CompTIA Security+ Certification
Security Operations
Implementing and Maintaining IAM
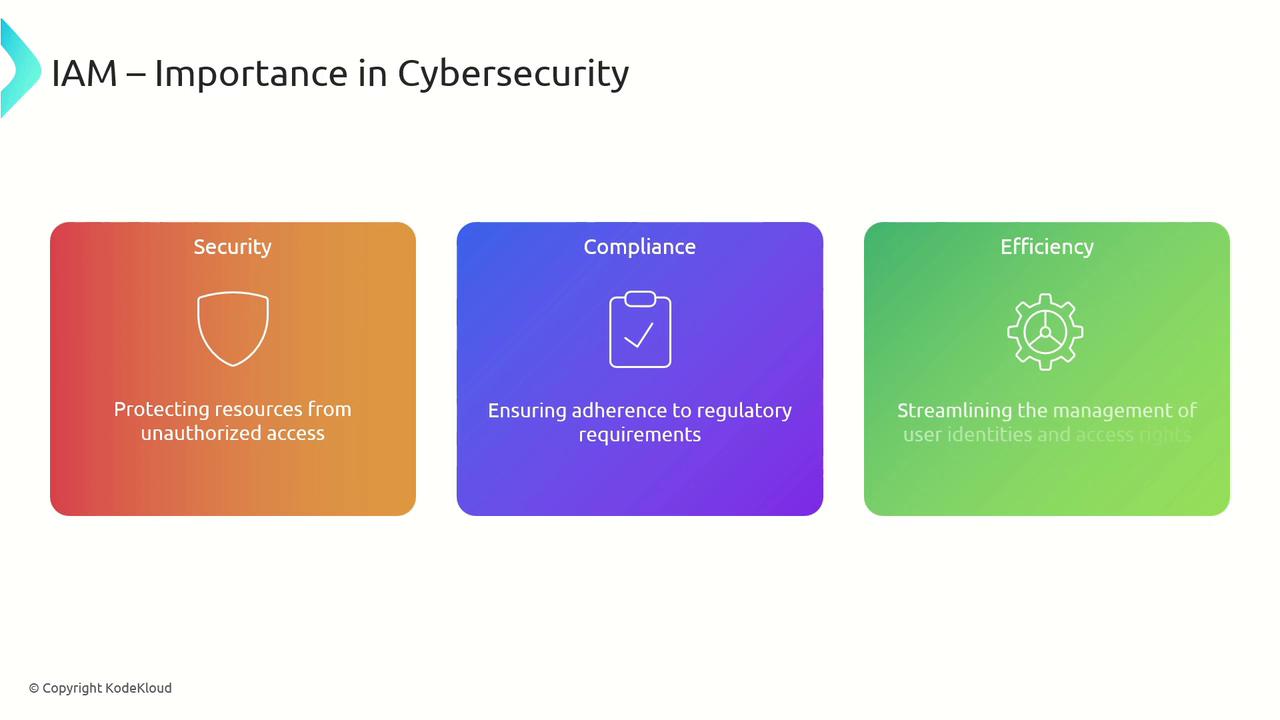
Welcome to this detailed guide on Identity and Access Management (IAM) for enterprise environments. In this lesson, we explore how to implement and maintain a robust IAM system that guarantees the right individuals have appropriate access to resources at the right time and for the right reasons. Effective IAM leverages policies and technology to control resource access, protect sensitive data, ensure regulatory compliance, and streamline user identity management.
Understanding Permission Assignments
Permissions specify the actions that users or groups can perform on resources. Key permission types include:
- Read: View data or resources.
- Write: Modify data or resources.
- Execute: Run applications or scripts.
- Delete: Remove data or resources.
- Special Custom Permissions: Provide specific access tailored to applications or systems.
These permissions are typically enforced through methods like access control lists (ACLs) or role-based access control (RBAC) policies.

