1. Assigning a Static Agent
By default, a Scripted Pipeline executes on the Jenkins controller when no agent label is specified. To delegate it to a static node:- Open your Jenkins dashboard and locate the agent you want to use.
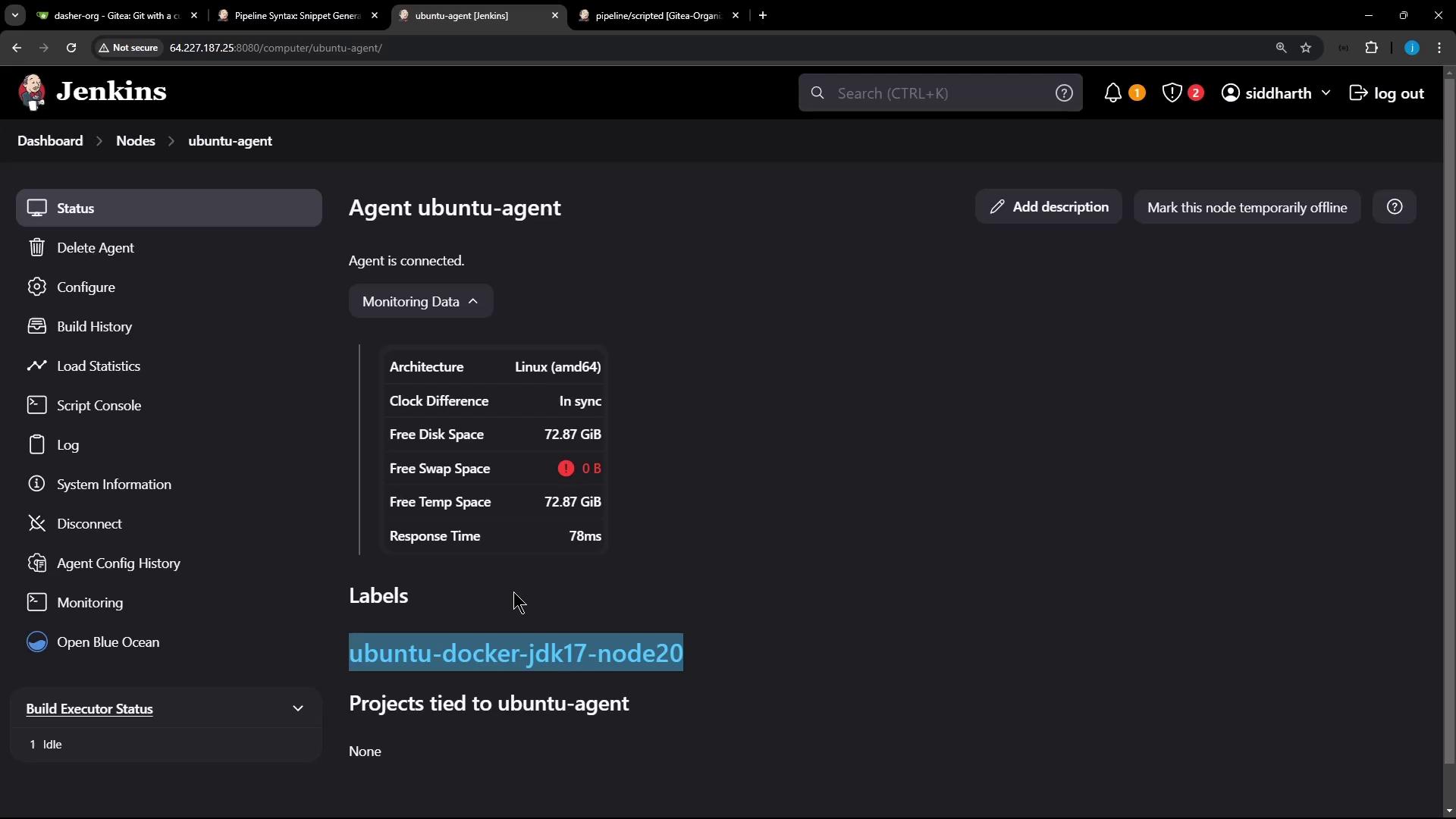
- Copy its label—in this example,
Ubuntu-Docker-JDK-17-node20.
node block with that label:
Ensure your static agent has Docker, JDK, and any required tools installed before running the pipeline.
