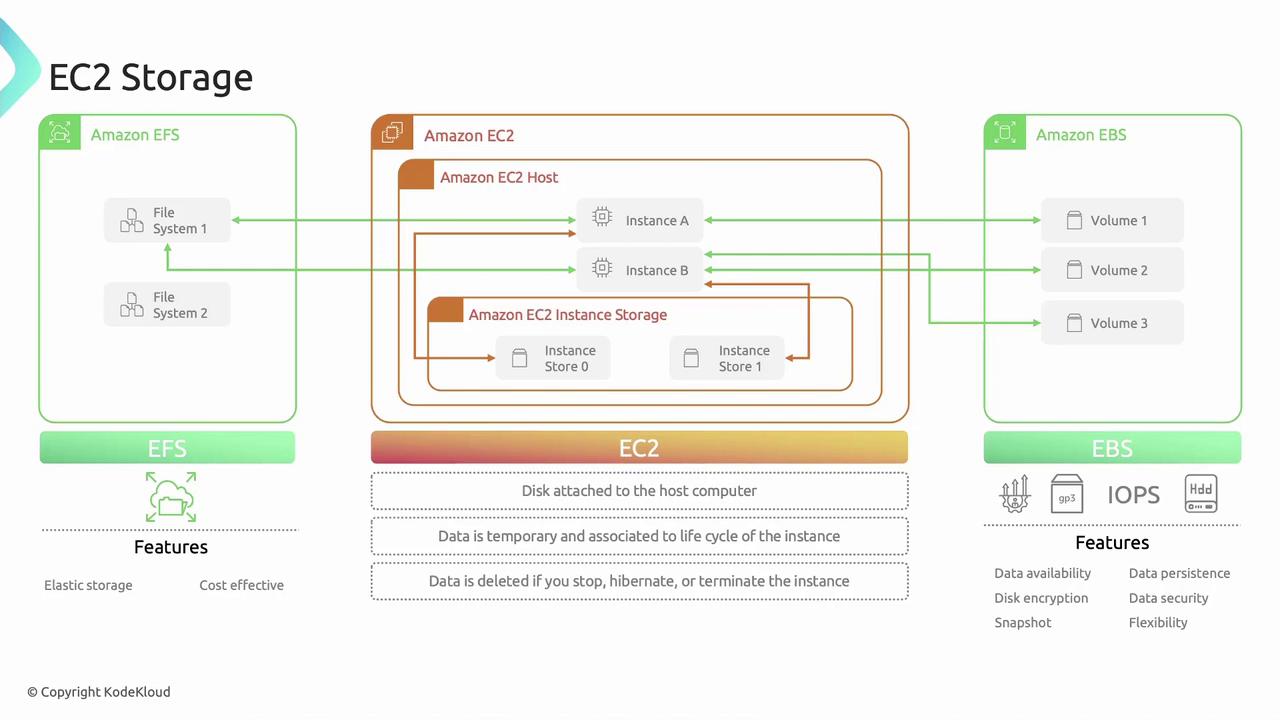
- Instance Store
- Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
- Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
1. Instance Store
Instance Store volumes are temporary, high-performance disks physically attached to the host server. They deliver very low-latency I/O but are ephemeral.Data on an Instance Store is lost if the instance stops, hibernates, or terminates. Use it only for non-persistent workloads.
- Ephemeral storage tied to instance lifecycle
- Ideal for scratch data, buffers, and caches
- Automatic deletion on stop/terminate (reboot retains data)
- Temporary caches (e.g., in-memory databases, processing buffers)
- Scratch disks for big data workloads
- High-speed swap or buffer space
2. Amazon Elastic File System (EFS)
Amazon EFS is a fully managed, elastic NFS file system that can be mounted concurrently by multiple EC2 instances across Availability Zones.EFS scales automatically—you pay only for the storage you consume.
- Elastic capacity: grows and shrinks as you add or remove files
- Shared access: mount the same file system on multiple instances
- Fully managed: AWS handles provisioning, patching, and maintenance
- Supports NFSv4.1 and NFSv4.2 protocols
- Web serving and content management
- Shared development or build environments
- Data science, analytics, and media workflows
3. Amazon Elastic Block Store (EBS)
Amazon EBS offers persistent, block-level storage that you can attach to a single EC2 instance at a time. Volumes behave like raw block devices you can format, mount, and use as you would an on-premises disk.| Volume Type | Use Case | Throughput/IOPS |
|---|---|---|
| General Purpose SSD | Balanced price/performance (web servers, apps) | Up to 16,000 IOPS (gp3) |
| Provisioned IOPS SSD | I/O-intensive databases (Oracle, SQL Server) | Up to 256,000 IOPS |
| Throughput Optimized HDD | Large, sequential workloads (big data, logs) | Up to 500 MB/s |
| Cold HDD | Infrequently accessed data (archival, backups) | Up to 250 MB/s |
- Data Persistence: volumes persist independently of the EC2 instance
- High Availability: data is replicated within the same AZ to prevent hardware failures
- Encryption: AES-256 at rest and in transit (managed with AWS KMS)
- Snapshots: create point-in-time backups stored in Amazon S3
- Dynamically adjustable: modify size, volume type, and IOPS without detaching
Storage Comparison at a Glance
| Feature | Instance Store | EBS | EFS |
|---|---|---|---|
| Persistence | Ephemeral | Persistent (AZ-level replica) | Persistent (region-wide) |
| Performance | Very high IOPS | High IOPS / throughput | Scalable throughput |
| Protocol | Direct-attached disk | iSCSI block device | NFSv4 |
| Shared Access | No | Single instance per volume | Multiple instances concurrently |
| Best for | Scratch, caches | Databases, boot volumes | Shared file storage, home directories |