CompTIA Security+ Certification
Security Operations
Access Controls
Welcome back. In this article, we delve into the critical topic of access controls. These mechanisms are essential for regulating who can access data, applications, and other resources in a computing environment. By understanding the various types of access controls and their applications, you can significantly enhance security, comply with regulatory standards, and ensure that sensitive information remains protected.

Access controls determine how users and systems interact with resources by specifying who is allowed to view or modify them. They act as a first line of defense against unauthorized access and play a pivotal role in maintaining the integrity of an organization's security infrastructure.

Below are the common types of access control mechanisms:
Mandatory Access Control (MAC)
In a MAC system, access is enforced by the operating system based on a set of predefined policies determined by an administrator. Users cannot modify these policies. Files and resources receive security labels (e.g., top secret or confidential), and access is granted based on the user's security clearance. This centralized approach ensures robust security.

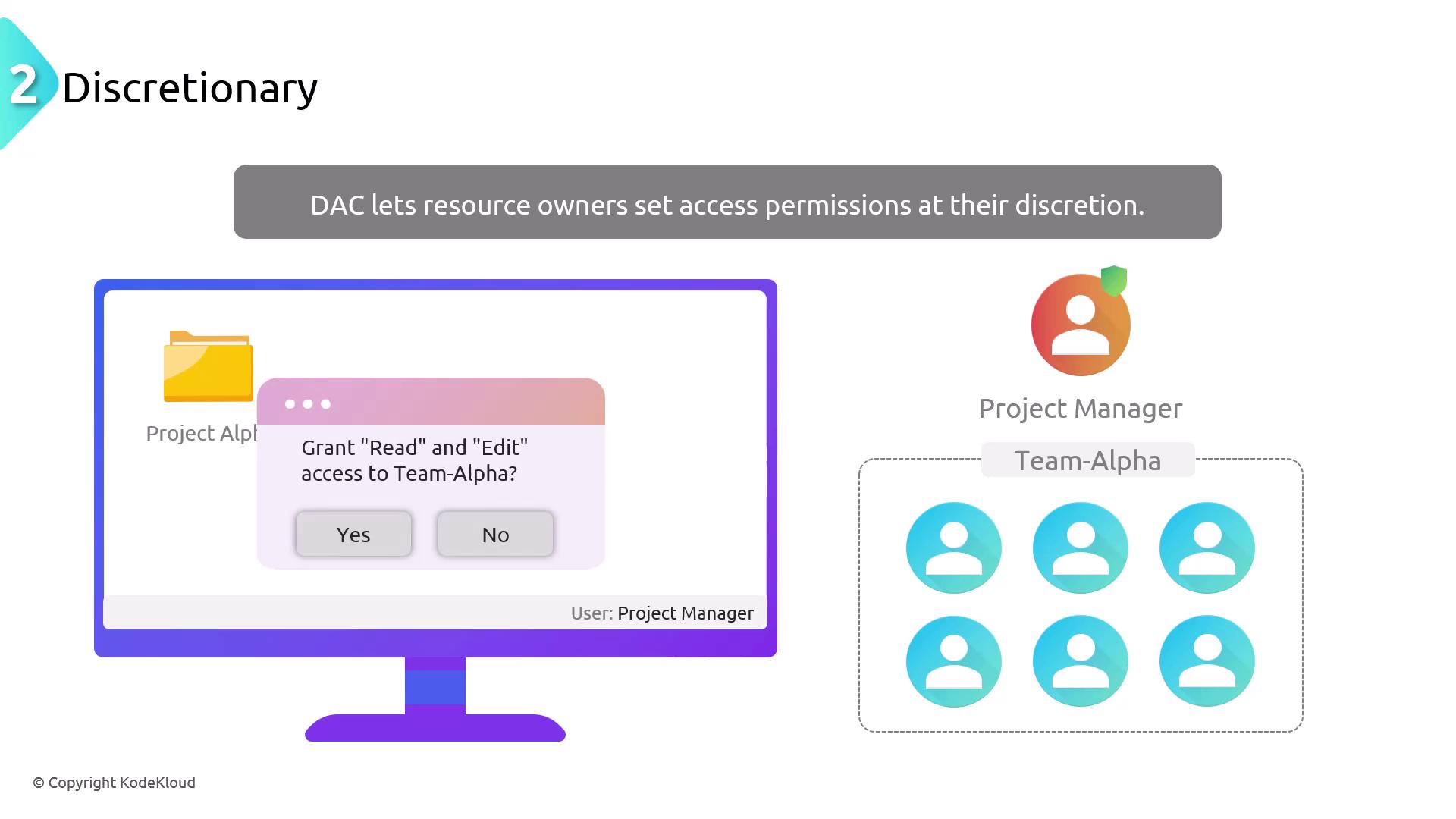
Discretionary Access Control (DAC)
DAC allows resource owners to manage access permissions. In this model, the owner sets the permissions, providing flexibility especially in personal or commercial computing environments. An example is when a Windows file owner grants specific read or write permissions to individual users or groups.
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
RBAC assigns permissions to users based on their roles within an organization. This method simplifies large-scale access management by granting permissions that align with job responsibilities and functions.

