- Deleting an object (e.g.,
file1.txt) removes it permanently. - Uploading a new object with the same key (e.g.,
file5.txt) overwrites the existing object, making any previous data unrecoverable.
Bucket Versioning States
You can configure versioning at the bucket level. An S3 bucket exists in one of three states:| State | Description |
|---|---|
| Unversioned | Versioning is disabled (default). New uploads overwrite existing objects without version IDs. |
| Enabled | All new and updated objects receive unique version IDs. |
| Suspended | Existing versions stay intact; new uploads behave like an unversioned bucket (null version ID). |
Enabling Versioning and Managing Object Version IDs
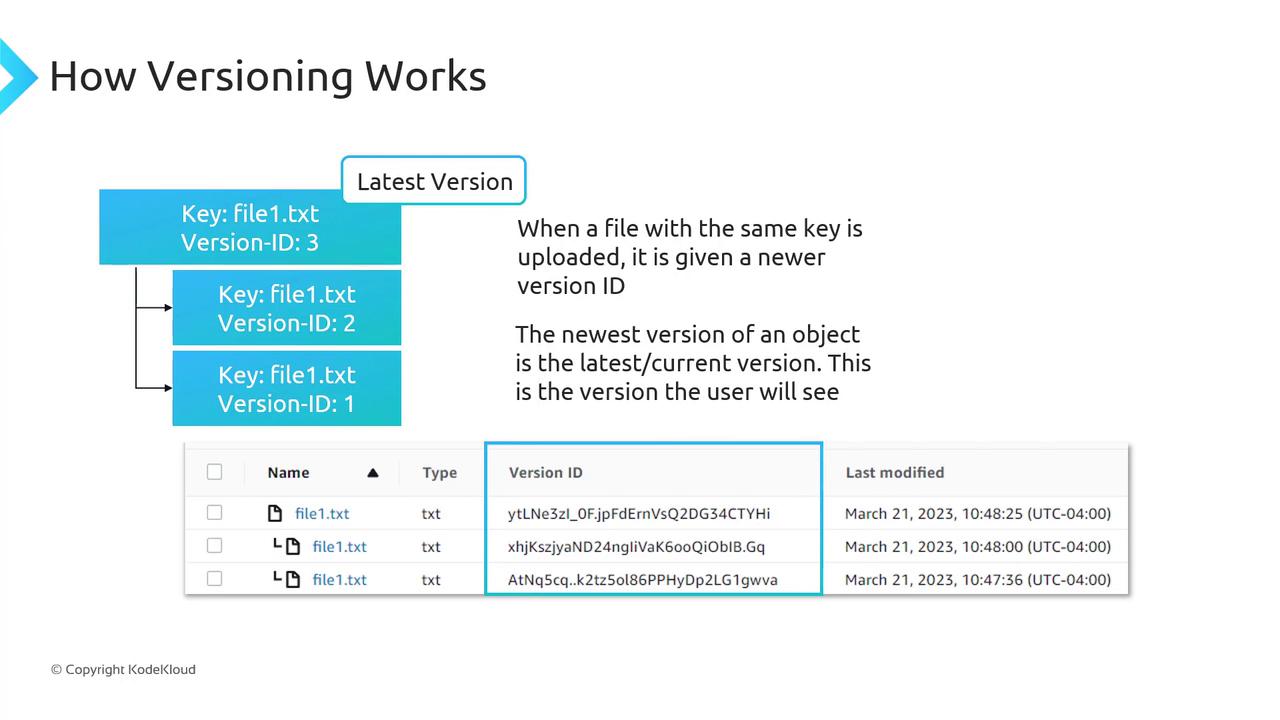
When versioning is Enabled:- The first upload of
file1.txtmight get version ID1. - Re-uploading the same key creates version ID
2, preserving version1. - A third upload assigns version ID
3, and so on.
versionId returns this version.
Enabling Versioning via Console and CLI
Console:- Open the S3 console.
- Select your bucket → Properties → Bucket Versioning → Enable → Save.
