Azure Kubernetes Service
AKS Security
Azure Policy for AKS
Before diving into Azure Policy for Azure Kubernetes Service (AKS), let's review Azure Policy fundamentals: what it is, why it exists, and how to use it.
As enterprises deploy resources in Azure, they need to enforce organizational requirements—such as restricting deployments by region or controlling VM types. Common scenarios include:
- Ensuring business-critical applications remain in Australia for data-residency compliance.
- Preventing AKS clusters from using costly GPU-enabled VMs.
Azure Policy enables you to define and apply governance and compliance rules at scale. It uses JSON-based definitions to validate resource configurations during provisioning and continuously audit existing resources.
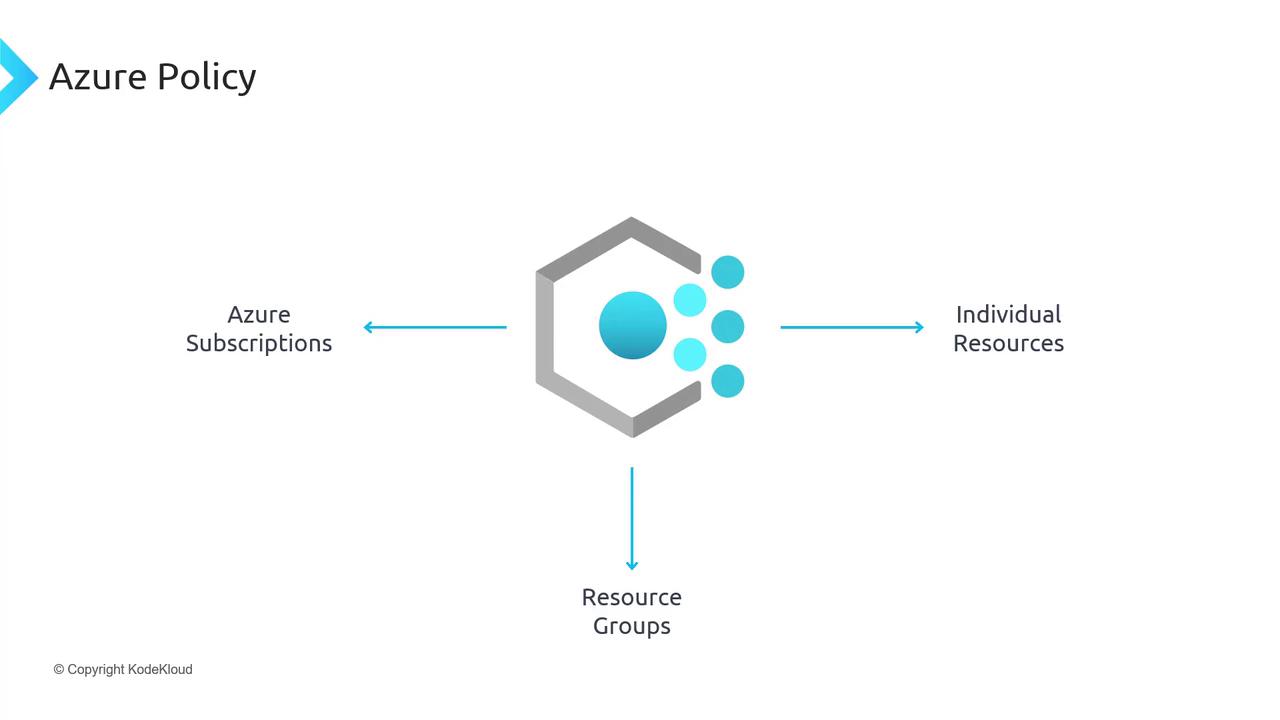
You can scope policies to subscriptions, resource groups, or individual resources, ensuring a consistent security posture across your Azure estate.
By enforcing policies, you reduce misconfiguration risks and maintain compliance with internal and external standards.
