A Real-World Analogy: Cody’s Pipeline
Imagine Cody, a successful cabinet merchant whose business was growing faster than his production line could handle:- He sourced premium wood from multiple suppliers.
- Each piece was sent to various shops for assembly.
- Finished cabinets were shipped by truck, train, boat, or plane.
Cody’s Pipeline is an analogy for how AWS CodePipeline automates your software delivery process.
What Is AWS CodePipeline?
AWS CodePipeline is a fully managed CI/CD service that orchestrates your release workflow:- Continuous Integration (CI): Merge and build code changes automatically.
- Continuous Delivery (CD): Test and deploy updates without manual steps.
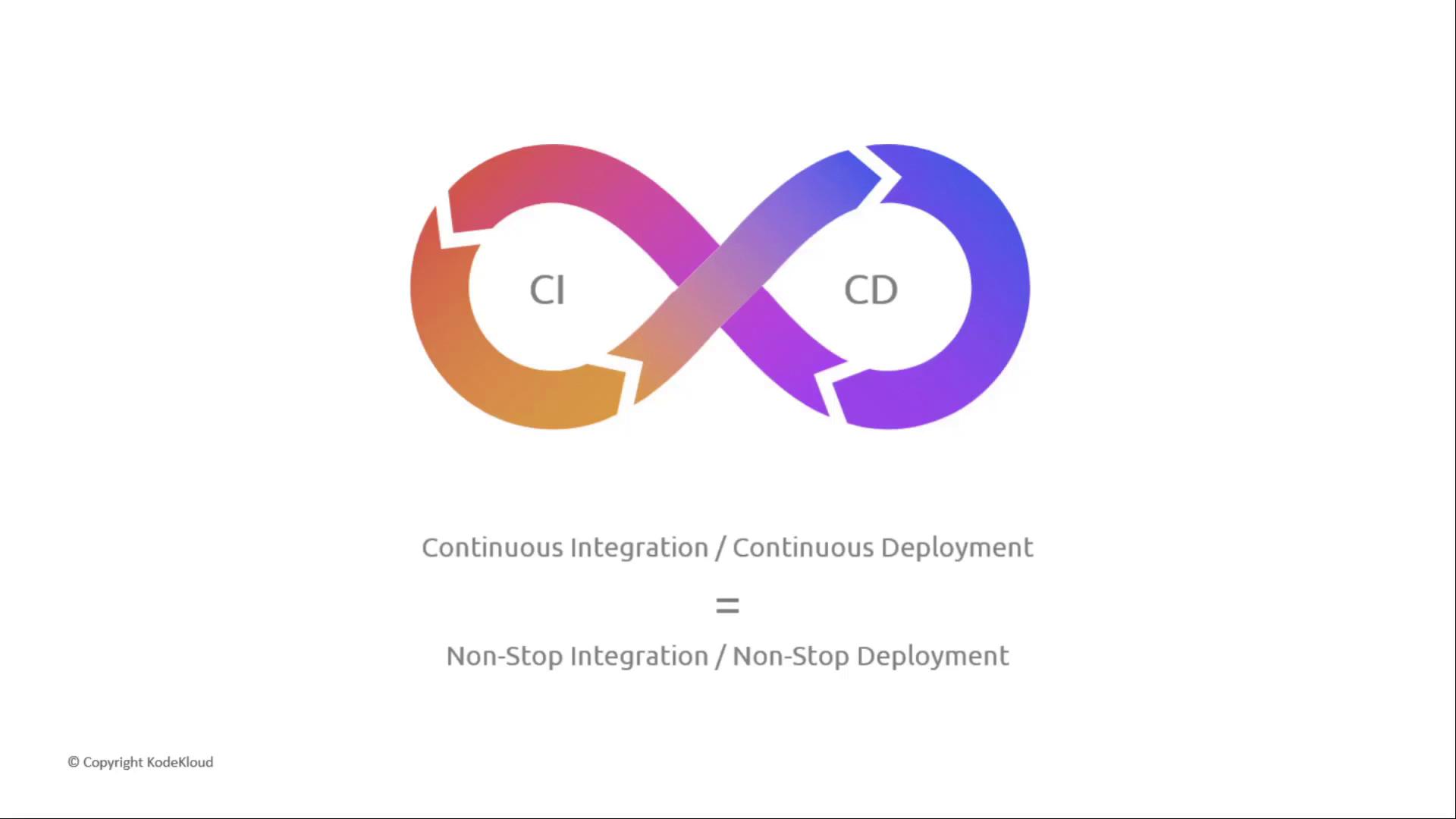
| Stage | Purpose | Example Tool |
|---|---|---|
| Source | Retrieve code artifacts from repos or buckets. | AWS CodeCommit, GitHub, S3 |
| Build | Compile, package, or transpile source code. | AWS CodeBuild, Jenkins |
| Test | Execute automated tests (unit, integration). | AWS CodeBuild, custom scripts |
| Deploy | Release to environments: containers, VMs, Lambda. | ECS, EKS, EC2, AWS Lambda |
Benefits of AWS CodePipeline
- Automation: Reduce manual steps and human errors.
- Scalability: Automatically scale pipelines and build resources.
- Visibility: Monitor execution history, logs, and notifications per stage.
- Customization: Integrate third-party tools, add manual approvals, or run custom scripts.
Be mindful of resource usage and execution costs. Review AWS Pricing before enabling long-running pipelines.