
Power Resilience
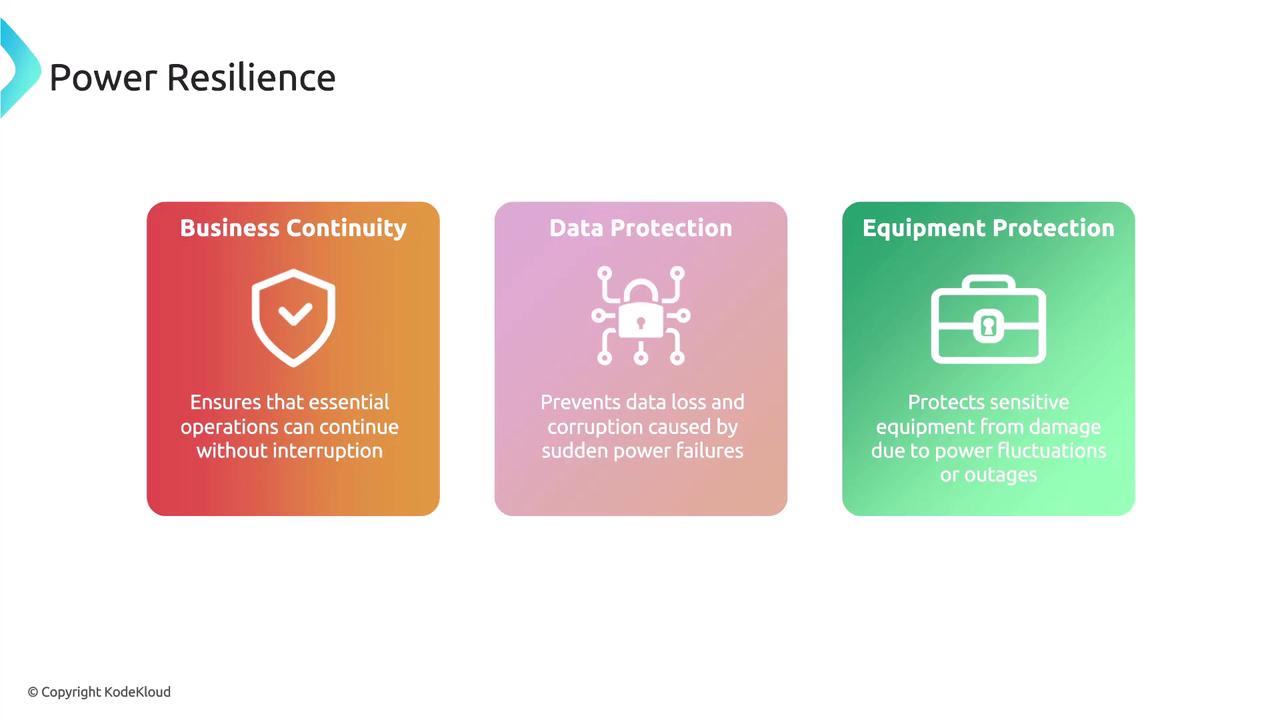
Power resilience is the ability of an organization to maintain a continuous power supply for critical systems and infrastructure even during outages or unexpected disruptions. This capability is key to:- Business Continuity: Keeping essential operations running despite power disturbances.
- Data Protection: Preventing data loss and corruption from sudden power failures.
- Equipment Protection: Shielding sensitive equipment from damage caused by power fluctuations or outages.