Assigning a Built-in Policy to Restrict AKS Deployments by Location
To block AKS clusters outside Australia, use a built-in Azure Policy definition:
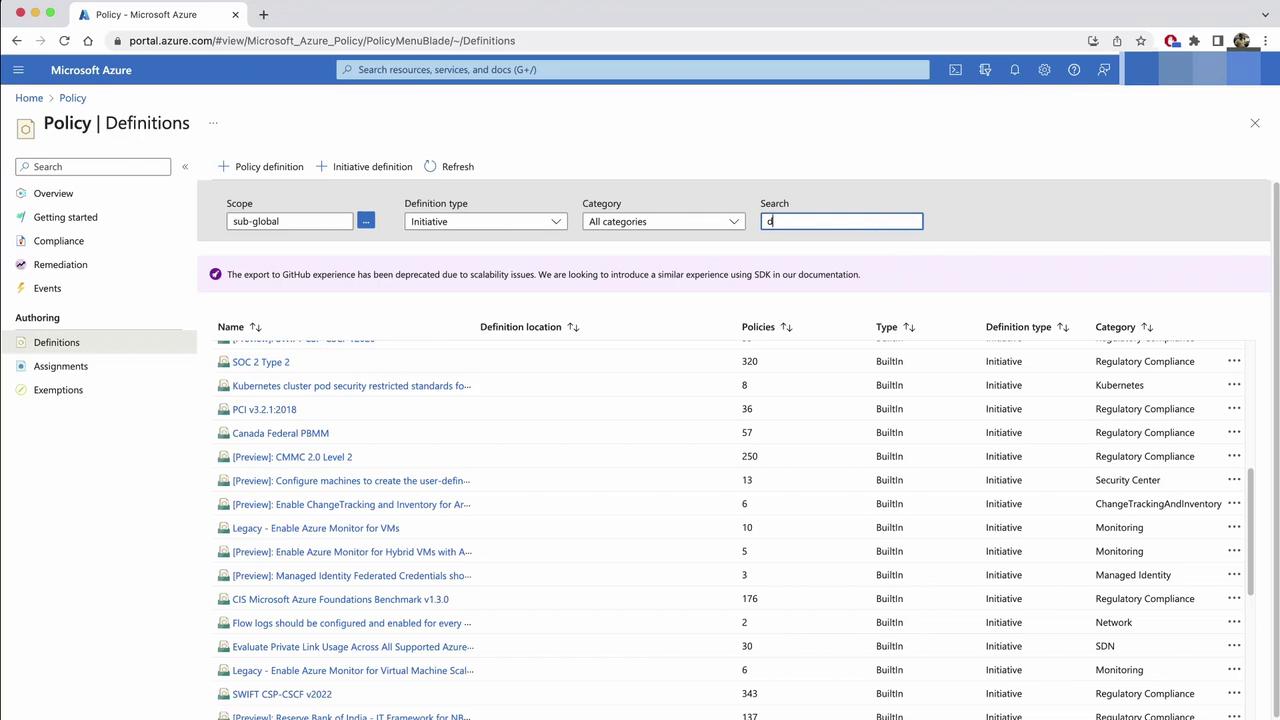
- In the Azure portal, navigate to Policy > Authoring > Definitions.
- Search for built-in definitions and filter by Type.

- Note the two definition types:
| Definition Type | Purpose |
|---|---|
| Policy | Single rule to enforce or audit (e.g., allowed locations) |
| Initiative | Logical grouping of multiple policies (e.g., AKS governance suite) |
- Find Allowed locations and click Assign.
- On the Assignment tab, set your subscription as the scope and click Next.
- (Optional) Under Advanced, exclude specific resource types if needed.
