- Traffic flow into Kubernetes clusters
- Advanced features of the Gateway API
- How VPC Lattice extends service networking across VPCs, accounts, and regions
Kubernetes Gateway API Overview
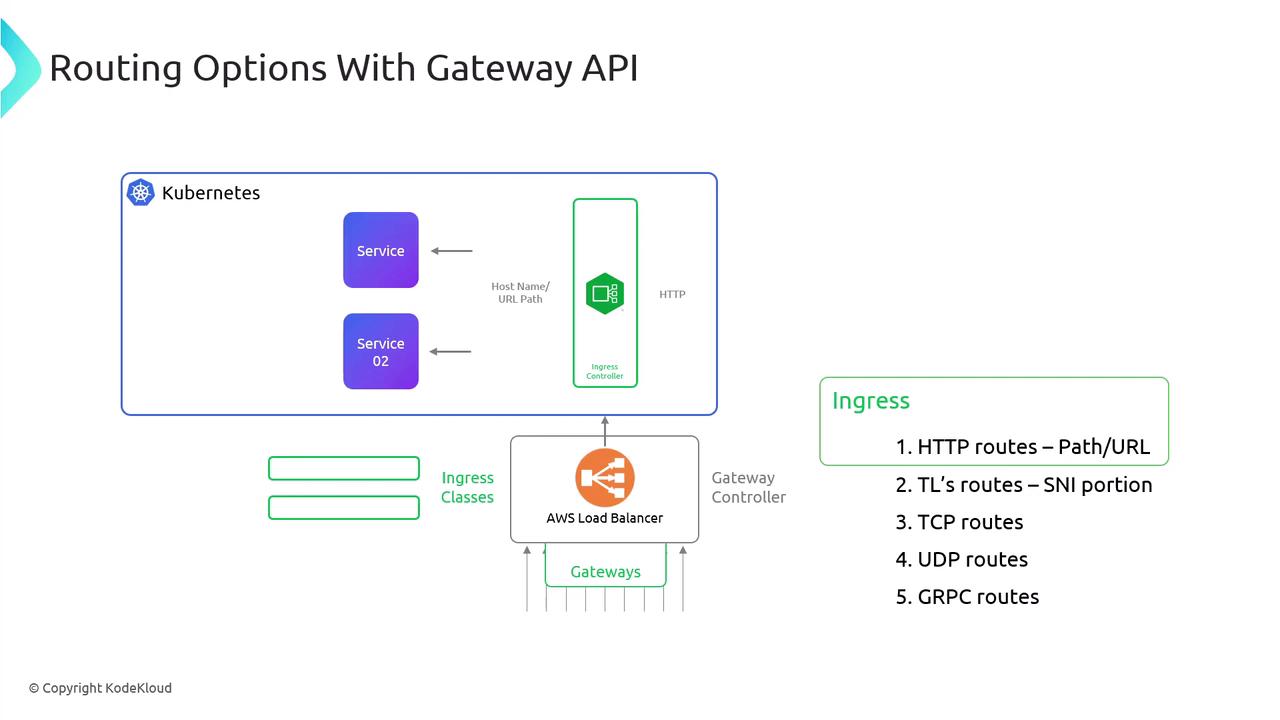
Ingress controllers route Layer 7 traffic based on hosts or URL paths. The Gateway API extends this by supporting multiple protocols (HTTP, TCP, UDP, gRPC, TLS) and offering more granular control.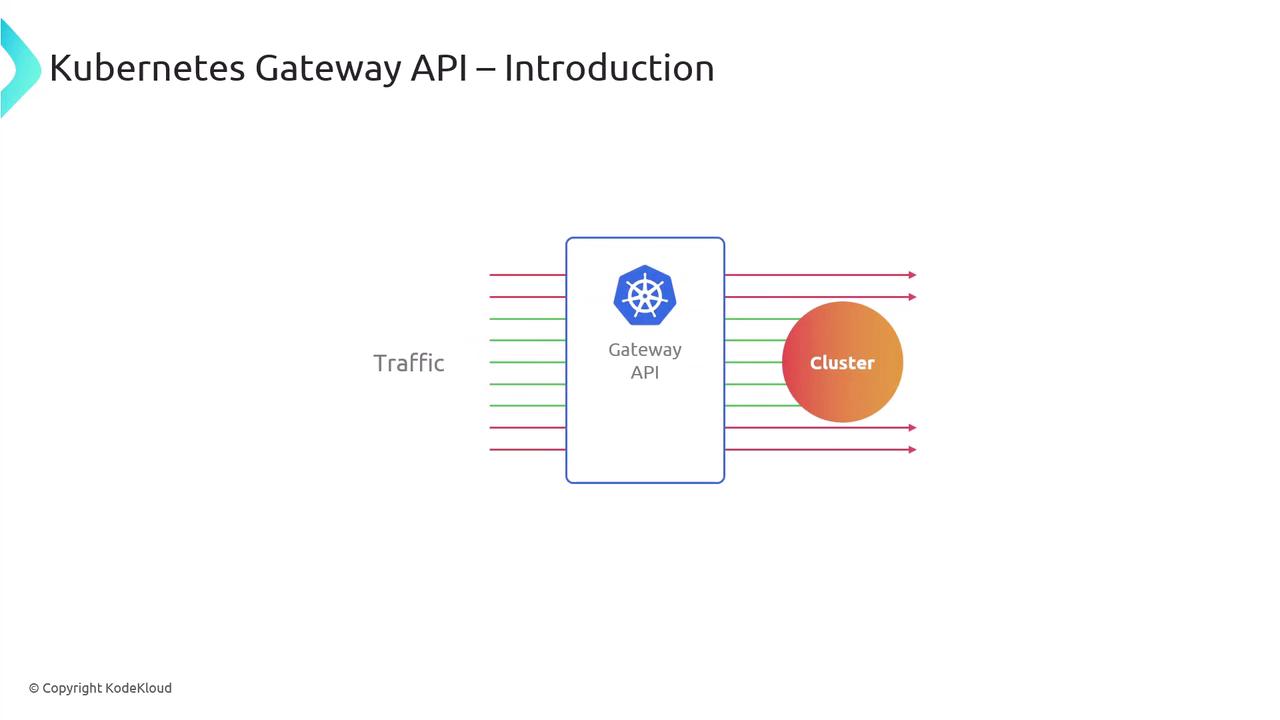