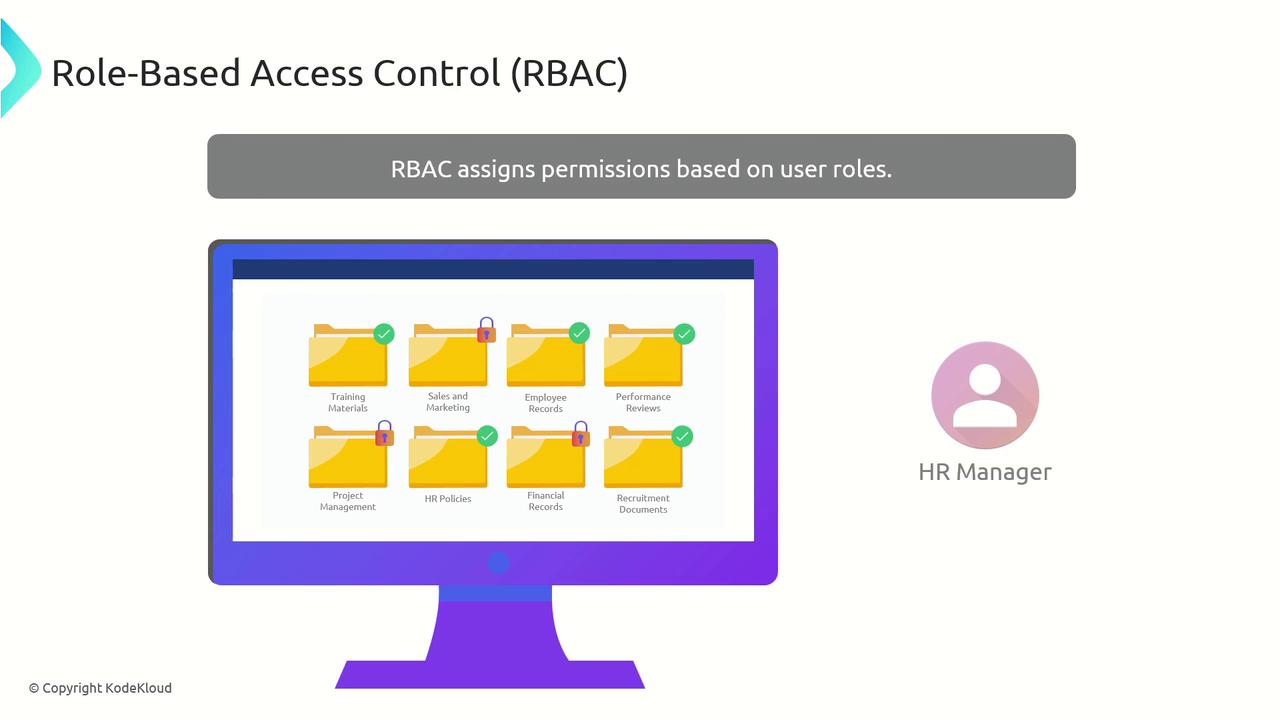
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC)
Role-Based Access Control (RBAC) is used to grant permissions based on user roles defined by job functions. This approach ensures users receive only the permissions necessary for their responsibilities.
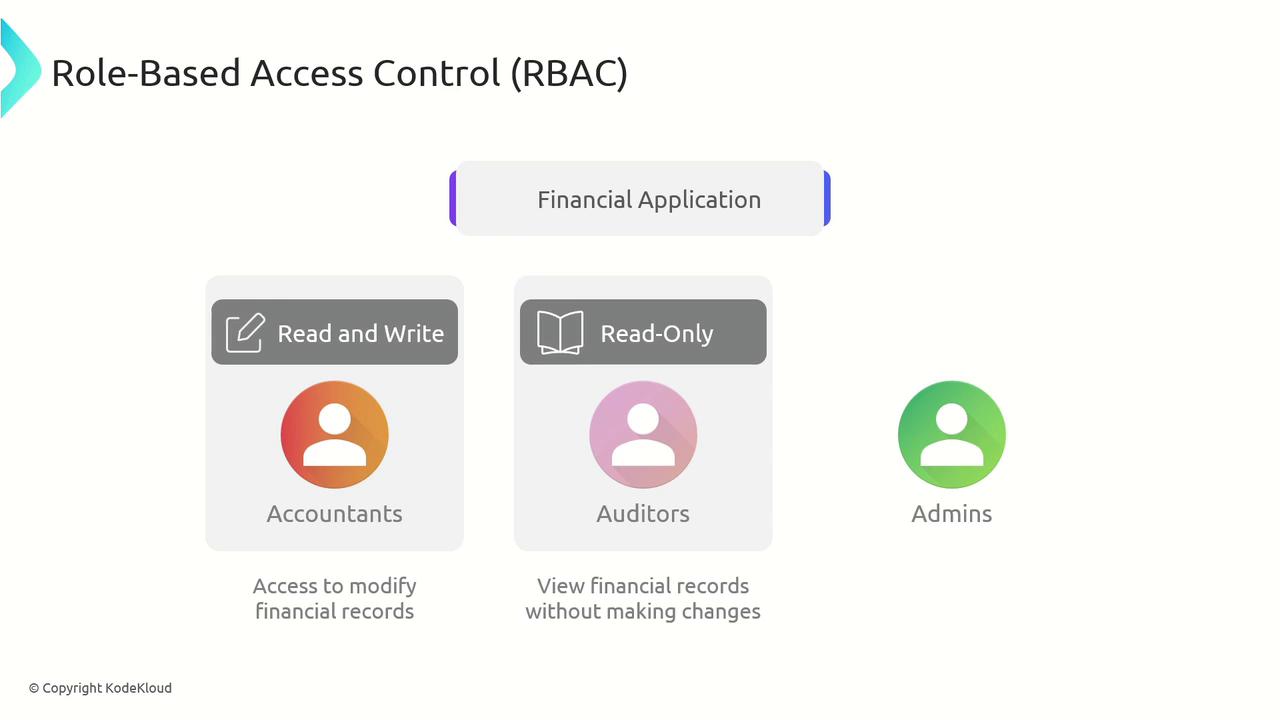
For example, in a financial application:
- Accountants require both read and write access to financial records.
