Advanced Jenkins
Shared Libraries in Jenkins
Loading the Shared Library in Pipeline
This guide demonstrates how to replace inline methods with a centrally managed Shared Library in Jenkins. By loading common steps—like Slack notifications—from a library, you simplify maintenance, enforce consistency, and version your pipeline logic.
Prerequisites
- Jenkins instance with Global Pipeline Libraries configured
- Access to the Git repository hosting your shared library
- Slack Plugin installed and a valid Slack bot token
Verify that your library appears under Manage Jenkins » Configure System » Global Pipeline Libraries:
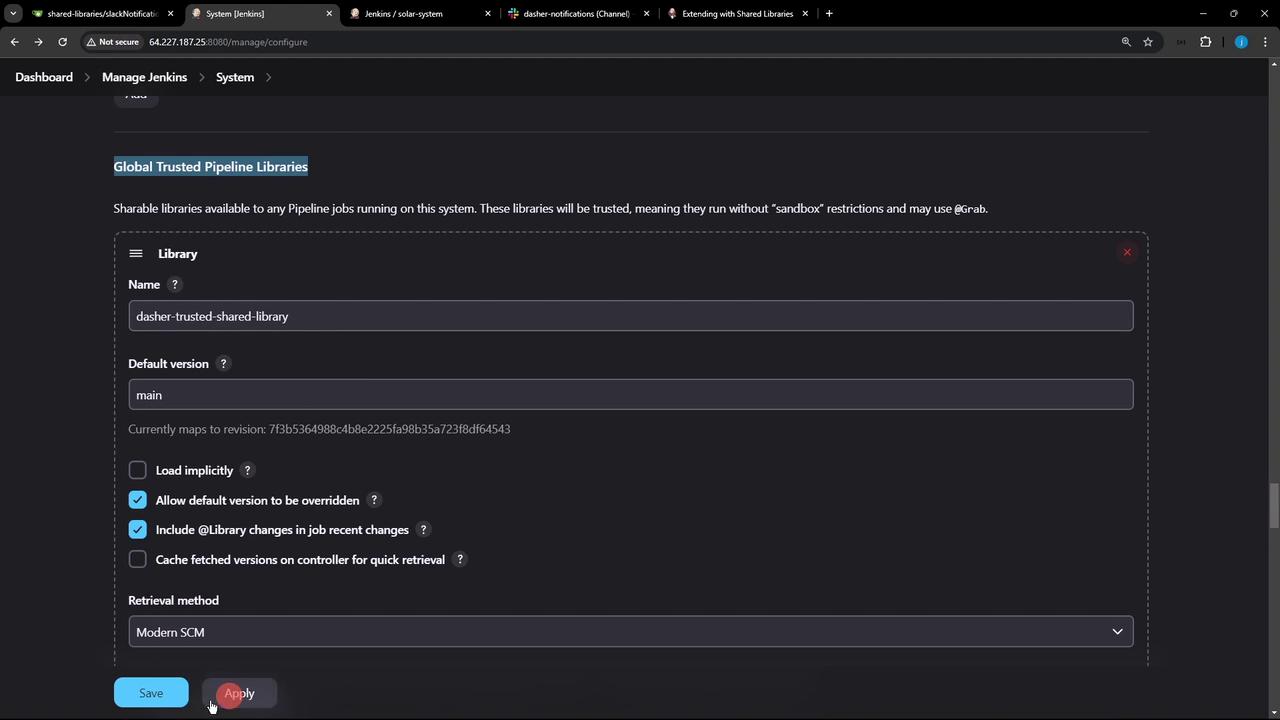
After you save and refresh, Jenkins connects to your Git repo and displays the commit ID from the default branch—confirming connectivity.
1. Inline Slack Notification (Before)
In a typical Jenkinsfile, you might define a slackNotificationMethod inline:
def slackNotificationMethod(String buildStatus = 'STARTED') {
buildStatus = buildStatus ?: 'SUCCESS'
def color = (buildStatus == 'SUCCESS') ? '#47ec05' :
(buildStatus == 'UNSTABLE') ? '#d5ee0d' :
'#ec2805'
def msg = "${buildStatus}: '${env.JOB_NAME}' #${env.BUILD_NUMBER}\n${env.BUILD_URL}"
slackSend(color: color, message: msg)
}
pipeline {
agent any
stages {
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'npm install --no-audit'
}
}
}
post {
always {
slackNotificationMethod()
}
}
}
Drawbacks of Inline Methods
- Duplication across multiple Jenkinsfiles
- Harder to maintain and version
- Inconsistent behavior if modified in one pipeline only
2. Switching to the Shared Library
Replace the inline function by adding the @Library annotation at the top of your Jenkinsfile:
@Library('dasher-trusted-shared-library') _
pipeline {
agent any
tools {
// ...
}
environment {
MONGO_URI = "mongodb+srv://supercluster.d83jj.mongodb.net/superData"
MONGO_DB_CREDS = credentials('mongo-db-credentials')
MONGO_USERNAME = credentials('mongo-db-username')
MONGO_PASSWORD = credentials('mongo-db-password')
SONAR_SCANNER_HOME = tool 'sonarqube-scanner-6'
GITEA_TOKEN = credentials('gitea-api-token')
}
options {
// ...
}
stages {
stage('Install Dependencies') {
steps {
sh 'npm install --no-audit'
}
}
}
post {
always {
// Delegates to vars/slackNotification.groovy in the shared library
slackNotification()
}
}
}
Note
The underscore (_) after @Library('…') completes the annotation syntax but doesn’t affect runtime behavior.
