AWS CloudWatch
Anatomy of Alarms
Built in and Custom Metrics
In this guide, we’ll explore the three primary metric types in AWS CloudWatch—built-in metrics, custom metrics, and usage metrics—and demonstrate how to apply them when monitoring an RDS instance in a VPC. By the end, you’ll understand how to gain a comprehensive view of your resource health, application performance, and usage quotas.
1. Metric Types Overview
CloudWatch collects and organizes data into different metric categories. Leveraging all three types helps you:
- Track core resource performance
- Gather application-specific insights
- Monitor service consumption against quotas
| Metric Type | Source | Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| Built-in | AWS-managed (70+ services) | CPU, disk I/O, network throughput, memory usage |
| Custom | User-defined via API or SDK | Transaction counts, cache hit rates, API response times |
| Usage | AWS service quotas and usage statistics | Track service limits, forecast capacity, avoid overruns |
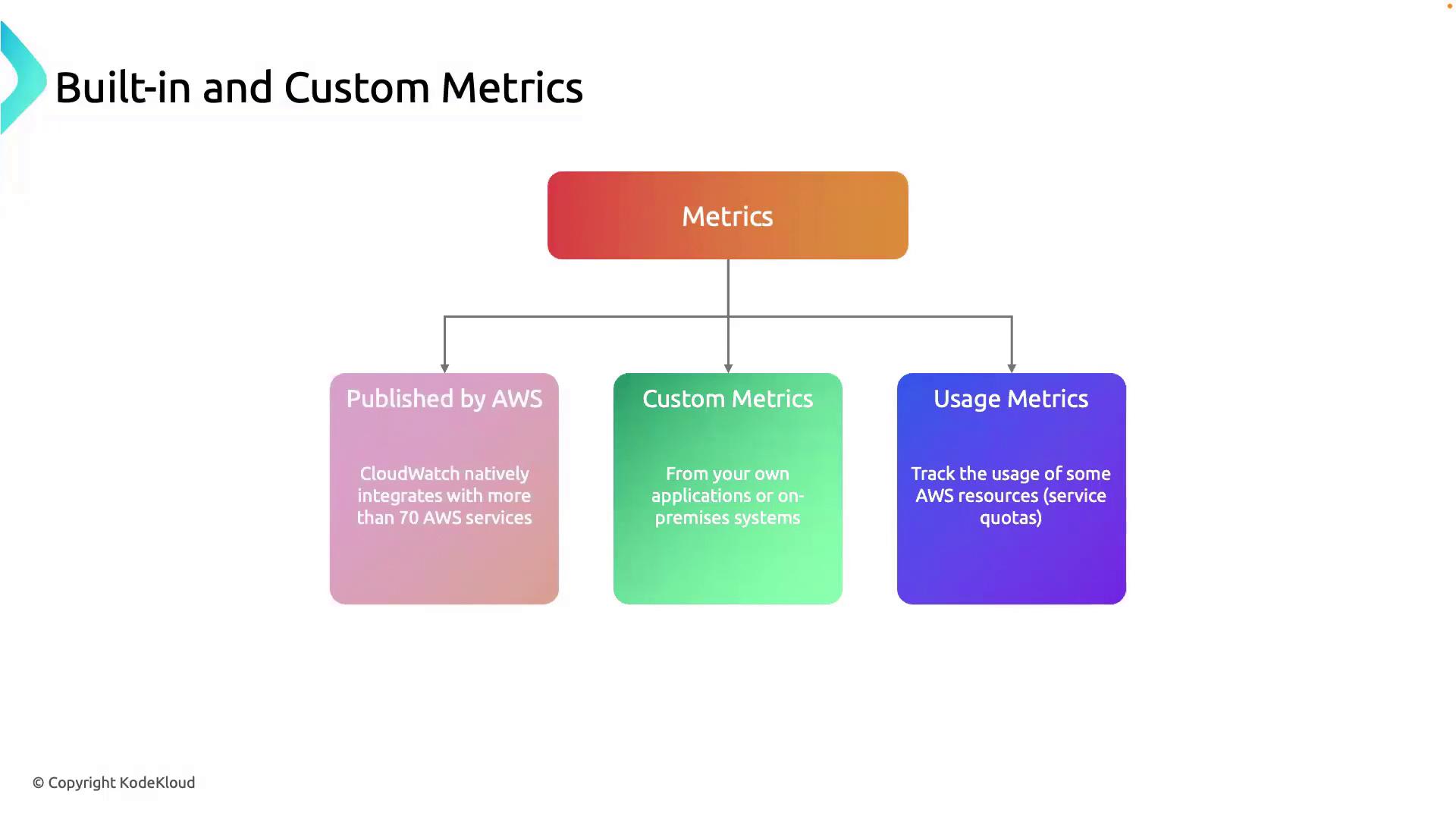
1.1 Built-in Metrics
CloudWatch automatically publishes metrics for over 70 AWS services. Examples include:
- CPUUtilization
- NetworkIn / NetworkOut
- DiskReadBytes / DiskWriteBytes
Note
Built-in metrics have a default 1-minute resolution. To enable 1-second (high-resolution) metrics for supported services, see the CloudWatch detailed monitoring documentation.
1.2 Custom Metrics
When default metrics aren’t enough, you can push any numeric data via the PutMetricData API. Common examples:
- Order processing rate
- Cache hit ratio
- Endpoint response time
Warning
Custom metrics incur additional charges. Review the CloudWatch pricing page before publishing high-cardinality or high-frequency data.
