AWS Networking Fundamentals
Core Networking Services
Elastic IP Demo
In this lesson, we’ll demonstrate how to allocate, associate, and manage Elastic IPs in AWS. Elastic IPs provide a static, public IPv4 address that remains constant across instance stop/start cycles, ensuring reliable access to your EC2 workloads.
Why Use Elastic IPs?
By default, EC2 instances in a public subnet receive a dynamic public IP that changes whenever you stop and start the instance. This can disrupt services or remote connections.
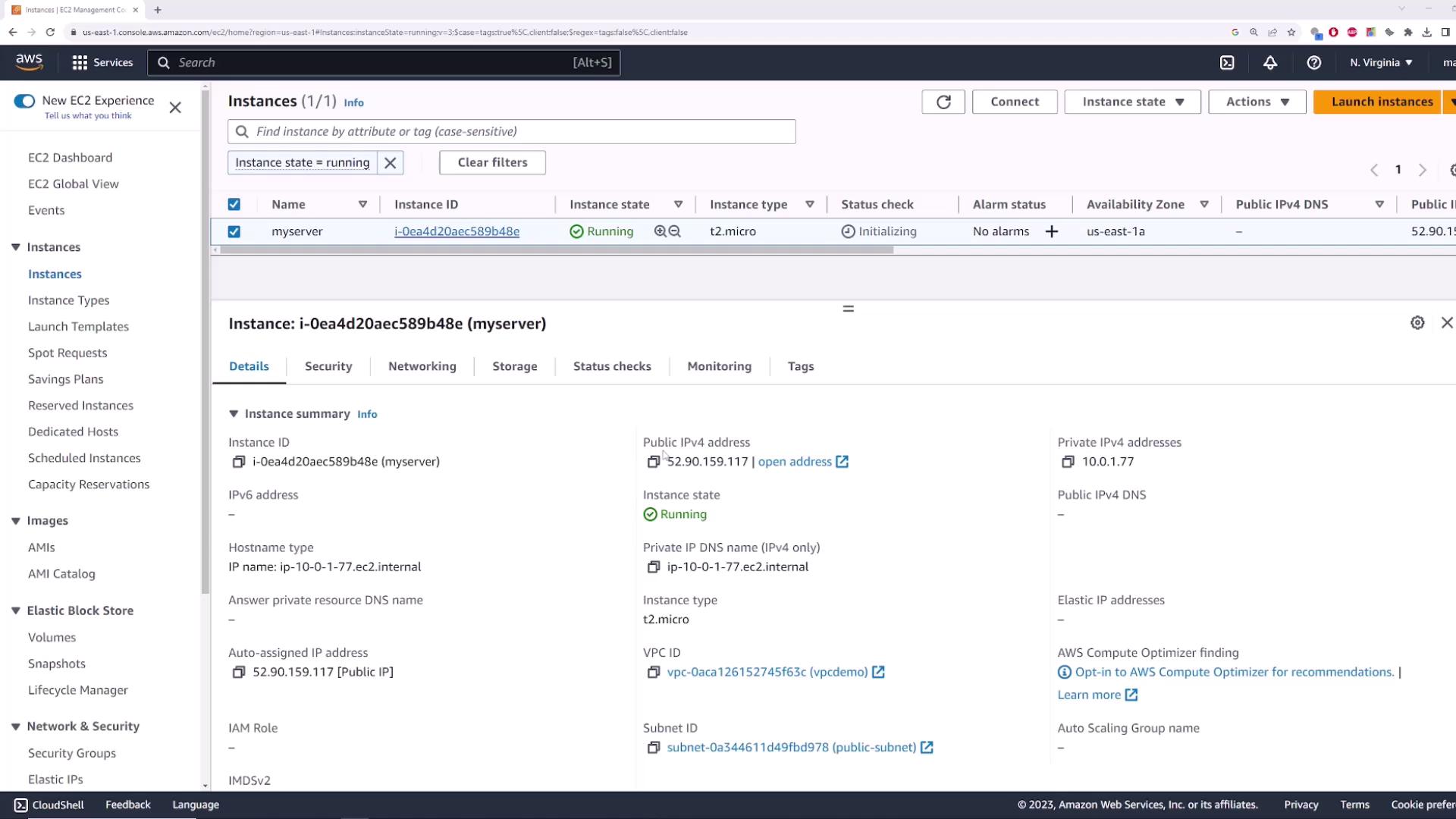
- Launch an EC2 instance named myserver in your VPC’s public subnet (with an Internet Gateway attached).
