Introduction
Amazon ECS Fargate is a serverless compute engine for containers that lets you run Docker workloads without provisioning or managing servers. In this experiment, we’ll deploy a Pet Adoption payment API as two Fargate tasks, fronted by an Application Load Balancer and backed by a Pet Adoption database. Then we’ll launch an AWS FIS experiment to inject I/O stress and observe the behavior.Before starting, ensure you have the following prerequisites:
- An AWS account with permissions to create FIS experiments, ECS clusters, IAM roles, and CloudWatch alarms.
- A running ECS Fargate service with at least two tasks.
- A target database (e.g., Amazon RDS) for the Pet Adoption back end.
Architecture Overview
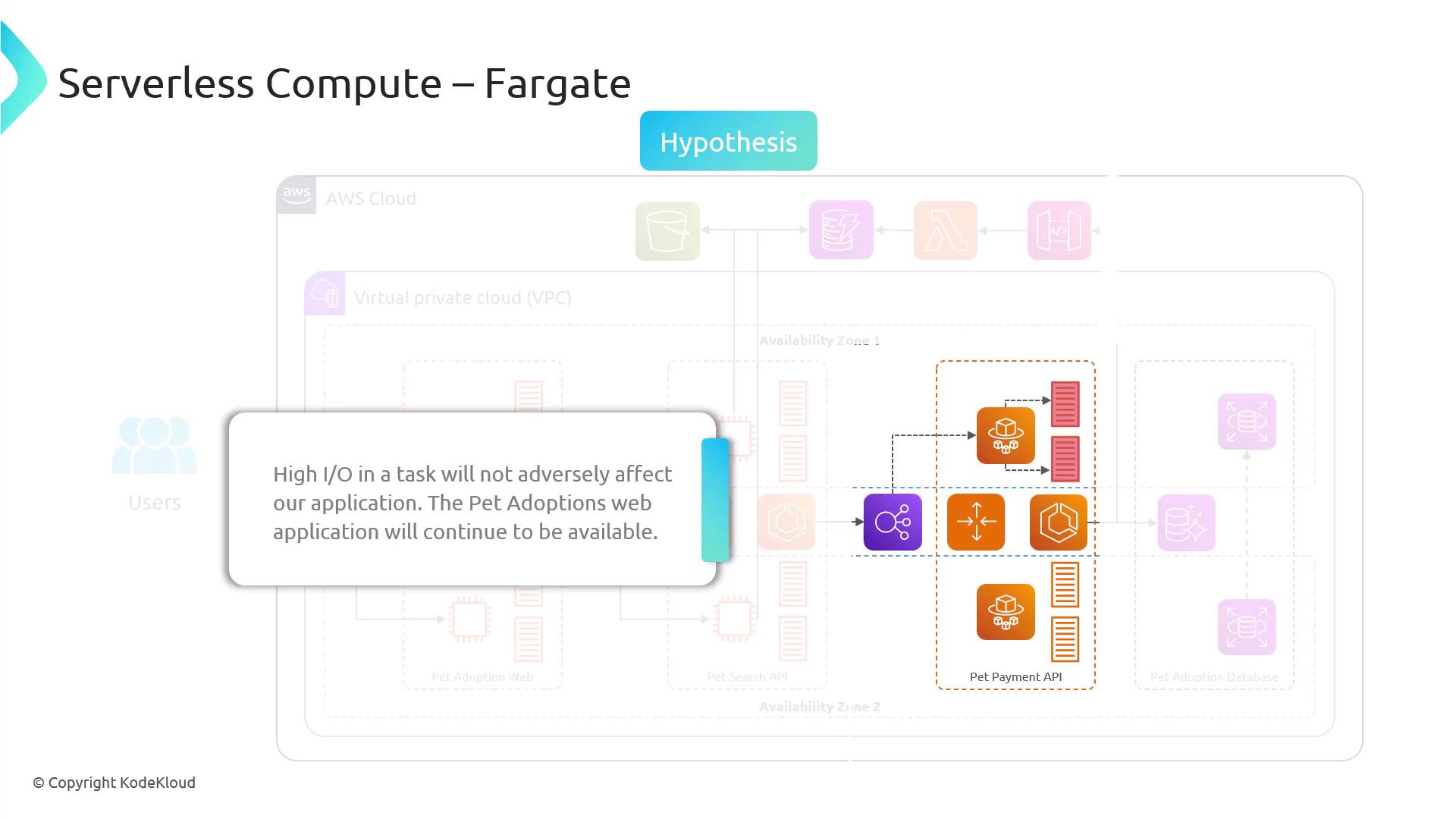
- Application Load Balancer distributes incoming traffic to Fargate tasks.
- ECS Fargate Tasks run the Pet Payment API.
- Pet Adoption Database serves as the back-end data store.
FIS Experiment Phases
Every AWS FIS experiment consists of two main phases:| Experiment Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| Given | The current running state of our ECS Fargate service and its infrastructure. |
| Hypothesis | The expected system behavior when an I/O fault is injected. |
1. Given
- Two Fargate tasks in an ECS service named
pet-payment-service. - An Application Load Balancer routing traffic to
pet-payment-serviceon port 80. - A connected Pet Adoption database (e.g., Amazon RDS or DynamoDB).
2. Hypothesis
We expect that under high I/O stress on each Fargate task:- The Pet Payment API remains responsive with < 5% error rate.
- The Pet Adoption web application continues to process payments without downtime.
- CloudWatch alarms trigger if latency or error thresholds are breached.
Injecting faults can impact production workloads. Always run experiments in a staging environment or during scheduled maintenance windows. Monitor performance and rollback criteria closely.
Next Steps
- Define IAM roles and permissions for AWS FIS.
- Create an FIS experiment template that targets the Fargate tasks.
- Configure CloudWatch metrics and alarms for latency, error rate, and CPU/I/O usage.
- Execute the experiment and review the results.