Key Features of Azure Virtual Desktop
AVD stands out with its robust capabilities:-
Remote Access:
Enjoy a full desktop experience from any location. Unlike standard Azure VMs that support only a single user at a time (forcing sign-outs for concurrent sessions), AVD enables multiple users to simultaneously access a single Windows 10 virtual machine, thus maximizing resource utilization. -
Security and Compliance:
Built upon the Azure Security Foundation, AVD offers continuously updated, integrated security measures that safeguard your data and help meet regulatory standards. -
Flexibility, Cost-Effectiveness, and Scalability:
- Flexibility: Connect using various devices including laptops, tablets, or smartphones, empowering a mobile workforce.
- Cost-Effective: Optimize expenses by leveraging existing licenses while paying solely for the resources you use.
- Scalability: Scale resources dynamically to match your organization’s requirements.

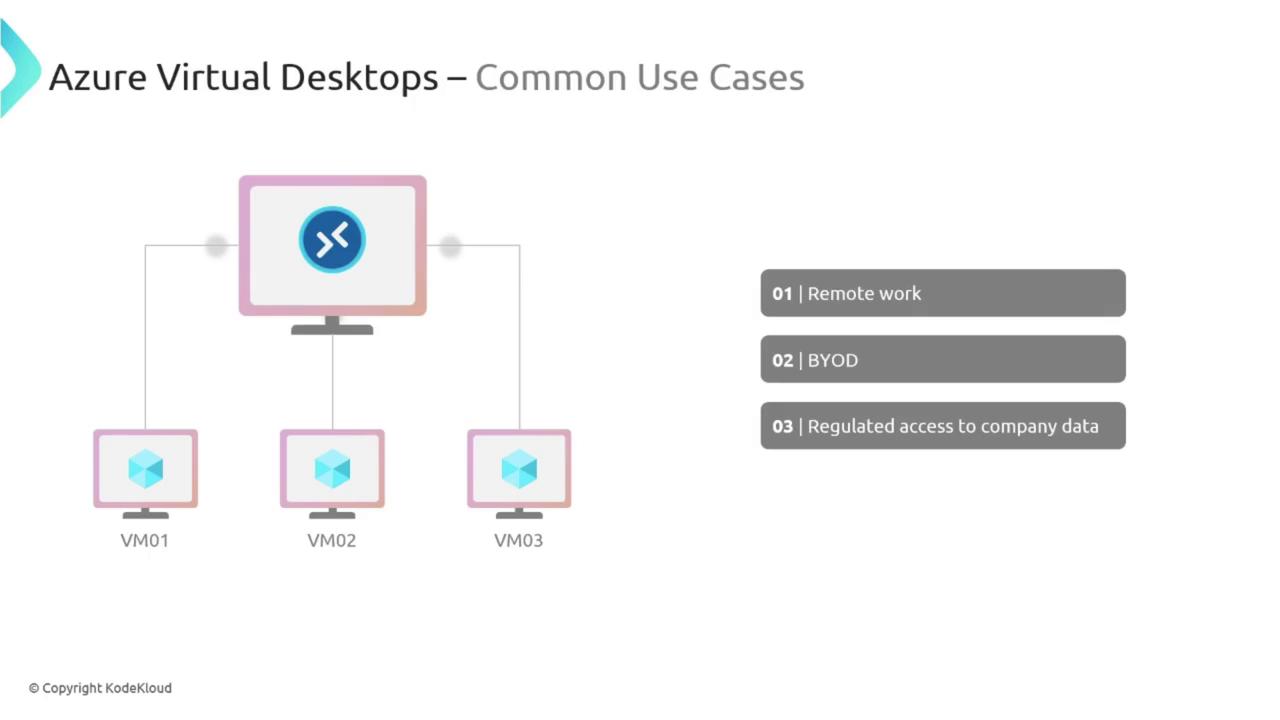
Common Use Cases
Azure Virtual Desktop is particularly effective in scenarios like remote work and BYOD (Bring Your Own Device) policies. It enables employees to securely access corporate desktops from their personal devices while ensuring adherence to company policies and robust data security.