- Note its current public IP (e.g.,
52.90.159.117). - Stop and then restart myserver via Instance state > Stop instance and Start instance.
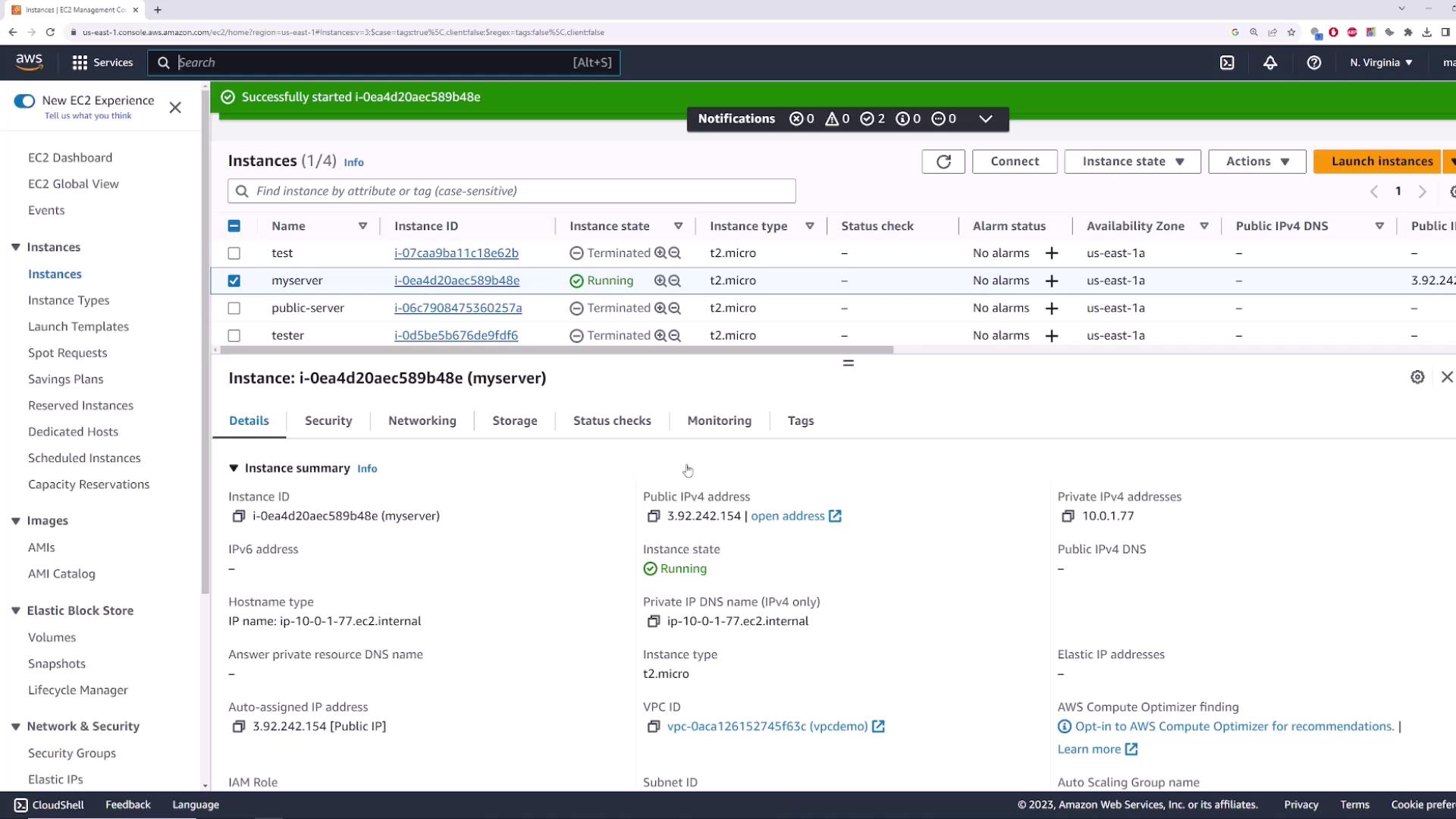
- Observe that its public IP has changed:
| Public IP Type | Persistence | Cost | Use Case |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dynamic Public IP | Changes on stop/start | Free | Short-lived, test instances |
| Elastic IP (EIP) | Remains until released | Charged when unattached | Static endpoint for production |
Note
Elastic IPs are free when associated with a running instance. AWS charges apply if you reserve an Elastic IP without attaching it.
