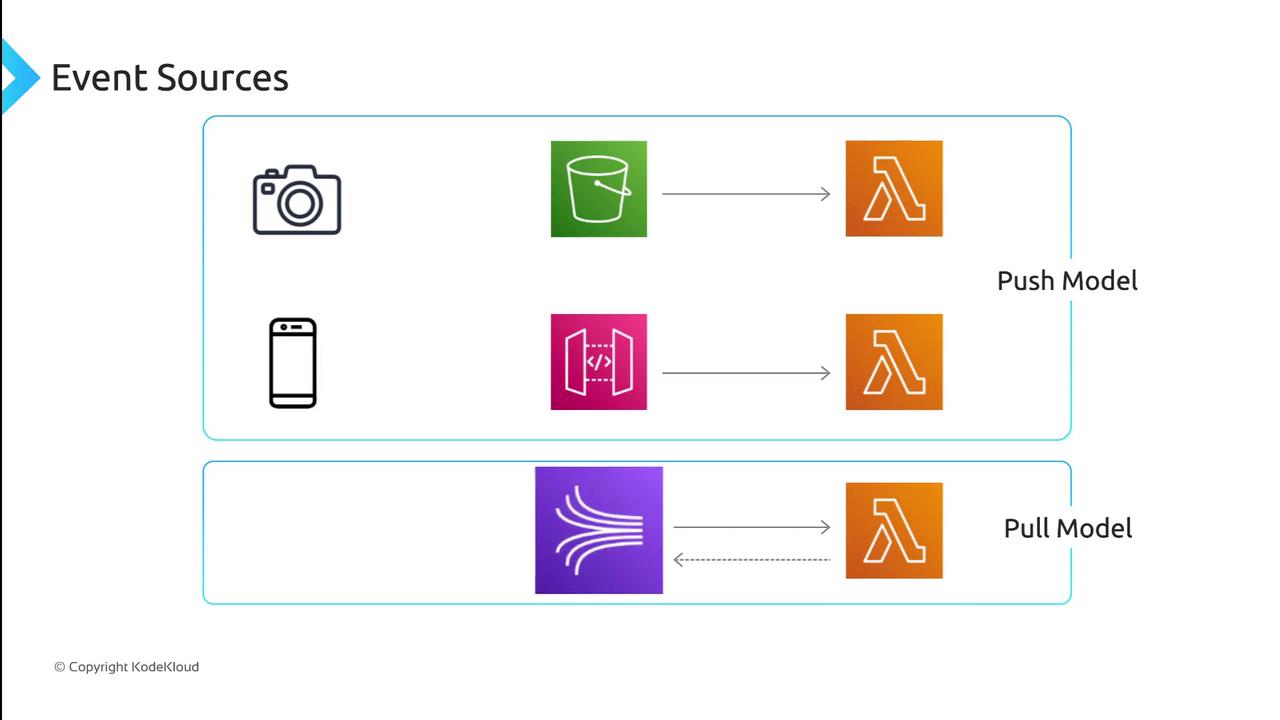
Invocation Models
AWS Lambda supports two primary invocation models:- Push model: An AWS service invokes your function directly when an event occurs.
- Pull model: Lambda polls streams or queues and triggers your function when new records or messages arrive.