A Glimpse into the AVD Setup Process
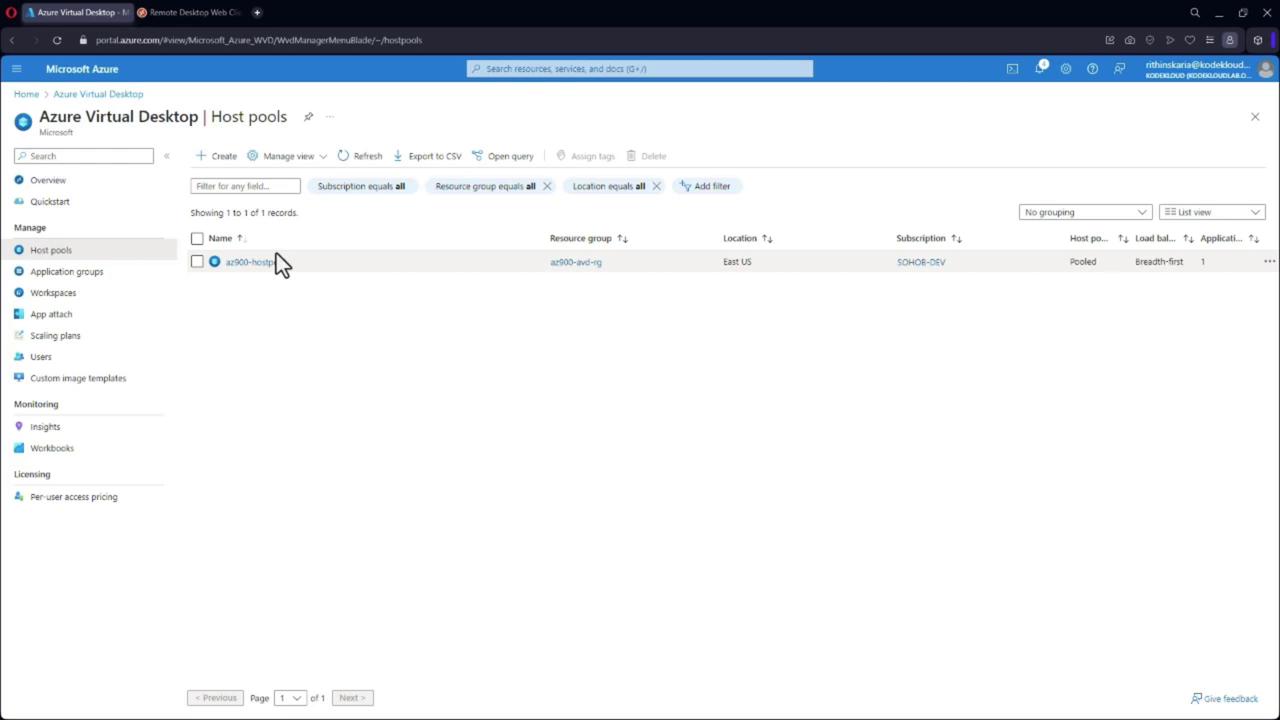
Setting up an Azure Virtual Desktop environment involves several key components, including host pools, workspaces, and application groups. Consider the following demo scenario to understand the process:- Creating a Host Pool:
Begin by logging into the Azure portal to create a host pool. A host pool is a collection of virtual machines that form the backbone of AVD, delivering flexible and enhanced virtual desktops.
-
Navigating the Virtual Machines Section:
In the Virtual Machines section, you will notice many machines prefixed with AVD. Although these are virtual machines under the hood, they are optimized to provide a superior desktop experience. -
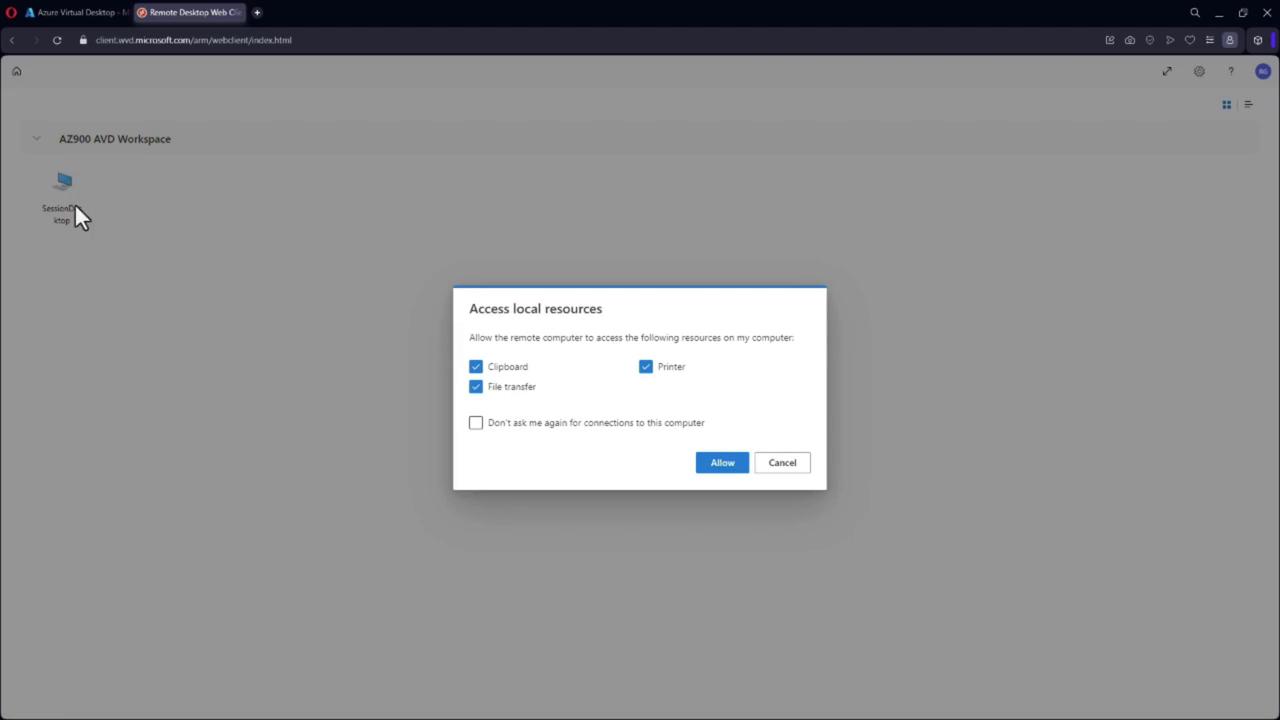
Connecting via the Remote Desktop Web Client:
Users can connect to these virtual desktops using the Remote Desktop Web Client, available both as a browser-based interface and as downloadable client applications for various devices (including tablets and smartphones).
