AZ-305: Microsoft Azure Solutions Architect Expert
Design a nonrelational data storage solution
Design for storage security
This article outlines essential security best practices for designing Azure storage accounts to ensure your data remains secure and accessible only to authorized users.
Limit Access to the Storage Account
Restrict access to your storage account to minimize exposure to the internet and unauthorized actors. Microsoft’s comprehensive Azure Security Baselines for Storage document details steps across network security, identity management, conditional access, credential controls, and privileged access. Below, we highlight key measures discussed in detail throughout this guide.
Note
For an in-depth understanding of these practices, refer to the official Azure documentation.
Use SAS Instead of Sharing Account Keys
Account keys provide full control over your storage account, including deletion, updates, and resource management. For scenarios requiring limited, time-bound permissions—such as read-only access from specific IP addresses and protocols—use Shared Access Signatures (SAS). In the AZ-104: Microsoft Azure Administrator course, you will learn how to create SAS tokens, read SAS details, and configure the necessary permissions.
Enable Firewall Policies
Azure Storage comes with an integrated firewall to restrict access to designated virtual networks and IP ranges. By default, access is permitted from all networks; however, you can tighten security by modifying settings to allow only selected virtual networks or specifying particular IP ranges.

Restrict Access Using Service Endpoints
Service endpoints enable you to securely connect your virtual network to Azure Storage (and other PaaS services) via private IP addresses. Although the storage account’s name resolves to its public IP address, connections originate from your virtual network’s private IP. This design ensures that while DNS resolution is public, access remains confined to your trusted network.
Enable Private Endpoint for Hybrid Scenarios
For hybrid environments where secure access from on-premises systems through ExpressRoute or VPN is necessary, enable a private endpoint. This configuration ensures that the storage account name resolves to a private IP, offering enhanced security for hybrid setups.
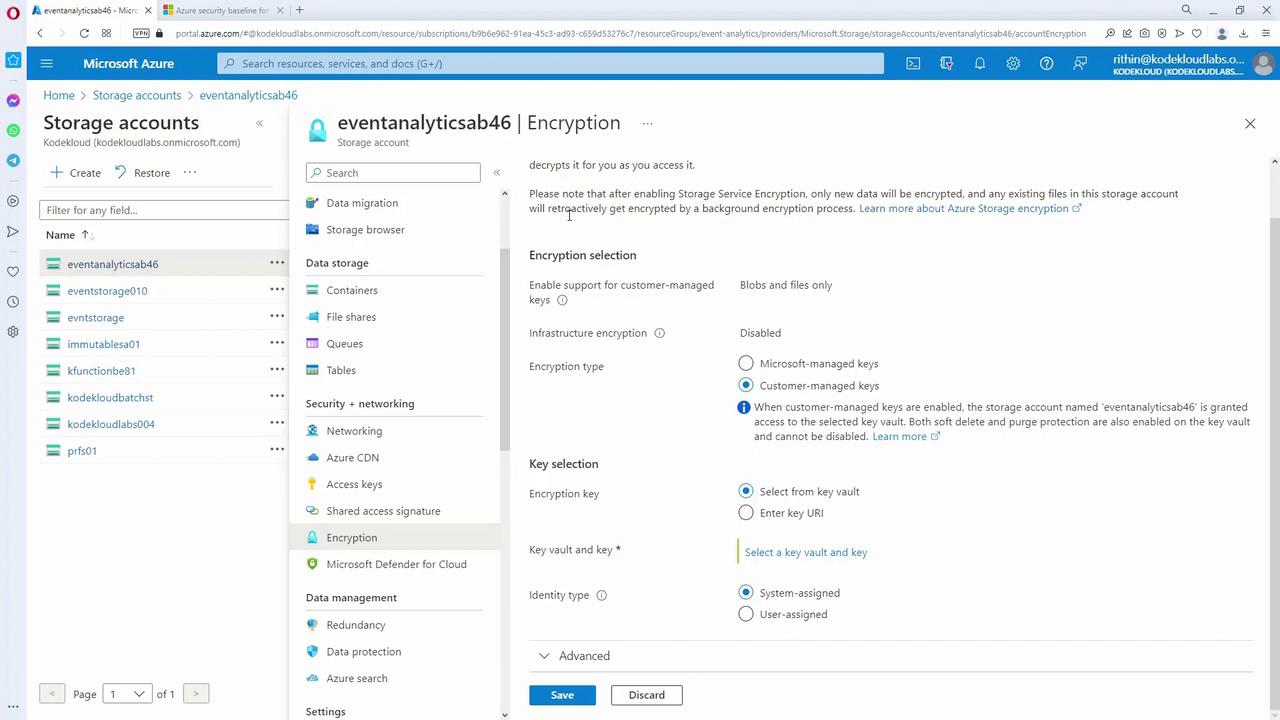
Use Customer-Managed Keys (CMK)
Customer-managed keys (CMK) allow you to control the encryption keys that secure your data, an essential feature for organizations with strict compliance and key rotation requirements. To utilize CMK, navigate to the encryption settings in your storage account and select a key from one of your Azure Key Vaults.

Enable Secure Transfer
Enforcing secure transfers ensures that all connections to your storage account use HTTPS. Any attempts to connect via an insecure channel are automatically blocked. This critical security feature is enabled by default when a storage account is created.
Conclusion
Implementing these security measures is vital for safeguarding your Azure storage account. For additional configurations and recommendations, review the Azure Security Baselines for Storage document provided by Microsoft.
Warning
Do not expose your storage account to the internet without proper restrictions, as this can lead to unauthorized access and potential data breaches.
Next, we will explore best practices for Cosmos DB and tables.
Watch Video
Watch video content