AWS Networking Fundamentals
Edge Networks
Cloudfront and LambdaEdge
Amazon CloudFront delivers content from the nearest AWS edge location, reducing latency and improving performance. By integrating CloudFront Functions and Lambda@Edge, you can inject custom logic into the request/response pipeline—right at the edge.
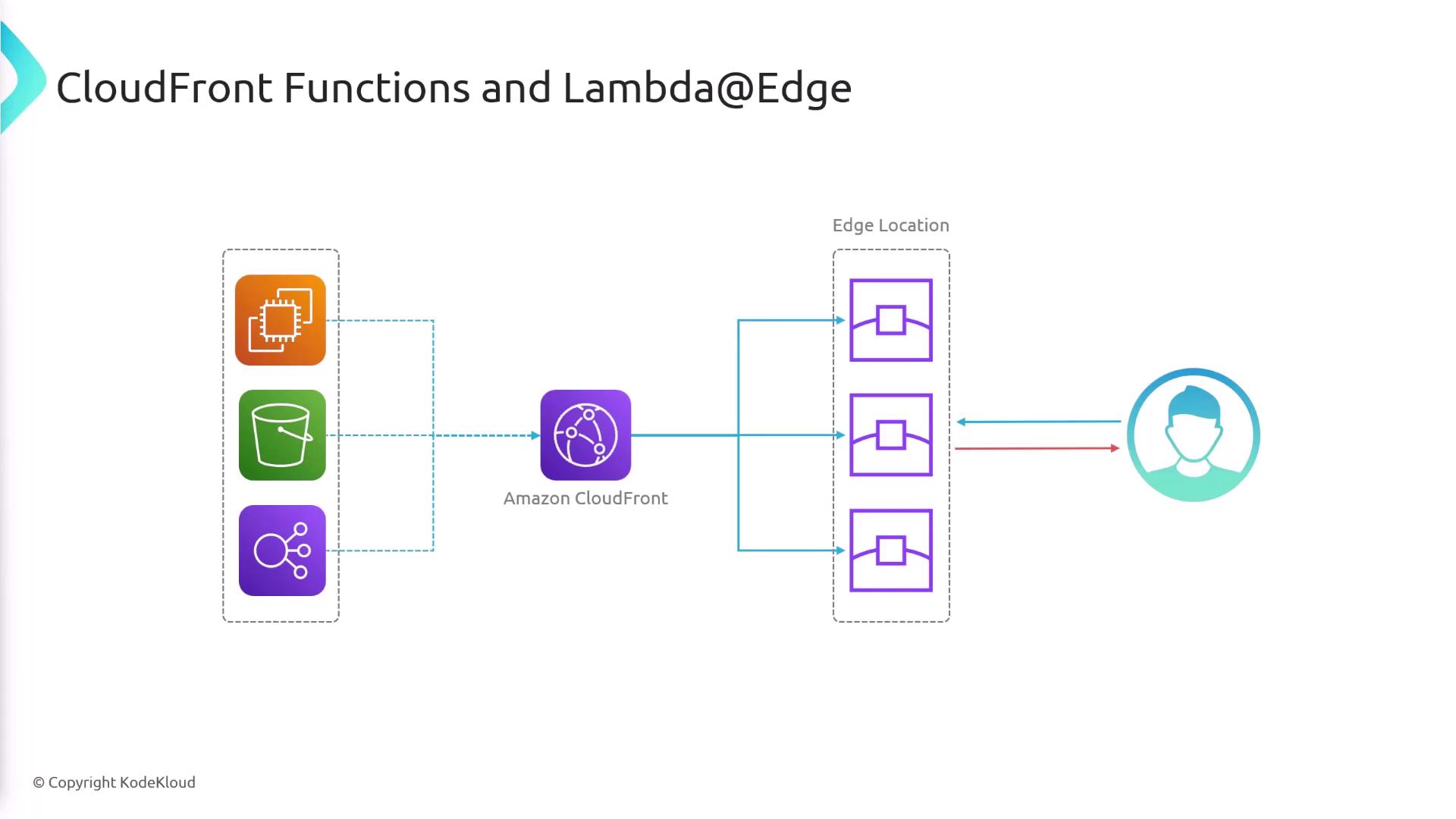
Supported Lifecycle Events
