CKA Certification Course - Certified Kubernetes Administrator
Troubleshooting
Solution Application Failure
This document outlines a comprehensive troubleshooting session for a two-tier application deployed across several namespaces. The goal of each deployment is to display a green webpage upon successful connection. Throughout this session, we inspect environment variables, service configurations, deployment settings, and port mappings to systematically identify and resolve the issues. The following cases illustrate the debugging process in each namespace.
Case 1: Alpha Namespace
In the alpha namespace, although the UI loads, the application state shows as failed. The error message indicates:
Environment Variables: DB_Host=mysql-service; DB_Database=Not Set; DB_User=root; DB_Password=paswrd; 2003: Can't connect to MySQL server on 'mysql-service:3306' (-2 Name does not resolve)
This error suggests that the application is unable to resolve the MySQL service name. The architecture diagram below outlines the two-tier design. The web service listens on port 8080 and is exposed via NodePort 30081, requiring a connection to the MySQL service.
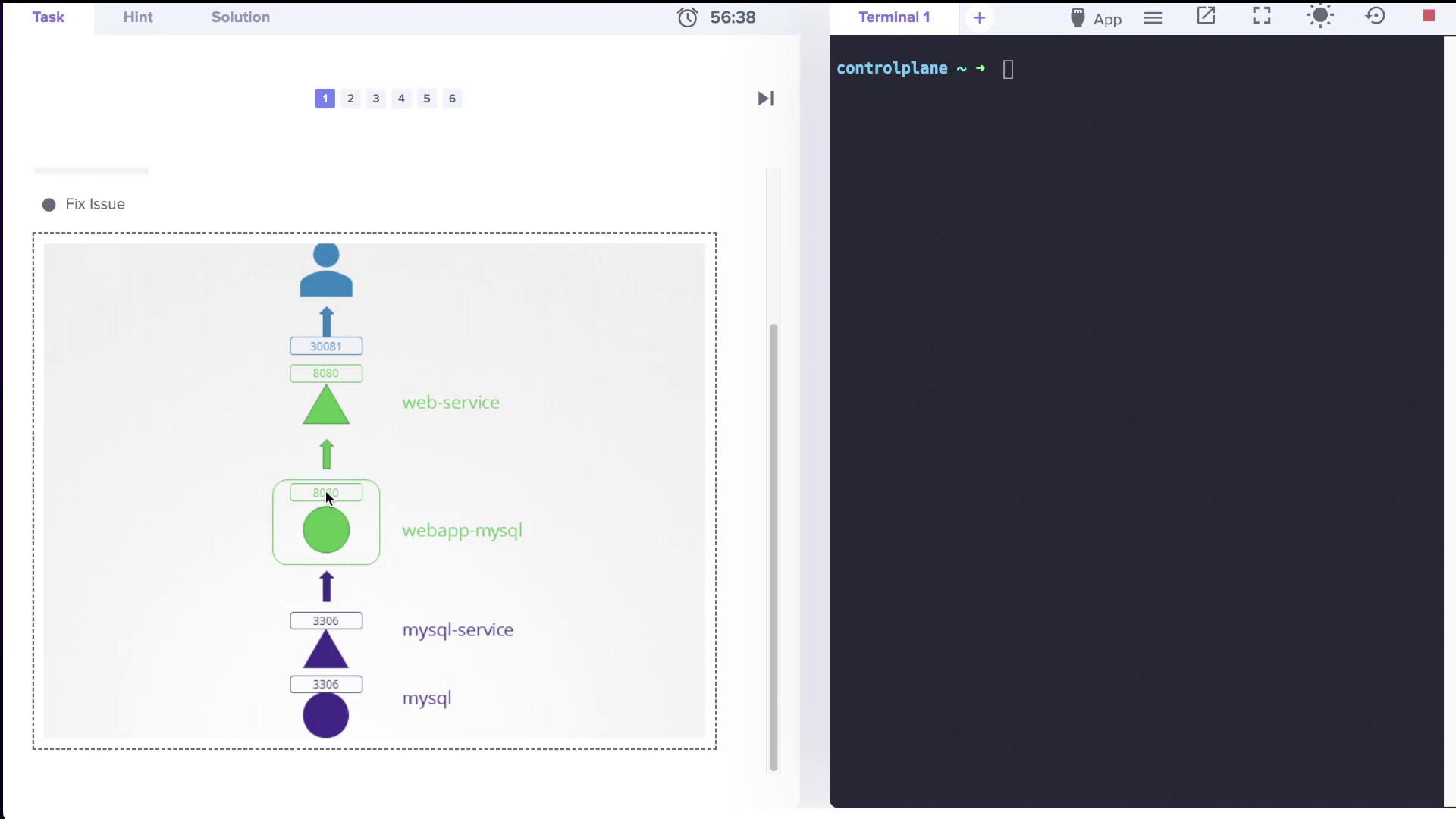
Troubleshooting Steps
Check Pods in the Alpha Namespace
Verify that the pods in the alpha namespace are running correctly.