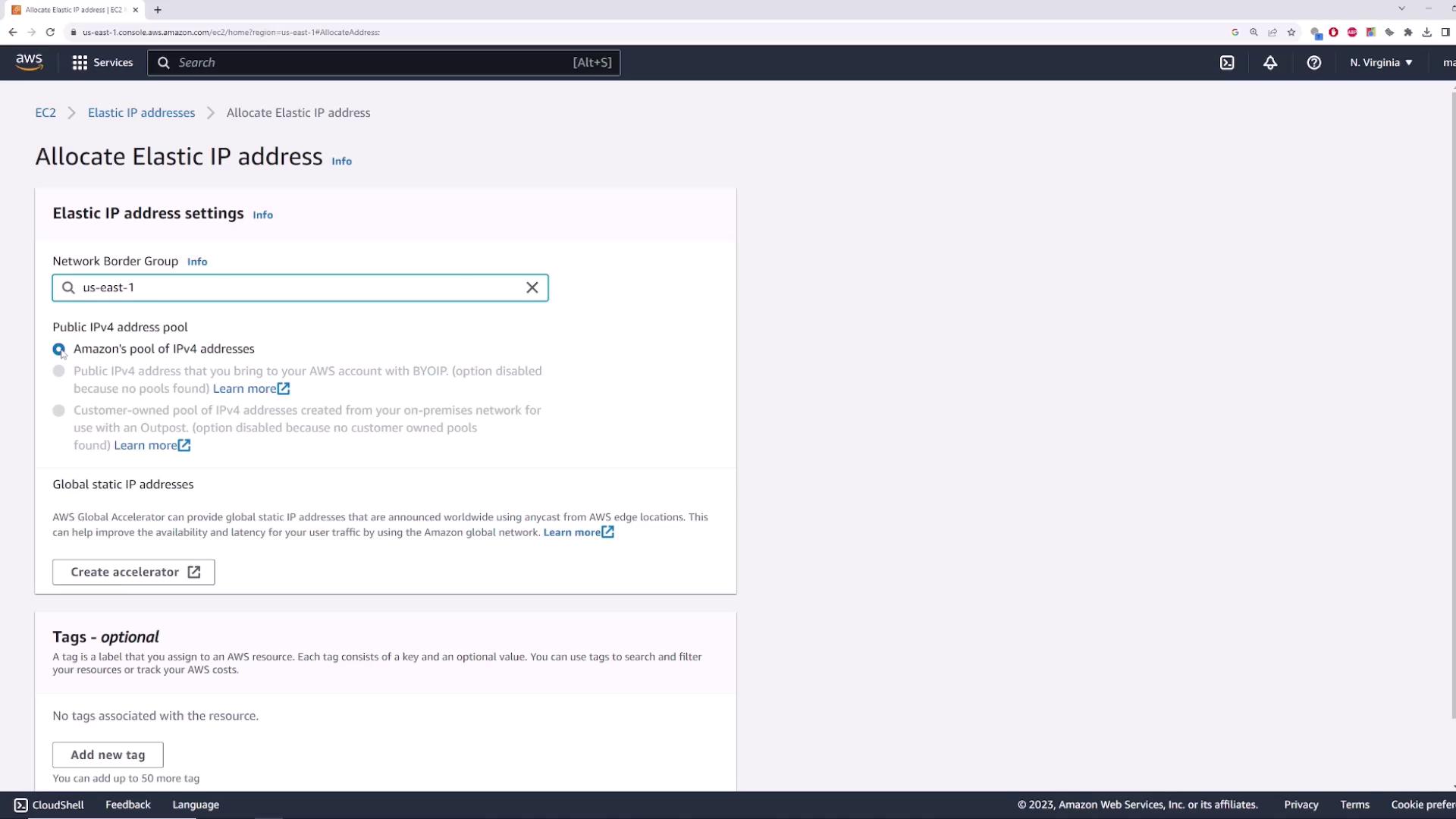
1. Allocating an Elastic IP
- In the EC2 console, select Elastic IPs.
- Click Allocate Elastic IP address.
- Accept the default settings (Amazon’s IPv4 pool) and click Allocate.
