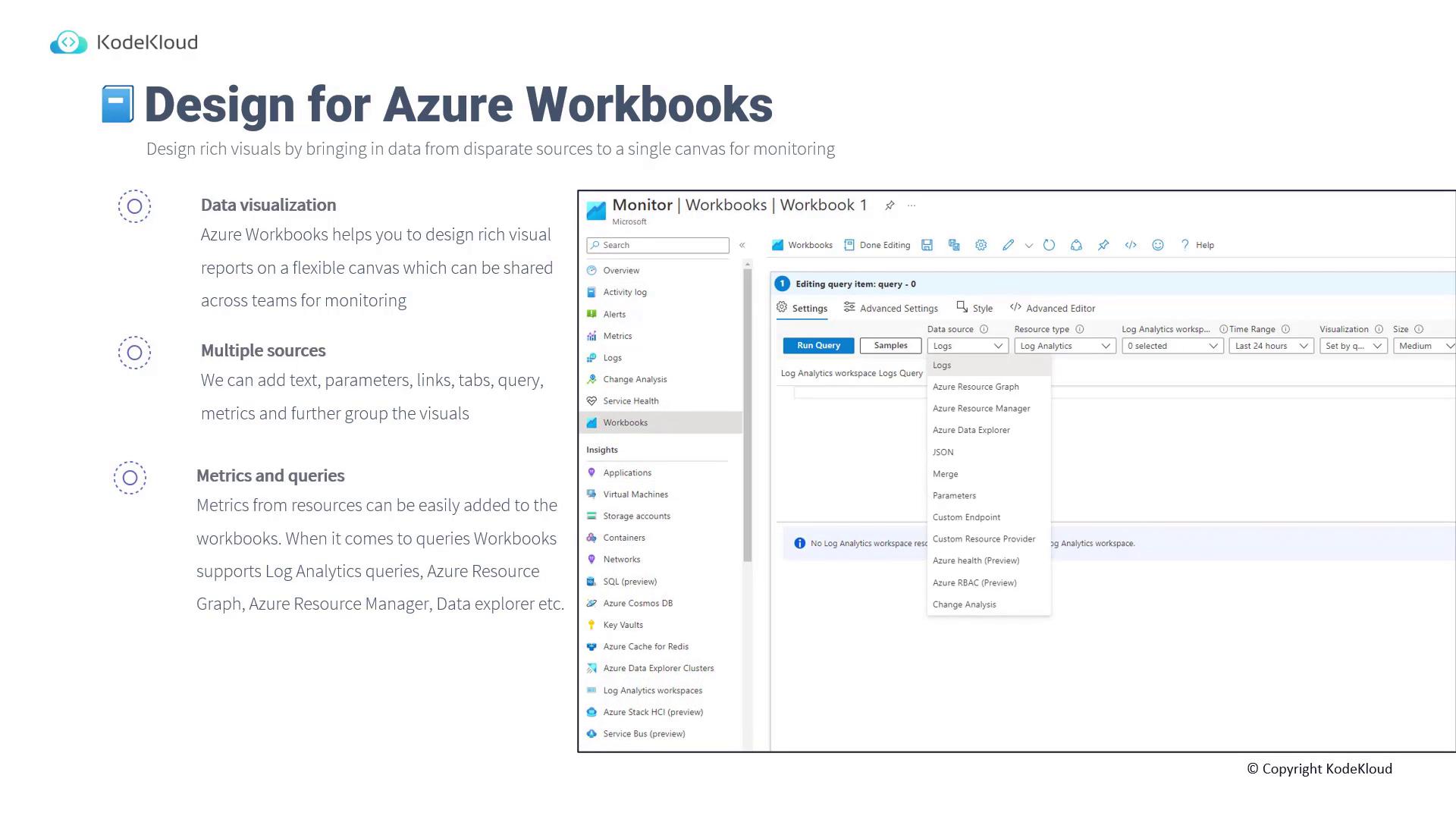
Creating a VM Performance Workbook in the Azure Portal
In this section, you will learn to build a simple workbook that monitors virtual machine (VM) performance. Follow these steps to create a dynamic dashboard showing performance metrics