Traditional Ingress vs. Gateway API
With a traditional Ingress setup, you deploy an Ingress Controller behind an external Load Balancer. The controller inspects HTTP requests and forwards them to Services by host or path.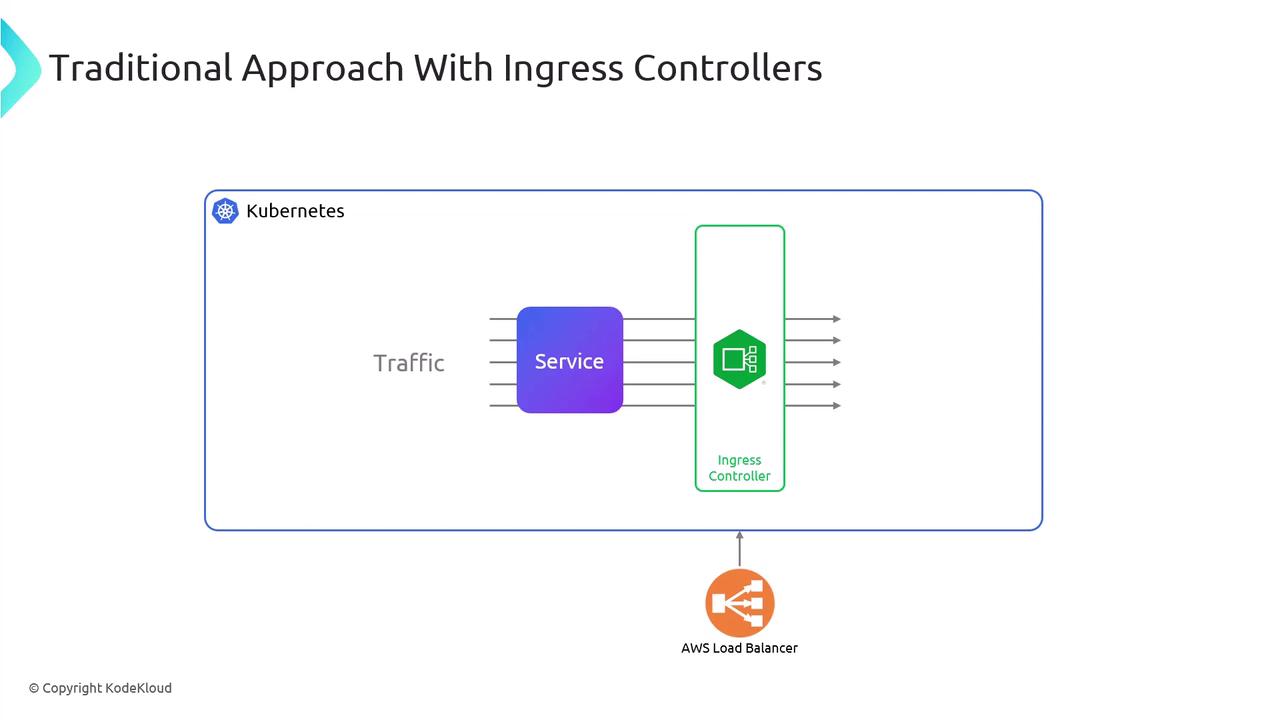
| Resource | Purpose | Example Use Case |
|---|---|---|
| GatewayClass | Selects the controller implementation (e.g., Lattice, Istio) | gateway.networking.k8s.io/v1beta1 |