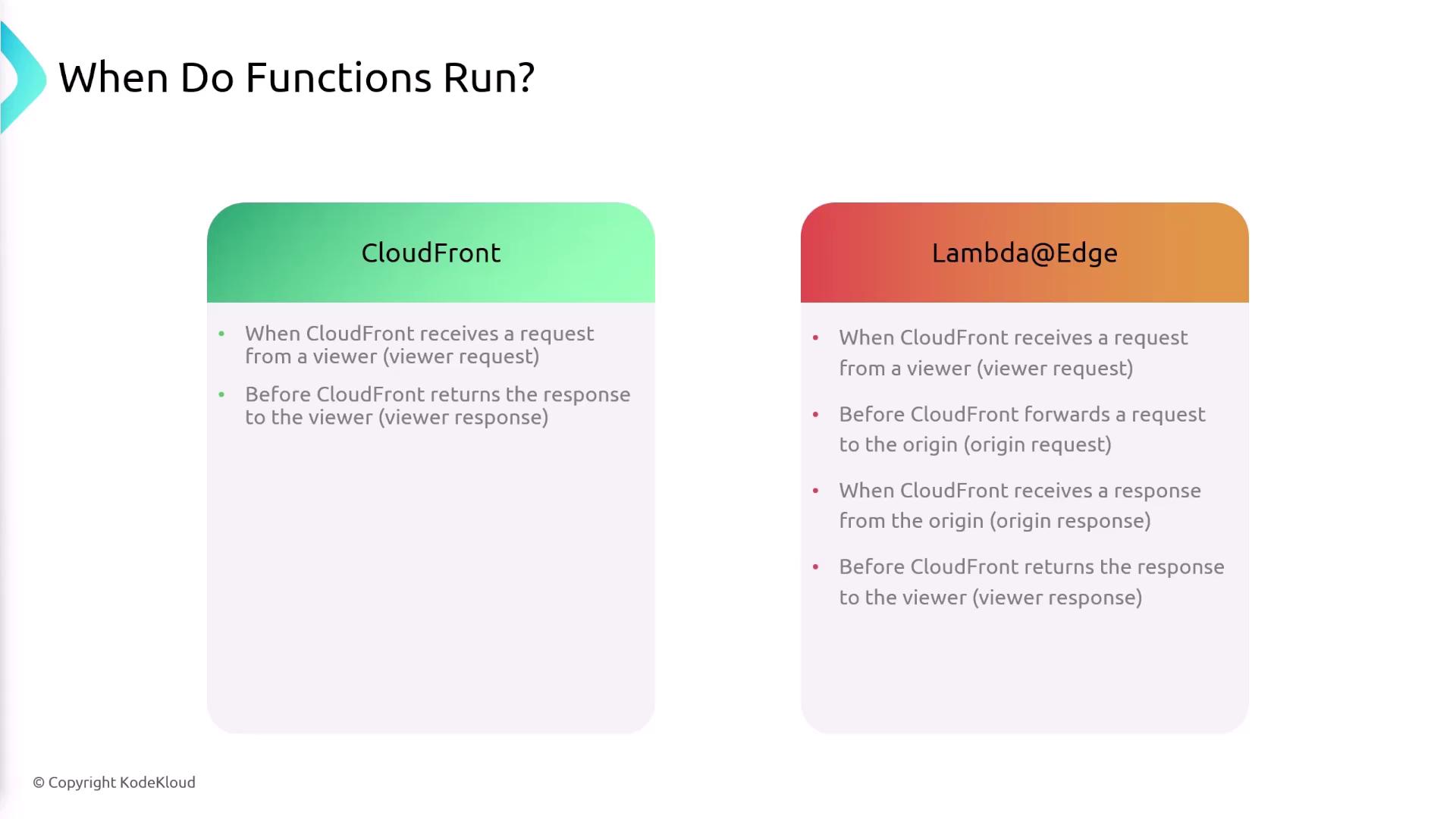
Edge functions trigger at specific points in CloudFront’s request/response cycle. Below is a quick reference:
| Function Type | Triggers |
|---|---|
| CloudFront Functions | viewer-request, viewer-response |
| Lambda@Edge | viewer-request, origin-request, origin-response, viewer-response |
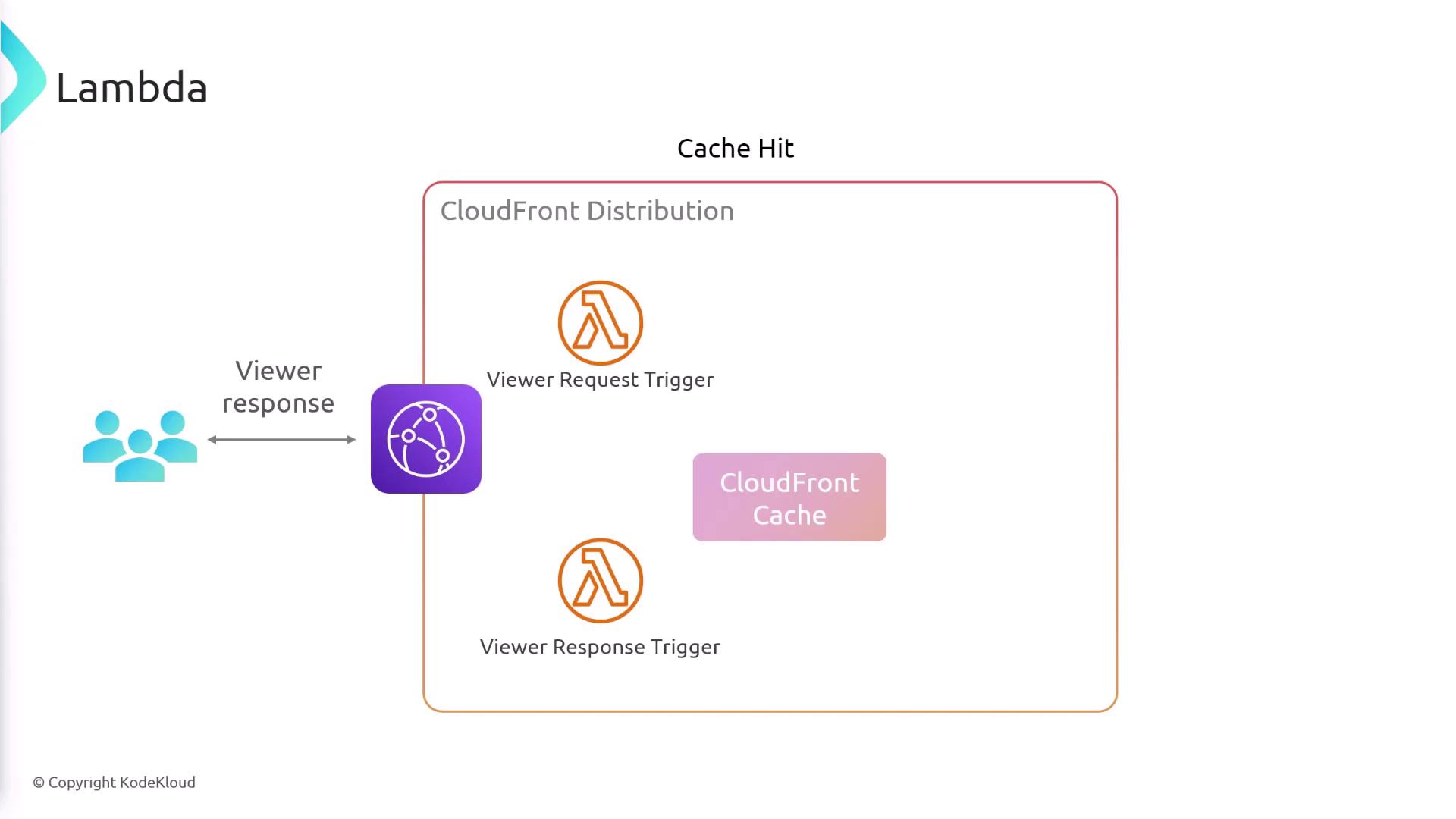
Detailed Request Flow
Viewer Request