Push Model
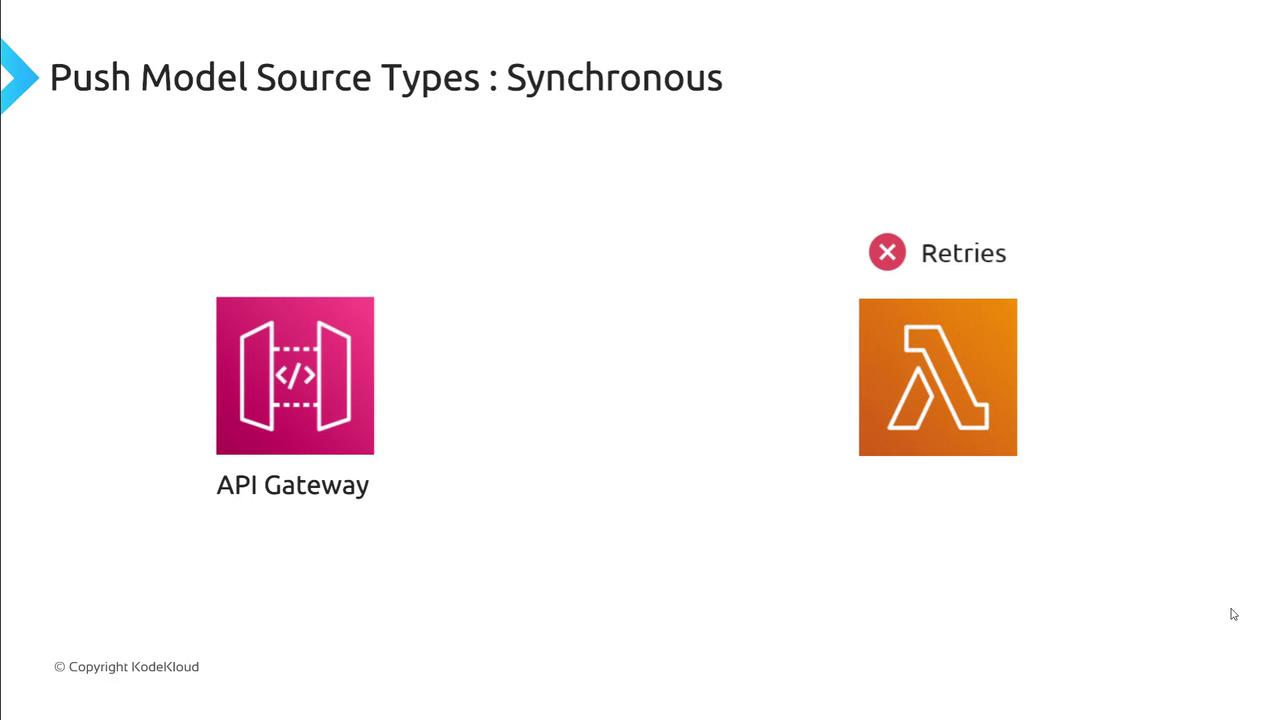
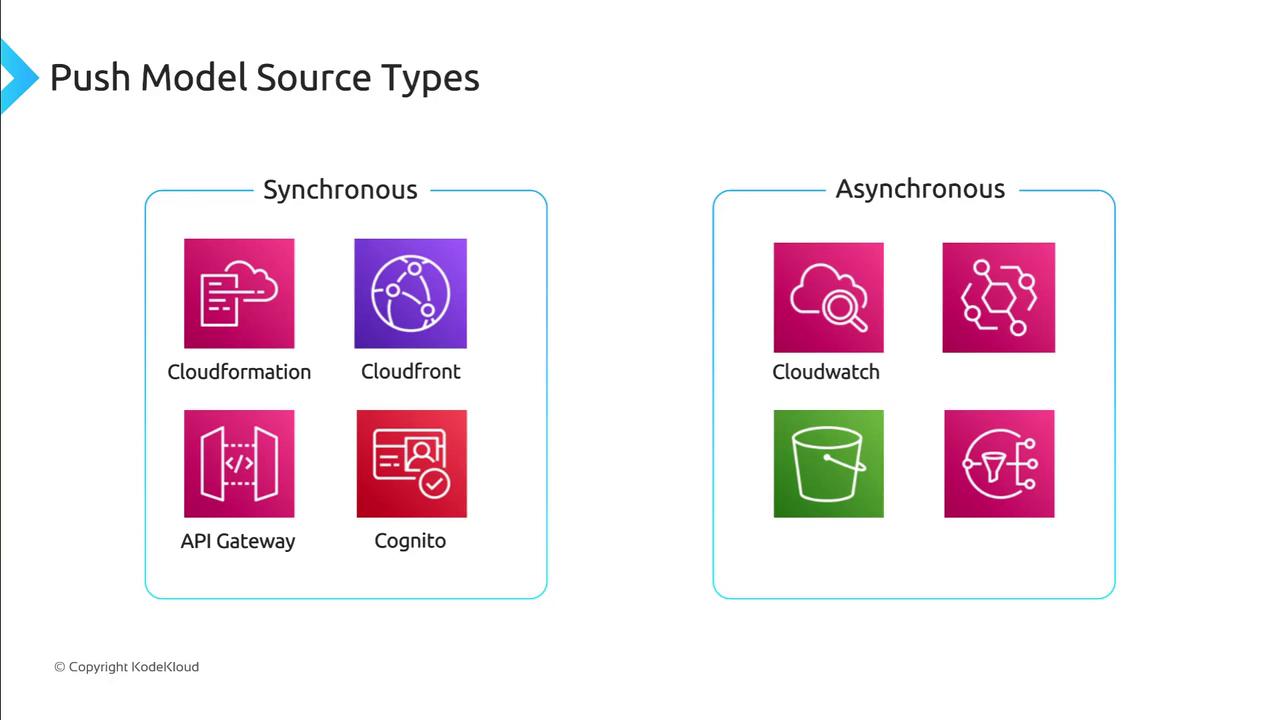
In the push model, event sources call Lambda directly. Push invocations are categorized as synchronous or asynchronous:Synchronous Invocations
- The caller waits for Lambda to finish and returns the function’s response.