| Gateway | Binds external listeners (ports/protocols) to Routes | Expose HTTP on port 80 |
| Route Types | Split by protocol: HTTPRoute, TLSRoute, TCPRoute, UDPRoute, GRPCRoute | Fine-grained traffic matching rules |
AWS VPC Lattice Service Networks
AWS VPC Lattice offers a service-mesh–style abstraction for your VPCs without the complexity of peering or Transit Gateways. Central to this model is the Service Network, which uses AWS Cloud Map to register endpoints and perform service discovery.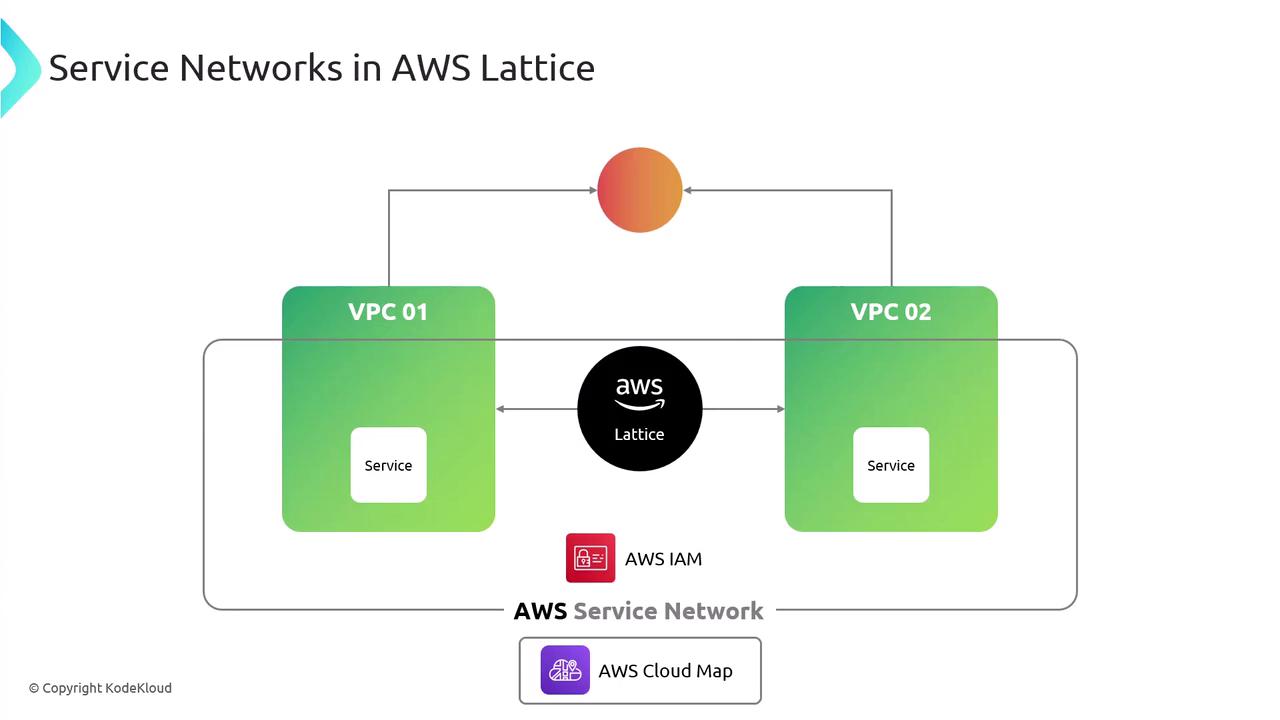
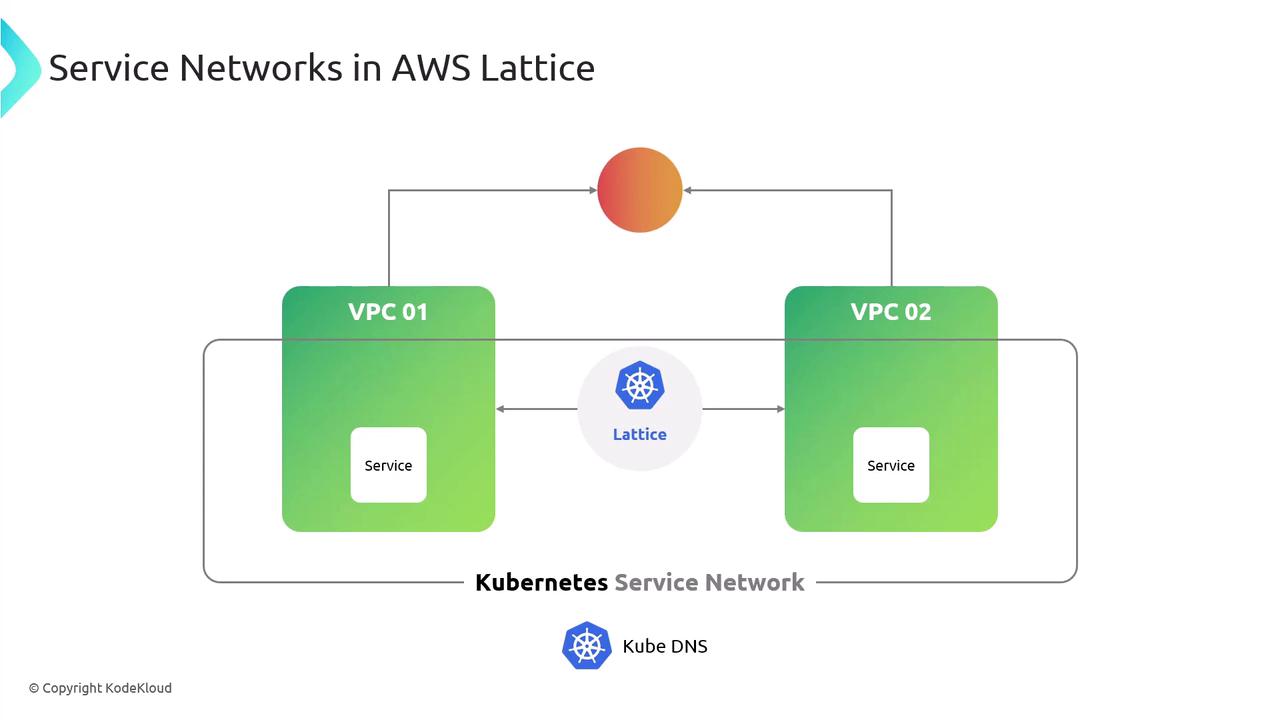
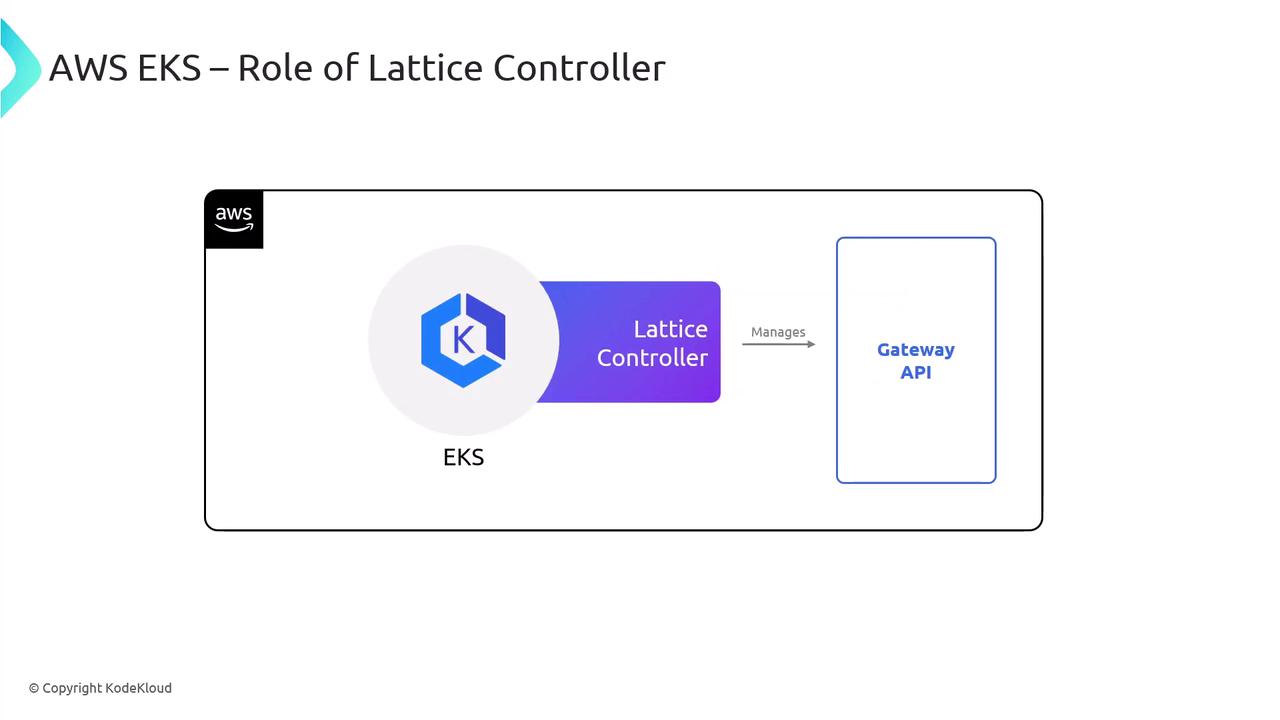
Integrating Kubernetes with VPC Lattice
Here’s how traffic flows when a pod communicates across the Service Network:- Pod sends a request to a Service Network DNS name.
- The Lattice Gateway Controller creates and updates service endpoints in Cloud Map.