like CPU usage, network statistics, and disk performance.Step 1: Adding a Markdown Heading
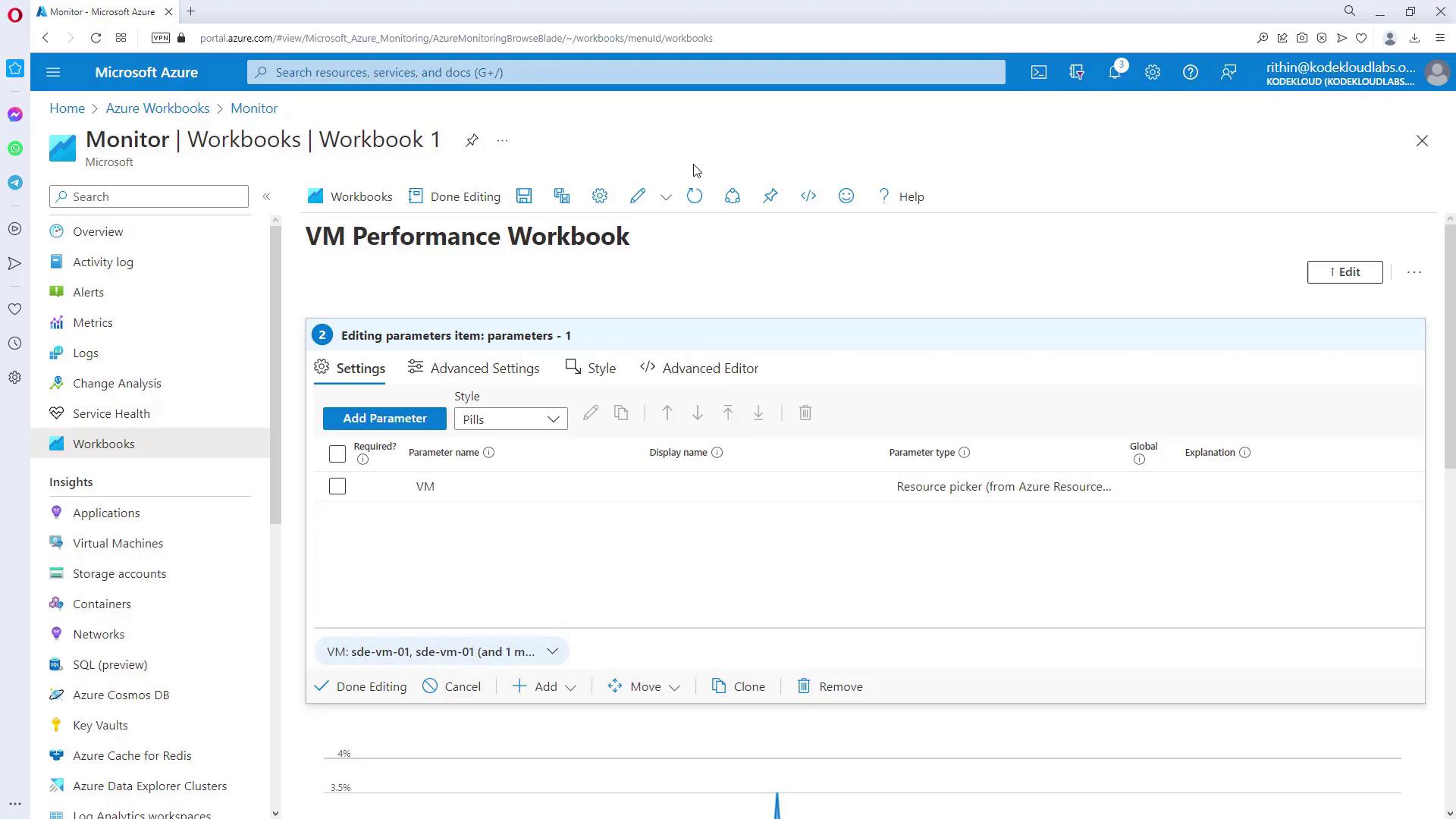
Begin by adding a Markdown text block to label your workbook. This heading identifies the purpose of your report:Step 2: Adding a Parameter for VM Selection