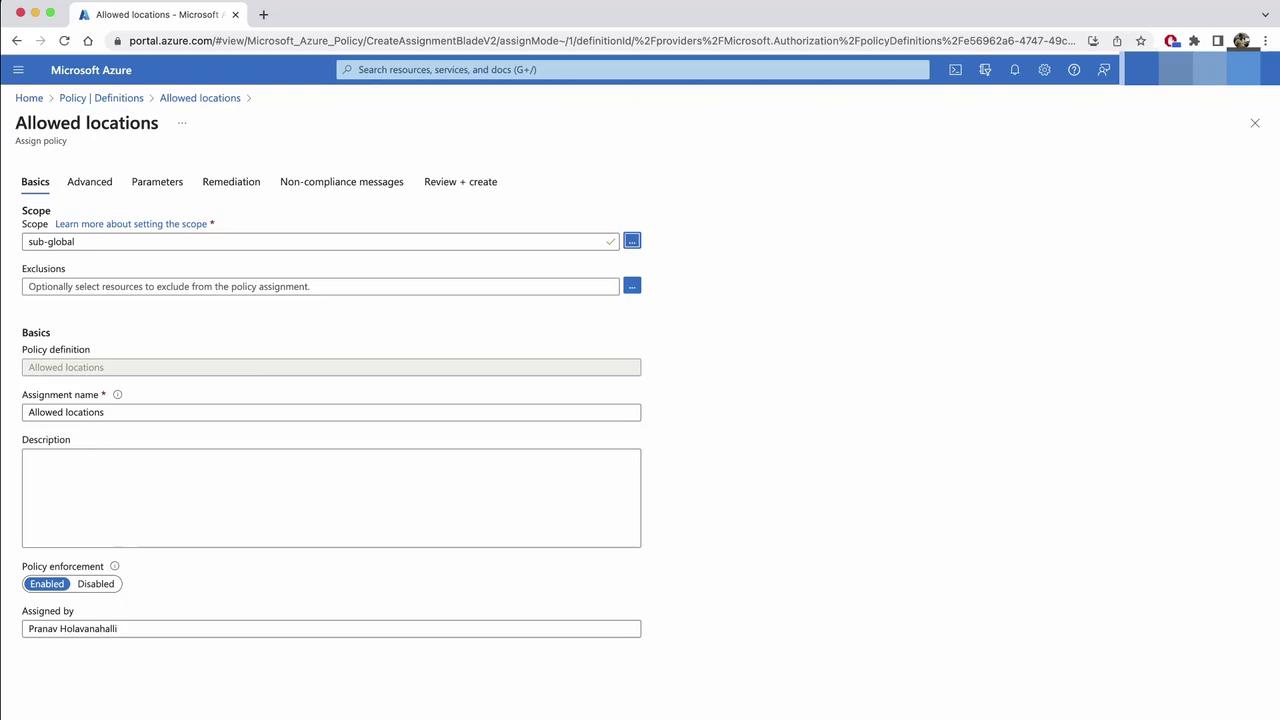
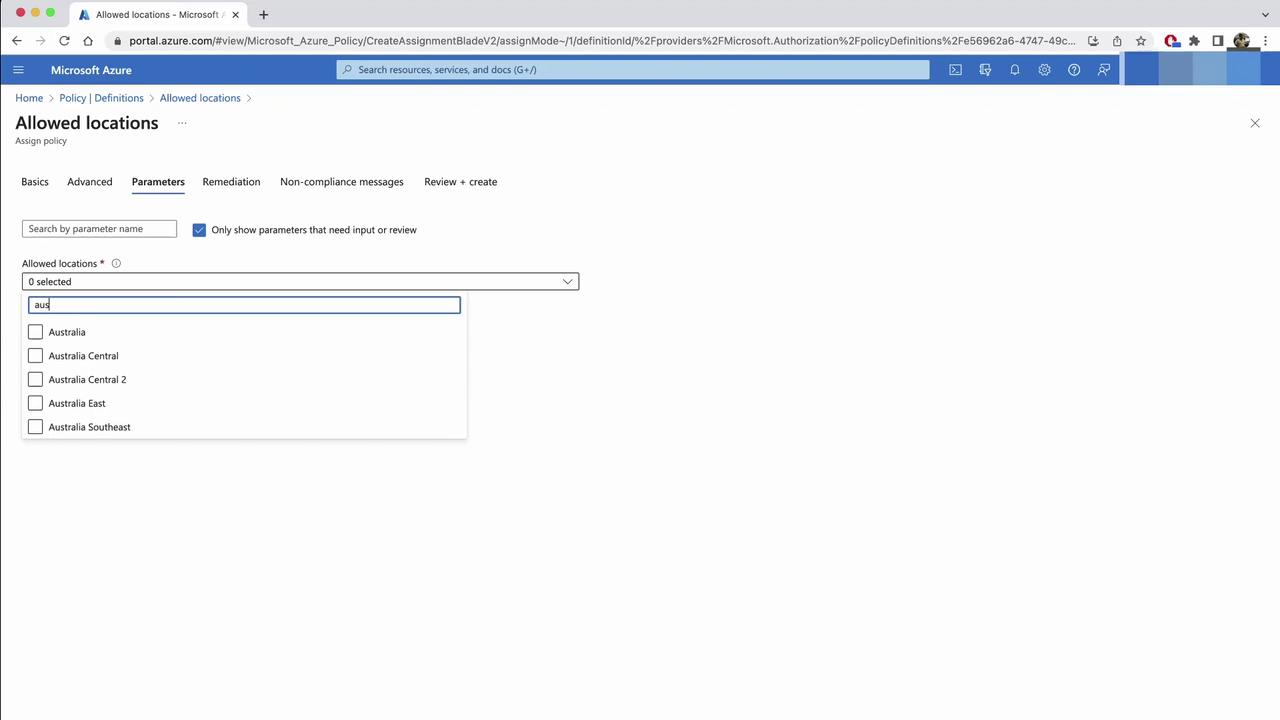
- In Parameters, pick
Australia EastandAustralia Southeast. Resources outside these regions will be denied.
