AWS - IAM
Configure AWS IAM at Scale
CloudTrail
CloudTrail provides a comprehensive audit trail of all API calls in your AWS account. In this guide, you’ll learn how to trace which IAM user issued the StopInstances command to shut down an EC2 instance.
Table of Contents
- Use Case: Investigating EC2 Shutdown
- How CloudTrail Works
- Key Features
- Demo: Finding the StopInstances Event
- Best Practices
- References
Use Case: Investigating EC2 Shutdown
When an unexpected EC2 instance stops, you need to know who performed that action. CloudTrail captures every API call, making it straightforward to identify the culprit.
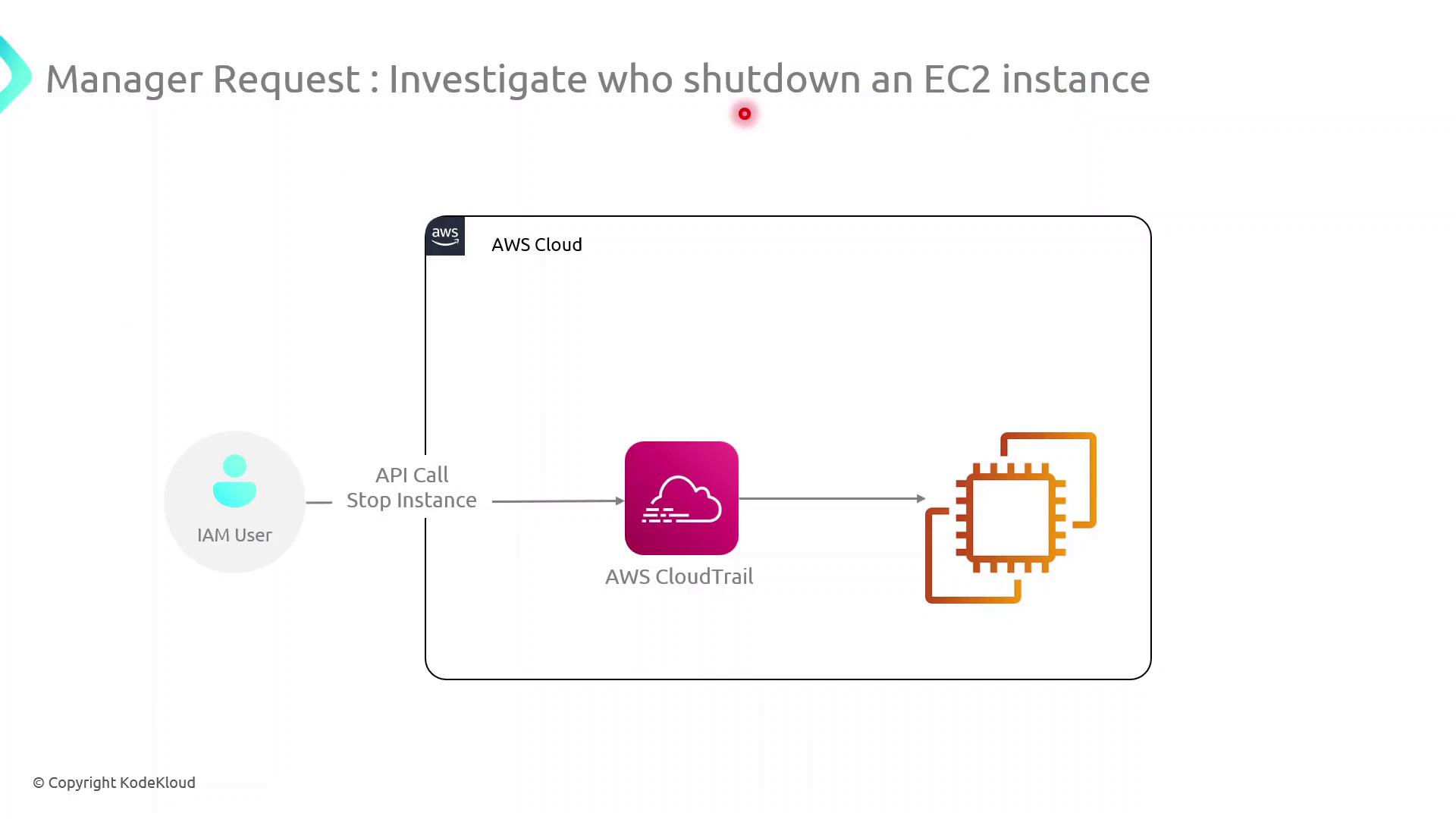
How CloudTrail Works
- An IAM user or role issues an API request (e.g.,
StopInstances). - CloudTrail records the request details: caller identity, API action, resource ARNs, and timestamp.
- Logs are delivered to an S3 bucket (or optionally to CloudWatch Logs) for storage and analysis.
Note
Make sure you have at least one active trail in the region where your EC2 instances run.
Configure multi-region logging for global coverage.
Key Features
| Feature | Description |
|---|---|
| Audit Trail | Complete history of all API calls for compliance and forensic use |
| Visibility & Security | Detect unusual behavior by monitoring account activity |
| Centralized Log Storage | Store logs in Amazon S3 for long-term retention |
| Real-time Monitoring | Integrate with CloudWatch Logs to trigger alerts instantly |
Demo: Finding the StopInstances Event
Follow these steps in the AWS Management Console or use the AWS CLI to locate the StopInstances event.
AWS Management Console
- Open the CloudTrail service.
- Click Event history.
- In the filter bar, select Event name and enter
StopInstances. - Review each entry’s:
- Event time
- Username (IAM user or role)
- Resources (affected EC2 instance ARNs)
AWS CLI
aws cloudtrail lookup-events \
--lookup-attributes AttributeKey=EventName,AttributeValue=StopInstances \
--max-results 10
This returns a JSON list of matching events. Inspect the Username, EventTime, and Resources fields to pinpoint who stopped the instance.
Warning
If your trail isn’t configured to deliver logs to CloudWatch Logs, you won’t get real-time alerts.
Enable CloudWatch integration in the trail settings to receive immediate notifications.
Best Practices
- Enable multi-region trails to capture global AWS API activity.
- Encrypt log files with SSE-KMS for data protection.
- Implement log file validation to ensure integrity.
- Configure lifecycle policies in S3 to archive or delete old logs.
References
- AWS CloudTrail User Guide
- AWS CloudTrail API Reference
- Monitoring CloudTrail with CloudWatch
- Managing S3 Lifecycle Policies
Watch Video
Watch video content