Understanding Cold Starts
AWS Lambda scales automatically by initializing new function instances on demand. The first invocation of each new instance—including scale-out events—can take hundreds of milliseconds. Traditional servers, in contrast, run continuously and respond immediately.How Provisioned Concurrency Works
With Provisioned Concurrency, AWS keeps a specified number of “warm” instances ready to serve requests. When your function is invoked, these pre-initialized environments handle the traffic in double-digit milliseconds.Steps to Configure Provisioned Concurrency
- Select your function
In the Lambda console, pick the function you want to optimize (e.g., KodeKloudSQSdemo).
- Publish a new version
Under Versions, choose Publish new version from$LATEST.
Once published, a version’s code and settings are immutable. Use versions to guarantee consistency.
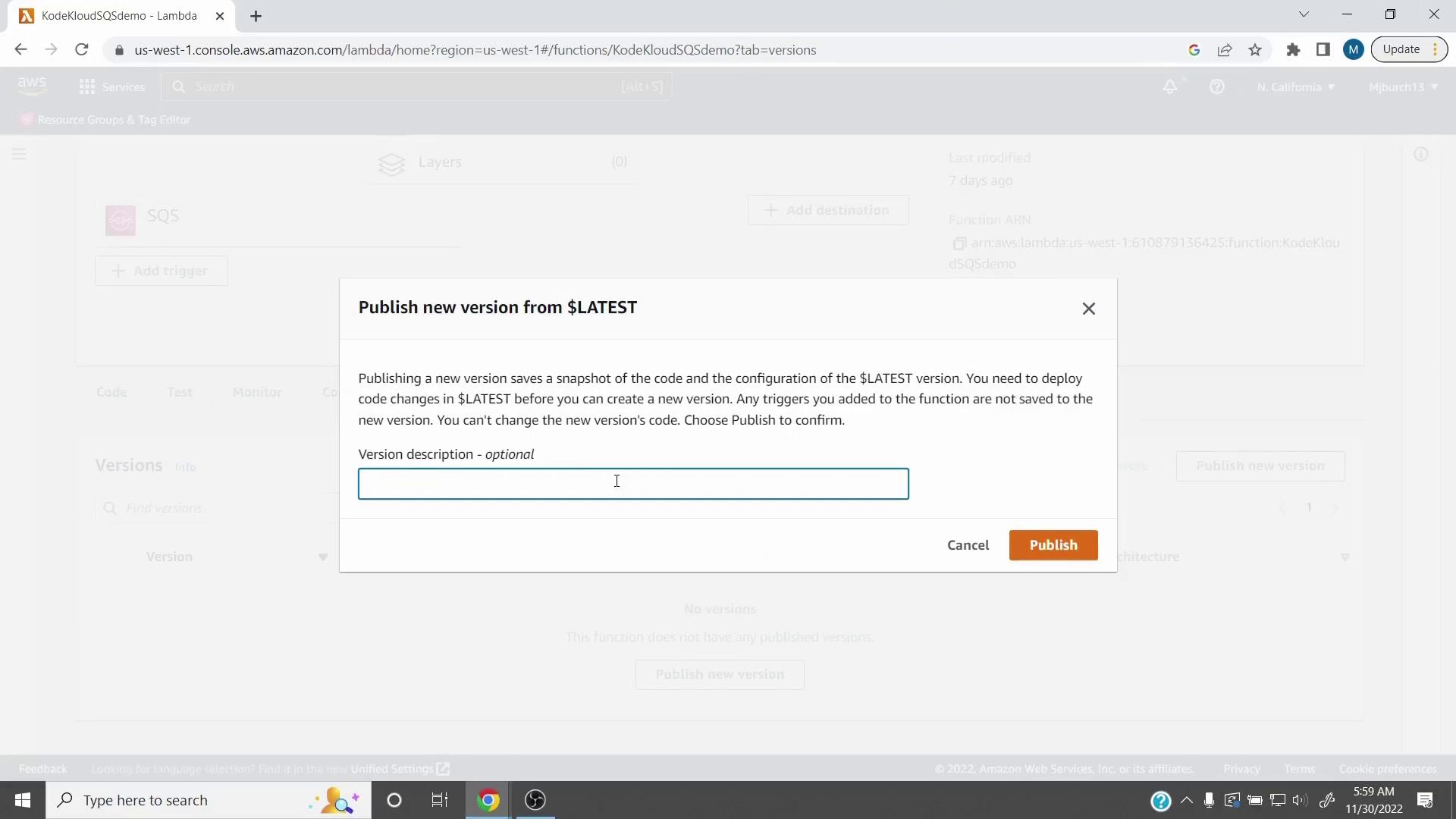
- Check your new version
After publishing (for example, Version 5), review its details and verify you can configure concurrency on that version.