After allocation, you’ll see your new Elastic IP (e.g., 35.173.92.86):
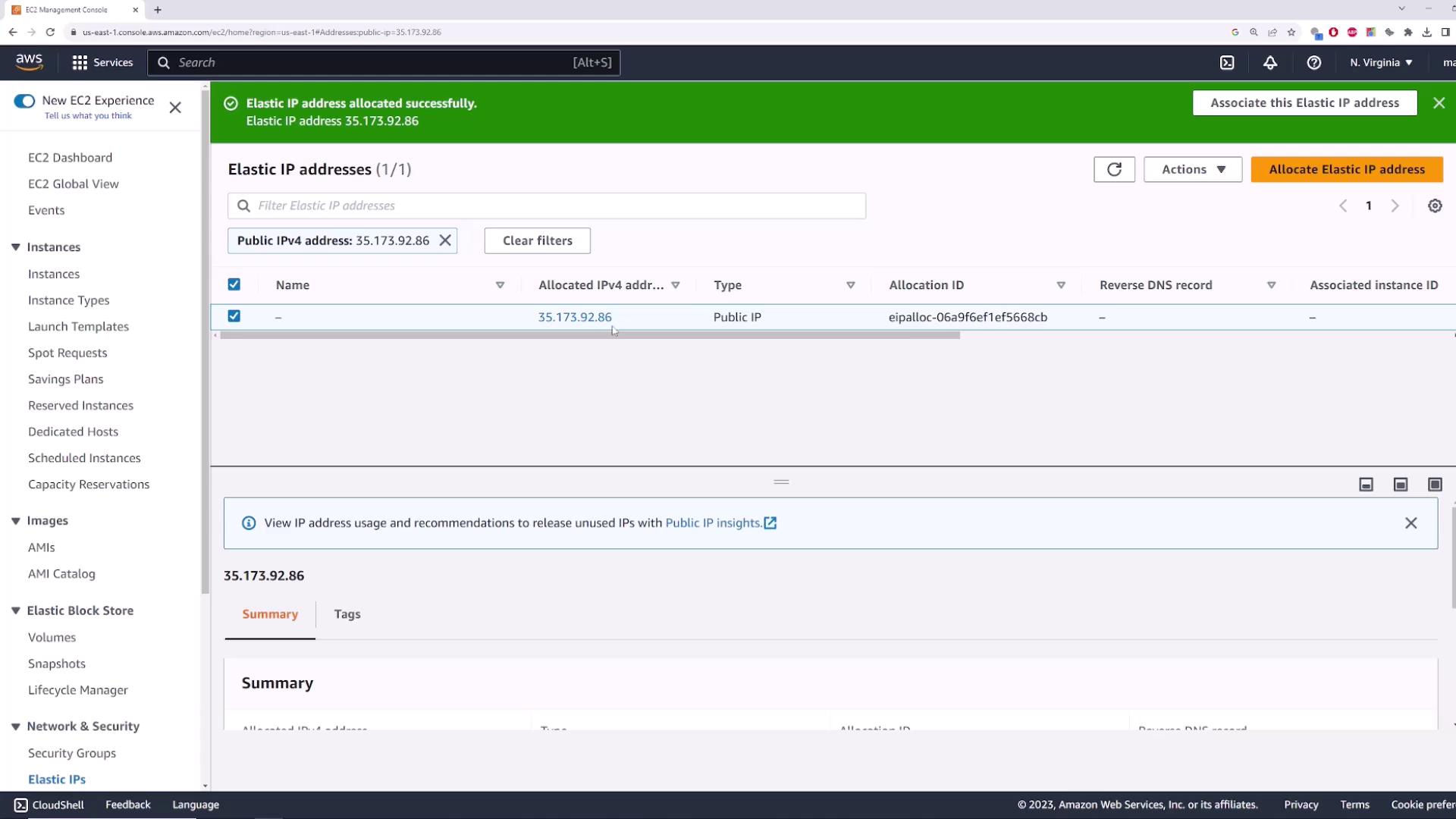
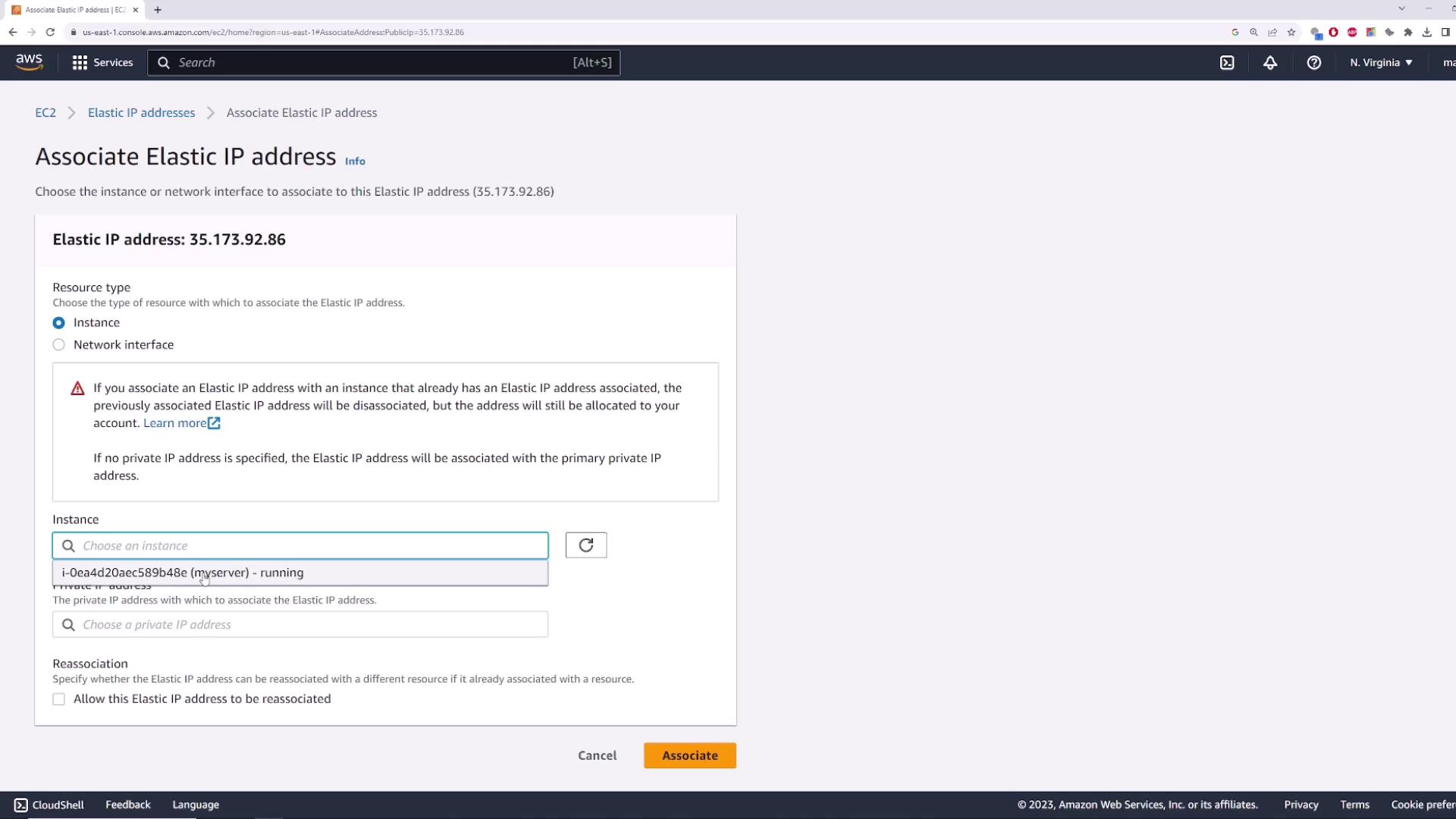
2. Associating the Elastic IP
- Select the allocated Elastic IP.
- Choose Actions > Associate Elastic IP address.
- For Resource type, pick Instance and select myserver.
- If applicable, choose the correct private IP, then click Associate.