Key Components of Power Resilience
Generators
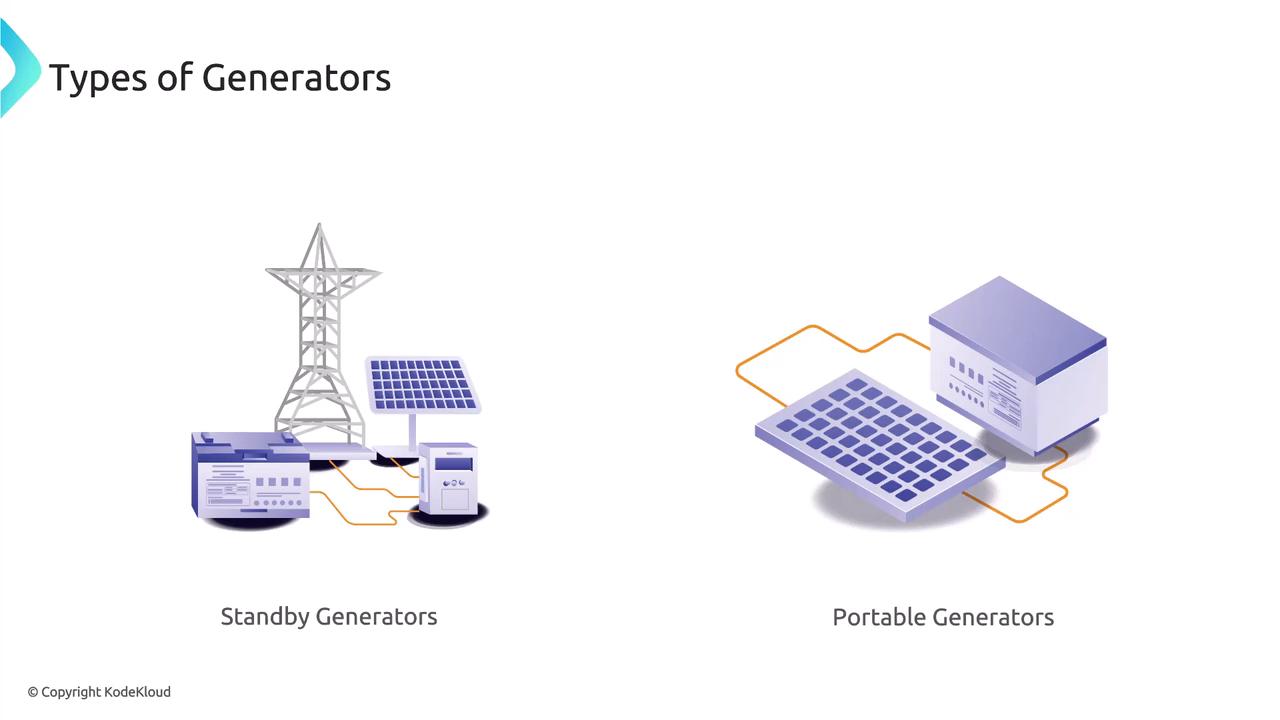
Generators provide backup power by converting mechanical energy into electrical energy during outages. Designed for extended power delivery, generators ensure that critical systems continue operating until regular power is restored. Various generator types include:- Standby Generators: These automatically activate during outages to supply backup power.
- Portable Generators: Manually operated and easily transportable to different locations as needed.

Implementing Generators
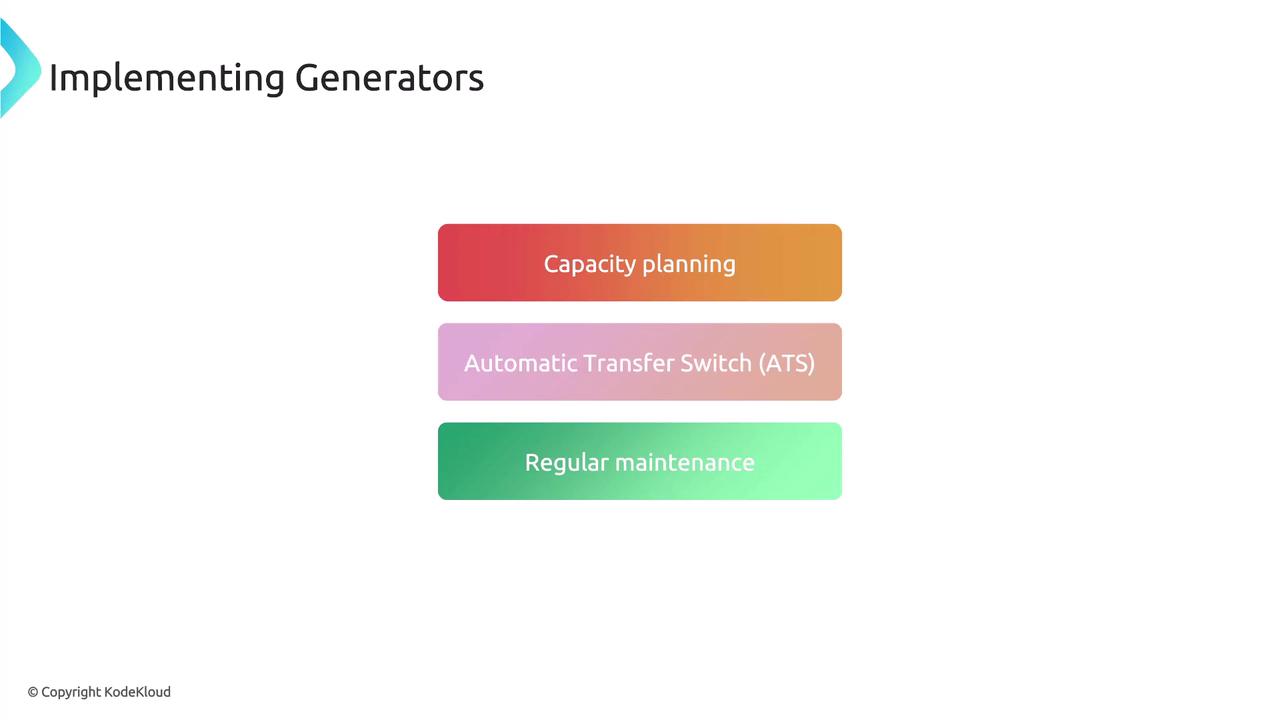
To successfully implement generators:- Evaluate the power requirements of your critical systems to choose the right generator capacity.
