Sequential (nested) stages are supported in Declarative Pipelines. They require Jenkins 2.138.3 or later and the Pipeline: Stage Step plugin.
1. Original Pipeline Snippet
Here’s a simple pipeline that runs everything in oneNodeJS 20 stage. It retries on failure but doesn’t distinguish between installing dependencies and running tests:
2. Defining Sequential (Nested) Stages
To break down the work, nest astages block inside your NodeJS 20 stage, creating two ordered steps: Install Dependencies and Testing.
3. What Happens on Failure
If Install Dependencies fails, Jenkins will:- Highlight the failure in the UI.
- Skip the downstream Testing stage.
- Surface the error in your console logs.
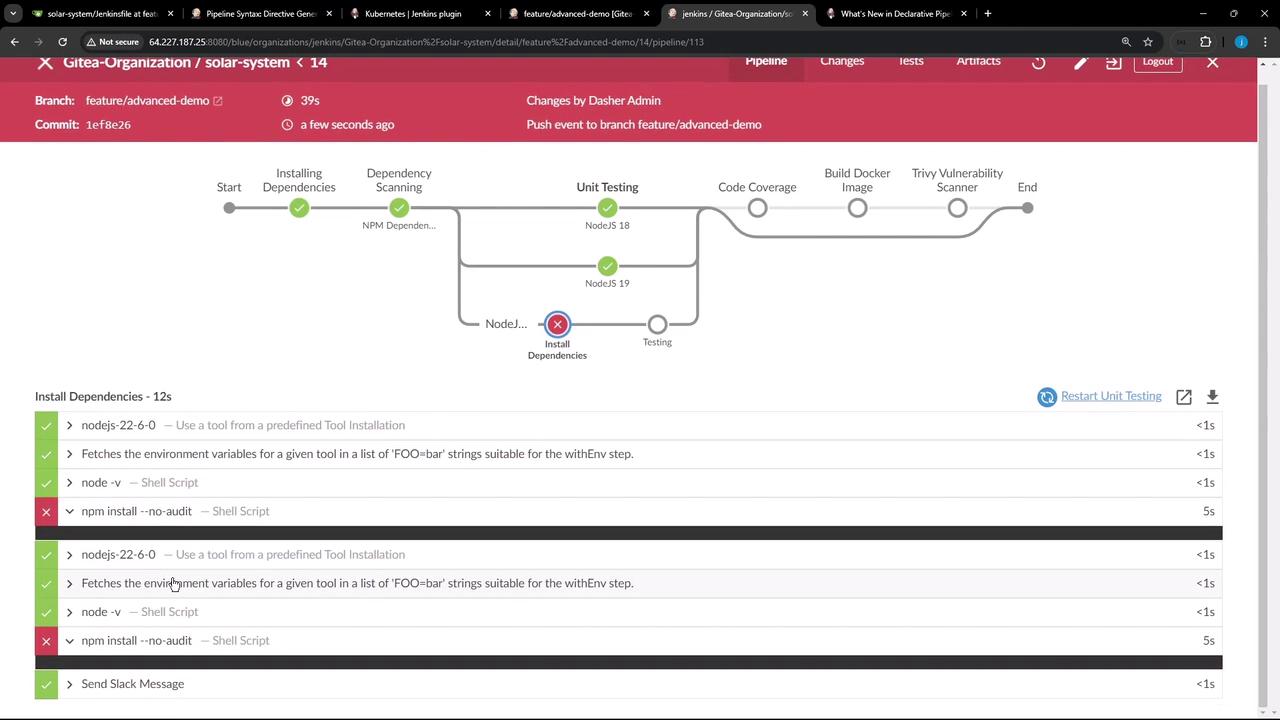
This failure is due to Node.js cache permissions, not Jenkins. You can fix it by changing the
--cache directory (npm install --cache /tmp/) or adjusting folder ownership (chown -R jenkins:jenkins /npm).4. Benefits of Sequential Stages
| Benefit | Description |
|---|---|
| Granular Visibility | See each step (install, test, package) as its own stage in the UI. |
| Fail-Fast Behavior | A failure in one nested stage blocks subsequent stages automatically. |
| Retry Control per Step | Apply options { retry(n) } individually to each nested stage for finer-grained retries. |
5. Summary & Next Steps
- Sequential stages let you organize tasks in a strict order within each branch.
- Failures halt all downstream nested stages, making it clear which step broke.
- Visibility and retry control improve your build diagnostics.