At the viewer edge, both CloudFront Functions and Lambda@Edge can inspect or modify incoming HTTP requests.Cache Hit
If the requested object is in cache, CloudFront returns it immediately. Use theviewer-responsetrigger to adjust headers or body content before it reaches the user.Cache Miss
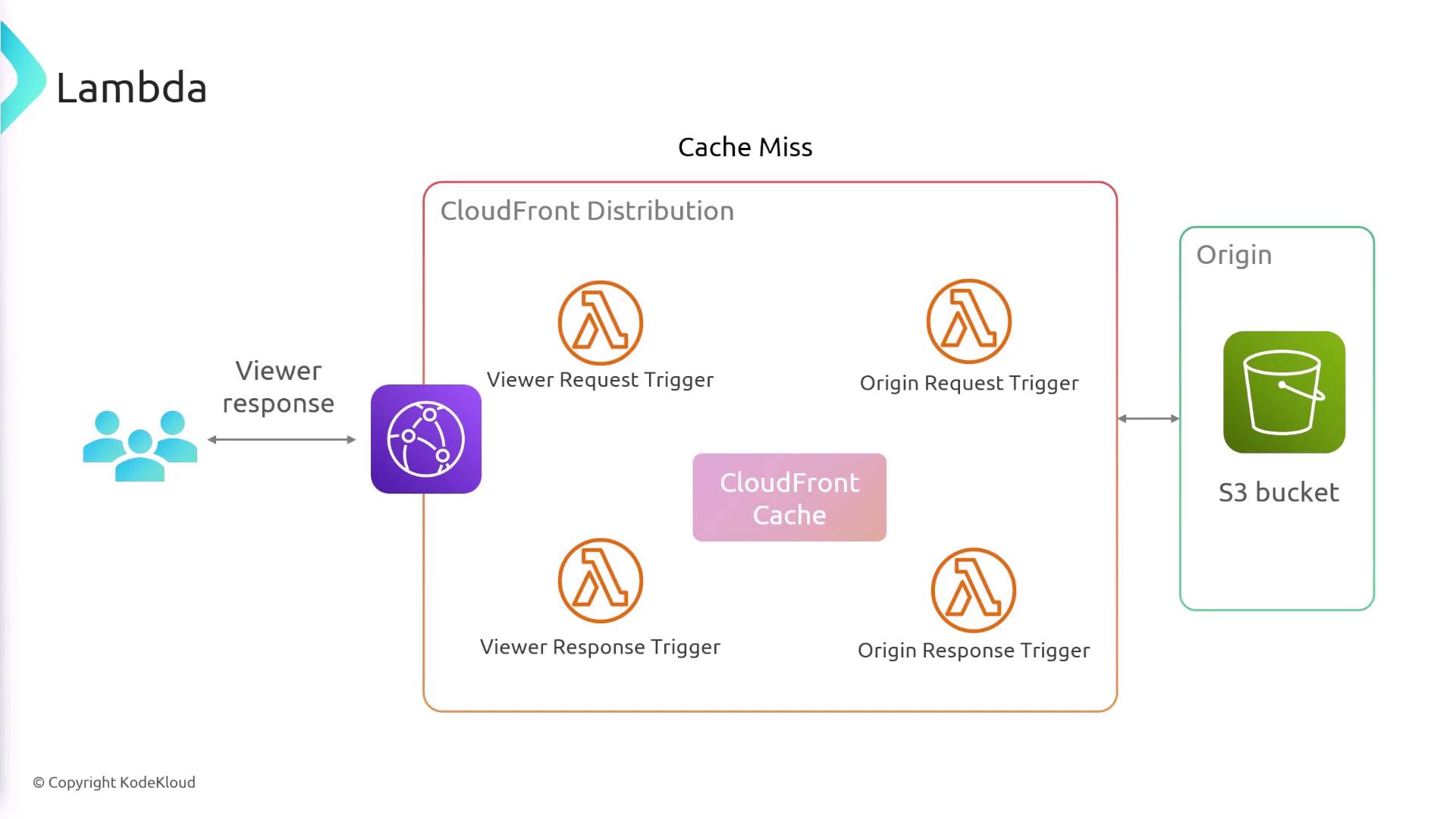
When an object isn't cached, CloudFront makes an origin request:- Lambda@Edge can run custom code during this origin request.
- After processing, the request is forwarded to your origin (e.g., Amazon S3, HTTP server).
Origin Response
On receiving data from the origin, use theorigin-responseLambda@Edge trigger to transform or filter the response before caching.Viewer Response
Finally, before dispatching to the viewer, both function types can adjust the response payload or headers.
