major data center regions worldwide along with 300-400 edge locations that cache and serve content locally. AWS’s local zones further extend this reach into many metropolitan areas, empowering you to deploy your applications globally with minimal latency and rapid scalability.

Summary
In conclusion, AWS cloud computing offers numerous benefits that empower your business to excel in today’s fast-paced environment:
- Transform large capital expenditures into manageable monthly operating expenses.
- Shift focus from managing data centers to enhancing customer service.
- Enjoy dynamic, on-demand scalability for fluctuating workloads.
- Benefit from reduced costs through economies of scale.
- Accelerate project deployment with rapid resource provisioning.
- Achieve global application deployment with a broad network infrastructure.
These advantages streamline operations and foster an environment of innovation and competitiveness.
Thank you for reading this lesson. We look forward to bringing you more insights in our next article.
For more information, visit the AWS Documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content