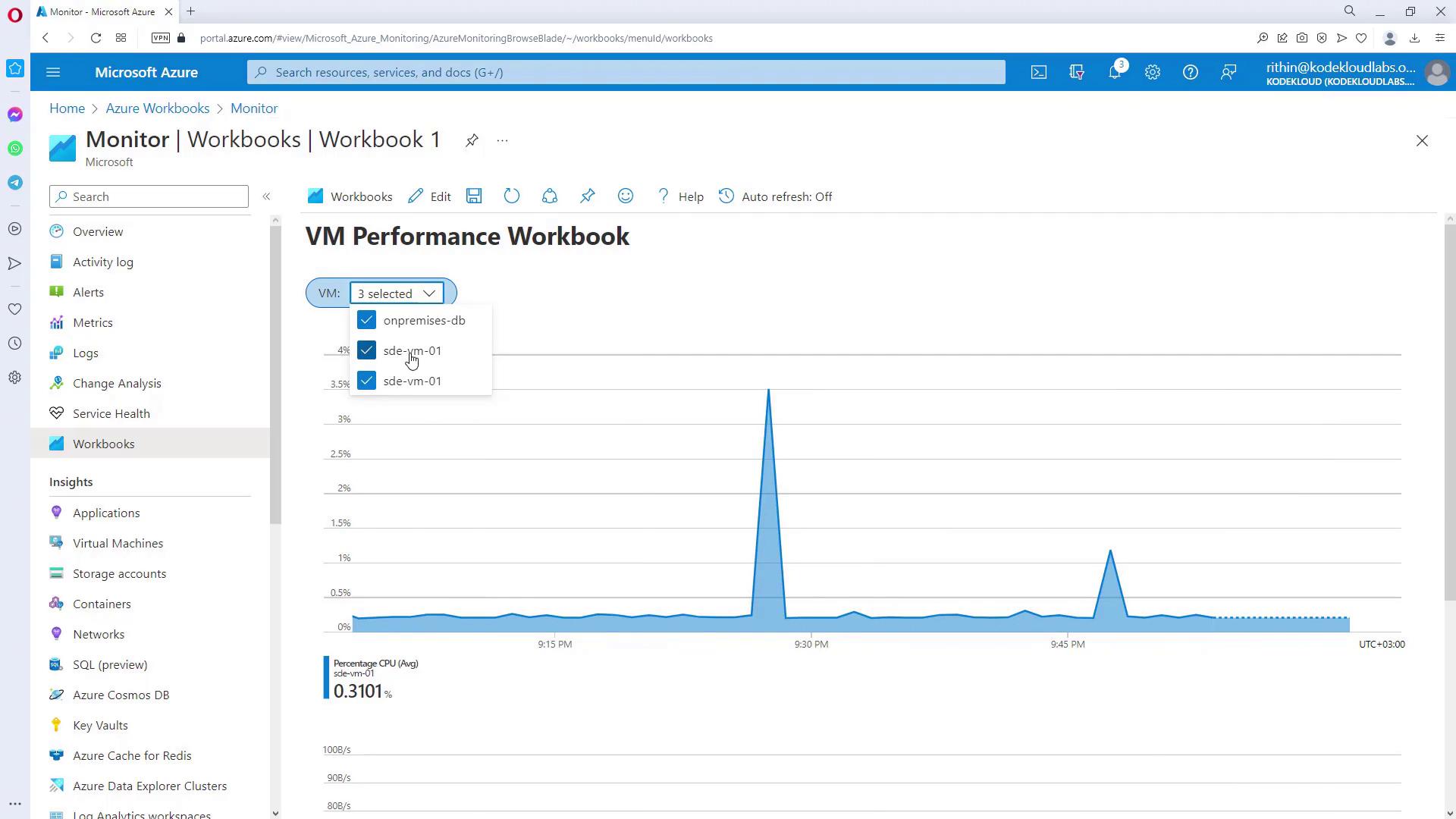
Next, add a parameter to create a drop-down menu for VM selection. This parameter can be set up using options such as drop-down, time range, resource picker, resource type picker, or location picker.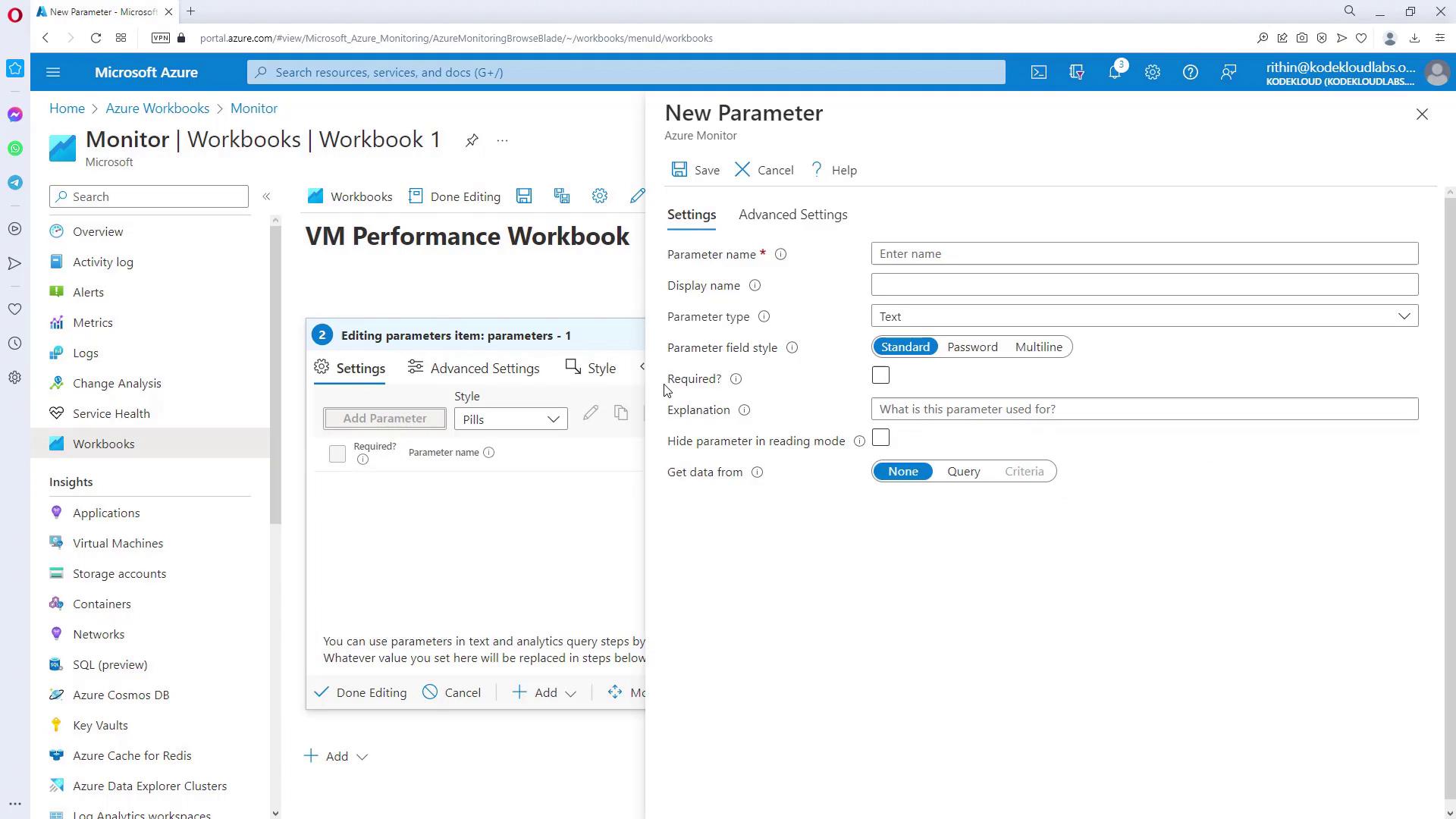