k get pods -n alpha NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE webapp-mysql-84fbfc644f-nhfv 1/1 Running 0 3m48s mysql 1/1 Running 0 3m48sSet Default Namespace to Alpha
To prevent repeatedly specifying the namespace, execute:
k config set-context --current --namespace=alphaInspect Deployments and Services
Confirm that the web application is deployed as a deployment and that the services for both the web application and MySQL exist.
To check deployments:
k get deploy NAME READY UP-TO-DATE AVAILABLE AGE webapp-mysql 1/1 1 1 5m4sTo check services:
k get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql ClusterIP 10.43.208.47 <none> 3306/TCP 5m12s web-service NodePort 10.43.232.249 <none> 8080:30081/TCP 5m12s
Resolve MySQL Name Resolution Issue
The error occurs because the application expects the MySQL service name to be
mysql-service, but the actual service is namedmysql. To fix this, update the MySQL service to match the expected name:Create a YAML file (for example,
/tmp/kubectl-edit-3970124164.yaml) with the following content:apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mysql-service namespace: alpha spec: clusterIP: 10.43.208.47 ports: - port: 3306 protocol: TCP targetPort: 3306 selector: name: mysql sessionAffinity: None type: ClusterIPThen, run:
kubectl delete svc mysql kubectl create -f /tmp/kubectl-edit-3970124164.yamlVerify the changes:
k get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE web-service NodePort 10.43.232.249 <none> 8080:30081/TCP 8m16s mysql-service ClusterIP 10.43.208.47 <none> 3306/TCP 4s
Note
After these corrections, the application is able to successfully connect to the MySQL service.
Case 2: Beta Namespace
In the beta namespace, the tutor application initially fails with the following error message:
Environment Variables: DB_Host=mysql-service; DB_Database=Not Set; DB_User=root; DB_Password=paswrd; 2003: Can't connect to MySQL server on 'mysql-service:3306' (111 Connection refused)
Troubleshooting Steps
Switch Context to Beta
k config set-context --current --namespace=betaVerify Pods and Services
Check the pods:
k get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE webapp-mysql-84fbfc644f-jwmc 1/1 Running 0 73s mysql 1/1 Running 0 74sCheck the services:
k get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql-service ClusterIP 10.43.114.115 <none> 3306/TCP 84s web-service NodePort 10.43.33.34 <none> 8080:30081/TCP 84s
Inspect Deployment for Environment Variables
Ensure that the deployment's configuration sets
DB_Hosttomysql-service:k describe deploy webapp-mysqlFix Target Port Mismatch
The issue was caused by a mismatch in port configuration; the MySQL service’s
targetPortwas set to 8080 rather than 3306. Update the service configuration:Sample YAML configuration:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: mysql-service namespace: beta spec: ports: - port: 3306 protocol: TCP targetPort: 3306 selector: name: mysql type: ClusterIPAfter editing, verify the update:
k describe svc mysql-service Name: mysql-service Namespace: beta Ports: - port: 3306/TCP targetPort: 3306/TCP Endpoints: 10.42.0.12:3306
Note
The adjustment of the target port enables the application to correctly connect to the MySQL service.
Case 3: Gamma Namespace
In the gamma namespace, both pods and services report running status, yet the application initially fails to load.
Troubleshooting Steps
Switch Context to Gamma
k config set-context --current --namespace=gammaVerify Pods and Services
Inspect pods:
k get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql 1/1 Running 0 75s webapp-mysql-84fbfc644f-wqm6v 1/1 Running 0 75sInspect services:
k get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql-service ClusterIP 10.43.31.131 <none> 3306/TCP 78s web-service NodePort 10.43.201.61 <none> 8080:30081/TCP 78s
Examine the Web Service Configuration
Confirm that the selectors and endpoints are set properly by describing the service:
k describe svc web-serviceThe output should indicate that the web service on port 8080 (exposed via NodePort 30081) correctly maps to the pod IP address (e.g., 10.42.0.1:8080).