Warning
If you enable Remediation, Azure Policy may move or delete non-compliant resources. Review potential impacts before proceeding.
- Optionally, configure Remediation to correct existing resources, then add a custom message and click Create.
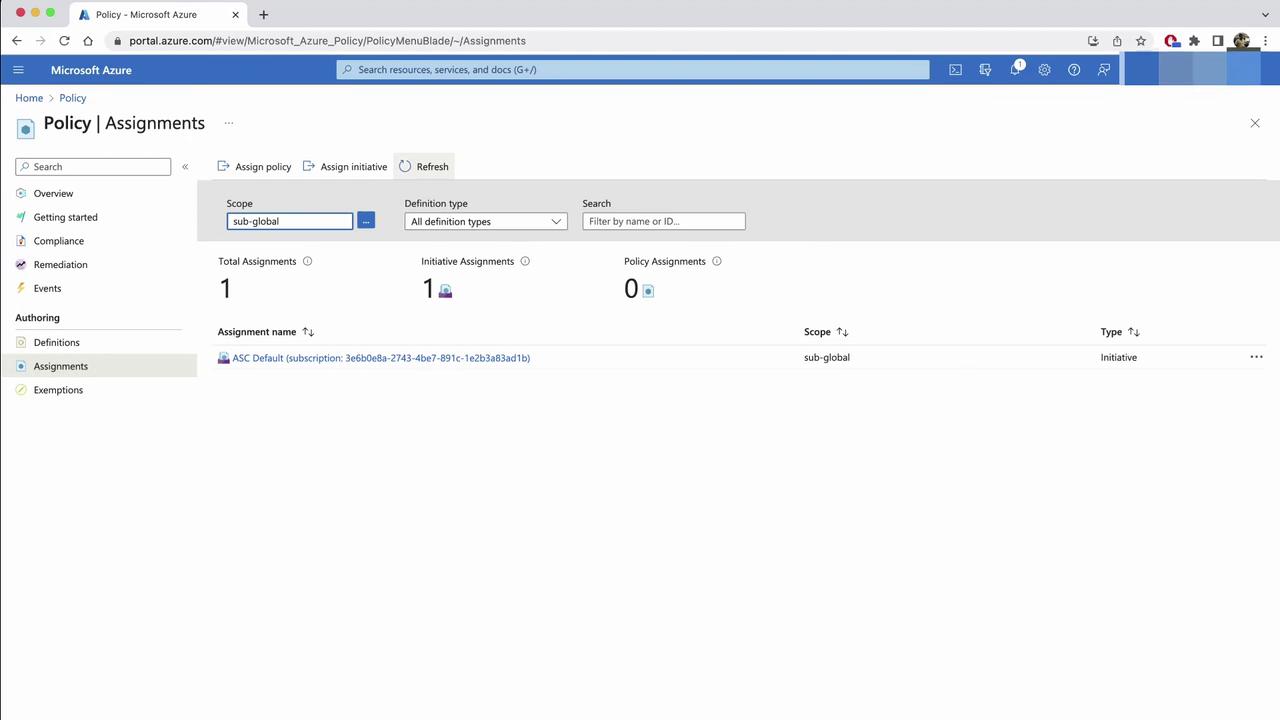
- Return to Policy > Assignments and refresh to confirm your new control.
