AWS Lambda
Advanced Topics
Reserved and Unreserved Concurrency
Managing concurrency in AWS Lambda ensures that high-priority functions always have the capacity they need. By default, your account’s unreserved concurrency sets a soft limit on total parallel executions. For mission-critical workloads, you can allocate reserved concurrency to specific functions.
What Is Concurrency?
Concurrency refers to how many Lambda function executions run in parallel. For example, 100 simultaneous invocations count as 100 concurrent executions.
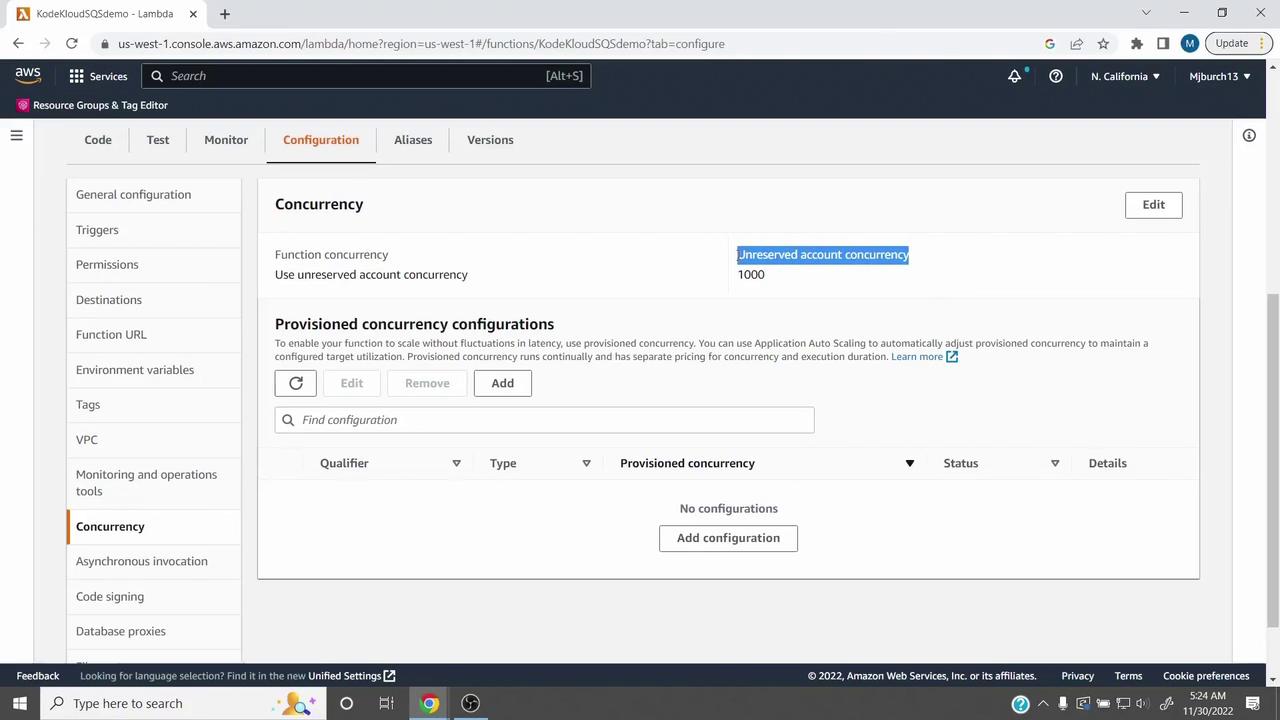
Viewing Concurrency Settings
To view or modify a function’s concurrency:
- Open the AWS Lambda console and select your function.
- Click Configuration.
- In the left navigation pane, choose Concurrency.
Note
We use an SQS cold start demo here. Substitute your own function for real-world testing.
Unreserved Concurrency
Unreserved (account) concurrency is the pool shared by all Lambda functions in an account. AWS sets a default soft limit of 1,000 concurrent executions per region.
- All functions combined cannot exceed this limit.
- To increase it, submit a support request.