Review the Deployment Configuration
Verify that the deployment’s environment variables (DB_Host, DB_User, DB_Password) and image configuration are correct:
k describe deploy webapp-mysqlCheck the MySQL Service Selector
If endpoints are missing from the MySQL service, confirm that its selector matches the MySQL pod labels. If necessary, adjust the selector:
k edit svc mysql-service
After these checks and adjustments, connectivity is restored, and the application becomes accessible.
Case 4: Delta Namespace
The delta namespace presents two issues. Initially, the application shows a connection error:
Environment Variables: DB_Host=mysql-service; DB_Database=Not Set; DB_User=sql-user; DB_Password=paswrd; 2003: Can't connect to MySQL server on 'mysql-service:3306' (111 Connection refused)
A subsequent error indicates “access denied for user sql-user,” implying incorrect credentials.
Troubleshooting Steps
Switch Context to Delta
k config set-context --current --namespace=deltaCheck Pods and Services
Inspect pods:
k get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql 1/1 Running 0 32s webapp-mysql-7fbcc4fb8f-dfmnw 1/1 Running 0 32sInspect services:
k get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE mysql-service ClusterIP 10.43.186.56 <none> 3306/TCP 34s web-service NodePort 10.43.18.113 <none> 8080:30081/TCP 34s
Review and Update Deployment Credentials
Describing the deployment shows that
DB_Useris set assql-user:k describe deploy webapp-mysqlTo resolve the credential issue (the correct user should be
root), edit the deployment:k edit deploy webapp-mysqlChange
DB_Userfromsql-usertorootand save the modification.Monitor the Pod Update
Ensure that the updated pod is running. Once the deployment refreshes, the application should successfully connect to the MySQL service.
Case 5: Epsilon Namespace
In the epsilon namespace, the initial error encountered is an "Access denied" message:
Environment Variables: DB_Host=mysql-service; DB_Database=Not Set; DB_User=sql-user; DB_Password=paswrd*1 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'sql-user'@'10.42.0.19' (using password: YES)
Troubleshooting Steps
Switch Context to Epsilon
k config set-context --current --namespace=epsilonVerify Pods
Confirm that both MySQL and the web application pods are running:
k get pods NAME READY STATUS RESTARTS AGE mysql 1/1 Running 0 54s webapp-mysql-7fbcc4fb8f-lcqvd 1/1 Running 0 54sEdit Deployment for Correct Credentials
Access and modify the deployment to change
