Jenkinsfiles in the same Git repository. By the end, you’ll understand the key differences in configuration, SCM handling, and runtime behavior.
Repository Structure
Our repo declarative-vs-scripted-pipeline has two branches (demo-1 and demo-2) and two Jenkinsfiles:
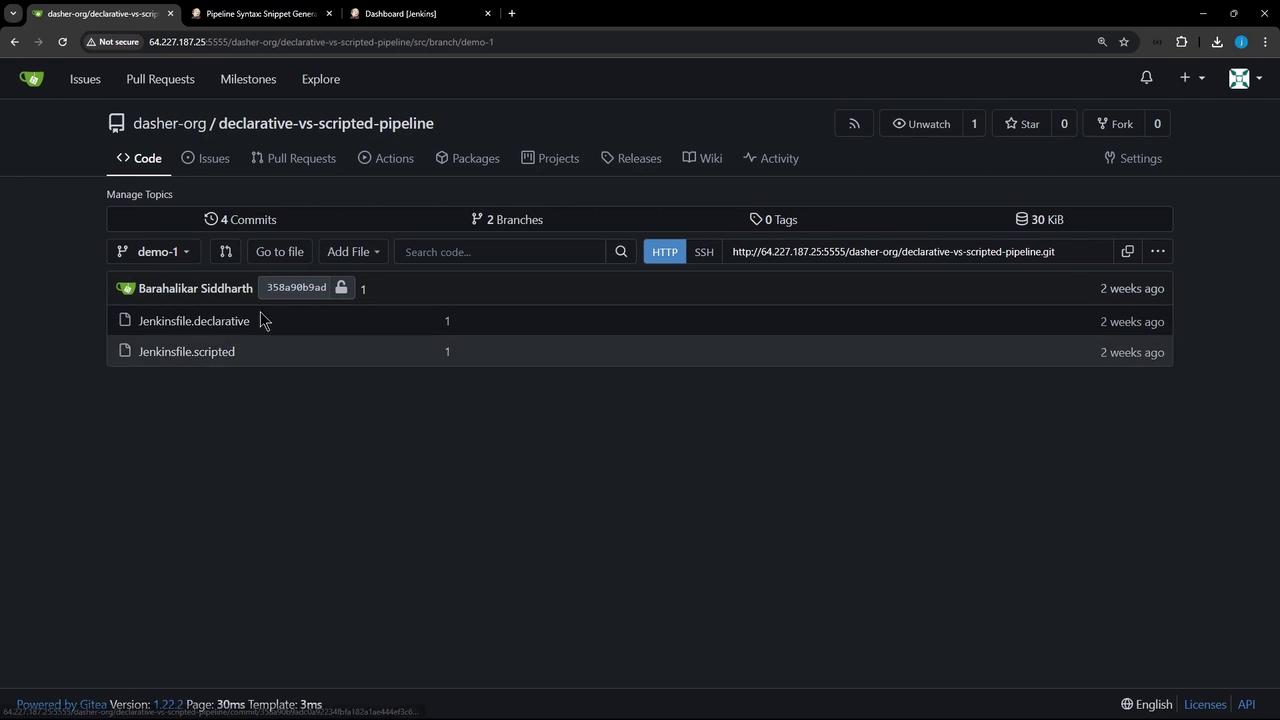
- Jenkinsfile.declarative
- Jenkinsfile.scripted
Jenkinsfile.declarative
The Declarative Pipeline syntax includes an implicit checkout and apost section for cleanup:
The