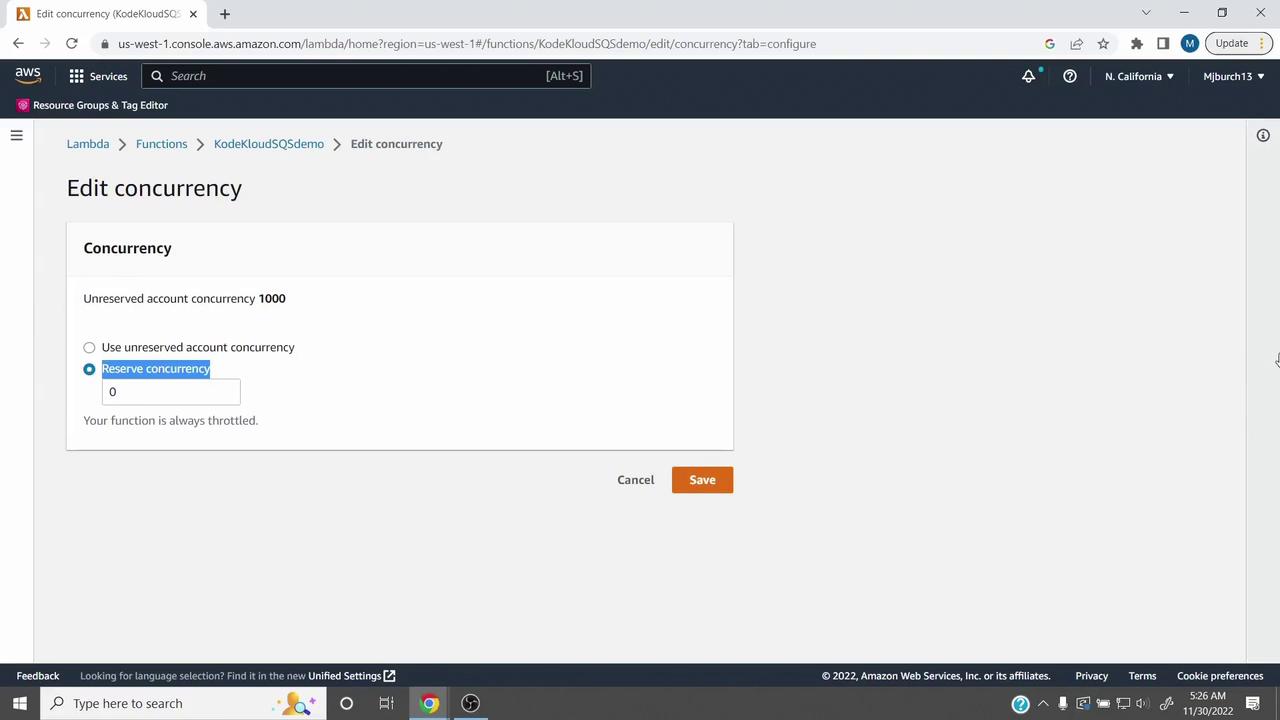
Reserving Concurrency for Critical Functions
Reserved concurrency guarantees a minimum number of concurrent executions for a specific function:
- In the Concurrency page, click Edit.
- Select Reserve concurrency.
- Enter the reservation amount (e.g.,
300). - Click Save.
Warning
If your function exceeds its reserved concurrency, additional invocations are throttled with 429 errors.
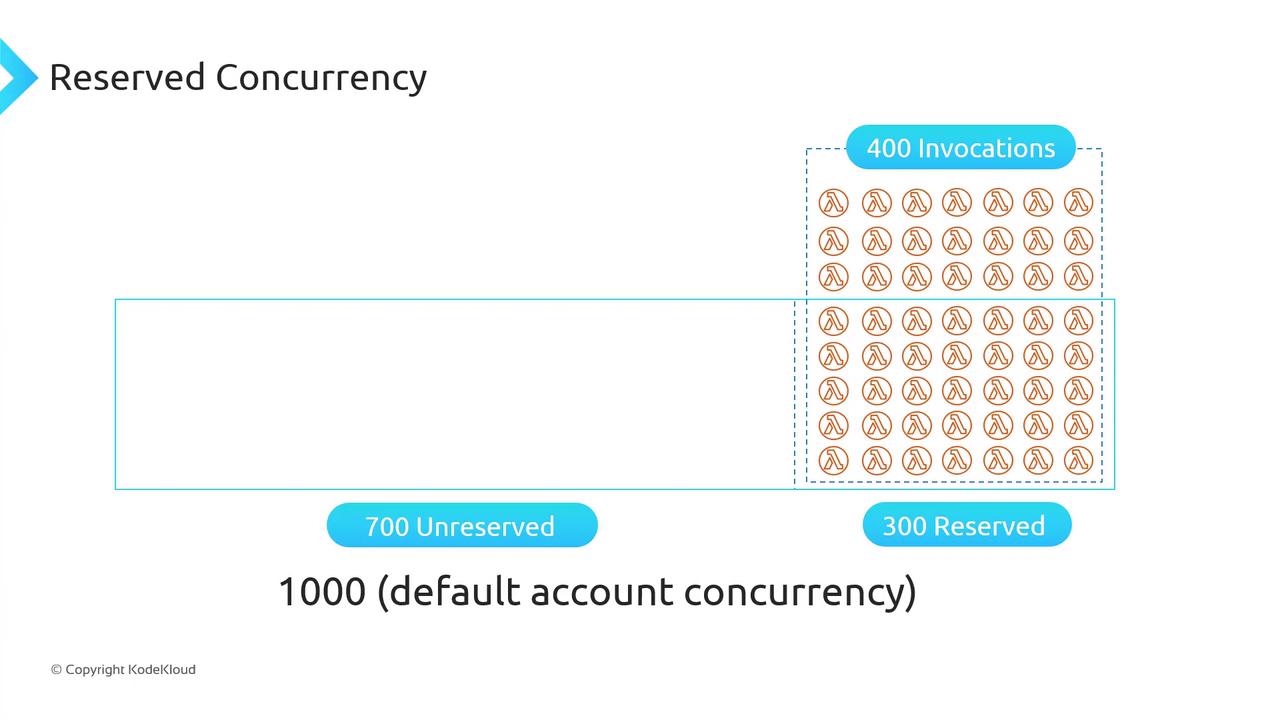
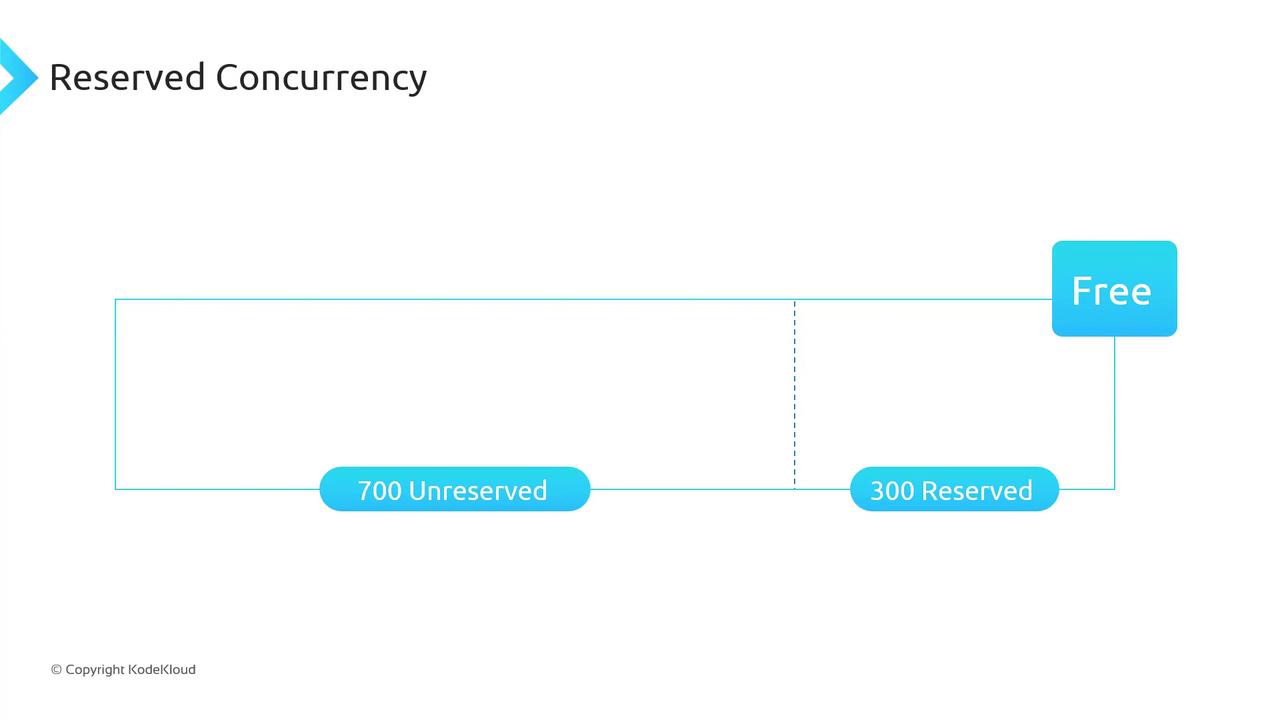
Reserving 300 concurrency reduces the unreserved pool from 1,000 to 700:
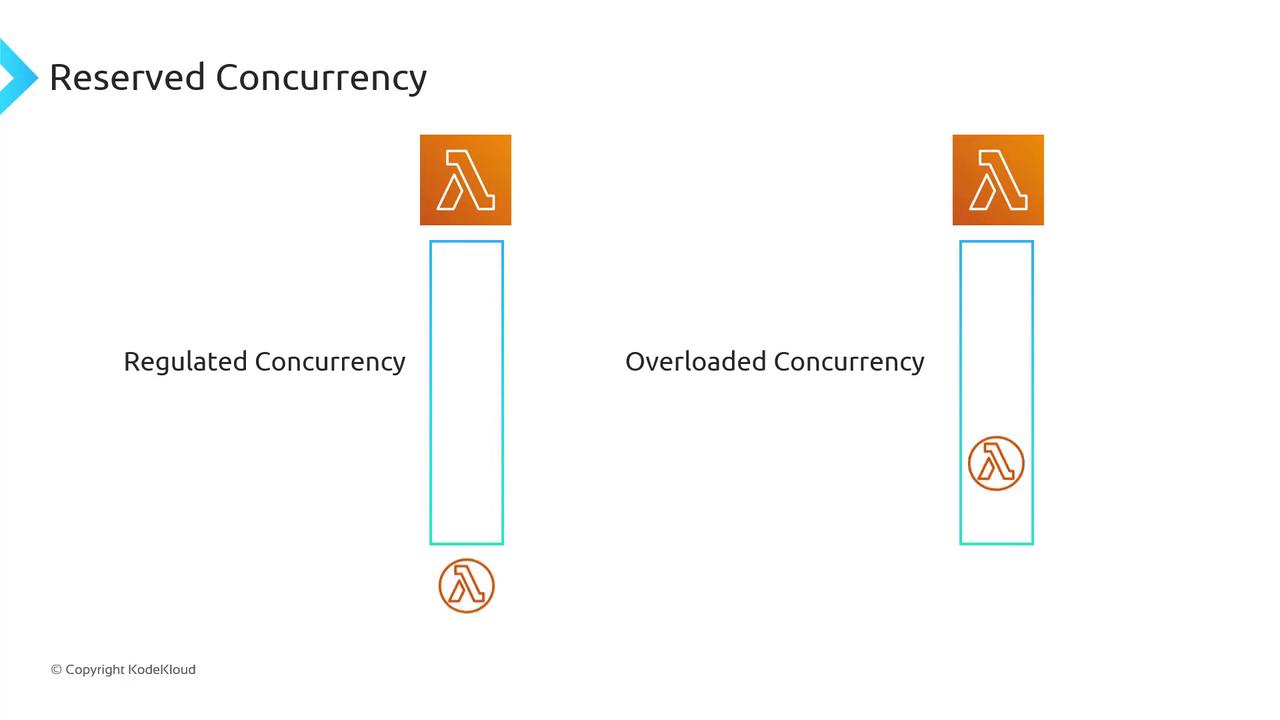
Use reserved concurrency to prevent downstream overload:
Note
There is no additional cost for reserved concurrency.
Unreserved Concurrency Limits
Your total unreserved concurrency is a per-account limit. In some regions, bursts up to 3,000 concurrent executions may occur temporarily, but sustained usage above the default requires a support request.

Reserved vs Unreserved Concurrency Comparison
| Concurrency Type | Definition | Default Limit | Ideal Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Unreserved (Account) | Shared pool for all Lambda executions | 1,000 | General workloads |
| Reserved (Function) | Dedicated capacity for a single high-priority job | N/A | Traffic-sensitive or rate-limited APIs |
Summary
- Unreserved concurrency sets the total pool for all functions.
- Reserved concurrency guarantees capacity for critical functions and avoids downstream throttling.
- No extra charge applies to reserved concurrency.
For advanced performance optimization and cold-start reduction, consider combining reserved concurrency with provisioned concurrency.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content