A GET or LIST operation on an unversioned bucket always shows
VersionId: null.Delete Markers
With versioning enabled, deleting an object without specifying a version ID does not remove its data. Instead, S3 inserts a delete marker, which becomes the current version and hides previous versions.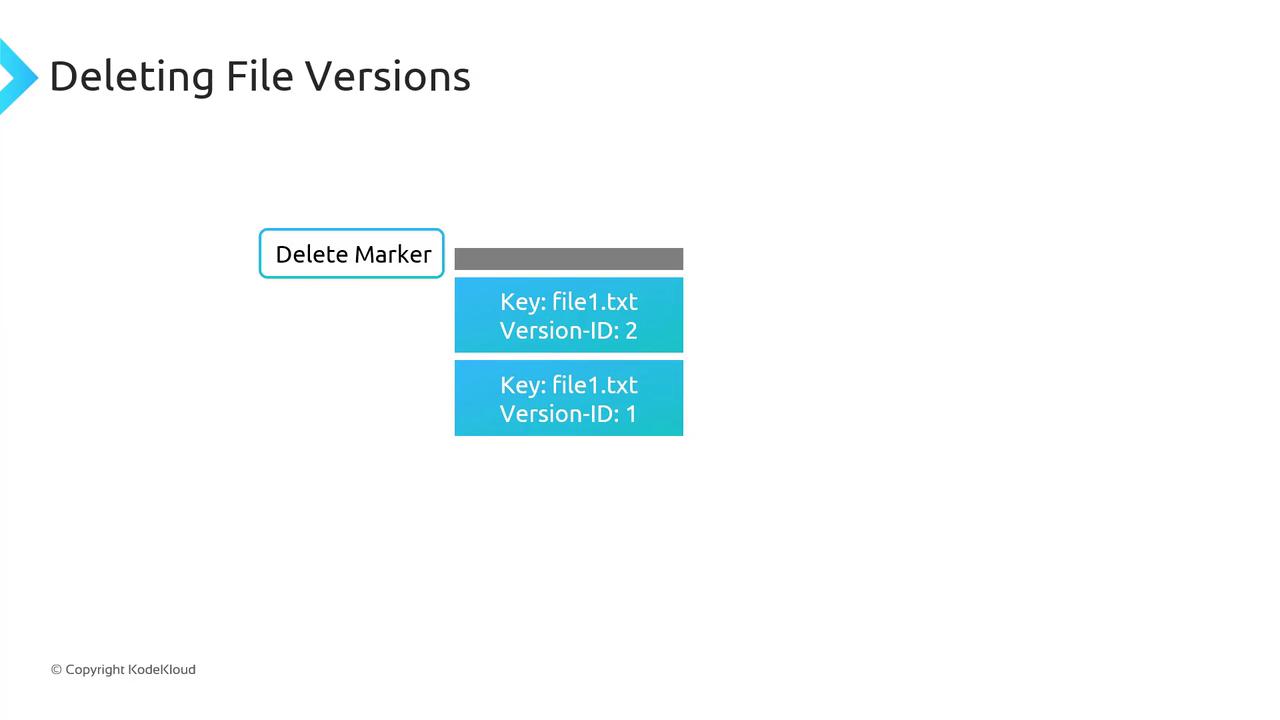
- To undelete, remove the delete marker; the next latest version immediately becomes current.
- To remove a specific version (e.g., version
2offile1.txt), delete that version ID directly—other versions remain intact.
Pricing Considerations
Every version of an object counts towards your storage usage. You pay for the sum of all versions:| Version | Size |
|---|---|
| Version 1 of file1.txt | 10 GB |
| Version 2 of file1.txt | 15 GB |
| Total billable | 25 GB |
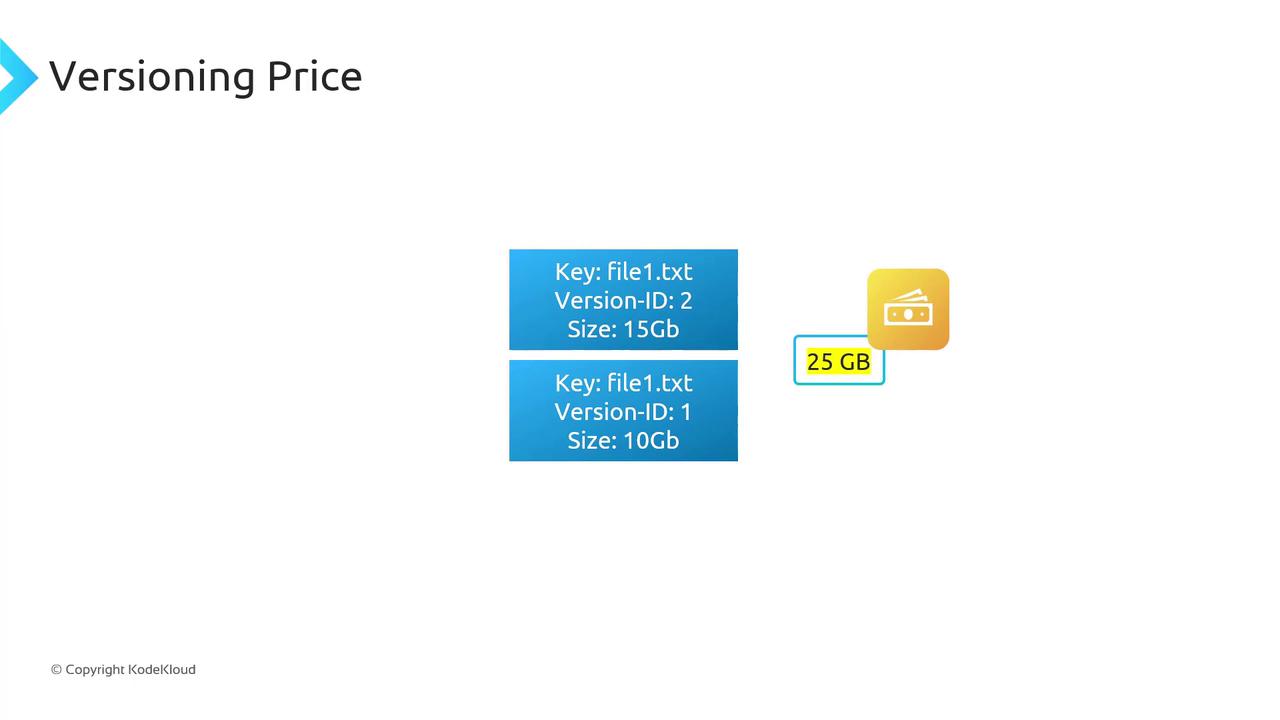
Enabling versioning can significantly increase your storage costs. Implement Lifecycle rules to expire or transition older versions to cheaper storage classes.
Suspending Versioning
When you suspend versioning on a bucket:- Existing object versions remain stored.
- New uploads receive a
nullversion ID and overwrite objects as in an unversioned bucket.
MFA Delete
Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA) Delete adds a security layer for versioning-related operations:- Changing the bucket’s versioning state (Enabled/Suspended) requires MFA.
- Permanently deleting object versions also requires MFA.
MFA Delete is only configurable via the AWS CLI.