Once associated, myserver will display the Elastic IP as its public address:
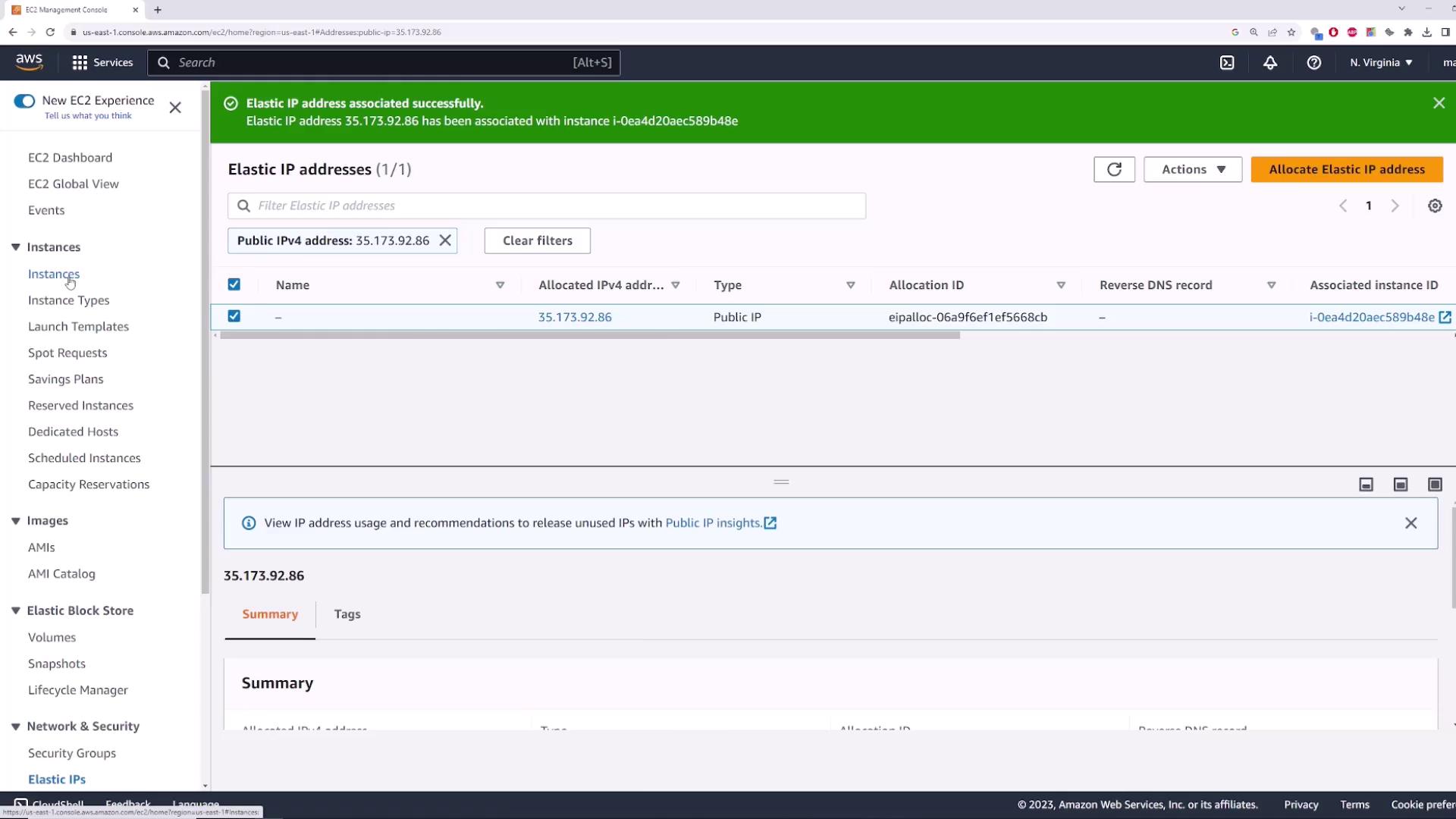
3. Verifying Reachability
Run a simple ping test from your local machine or CloudShell:
PS C:\> ping 35.173.92.86
Pinging 35.173.92.86 with 32 bytes of data:
Reply from 35.173.92.86: bytes=32 time=22ms TTL=112
Reply from 35.173.92.86: bytes=32 time=21ms TTL=112
Reply from 35.173.92.86: bytes=32 time=15ms TTL=112
Reply from 35.173.92.86: bytes=32 time=19ms TTL=112
Ping statistics for 35.173.92.86:
Packets: Sent = 4, Received = 4, Lost = 0 (0% loss),
Approximate round trip times in milli-seconds:
Minimum = 15ms, Maximum = 22ms, Average = 19ms
Stop and start myserver again. Notice that 35.173.92.86 remains unchanged—your Elastic IP stays attached throughout.
4. Cleaning Up (Optional)
To prevent unnecessary charges, release the Elastic IP when you’re done:
- Select the Elastic IP, then Actions > Disassociate Elastic IP address.
- After it’s disassociated, choose Actions > Release Elastic IP address.
- Confirm to remove the reservation from your account.
Warning
Releasing an Elastic IP makes it available to other AWS customers. You cannot reclaim the same address once released.
Links and References
Watch Video
Watch video content