2. Adding a Unit Test Stage with MongoDB Credentials
We’ll introduce a Unit Testing stage that runsnpm test. Since these tests connect to MongoDB, we inject credentials at runtime using Jenkins’ withCredentials.
- Navigate to Pipeline Syntax in Jenkins.
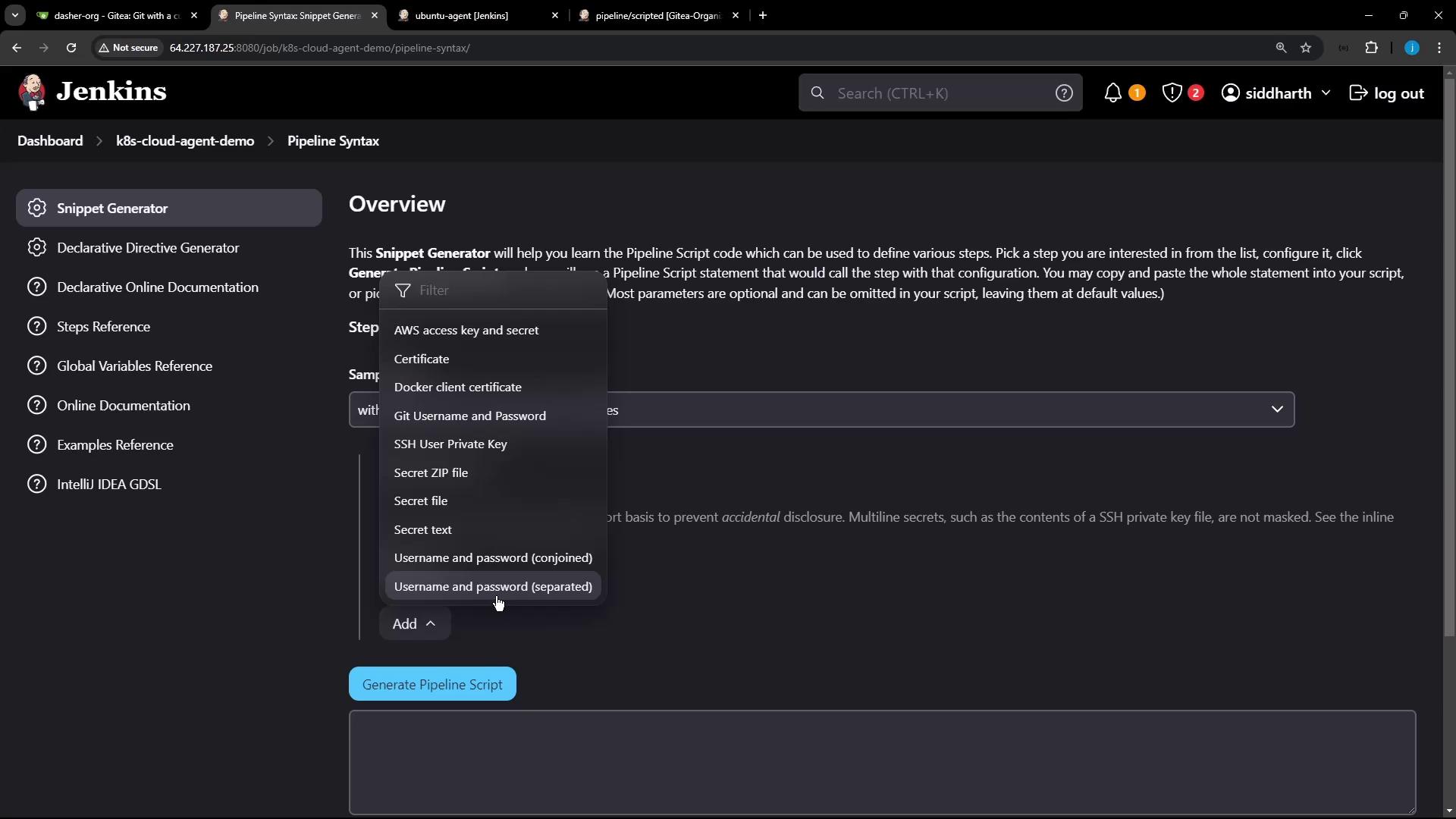
- Open the Snippet Generator.
- Select withCredentials: Username and password (separated).