Common Use Cases
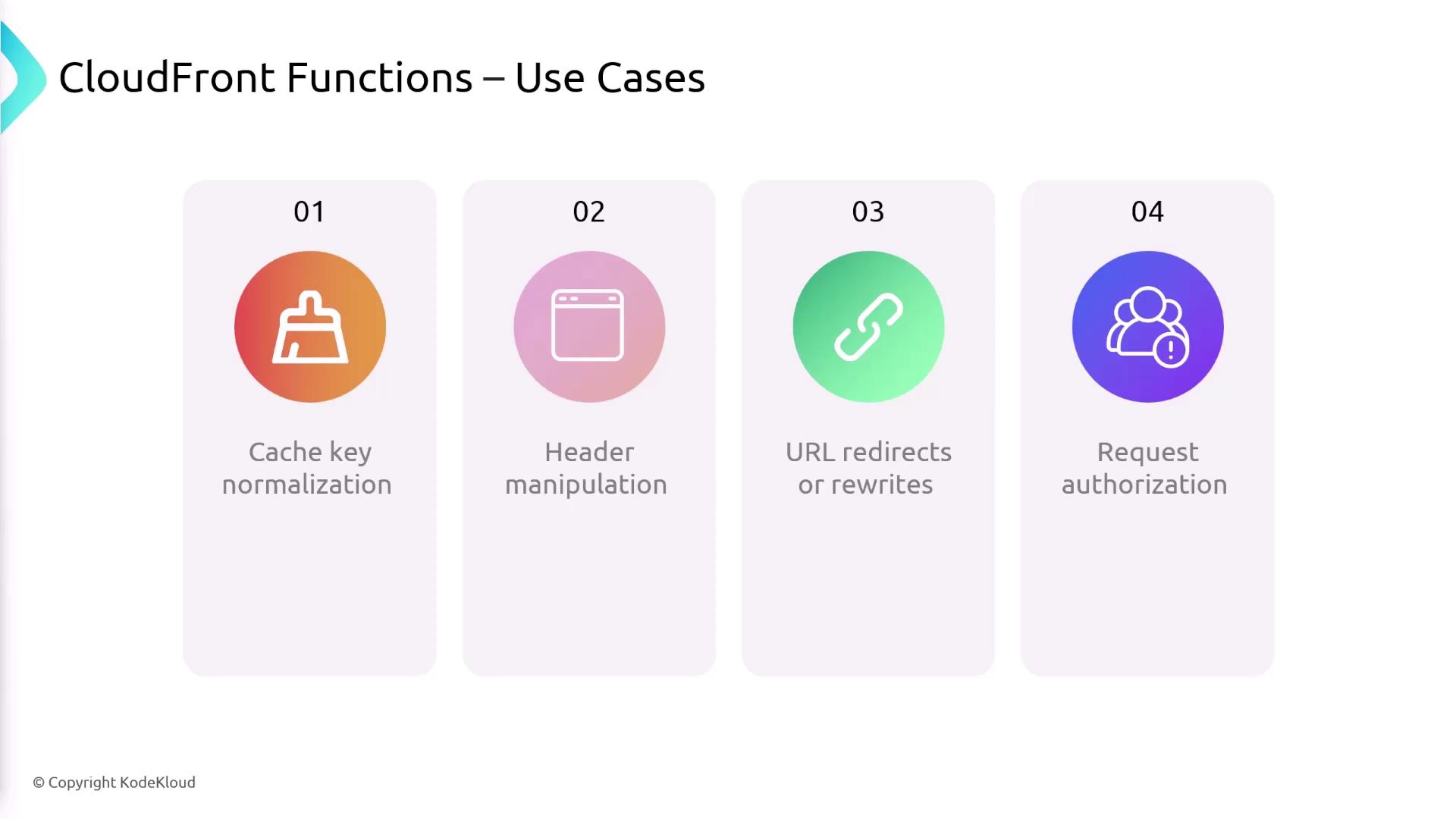
CloudFront Functions
- Cache Key Normalization
Transform request attributes (like query strings or headers) to optimize cache keys. - Header Manipulation
Add, modify, or strip HTTP headers in requests or responses. - URL Redirects / Rewrites
Implement redirects or rewrite URLs at the edge without touching your origin. - Request Authorization
Perform lightweight token validation (e.g., JWT) by inspecting authorization headers.
Lambda@Edge
- Complex or Long-Running Logic
Execute heavier workloads requiring more CPU, memory, or execution time. - Third-Party Libraries
Package external dependencies with your function for richer functionality. - External Network Access
Connect to APIs, databases, or other services outside the AWS network. - File System Operations
Read/write temporary files in/tmpor process request bodies with custom logic.