DB_Userfromsql-usertoroot:k edit deploy webapp-mysqlAfter updating and saving, verify that the error now reflects the root user.
Check MySQL Pod Configuration
Describe the MySQL pod to confirm the
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD:k describe pod mysqlIf the
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDdoes not matchpaswrdas expected, update the MySQL configuration. Since changing pod configurations may require recreating the pod, use the command below:k replace --force -f /tmp/kubectl-edit-31959777508.yaml
After these modifications, the application within the epsilon namespace connects successfully.
Production Note
In production, environment variables are best managed with ConfigMaps and Secrets rather than being hard-coded in deployments.
An image below illustrates the troubleshooting process in the epsilon namespace:
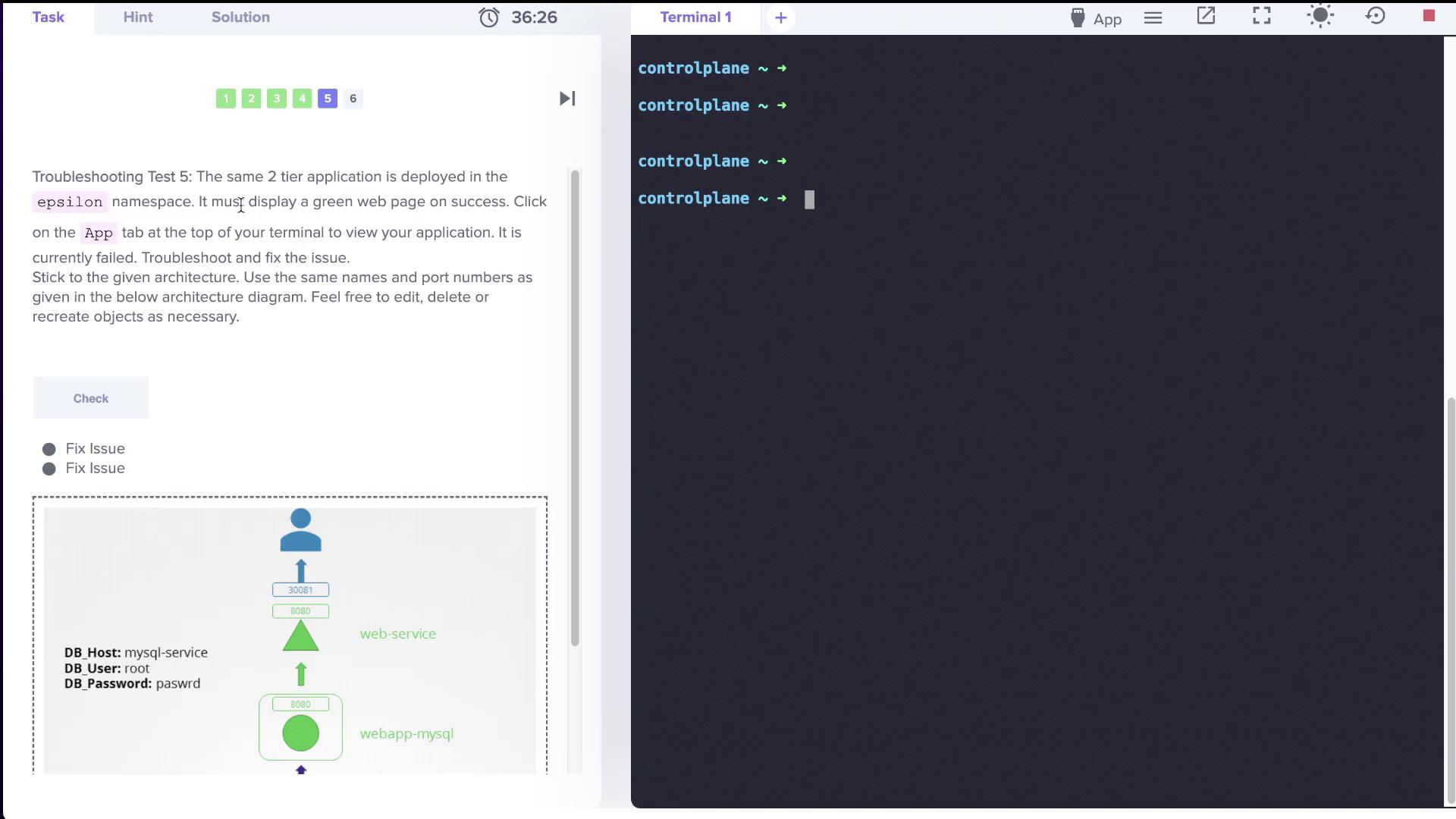
Case 6: Zeta Namespace
The zeta namespace initially returned a "Bad Gateway" error.
Troubleshooting Steps
Switch Context to Zeta
k config set-context --current --namespace=zetaInspect the Web Service Configuration
On examining the service, it was discovered that the NodePort was set incorrectly (e.g., 30088 instead of the required 30081). To update the NodePort, edit the web service with the following YAML:
apiVersion: v1 kind: Service metadata: name: web-service namespace: zeta spec: type: NodePort ports: - port: 8080 targetPort: 8080 nodePort: 30081 protocol: TCP selector: name: webapp-mysqlSave the file and verify the update:
k get svc NAME TYPE CLUSTER-IP EXTERNAL-IP PORT(S) AGE web-service NodePort 10.43.72.229 <none> 8080:30081/TCP ...Update Deployment Credentials
An "Access denied" error still appeared, indicating that
DB_Userwas set tosql-userinstead ofroot:Environment Variables: DB_Host=mysql-service; DB_Database=Not Set; DB_User=sql-user; DB_Password=paswrd; 1045 (28000): Access denied for user 'sql-user'@'10.42.0.22' (using password: YES)Edit the deployment to update the credential:
k edit deploy webapp-mysqlChange
DB_Userfromsql-usertorootand save. Deploy the updated configuration and verify that the pod is running with the correct credentials.Verify MySQL Pod Password
Lastly, check that the MySQL pod's
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORDis correctly configured. If it is not, update the value using:k replace --force -f /tmp/kubectl-edit-31959777508.yaml
After these corrections, the application in the zeta namespace becomes fully accessible and establishes a successful database connection.