post { always { rm -rf * } } step will delete all files in the workspace. Use with caution.Jenkinsfile.scripted
Scripted Pipelines rely on explicit SCM operations and Groovy control flow:Scripted Pipelines do not perform an automatic
checkout scm. You must add it manually where needed.1. Create the Pipeline Job
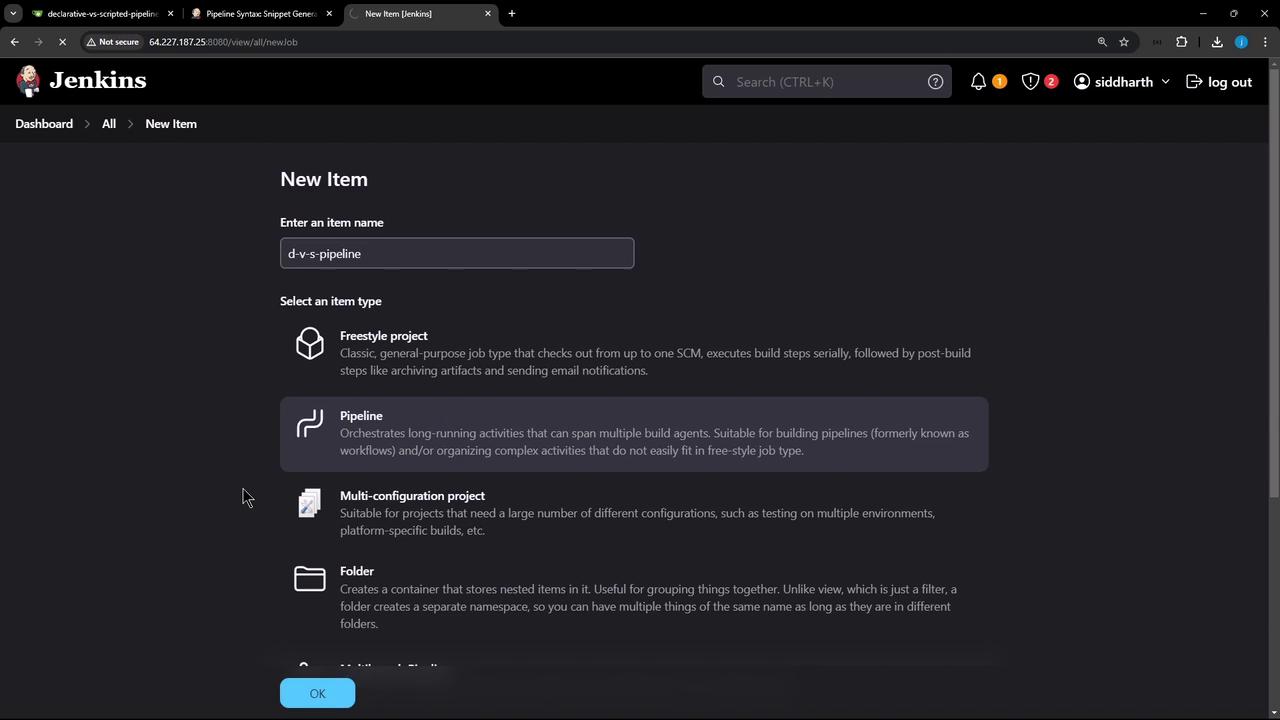
- In Jenkins, click New Item.
- Enter d-v-s-pipeline, select Pipeline, and click OK.
2. Configure the Declarative Pipeline
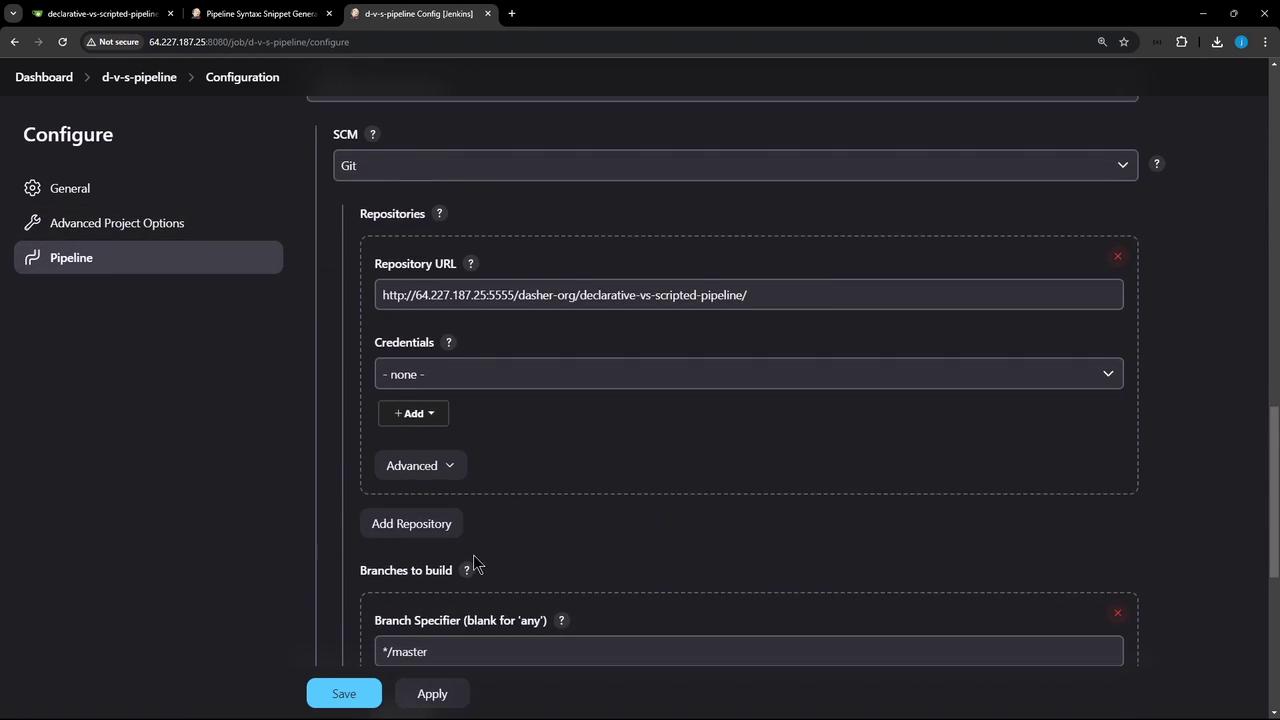
- Under Pipeline → Definition, choose Pipeline script from SCM.