- Install an Automatic Transfer Switch (ATS) to facilitate the automatic switch to generator power during outages.
- Conduct regular maintenance and testing to verify that the generator functions correctly when needed.
For example, data centers often deploy standby generator systems to guarantee uninterrupted power supply during extended outages.
Uninterruptible Power Supplies (UPS)
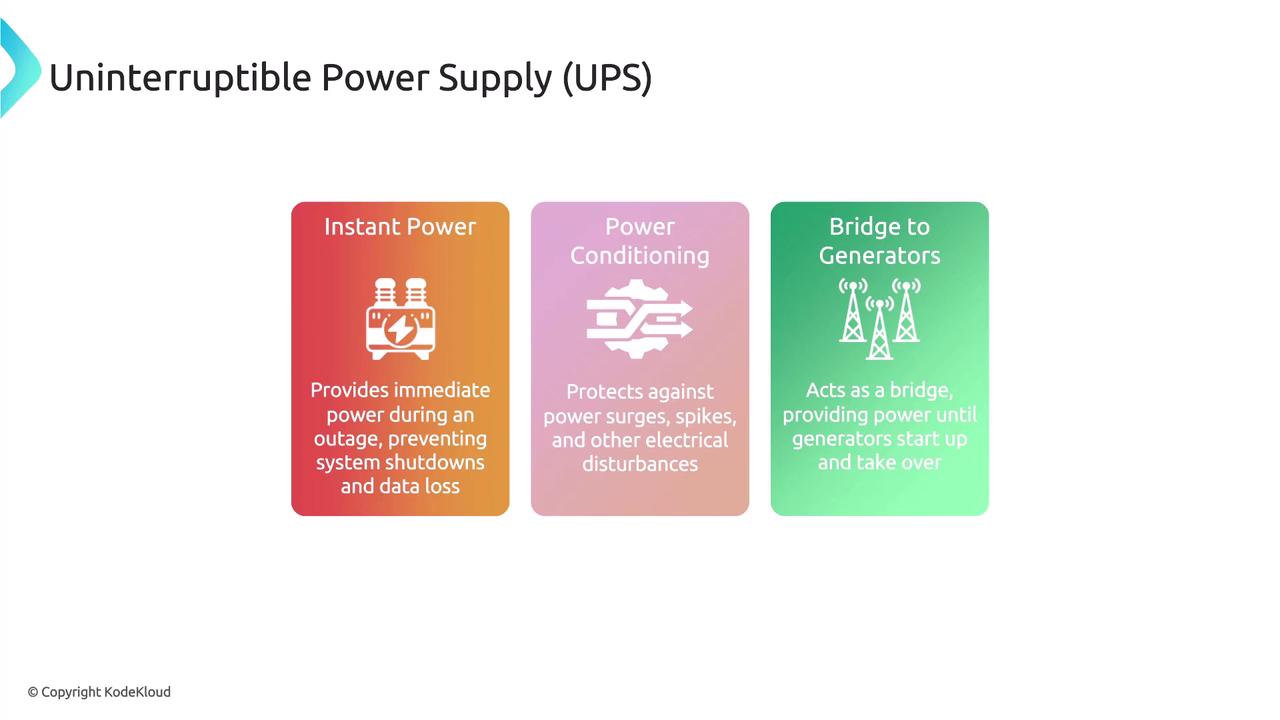
A UPS system offers immediate, short-term power backup to critical systems during outages by using batteries or other energy storage methods. The primary advantages of UPS systems include:- Instant Power Delivery: Preventing system shutdowns and data loss by providing power immediately during outages.