- Typical sources: API Gateway, Amazon CloudFront, Amazon Cognito.
- Failures are returned immediately; no automatic retries.
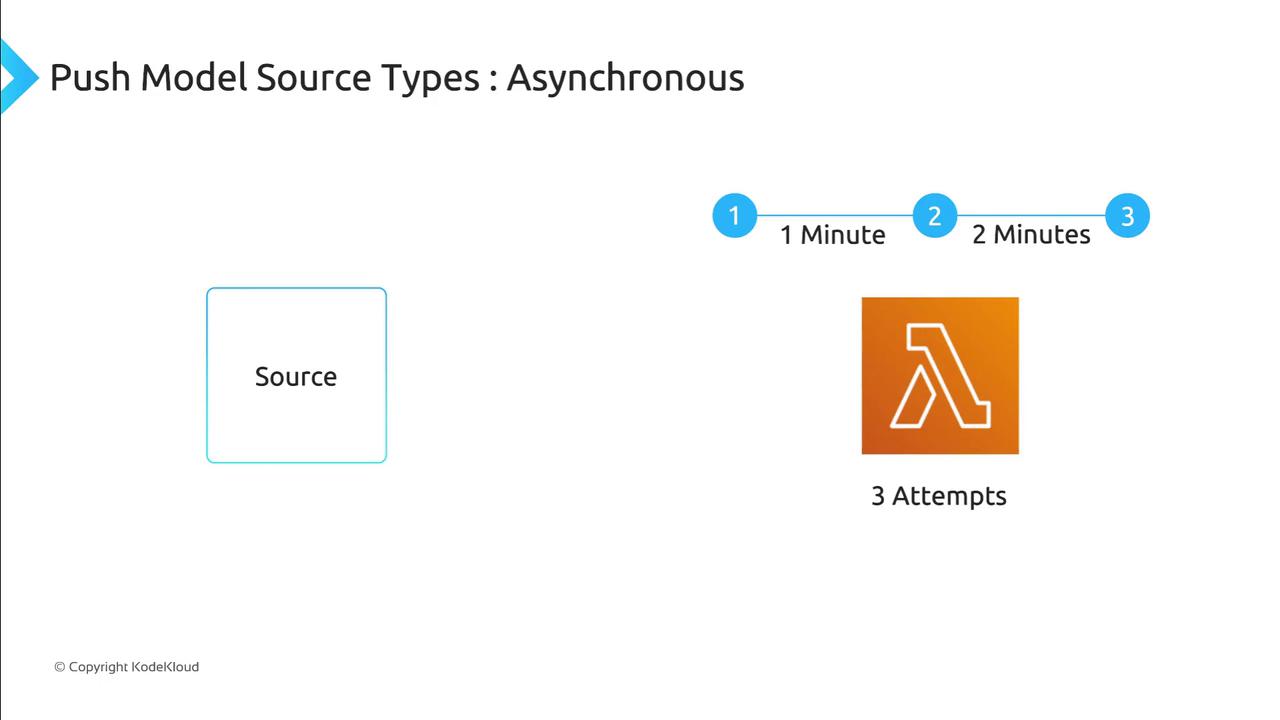
Asynchronous Invocations
- The service acknowledges receipt immediately, while Lambda processes the event in the background.