Step 3: Setting Up the Resource Graph Query
Utilize the Kusto Query Language (KQL) to list all Virtual Machines with a concise query. Instead of using multiple repetitive queries, implement the refined query below:Step 4: Adding Performance Metrics
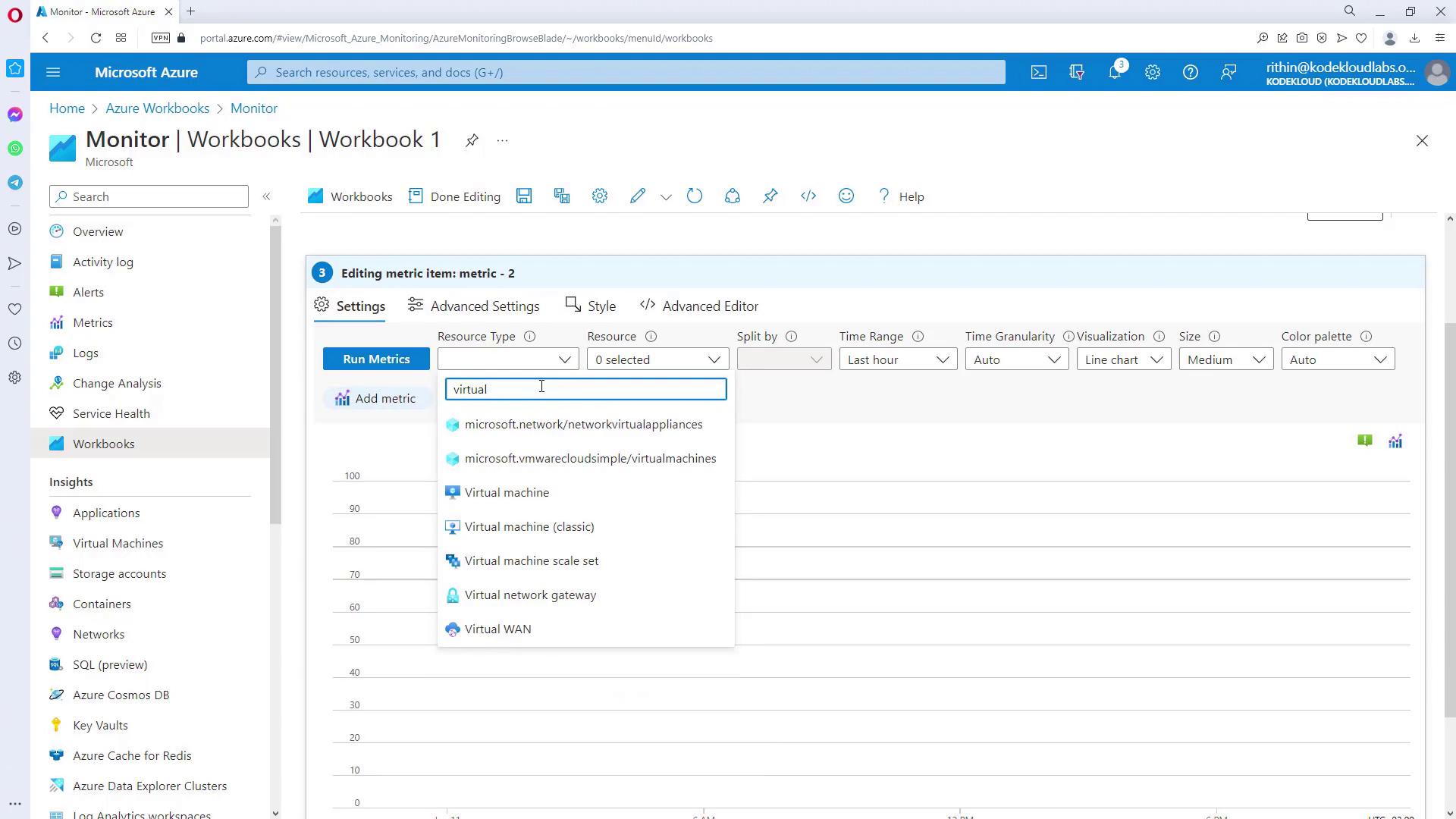