- Enter:
- Credential ID:
mongo-db-creds - Username Variable:
MONGO_USERNAME - Password Variable:
MONGO_PASSWORD
- Credential ID:
3. Complete Jenkinsfile
Below is the fullJenkinsfile that checks out the code, installs dependencies, and runs unit tests with MongoDB credentials:
Jenkinsfile, commit and push it to a new branch:
4. Verifying the Build
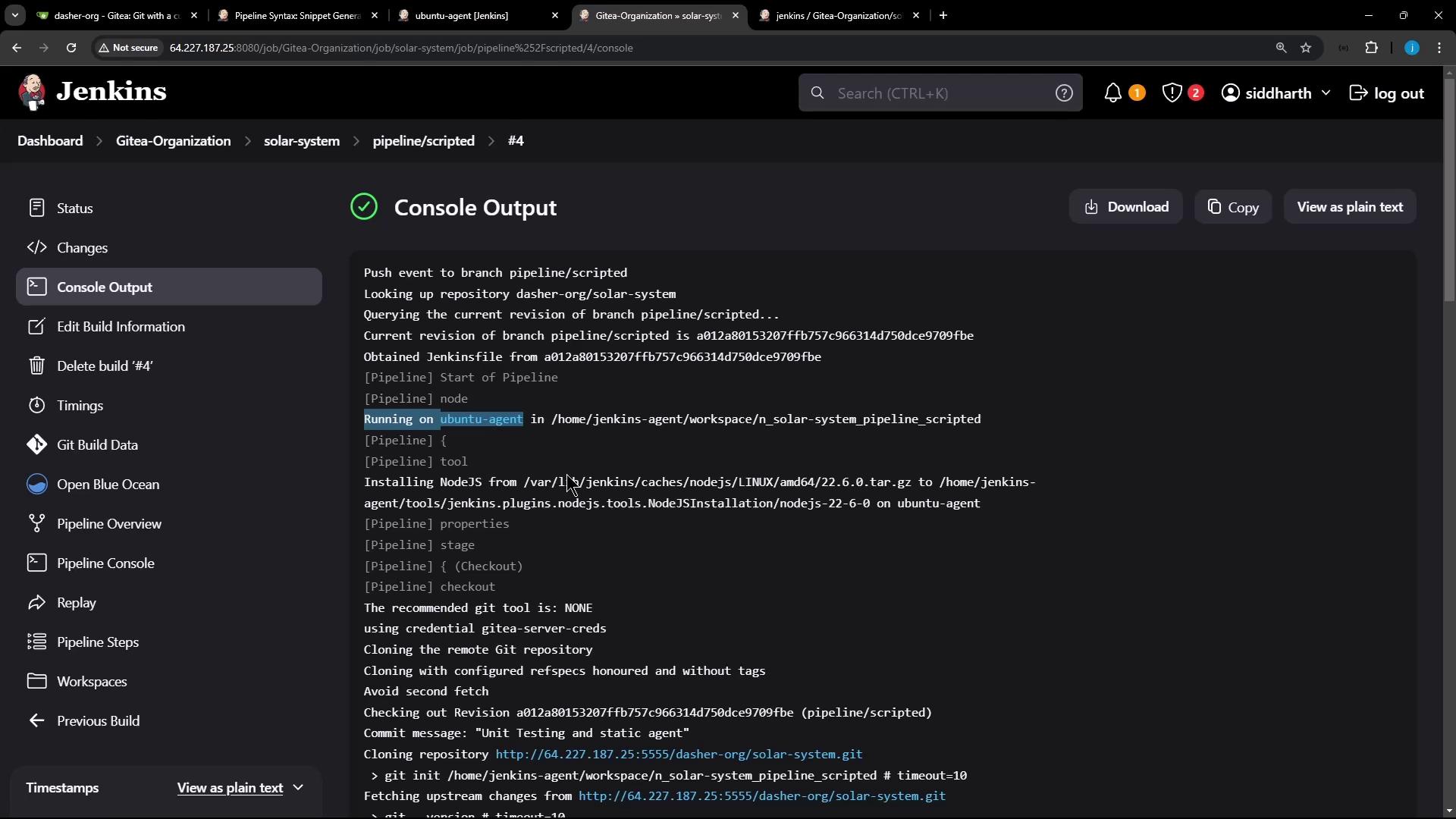