1.3 Usage Metrics
Usage metrics track how close you are to AWS service quotas (limits). These are crucial for:
- Monitoring API call volumes
- Ensuring you don’t exceed resource limits
- Forecasting future capacity needs
2. Practical Example: Monitoring RDS in a VPC
Let’s apply these metric types to an Amazon RDS instance running in a Virtual Private Cloud.
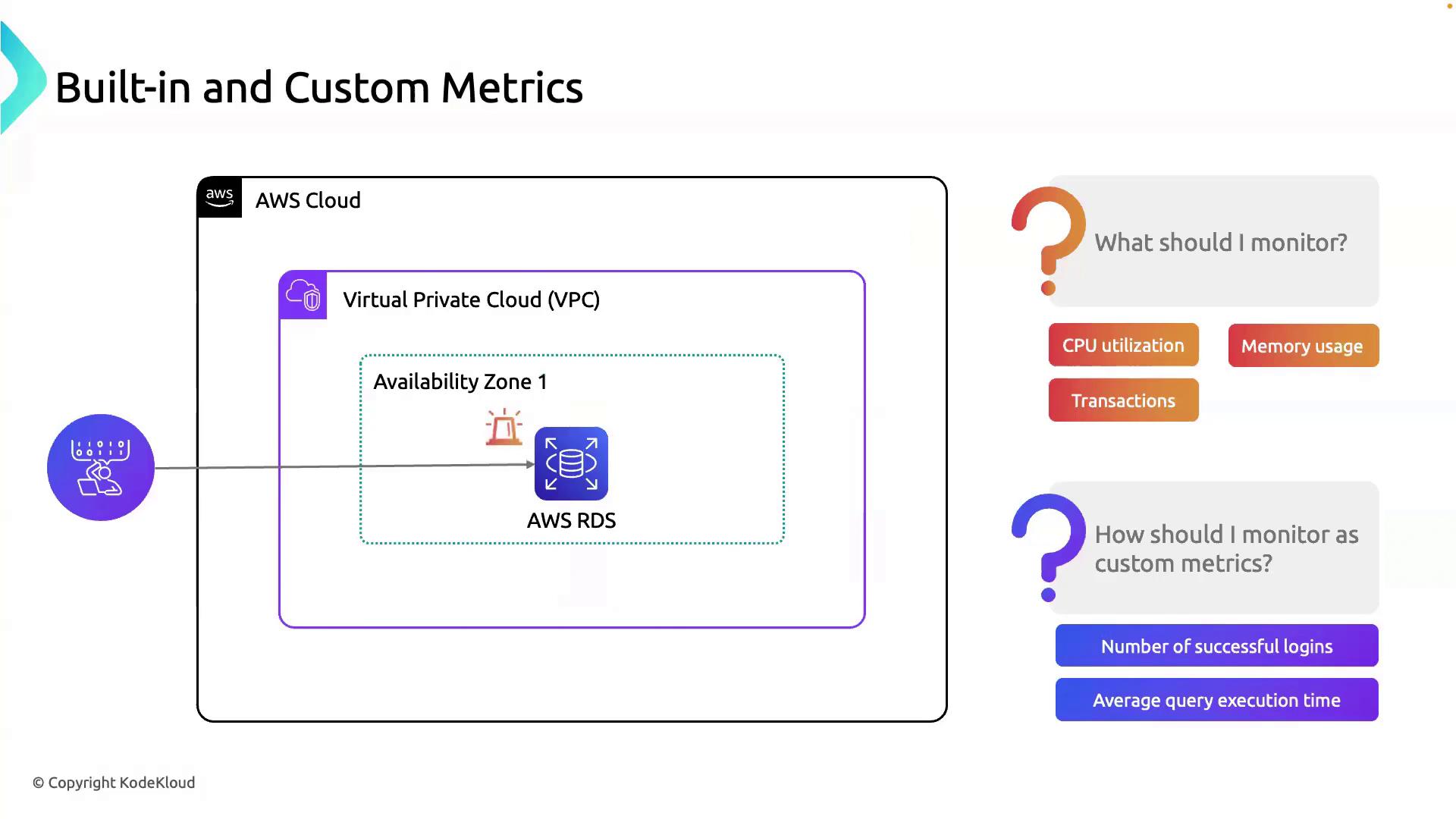
2.1 Built-in RDS Metrics
AWS RDS publishes dozens of metrics by default. Key ones include:
| Metric Name | Description | Unit |
|---|---|---|
| CPUUtilization | Percentage of CPU in use | Percent (%) |
| FreeableMemory | Available RAM in the instance | Bytes |
| ReadIOPS / WriteIOPS | Disk read/write operations per sec | Count/sec |
| DatabaseConnections | Active connections to the DB | Count |
2.2 Custom RDS Metrics
Enhance observability with application-specific data:
| Metric Name | Description | Collection Interval |
|---|---|---|
| LoginsPerMinute | Number of successful user logins | 1 minute |
| AvgQueryExecutionTime | Average time to execute SQL queries | 1 minute |
| CacheHitRatio | Percentage of cache hits vs. total requests | 1 minute |
Note
Use the AWS SDK or CLI command aws cloudwatch put-metric-data to publish custom metrics from your application or monitoring scripts.
3. Next Steps
With metrics in place, you can now:
- Set up CloudWatch Alarms to get notified on thresholds
- Build CloudWatch Dashboards for real-time visualization
- Integrate with AWS CloudWatch Logs for log monitoring
Links and References
- AWS CloudWatch Metrics and Dimensions
- Amazon RDS Monitoring
- CloudWatch Pricing
- AWS SDK for Go CloudWatch Guide
Watch Video
Watch video content