Environment Variables Reference
| Variable | Description | Source |
|---|---|---|
| MONGO_URI | MongoDB connection string | Hardcoded |
| MONGO_DB_CREDS | MongoDB credentials (ID and secret) | mongo-db-credentials |
| MONGO_USERNAME | MongoDB username (secret text) | mongo-db-username |
| MONGO_PASSWORD | MongoDB password (secret text) | mongo-db-password |
| SONAR_SCANNER_HOME | SonarQube Scanner installation directory | Jenkins Tool |
| GITEA_TOKEN | API token for Gitea | gitea-api-token |
Warning
Always store sensitive data—like database credentials or API tokens—as Jenkins Credentials.
Never hardcode secrets directly in your Jenkinsfiles.
3. Shared Library Implementation
In your shared library repository, under vars/slackNotification.groovy, define the call method Jenkins will load:
// vars/slackNotification.groovy
def call(String buildStatus = 'STARTED') {
buildStatus = buildStatus ?: 'SUCCESS'
def color = (buildStatus == 'SUCCESS') ? '#47ec05' :
(buildStatus == 'UNSTABLE') ? '#d5ee0d' :
'#ee2805'
def msg = "${buildStatus}: '${env.JOB_NAME}' #${env.BUILD_NUMBER}\n${env.BUILD_URL}"
slackSend(color: color, message: msg)
}
This single implementation is now reusable across any pipeline that loads the library.
4. Triggering and Verifying the Build
After committing your updated Jenkinsfile on the feature/advanced-demo branch, Jenkins will detect the change and queue a new build:
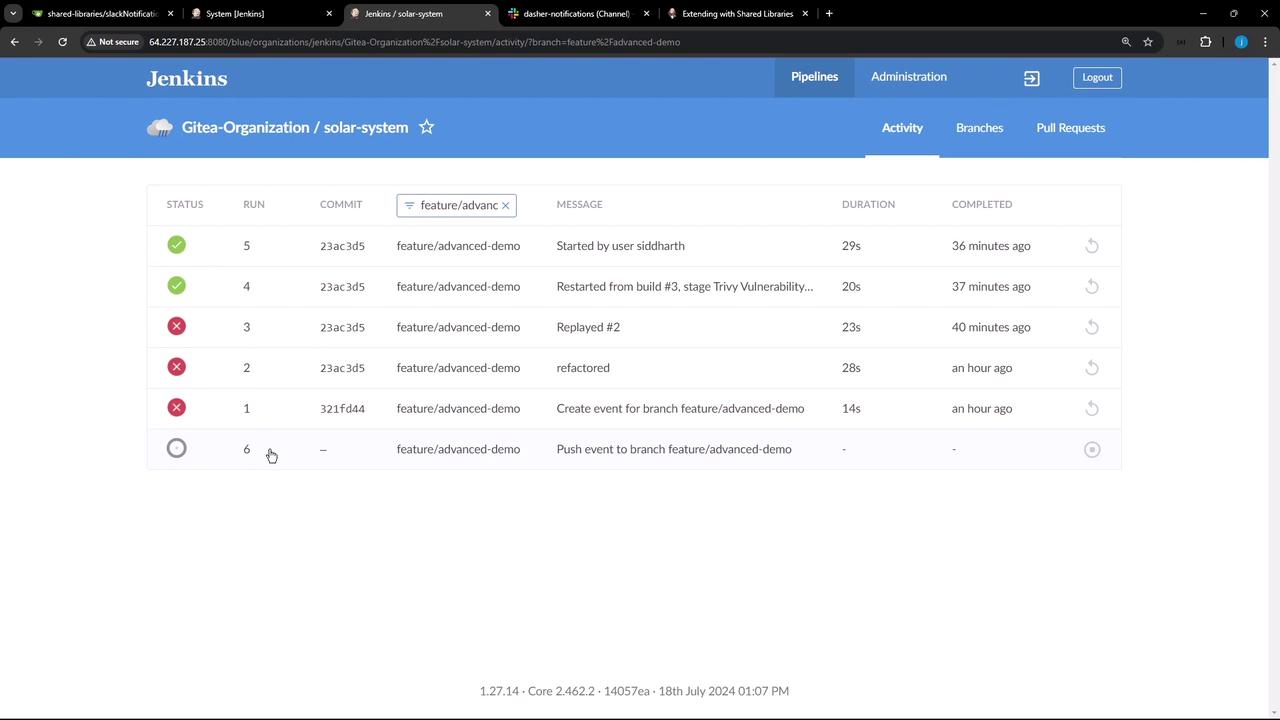
The pipeline runs successfully and posts a notification to Slack for build #6.
5. Confirming Library Loading in Console
To see how Jenkins fetches and loads your shared library, review the classic console output and filter for library:
> git ls-remote -h http://64.227.187.25:5555/dasher-org/shared-libraries # timeout=10
> git init /var/lib/jenkins/workspace/feature/advanced-demo/libs/dasher-org/shared-libraries
[Pipeline] library
Loading library dasher-trusted-shared-library @ main from http://64.227.187.25:5555/dasher-org/shared-libraries
> git fetch --no-tags --force --progress -- http://64.227.187.25:5555/dasher-org/shared-libraries +refs/heads/main:refs/remotes/dasher-org/shared-libraries/main
Later in the log, you’ll see the Slack step using values defined in the library:
Slack Send Pipeline step running, values are -
baseUrl: <empty>,
teamDomain: Jenkins,
channel: dasher-notifications,
color: #47ec05,
botUser: true,
tokenCredentialId: slack-bot-token,
notifyCommitters: false
Conclusion
By centralizing common pipeline logic in Jenkins Shared Libraries, you:
- Reduce code duplication
- Simplify maintenance and updates
- Manage multiple library versions via Git branches or tags
Now you can create additional reusable steps or even combine multiple libraries for more complex workflows.
References
Watch Video
Watch video content