Once the branch is pushed, Jenkins automatically triggers the pipeline. In Blue Ocean, you’ll see each stage execute on the specified Ubuntu agent: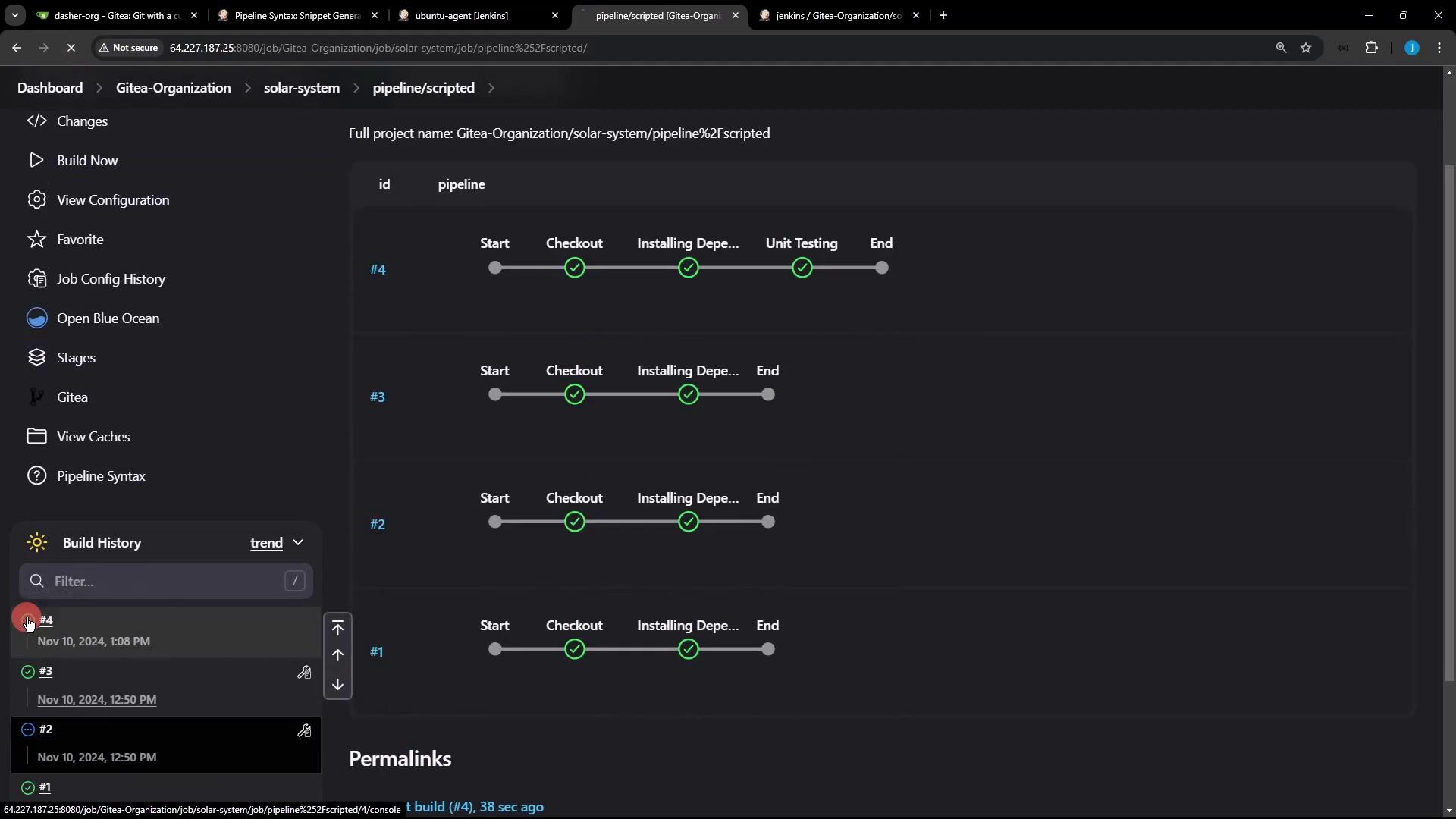
Pipeline Stages Summary
| Stage | Purpose | Command |
|---|---|---|
| Checkout | Clone source code from SCM | checkout scm |
| Install Dependencies | Install npm modules | sh 'npm install' |
| Unit Testing | Run tests using injected MongoDB creds | sh 'npm test' |