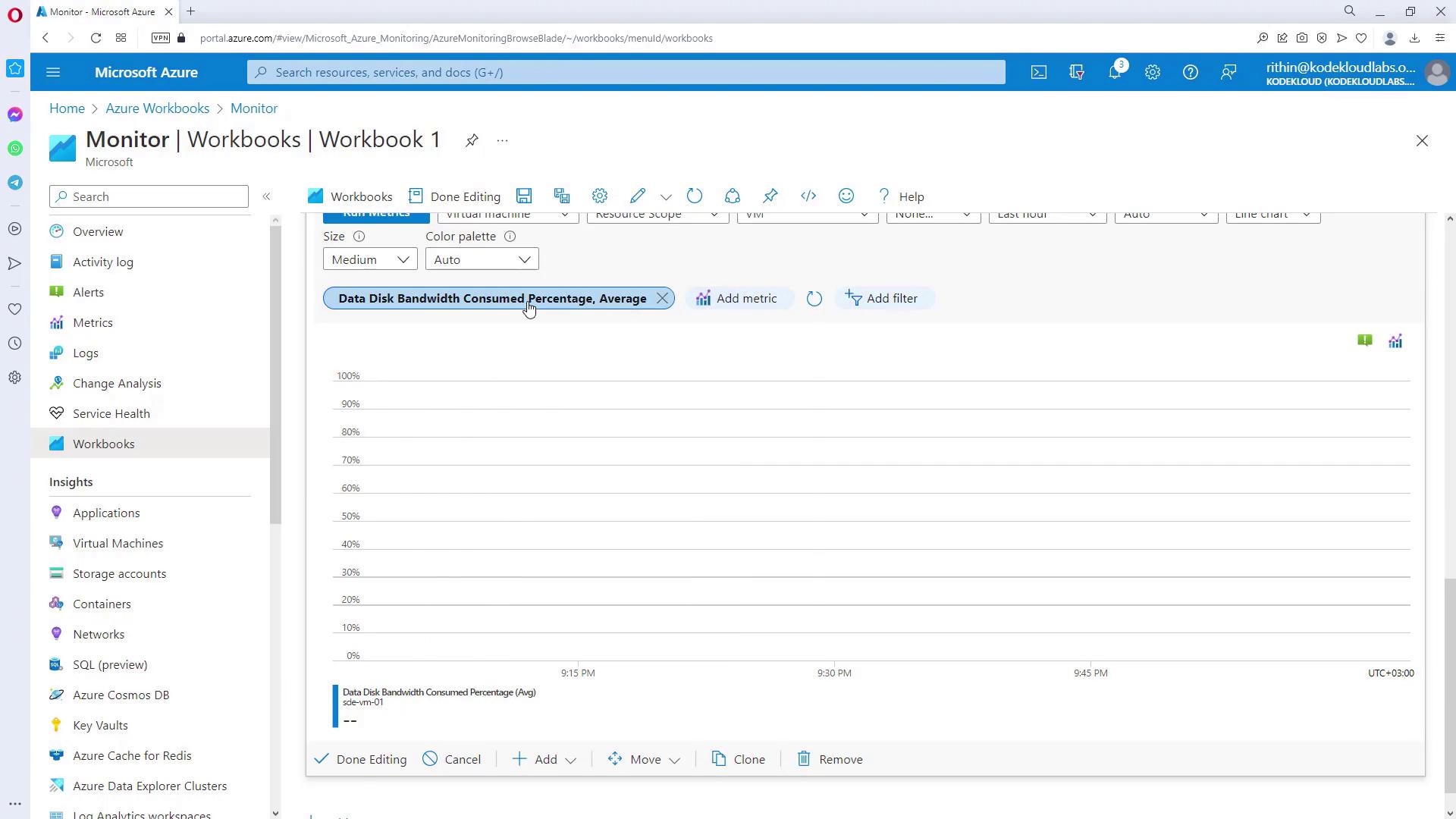
Now, add performance metrics to visualize the data for the selected VMs. Follow these steps:- Click “Add Metric” and configure the resource type to Virtual Machine, linking it to the previously defined parameter for dynamic selection.
- Choose the metric you want to display (e.g., CPU percentage) and set the aggregation method (such as Average).
- Click “Run Metrics” to generate the visualization. You can adjust the visualization type (bar chart, area chart, etc.) and the graph size as needed.