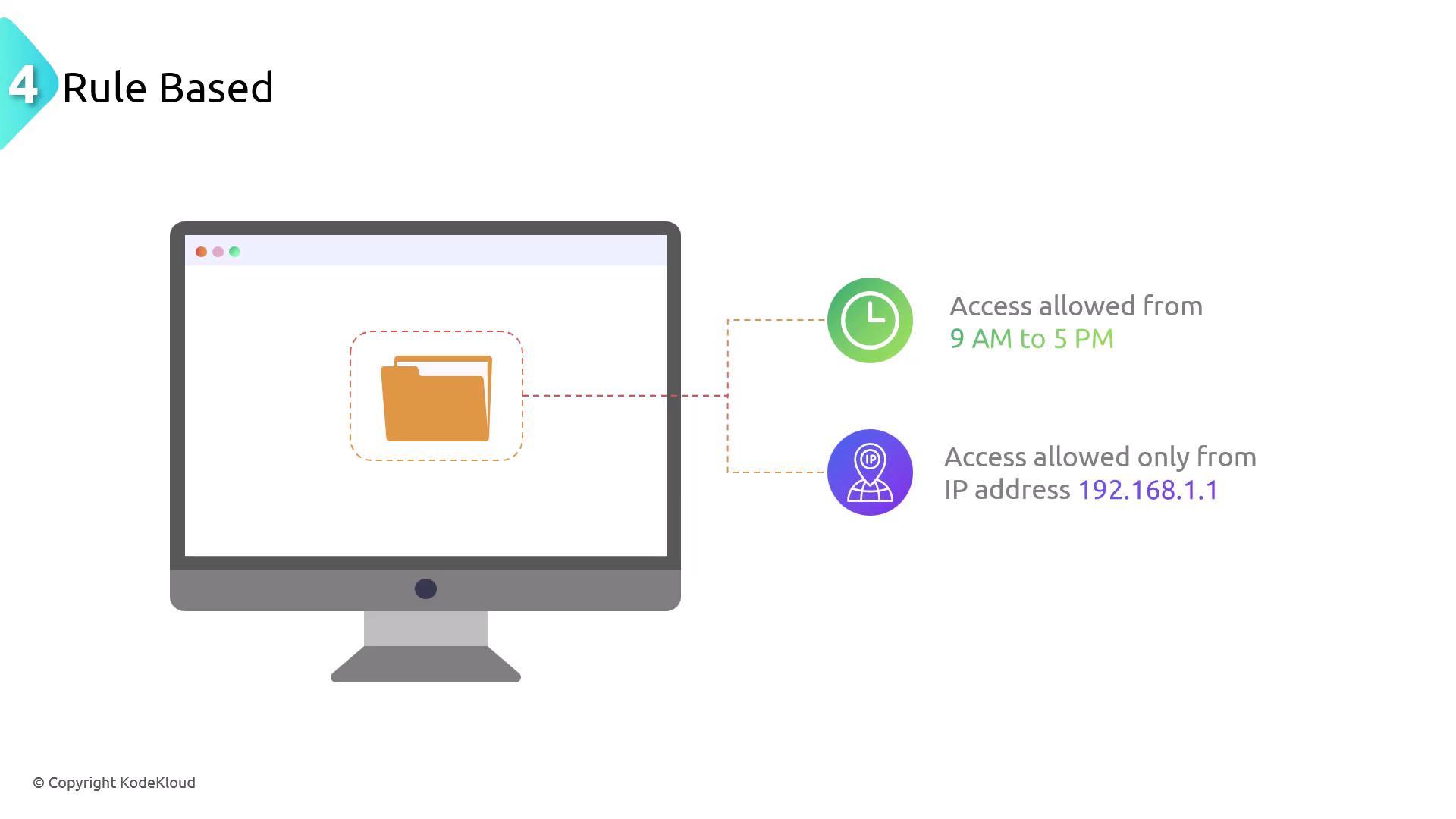
Rule-Based Access Control
Rule-based access control relies on predefined rules to determine access permissions based on conditions such as time, location, or other specific factors. This dynamic method allows decisions to adapt to changing environmental conditions, such as restricting access outside of business hours or from unauthorized IP addresses.
Attribute-Based Access Control (ABAC)
ABAC uses distinct attributes of users, resources, and the environment to make nuanced access decisions. Attributes like user roles, resource types, and access time enable fine-grained control that can be tailored to specific scenarios. For example, access to a resource may depend on a combination of a user's department, role, and the time of access.


Note
Implementing the right access control model is vital for safeguarding sensitive data and ensuring compliance with security regulations. Choosing the appropriate model depends on an organization’s specific needs.
In conclusion, understanding and applying various access control methods is essential for maintaining a secure environment. Leveraging models such as Mandatory, Discretionary, Role-Based, Rule-Based, and Attribute-Based Access Control can significantly strengthen an organization’s security posture, streamline access management, and ensure regulatory compliance.
Thank you for reading.
Watch Video
Watch video content