- Power Conditioning: Protecting equipment from surges, spikes, and other electrical disturbances.
- Bridge Power: Serving as an interim power solution until generators begin supplying full power.
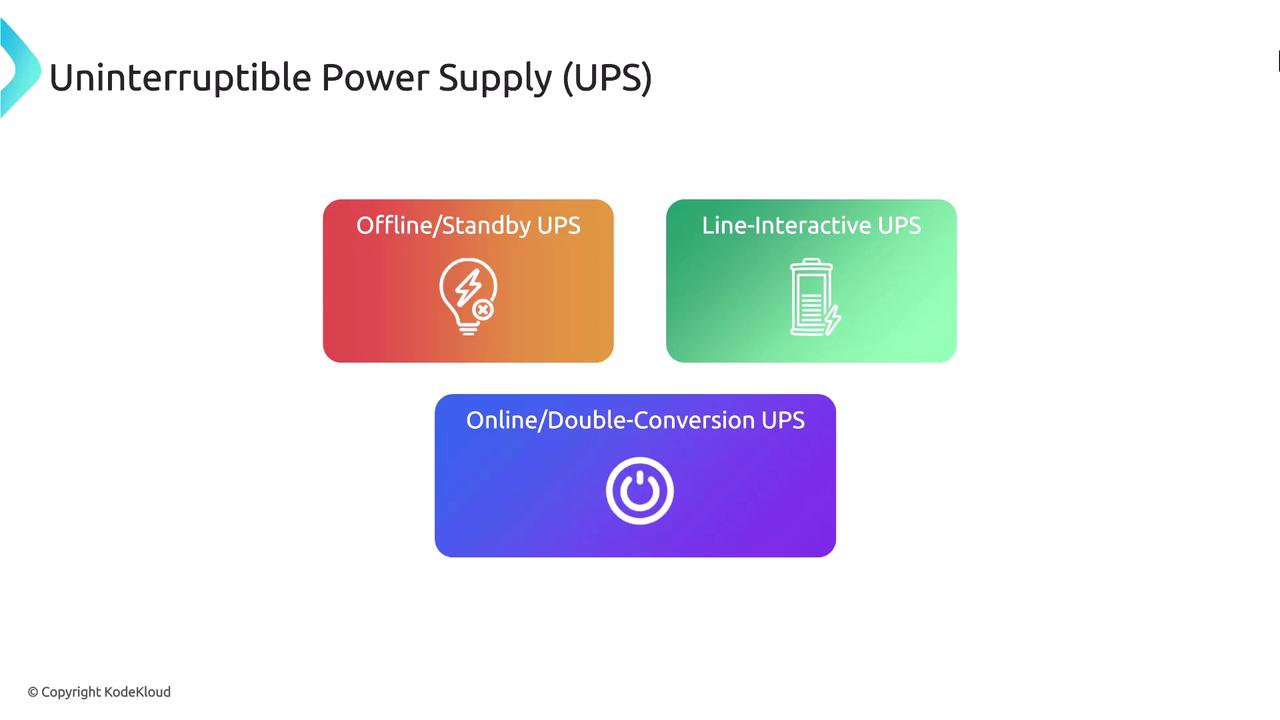
- Offline/Standby UPS: Offers basic battery backup, switching to battery power during an outage.