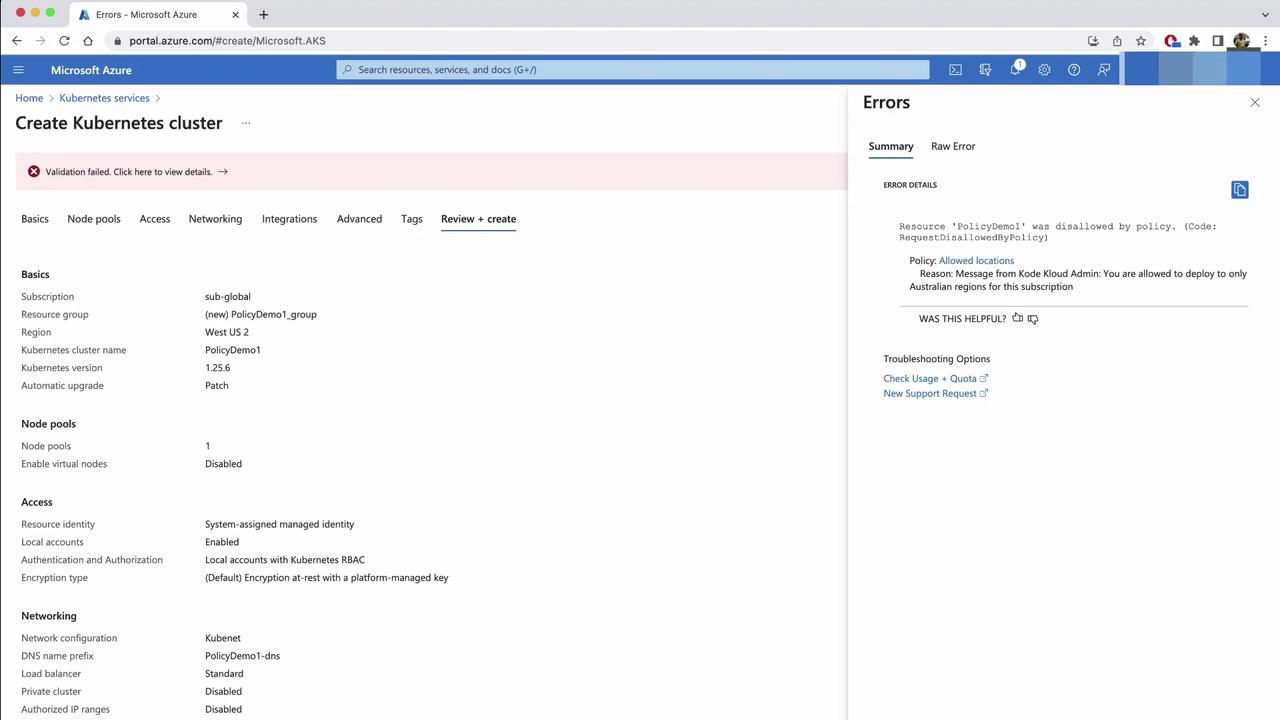
Testing the Location Policy
Attempt to create an AKS cluster in East US:
- In the Create a Kubernetes cluster wizard, select East US, then Review + create.
- The deployment will fail with your custom message.