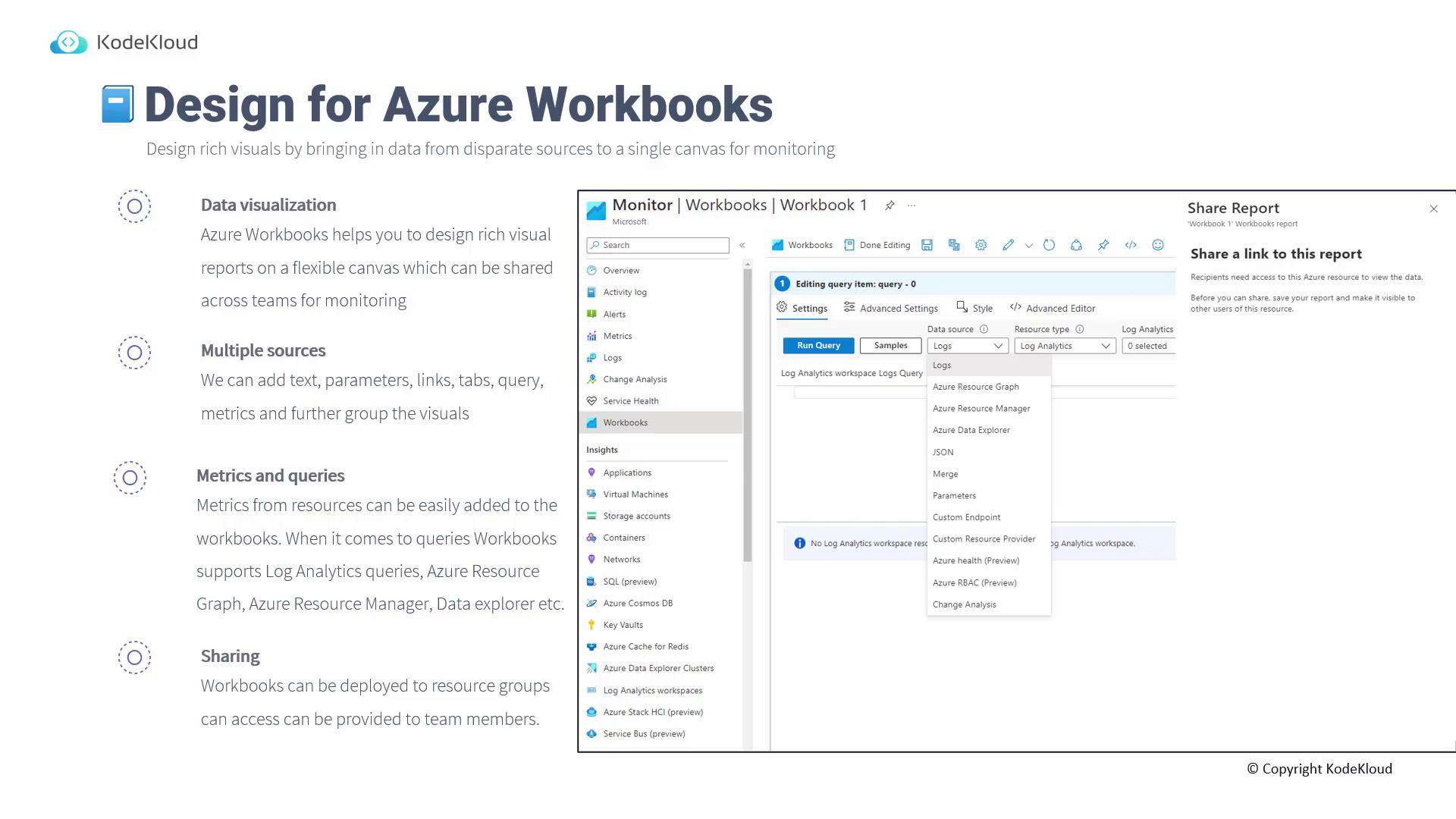
Remember to save and share your workbook when you’re done to enable team-wide collaboration.