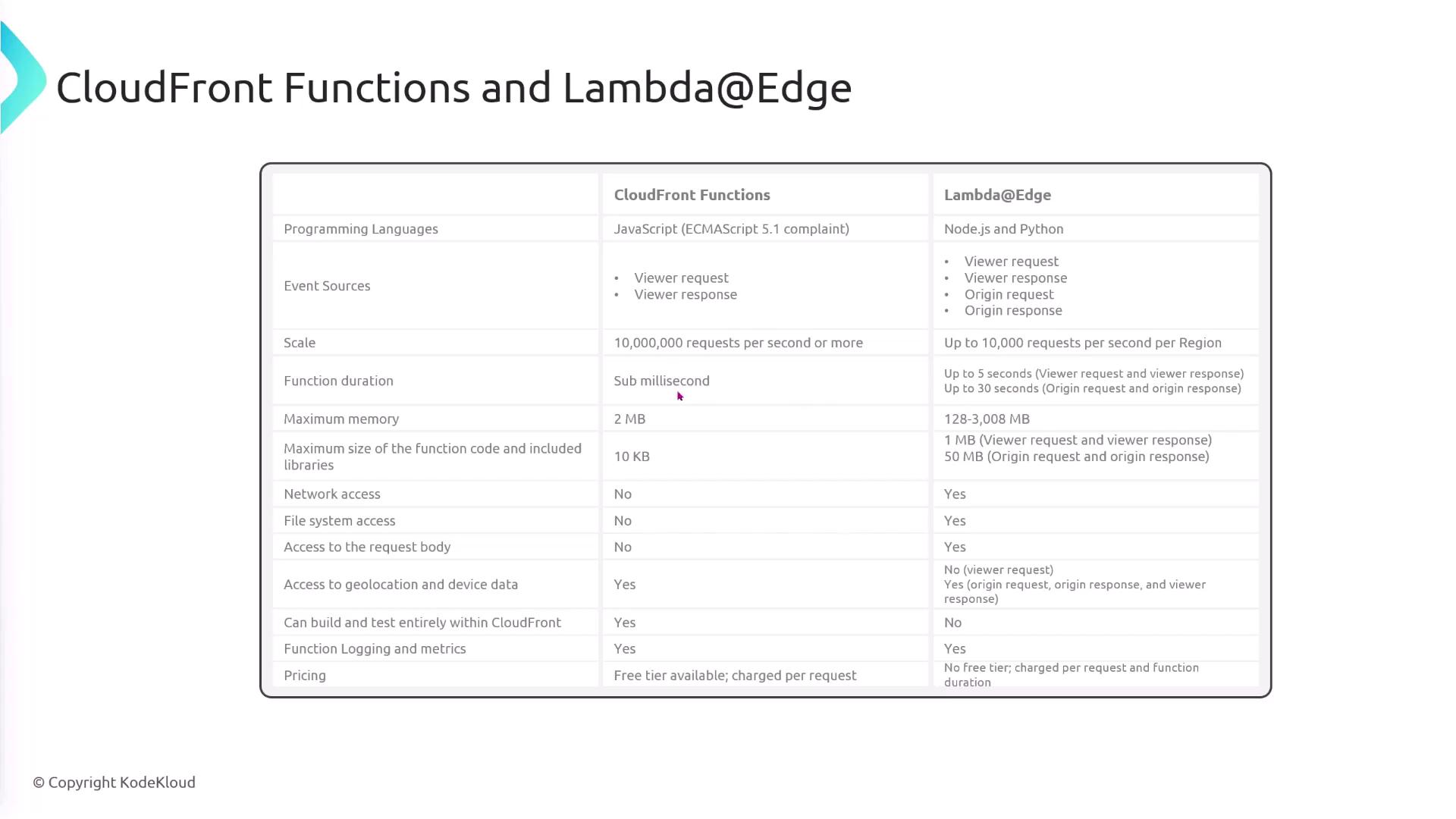
Feature Comparison
Note
Use CloudFront Functions when you need sub-millisecond execution with minimal dependencies. Choose Lambda@Edge for advanced workloads or when you require external network and file system access.
Choosing the Right Option
| Criteria | CloudFront Functions | Lambda@Edge |
|---|---|---|
| Execution time | < 1 ms | Up to 5 minutes |
| Supported languages | JavaScript (ECMAScript 6) | Node.js, Python, etc. |
| Package size & libraries | Must be very small, no external packages | Supports larger bundles & dependencies |
| Network & filesystem | No | Yes |
Warning
Deployments with Lambda@Edge are replicated across all edge locations. Updates can take several minutes to propagate globally.
Summary
Both CloudFront Functions and Lambda@Edge extend your CDN with programmable logic at AWS edge locations.
- Choose CloudFront Functions for lightweight, high-scale tasks such as header manipulation, redirects, or cache key normalization.
- Opt for Lambda@Edge when you need longer execution, external network access, or advanced libraries.

References
Watch Video
Watch video content