Extending Governance Inside AKS with OPA & Gatekeeper
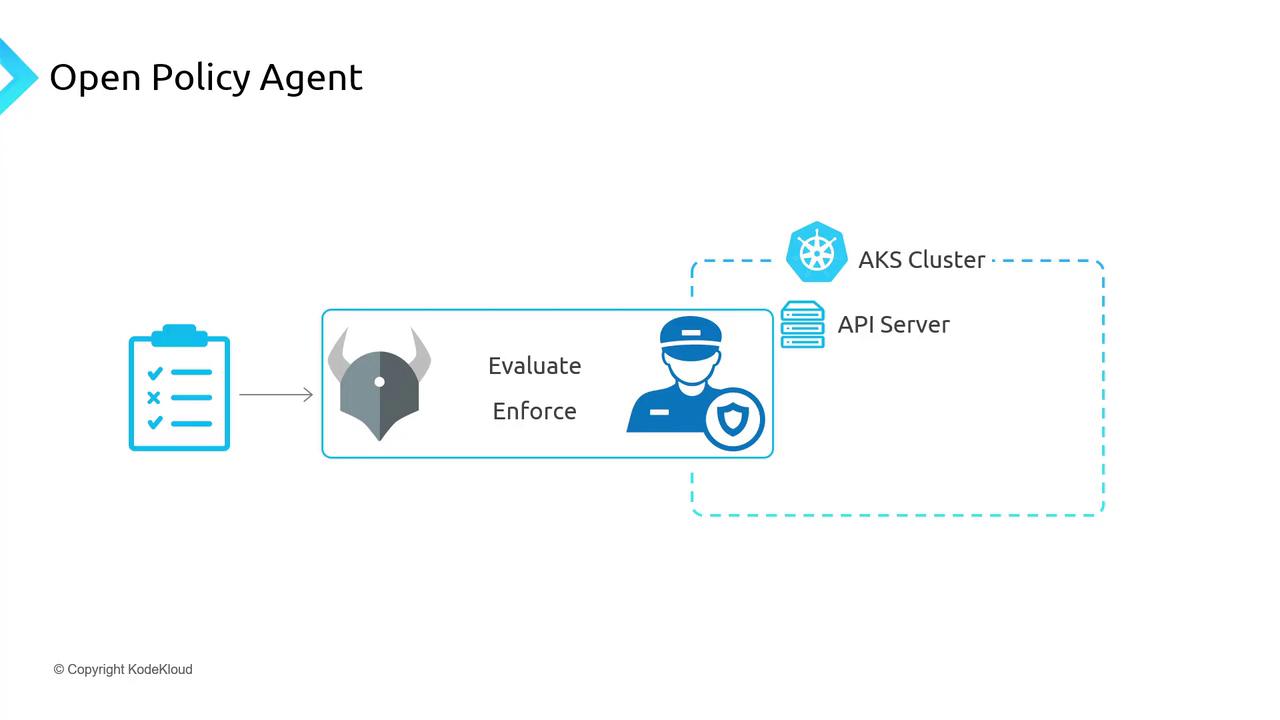
Azure Policy enforces resource-level rules but doesn’t inspect workloads inside AKS. For cluster-native policy enforcement, integrate Open Policy Agent (OPA) with Gatekeeper:
- OPA: cloud-native policy engine.
- Gatekeeper: Kubernetes admission controller for OPA policies.
Gatekeeper intercepts API requests, applies policies, and rejects non-compliant objects.
Enabling the Azure Policy Add-on in AKS
To deploy OPA Gatekeeper via Azure Policy:
- Create an AKS cluster—e.g.,
AKSPolicyDemo. - In the Azure portal, open the cluster’s Policies blade (initially disabled).
- From your CLI:
# Check if azure-policy add-on is enabled
az aks show \
--resource-group AKSPolicyDemo \
--name AKSPolicyDemo \
--query addonProfiles.azurepolicy
# Enable the Azure Policy add-on
az aks enable-addons \
--resource-group AKSPolicyDemo \
--name AKSPolicyDemo \
--addons azure-policy
This installs:
- An azure-policy deployment in
kube-system. - Gatekeeper pods in
gatekeeper-system.
Validate:
# Azure Policy components
kubectl get pods -n kube-system | grep policy
# Gatekeeper components
kubectl get pods -n gatekeeper-system
Example output:
# kube-system
azure-policy-58b80f747-lbkcn 1/1 Running 0 70s
azure-policy-webhook-rcf579d-4khjy 1/1 Running 0 70s
# gatekeeper-system
gatekeeper-audit-c99f9f6d-5mlqt 1/1 Running 0 99s
gatekeeper-controller-6d47b67cbc-xsgvd 1/1 Running 0 99s
gatekeeper-controller-6d47b67cbc-7g1lr 1/1 Running 0 99s
Enforcing Kubernetes-Native Policies
Next, apply a service-port policy:
- In Azure portal Policy > Definitions, search for Kubernetes clusters should only expose allowed ports on services.
- Click Assign, select scope, and set allowed ports to
80and443.
