Before diving deeper, ensure your infrastructure hosts are secure by disabling root access, disabling password-based authentication, and exclusively using SSH key-based authentication.
Securing Kubernetes Cluster Hosts
The foundation of a secure Kubernetes environment is protecting the underlying physical or virtual infrastructure. Ensure that your cluster hosts adhere to industry security best practices:- Disable root access.
- Turn off password-based authentication.
- Enable SSH key-based authentication.
Protecting the Kube API Server
At the heart of Kubernetes lies the Kube API Server, which serves as the gateway for all operations—be it throughkubectl or direct API calls. As such, strict control over who can access the cluster and what actions they can perform is vital.
Authentication Methods
Authentication determines the identity of a user or a process accessing the API server. Kubernetes supports multiple authentication mechanisms, including:- User IDs and Passwords: Stored in static files.
- Tokens: Issued for API access.
- Certificates: Securing communications.
- External Authentication Providers: For example, LDAP.
- Service Accounts: For machine-to-machine interactions.

Authorization Strategies
Once authenticated, authorization dictates what actions users are permitted to perform. Kubernetes primarily employs Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) to manage permissions. Additional strategies include:- Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
- Node Authorization
- Webhook Modes

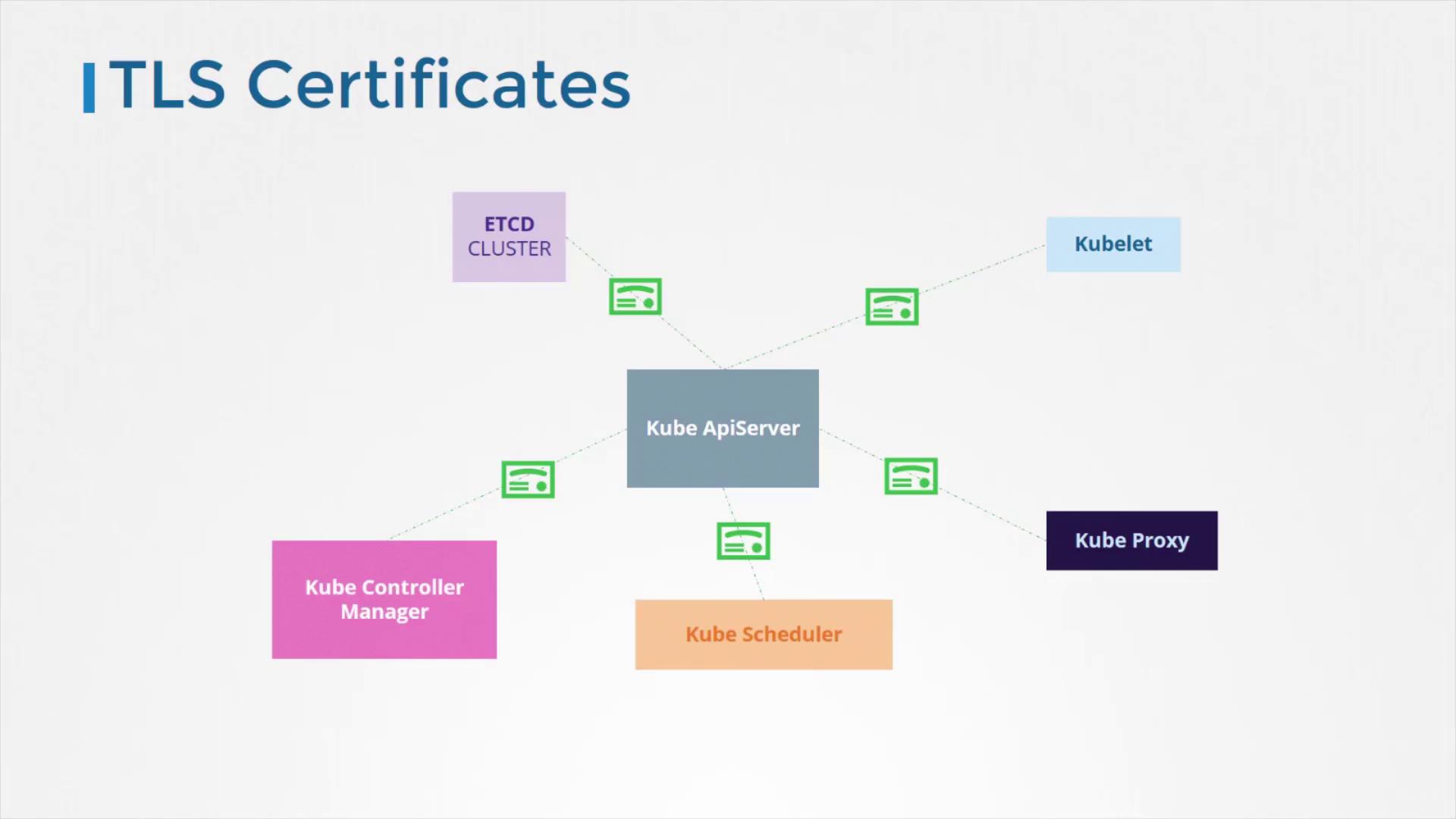
Securing Inter-Component Communications
Every component within Kubernetes communicates over a network, sometimes traversing untrusted networks. To ensure data security, Kubernetes uses TLS encryption for communications among critical components such as:- Kube API Server
- etcd Cluster
- Kube Controller Manager
- Kube Scheduler
- Kubelet and Kube Proxy on worker nodes
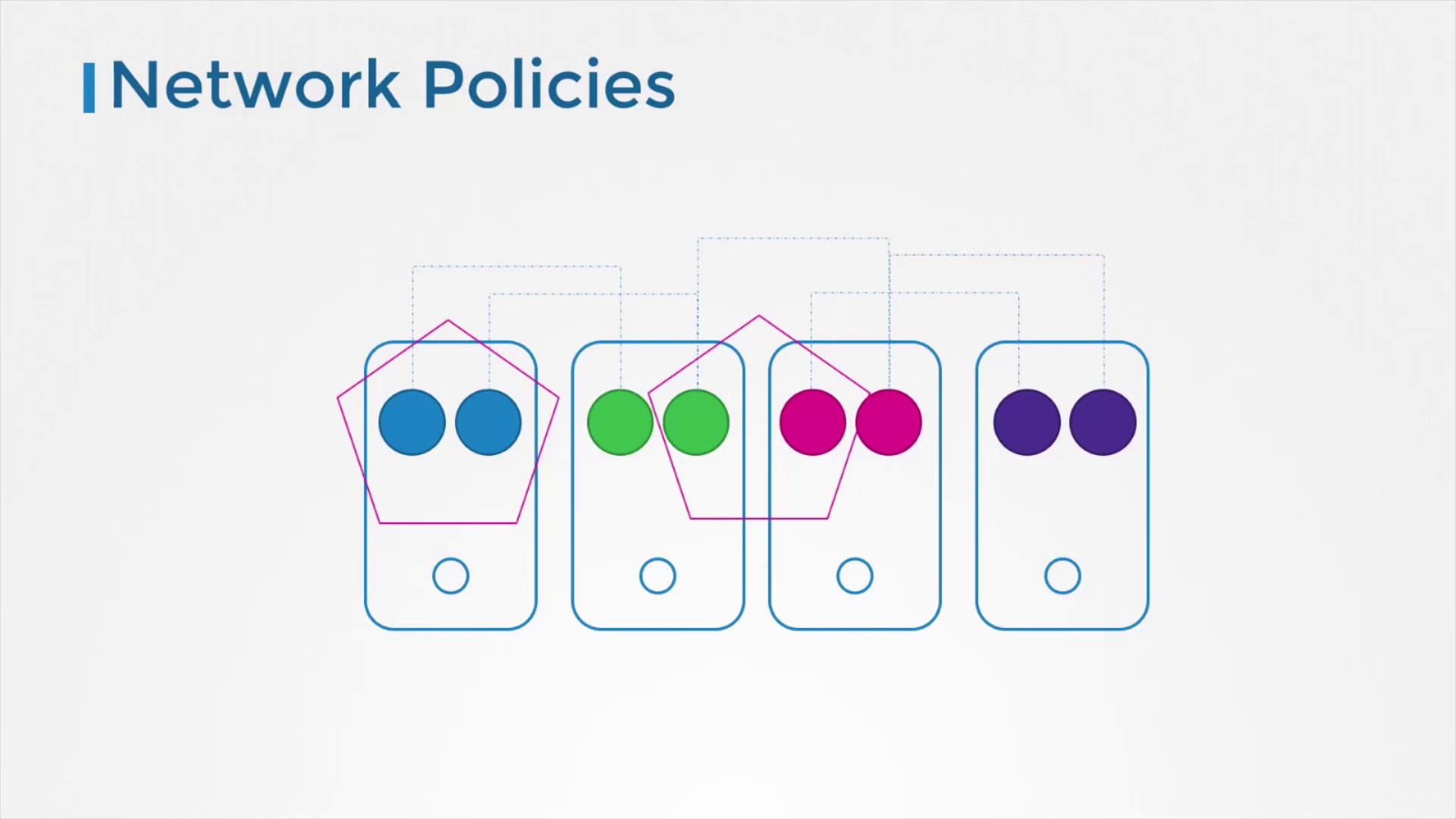
Managing Pod Communications with Network Policies
By default, all pods within a Kubernetes cluster can communicate freely, which may not be desirable for every workload or application. Network policies allow administrators to define rules that restrict pod-to-pod interactions, thereby reducing potential attack vectors and isolating sensitive components.