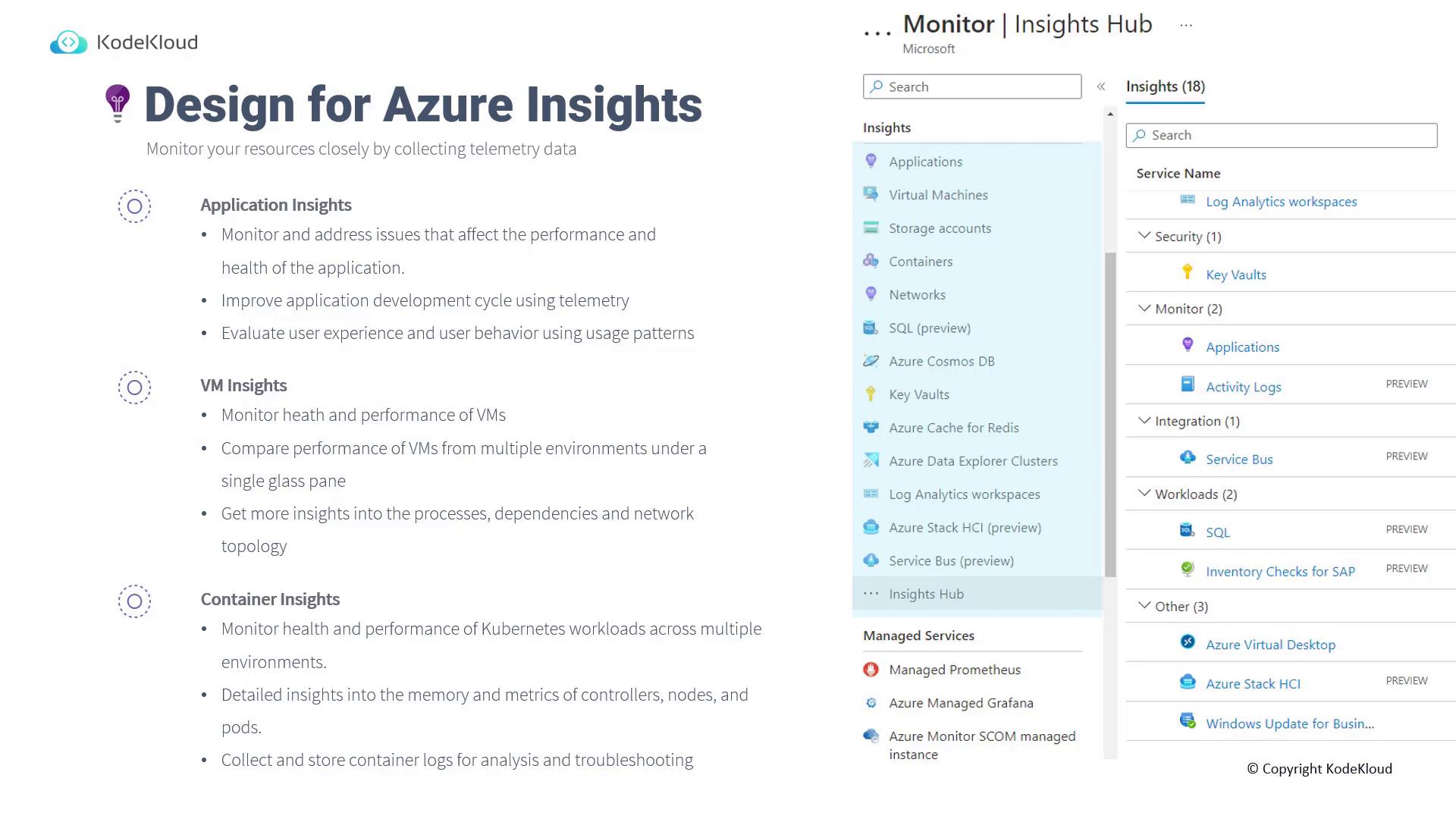
Designing for Azure Insights
Azure Insights extends your monitoring capabilities by providing telemetry data for a broad range of services. In the Azure Monitor, Insights are available for services such as applications, virtual machines, storage accounts, containers, networks, and SQL databases. For exam purposes, focus on the following three core services:- Application Insights
- VM Insights
- Container Insights
Application Insights
Application Insights is designed to help you monitor and troubleshoot your application’s performance and health. It enables you to track:- Query and request volumes along with their sources.
- Metrics like availability, performance, latency, and dependency health.
- User behavior and engagement patterns to identify areas for improvement.
- Overall application stack performance through in-depth telemetry data.
VM Insights
VM Insights offers a detailed overview of the health and performance of your virtual machines. With VM Insights, you can:- Compare the performance of multiple VMs across different environments.
- Access information on VM properties, running processes, dependencies, and network topology.
Container Insights
Tailored for Kubernetes workloads, Container Insights monitors containerized environments by providing:- Detailed performance and memory usage metrics for controllers, nodes, and pods.
- Centralized log collection to facilitate troubleshooting and analysis.
With these guidelines and steps, you now understand how to design robust Azure Workbooks and implement Azure Insights for monitoring resource performance and gathering actionable telemetry data. This approach not only enhances visibility into your environment but also empowers your team to make informed decisions based on real-time metrics and trends. Next, we will move on to the final topic: Design for Azure Data Explorer.