- The request traverses the Service Network to reach the target endpoint (pod, EC2, or Lambda).
- A gateway at the target side injects traffic into its local CNI or compute runtime.
AWS Lattice supports hybrid environments—traffic can route to other EKS clusters, EC2 instances, AWS Lambda, or external services registered in Cloud Map.
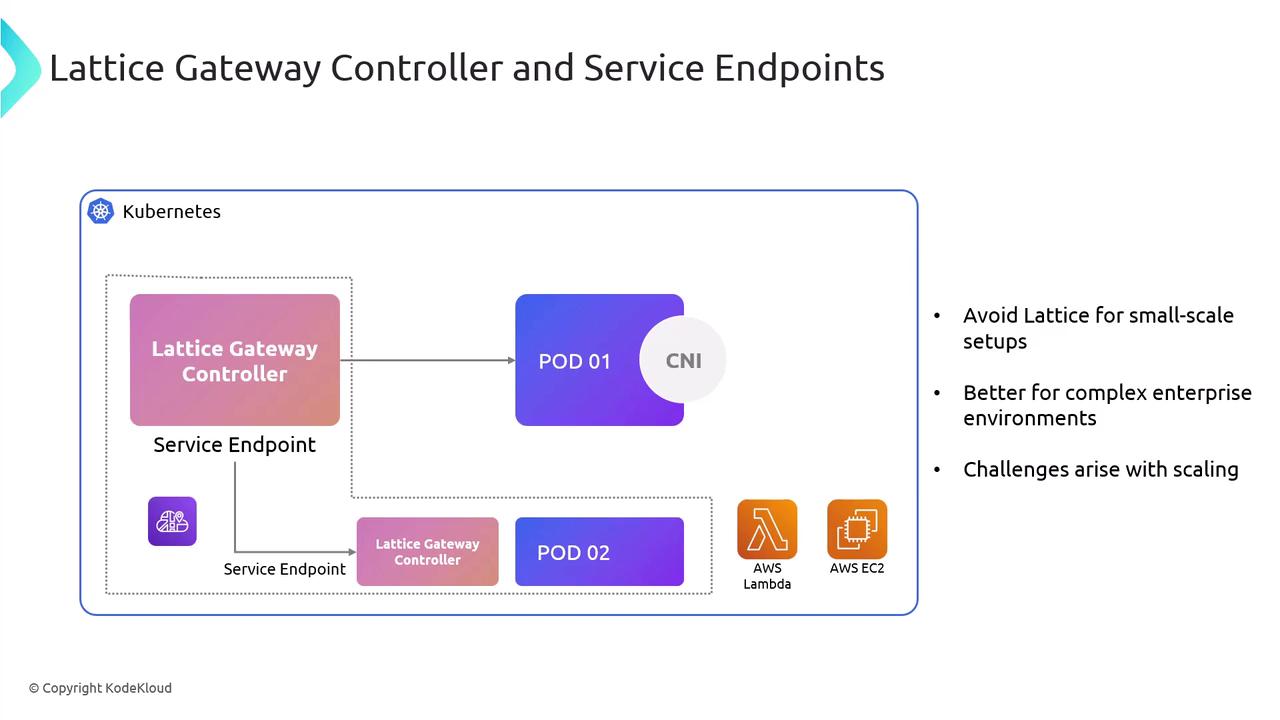
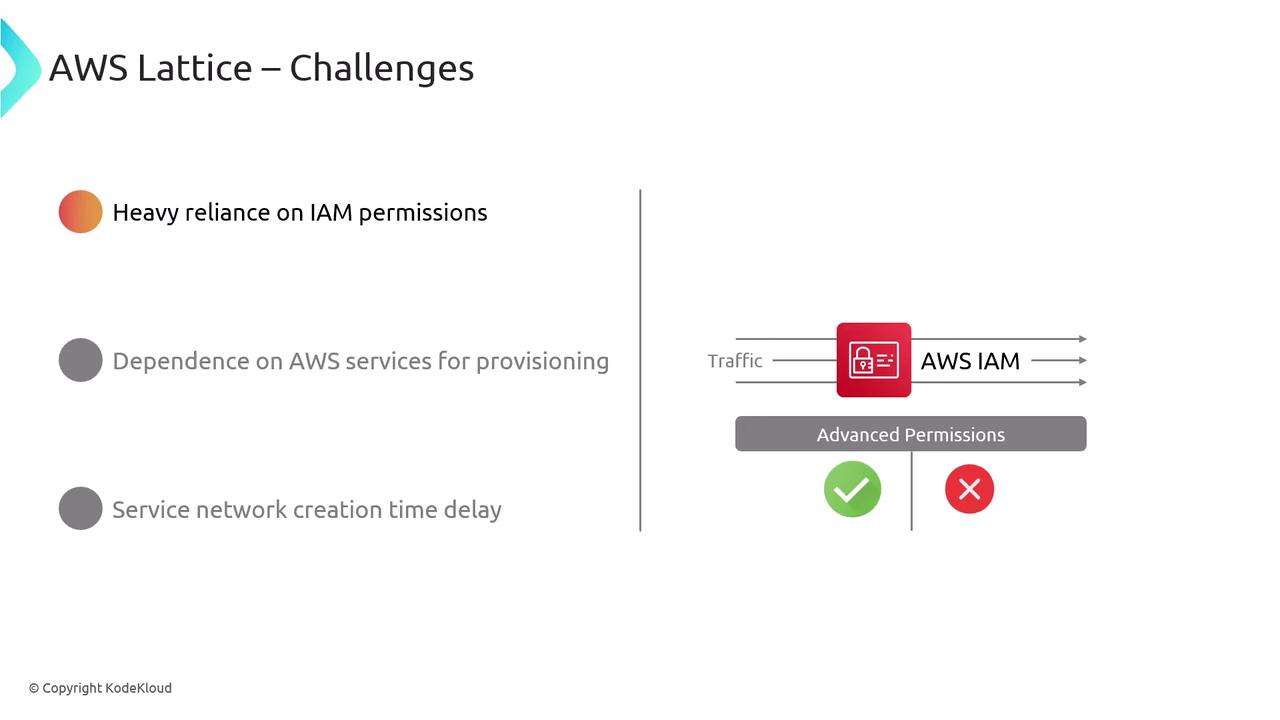
Considerations and Challenges
While VPC Lattice streamlines cross-VPC communication, there are trade-offs:| Challenge | Impact |
|---|---|
| IAM Dependency | Every service call relies on IAM policies—complex rules for pods/services |
| Provisioning Latency | Service Network and Cloud Map updates can take 5–10 minutes to complete |
Frequent Gateway API or Service Network changes may incur delays. Plan your deployment workflows to batch updates when possible.