- Line-Interactive UPS: Provides enhanced power conditioning and backup, making it suitable for areas with frequent fluctuations.
- Online/Double Conversion UPS: Delivers the highest protection by constantly converting incoming AC power to DC and back to AC.
Implementing UPS Systems
To implement a UPS system effectively:- Assess the power needs of your critical systems and determine the desired backup duration.
- Choose a UPS system that fits both the power capacity and runtime requirements.
- Regularly test the UPS and replace batteries as needed to maintain peak performance.
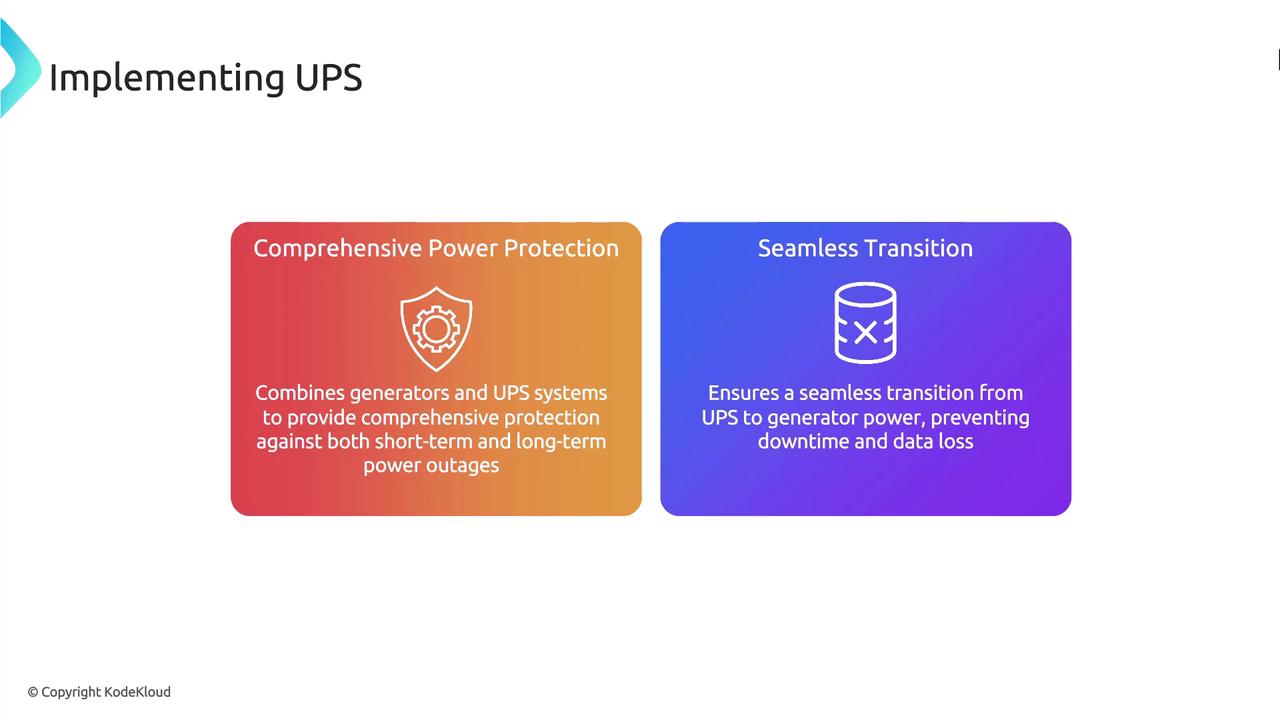
Integrating both generators and UPS systems offers a robust solution by providing comprehensive short-term and long-term power protection.
Conclusion
Maintaining a reliable power supply is crucial for uninterrupted business operations and the protection of critical systems and data. Implementing both generators and UPS systems enhances your organization’s resilience and recovery capabilities by providing seamless protection against both short-term and long-term power outages.