- Enter your Git Repository URL, credentials (if any), and branch
demo-1. - In Script Path, set
Jenkinsfile.declarative. - Save and click Build.
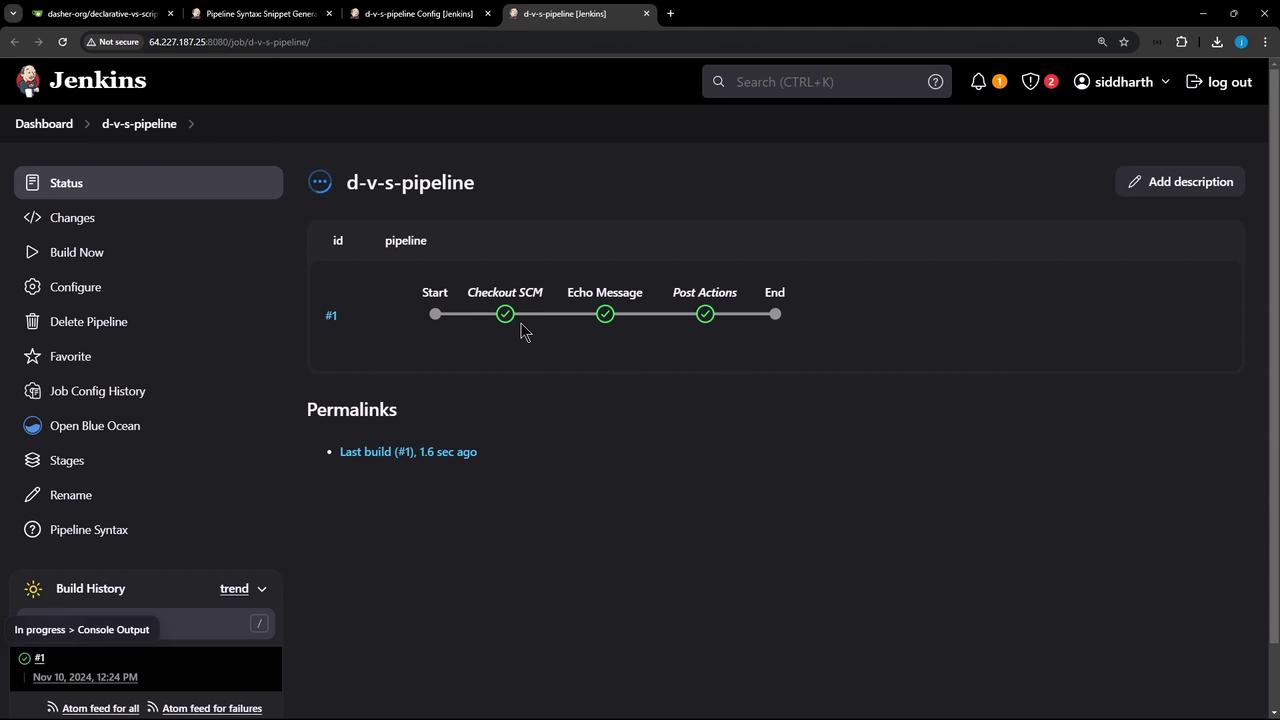
3. Running the Declarative Pipeline
After the build starts, you’ll see these stages:- Declarative: Checkout SCM (automatic)
- Echo Message
- Declarative: Post Actions
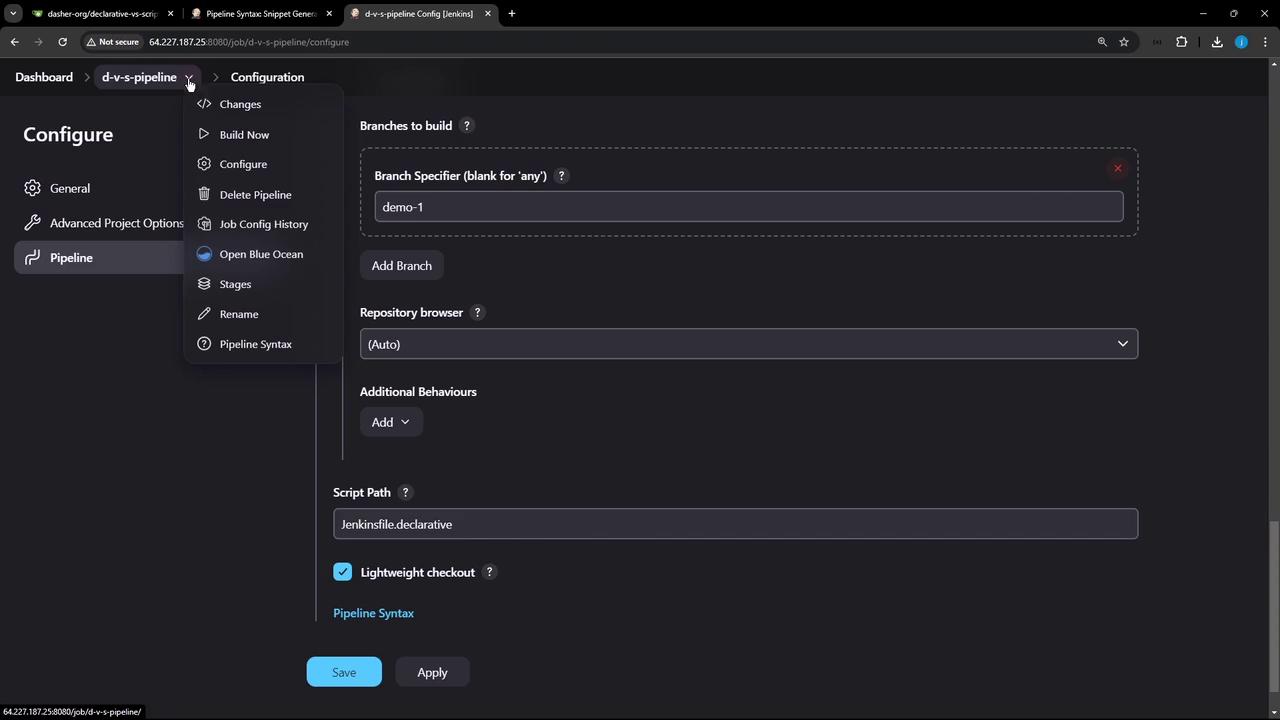
4. Switch to the Scripted Pipeline
- Return to Configure.
- Change Script Path to
Jenkinsfile.scripted. - Save and Build.
5. Add Checkout to Scripted Pipeline
Edit Jenkinsfile.scripted to includecheckout scm inside the stage:

Summary of Differences
| Feature | Declarative Pipeline | Scripted Pipeline |
|---|---|---|
| SCM Handling | Implicit checkout scm | Requires manual checkout scm |
| Post-/Cleanup Actions | Built-in post {} blocks | try/catch/finally in Groovy |
| Stage Restart | Supported out of the box | Not supported |
| Syntax | Simplified, YAML-like structure | Full Groovy with scripting power |