- Automatic retry policy:
- First retry after 1 minute
- Second retry after 2 minutes
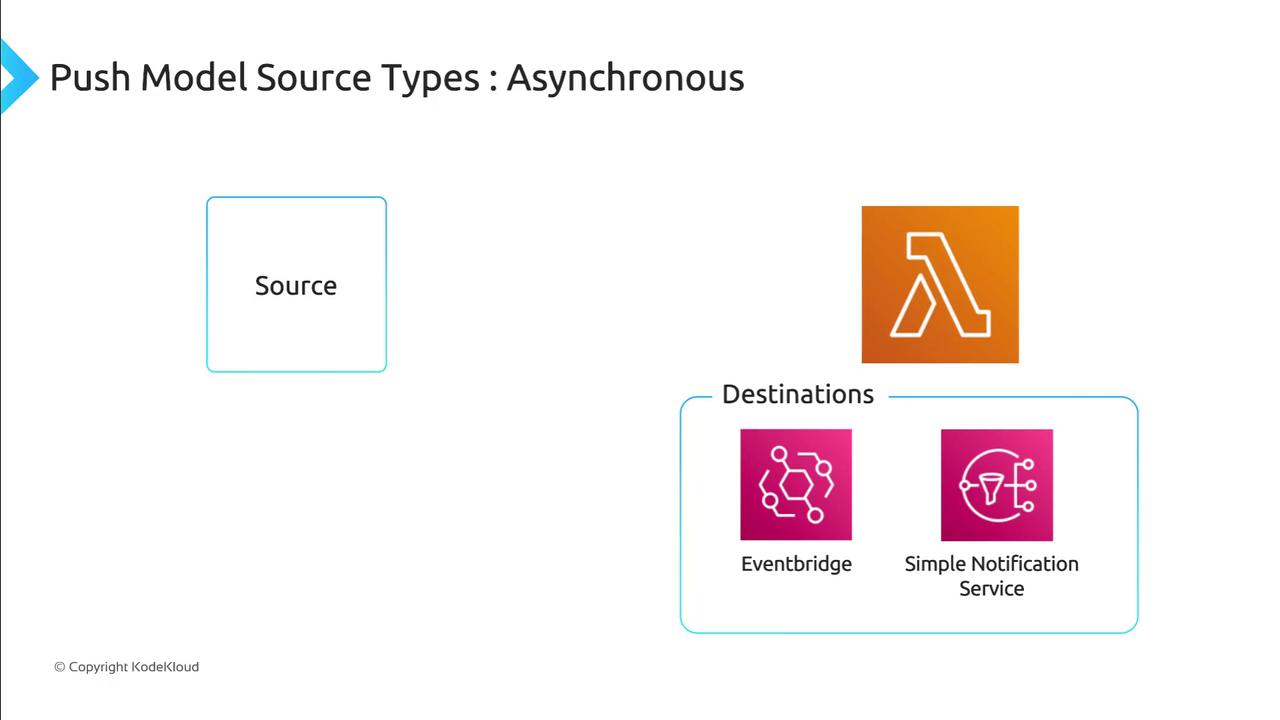
- Failed events can be routed to a dead-letter queue (DLQ) or destinations (e.g., EventBridge for failures, SNS for successes).
Configure a dead-letter queue or destinations to capture events after retry attempts are exhausted.