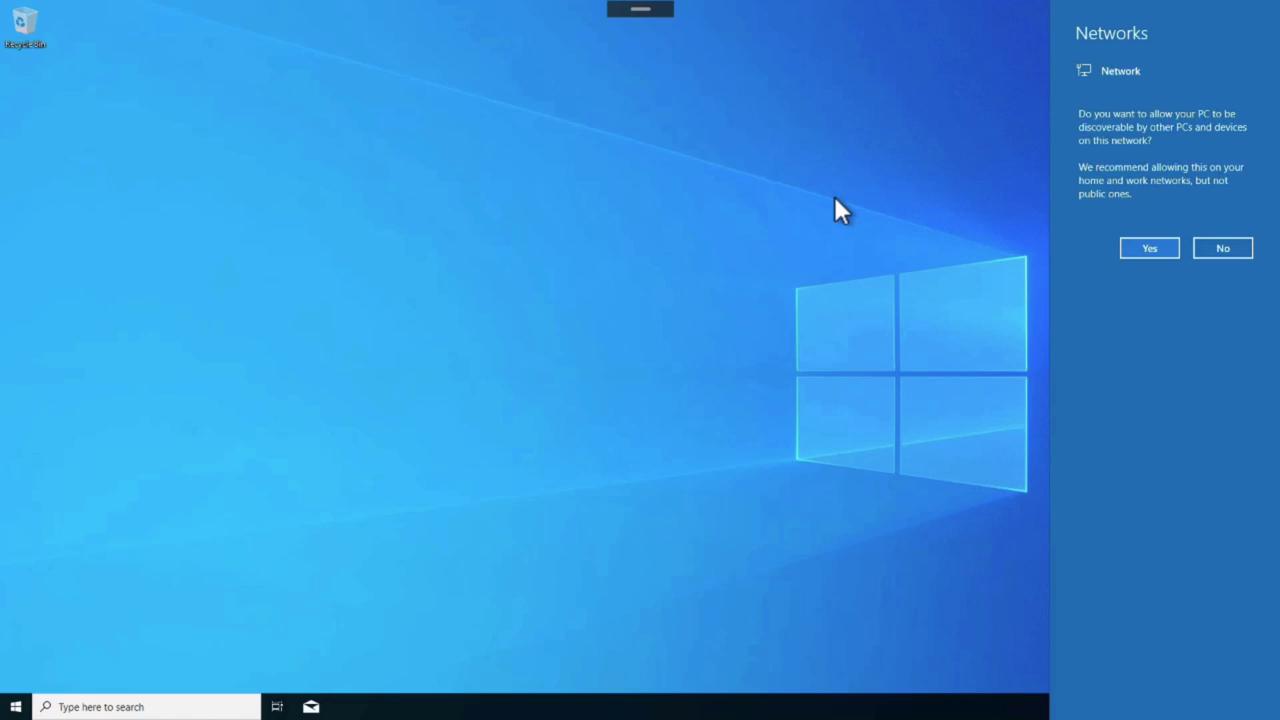
When connecting through a browser, a session prompt will request permission to access local resources such as clipboard, printers, and file transfers to ensure a smooth remote experience.
- Experiencing the Full Desktop Session:
Once connected, the Windows 10 desktop session loads completely, offering familiar features such as a full-screen mode and access to essential applications like Office, OneDrive, and SharePoint.
Conclusion
Azure Virtual Desktop leverages the advanced capabilities and security of Azure to deliver a scalable and cost-effective cloud-based desktop solution. Its ability to provide secure remote access, optimize resource utilization, and support a flexible, mobile workforce makes it an essential tool for modern businesses. Next, we will explore another essential Azure service: App Service.