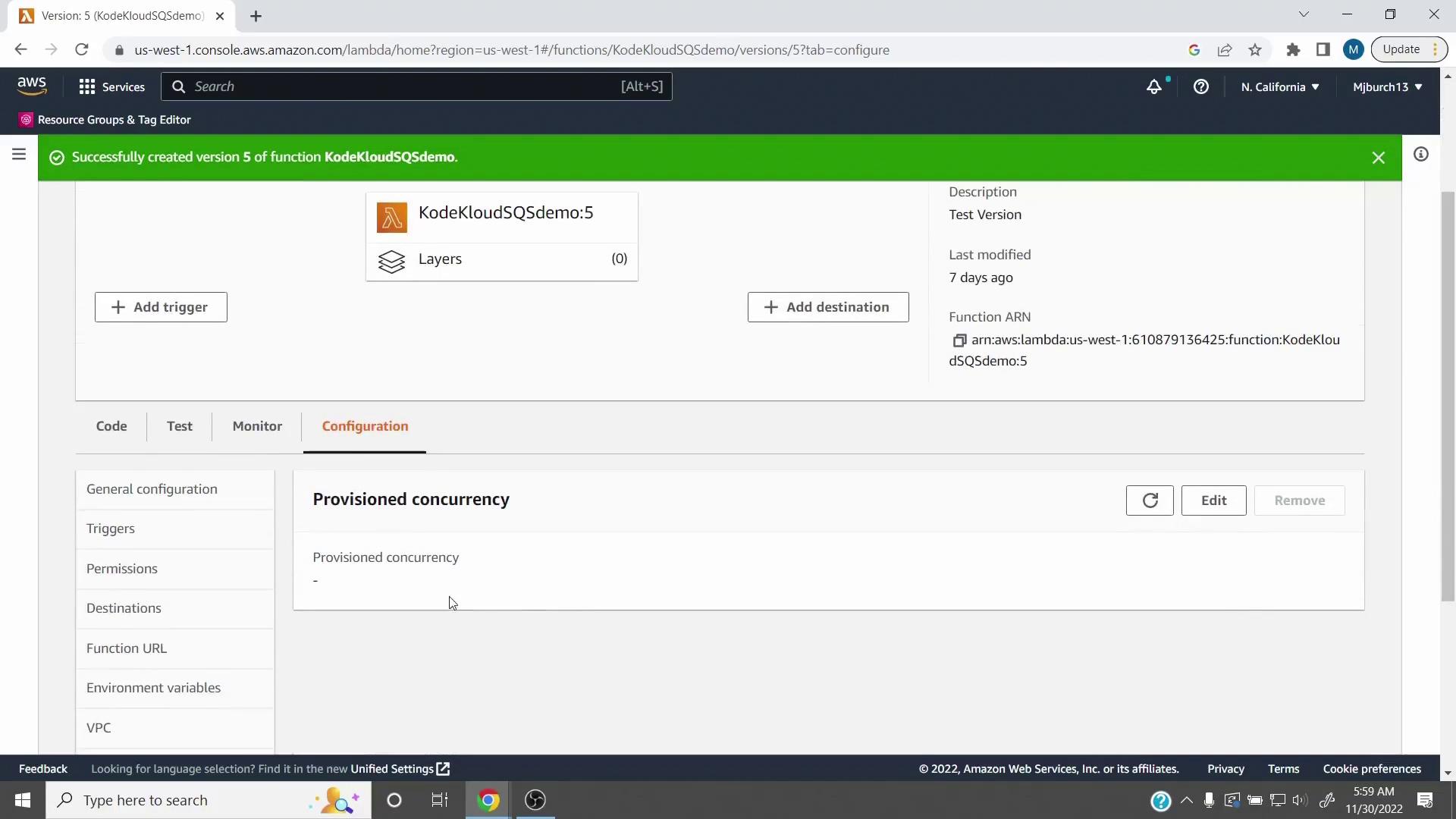
- Create an alias
Go to Aliases, click Create alias, name it (for example, TestAlias), and point it at your new version (5).
