AWS CloudWatch
CloudWatch Logs
Introduction to CloudWatch Logs
AWS CloudWatch Logs is a fully managed service for collecting, monitoring, and storing log files from AWS resources and on-premises servers. When paired with the CloudWatch Agent, you gain deep visibility into system-level metrics (CPU, memory, disk) and custom application logs.
Together, these capabilities help you:
- Maintain application health
- Simplify troubleshooting
- Support security and compliance audits
Key Capabilities of CloudWatch Logs
| Capability | Description | AWS CLI Example |
|---|---|---|
| Retention | Store logs indefinitely or for a custom retention period | aws logs put-retention-policy --log-group-name MyGroup --retention-in-days 30 |
| Real-time search | Search and filter log data on the fly | aws logs filter-log-events --log-group-name MyGroup --filter-pattern "ERROR" |
| Metric Filters | Convert log patterns into CloudWatch metrics | aws logs put-metric-filter --filter-name ErrorCount --log-group-name MyGroup --filter-pattern "ERROR" --metric-transformations metricName=ErrorCount,metricNamespace=AppMetrics,metricValue=1 |
| Alarms & Actions | Trigger alarms or automated actions based on log-derived metrics | aws cloudwatch put-metric-alarm --alarm-name HighErrorRate --metric-name ErrorCount --namespace AppMetrics --statistic Sum --period 60 --threshold 1 --comparison-operator GreaterThanOrEqualToThreshold --evaluation-periods 1 --alarm-actions arn:aws:sns:us-east-1:123456789012:NotifyMe |
Warning
Defining an indefinite retention policy can increase storage costs. Always monitor your log volume and set a realistic retention period.
Installing and Configuring the CloudWatch Agent
You install the CloudWatch Agent on EC2 instances or on-premises servers to collect metrics and logs:
# 1. Install the agent (Amazon Linux example)
sudo yum install -y amazon-cloudwatch-agent
# 2. Generate a JSON configuration
sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-config-wizard
# 3. Start the agent service
sudo systemctl start amazon-cloudwatch-agent
After installation, update the JSON config to specify:
- Log files to monitor
- Metrics to collect
- Destination (CloudWatch Logs or CloudWatch Metrics)
Note
You can also store your agent configuration in SSM Parameter Store and reference it in the start command:sudo /opt/aws/amazon-cloudwatch-agent/bin/amazon-cloudwatch-agent-ctl -a fetch-config -m ec2 -c ssm:YourParameterName -s
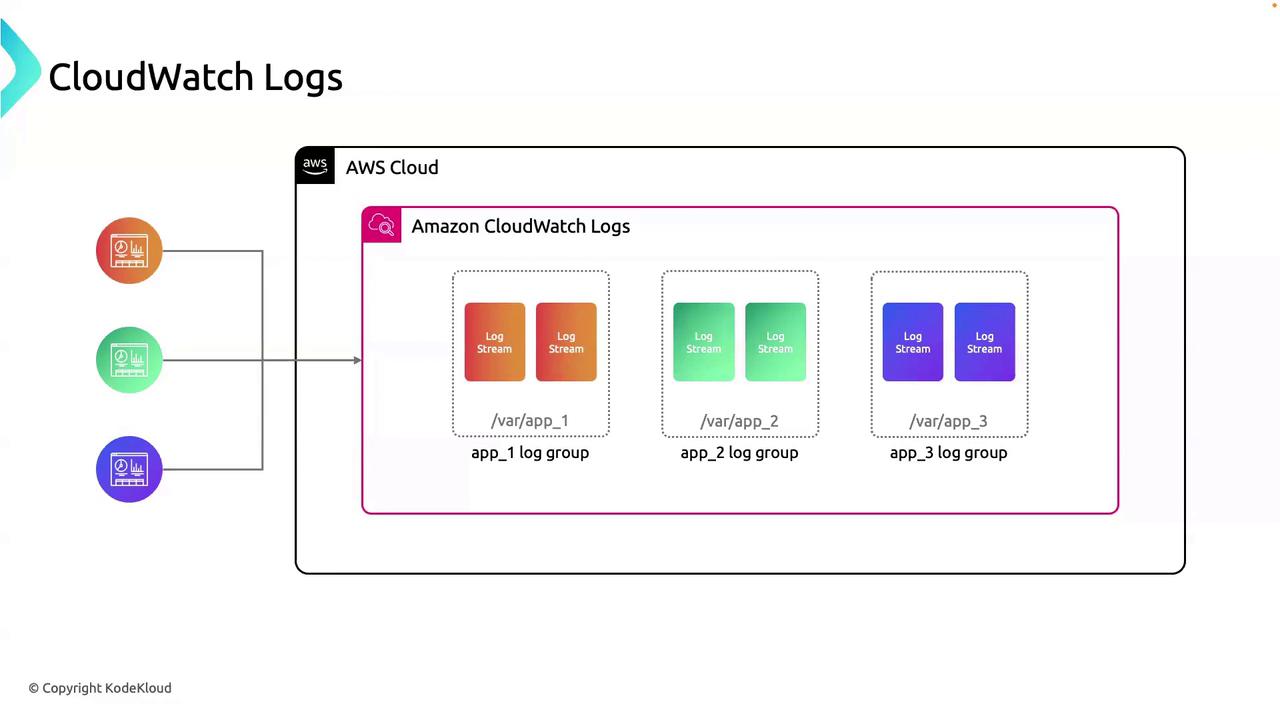
Core Concepts: Log Groups vs. Log Streams
CloudWatch Logs structures data using two primary concepts:
| Concept | Definition | AWS CLI Example |
|---|---|---|
| Log Group | A container for log streams with shared retention and ACLs. | aws logs create-log-group --log-group-name app_01 |
| Log Stream | An ordered sequence of log events from a single source. | aws logs create-log-stream --log-group-name app_01 --log-stream-name stream_2024-06-01 |
- Log Group: Use to separate environments (dev, prod) or applications.
- Log Stream: Each instance or component can have its own stream.
Here’s how your applications integrate:
Use Case: Debugging with CloudWatch Logs
When troubleshooting app_01:
- Go to the app_01 log group.
- Select the relevant log stream for your instance or task.
- Use real-time filtering (e.g.,
ERROR,WARN) to pinpoint exceptions. - If needed, create a metric filter to track error rates over time.
This structured approach avoids sifting through unrelated logs and accelerates root-cause analysis.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content