An image confirming the successful deployment is shown below:
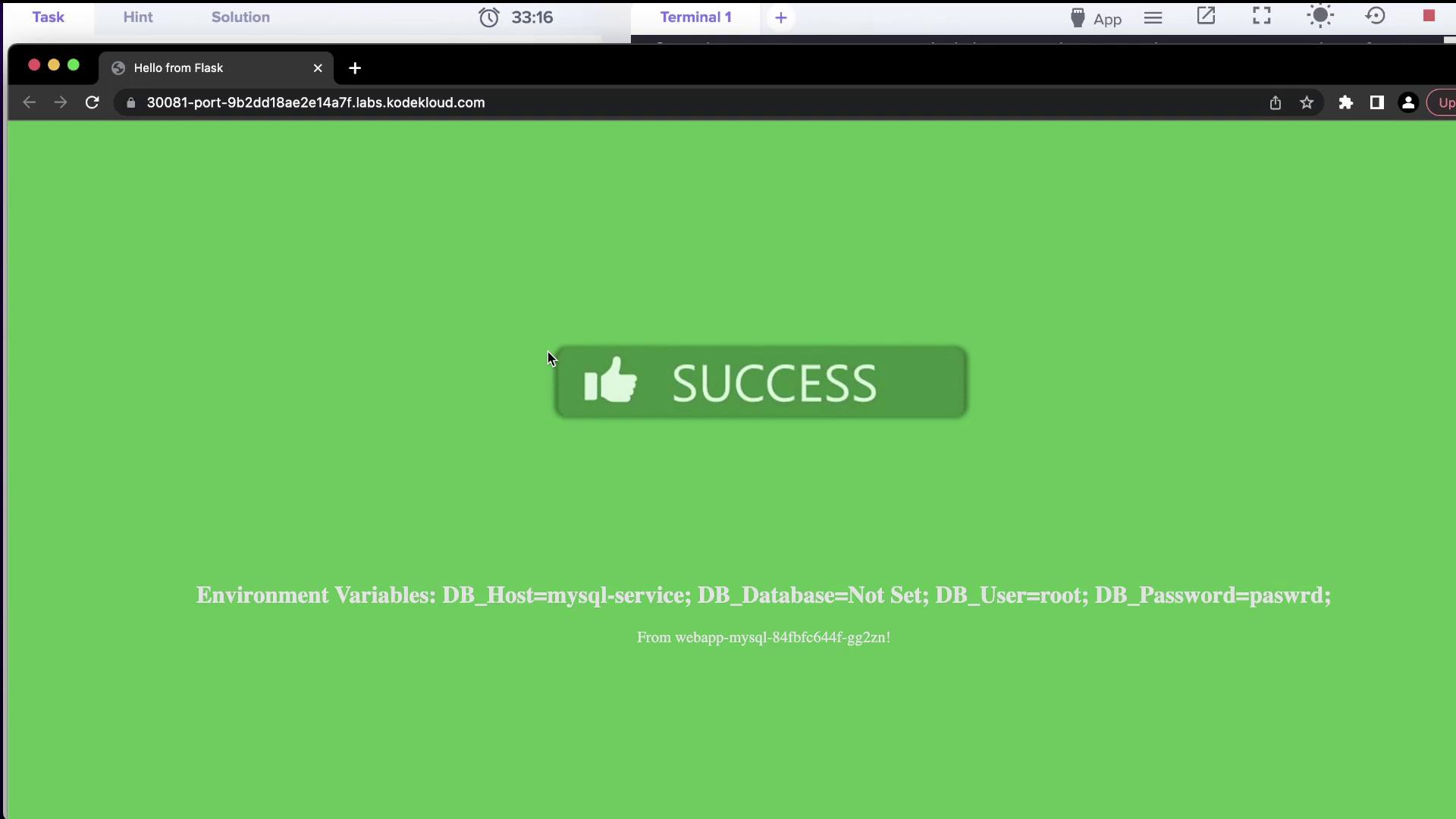
Conclusion
This troubleshooting session illustrates the importance of verifying pod status, inspecting service configurations, and maintaining correct environment variables across Kubernetes namespaces. The table below summarizes the key challenges and their resolutions:
| Namespace | Common Issues | Resolution Steps |
|---|---|---|
| Alpha | Service name mismatch | Renamed service from "mysql" to "mysql-service" |
| Beta | Incorrect target port | Updated MySQL service targetPort from 8080 to 3306 |
| Gamma | Selector misconfiguration | Verified endpoints and corrected selectors for MySQL service |
| Delta | Incorrect DB credentials | Updated deployment DB_User from sql-user to root |
| Epsilon | "Access denied" due to wrong credentials | Modified deployment and ensured correct MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD |
| Zeta | Wrong NodePort and credential issues | Adjusted NodePort to 30081 and updated deployment credentials |
Following these systematic troubleshooting methods helps ensure that service names, port configurations, selectors, and credentials are properly set, leading to a successful connection between the web and database components.
Happy troubleshooting, and stay tuned for more labs and lessons in upcoming sessions!
For more in-depth Kubernetes information, check out the Kubernetes Documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content