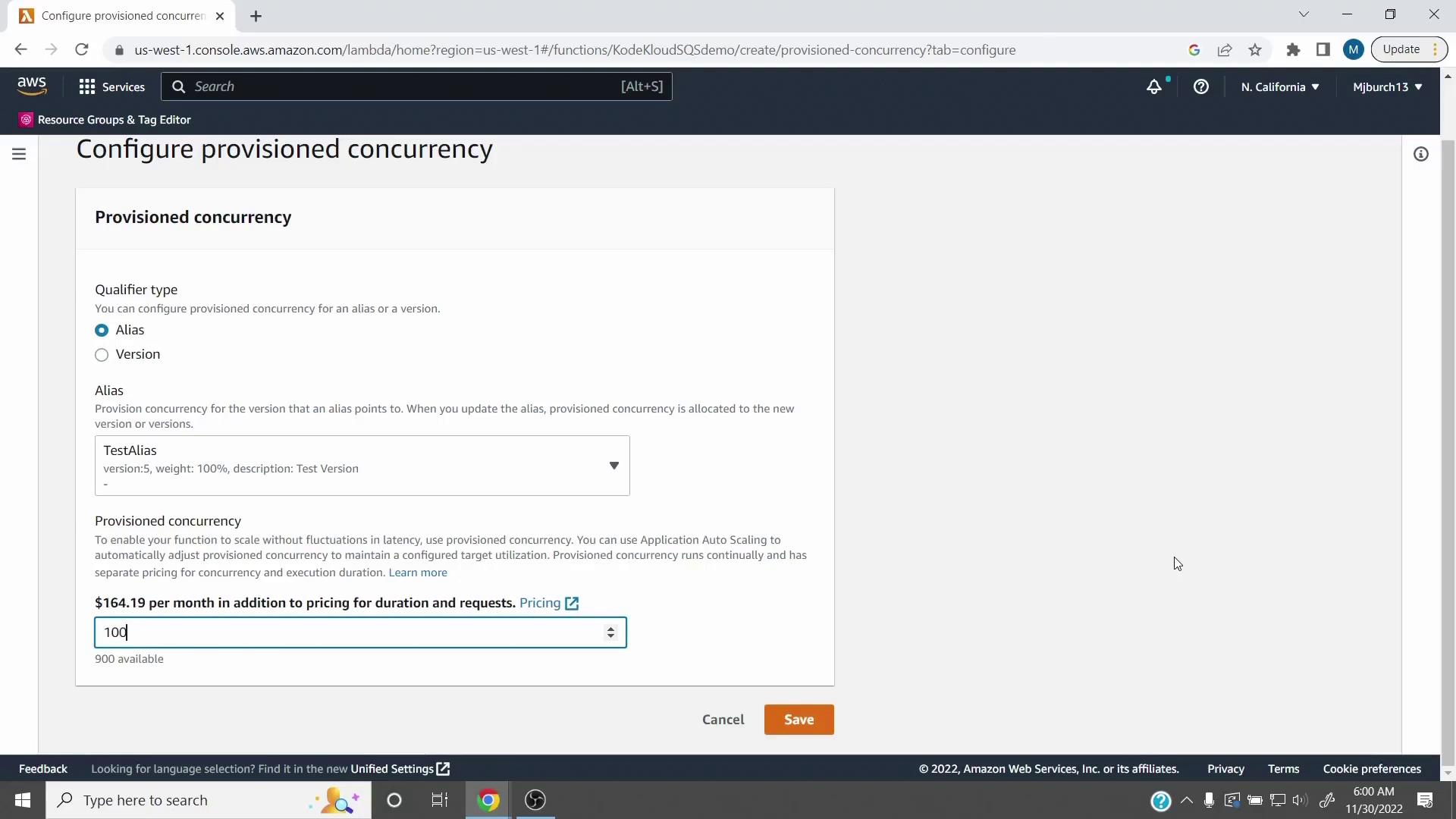
- Enable Provisioned Concurrency
Open Configuration > Concurrency, select Provisioned Concurrency, choose your alias (e.g., TestAlias), and enter the number of pre-warmed instances.
Cost Considerations
Provisioned Concurrency charges apply for every allocated instance, whether it’s handling requests or idle.You incur hourly rates for each provisioned instance plus normal invocation costs. Monitor usage closely to optimize performance versus cost.
| Pricing Metric | Description | Example Rate |
|---|---|---|
| Provisioned Instance | Hourly price per pre-warmed Lambda instance | $0.00001667 per LCUs per hr |
| Invocation Charges | Standard Lambda invocation pricing | $0.20 per million requests |
| Memory Allocation | Billed based on allocated memory per instance | 128 MB, 256 MB, etc. |
Summary
- Cold starts introduce latency in serverless functions.
- Provisioned Concurrency keeps instances warm for consistent performance.
- Publish a version, create an alias, and set your desired concurrency level.
- Remember that provisioned instances incur continuous charges.