Deploy an NGINX service on port 80:
# KK-AKSPolicyDemo.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-allow-ports
spec:
type: ClusterIP
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 80
kubectl apply -f KK-AKSPolicyDemo.yaml
Works because port 80 is permitted. Next, try port 8080:
# KK-AKSPolicyDemo2.yaml
apiVersion: v1
kind: Service
metadata:
name: service-allow-port-8080
spec:
type: NodePort
selector:
app: nginx
ports:
- protocol: TCP
port: 8080
kubectl apply -f KK-AKSPolicyDemo2.yaml
Gatekeeper denies it:
Error from server (Forbidden): admission webhook "validation.gatekeeper.sh" denied the request:
[azurepolicy-k8sazurerv1serviceallowedports=...]
Port 8080 for service service-allow-port-8080 has not been allowed.
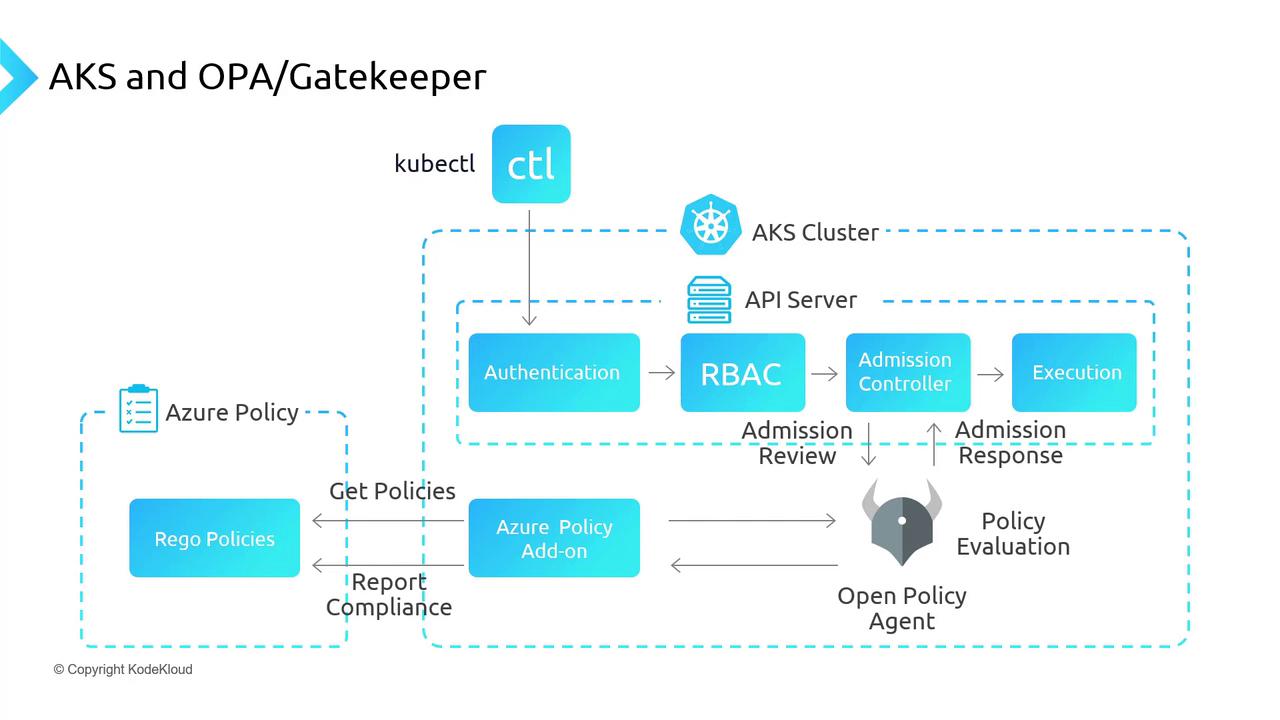
How Policy Enforcement Works
When the Azure Policy add-on is active, Gatekeeper syncs assignments every 15 minutes and integrates into the Kubernetes API flow:
- kubectl → API Server
- Authentication
- Authorization (RBAC)
- Admission Controllers (including Gatekeeper)
- Execution
Gatekeeper validates resource definitions against your policies before finalizing the operation.
Additional Resources
Watch Video
Watch video content