Push Model Sources Overview
| Invocation Type | Event Sources | Retry Behavior |
|---|---|---|
| Synchronous | API Gateway, CloudFront, Cognito | No retries |
| Asynchronous | S3, CloudWatch Events, SNS, EventBridge, IoT | 2 retries (1m, 2m) |
Pull Model
Lambda polls data sources for new records or messages, then invokes your function:- Streams (e.g., Amazon Kinesis Data Streams, DynamoDB Streams)
- Queues (e.g., Amazon SQS)
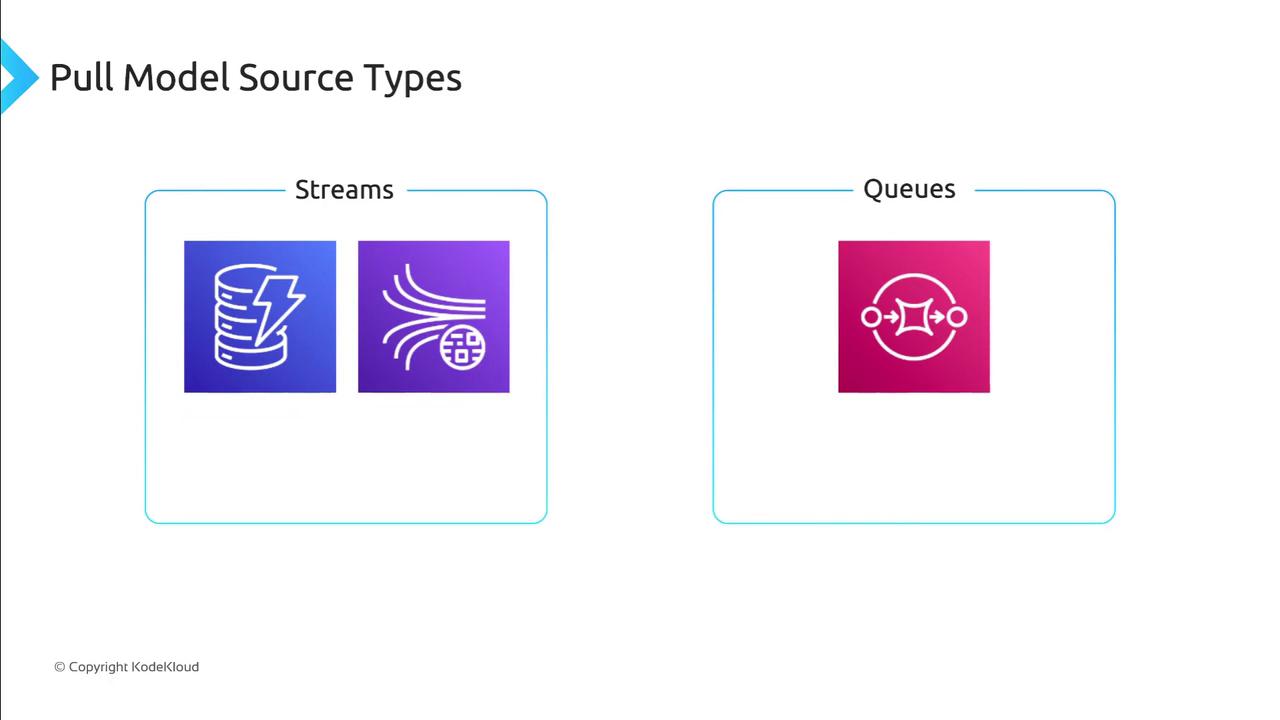
Streams
- Ideal for continuous data flows: application logs, metrics, real-time analytics.
- Lambda polls each shard in sequence and sends batches of records.
- On a processing failure, polling for that shard halts until the issue is resolved.
Queues
- Used for discrete messages that are processed individually or in batches.
- Lambda polls the queue at regular intervals and invokes your function with messages.

| Pull Model Type | AWS Service | Retry & DLQ Support |
|---|---|---|
| Streams | Kinesis Data Streams, DynamoDB | Stops on failure per shard |
| Queues | Amazon SQS | Retries until TTL; DLQ |
Ensure your function’s IAM role has permission to poll streams or read from queues and to write to DLQs if configured.
This covers how AWS Lambda handles events via push and pull models. Next, we’ll explore the IAM permissions and security best practices for Lambda event sources.