- Auditors are given read-only access to maintain data integrity.
- Administrators have full access to manage users and permissions.
Best Practices in Permission Management
Adhering to best practices in permission management is essential for maintaining system security:
- Principle of Least Privilege: Grant only the minimum level of access needed for users to perform their tasks.
Note
Implementing least privilege dramatically reduces the risk of unauthorized actions.
- Segregation of Duties: Distribute tasks and authoritative functions among multiple users to minimize risks of errors and fraud.


Regular access reviews and audits are critical. By routinely examining user permissions, organizations can ensure compliance and remove any unnecessary access rights.

Steps to Implement Permission Assignments
Follow these structured steps to implement effective permission assignments:
- Identify Roles and Responsibilities:
Define clear roles based on job functions within the organization. - Assign Permissions to Roles:
Determine the necessary permissions corresponding to each role. - Assign Roles to Users:
Map user responsibilities with the appropriate roles. - Review and Audit:
Continuously audit permissions to ensure they remain compliant and appropriate.

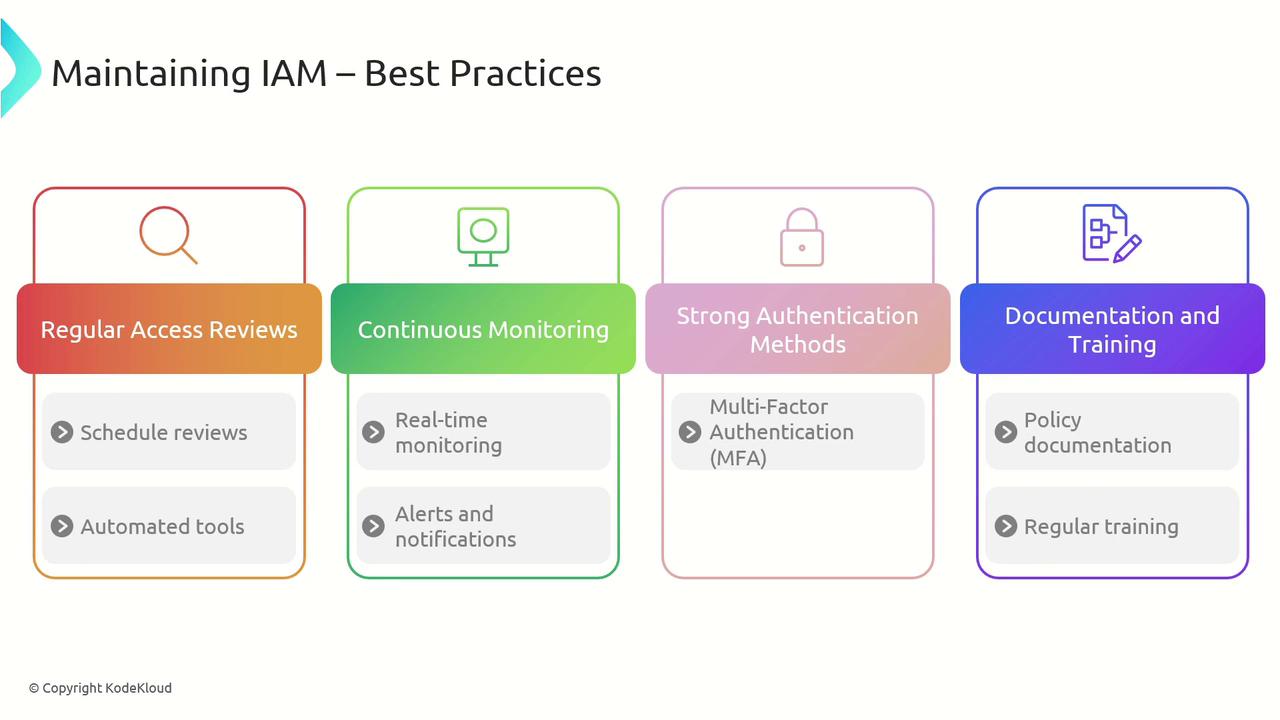
Best Practices for Maintaining IAM
To maintain an effective IAM system, consider incorporating these best practices:
- Regular Access Reviews:
Continuously verify that user permissions are current and appropriate. - Automated Monitoring:
Use automated tools to simplify reviews, detect anomalies, and generate compliance reports. - Continuous Monitoring:
Set up alerts and notifications for significant access events or modifications. - Strong Authentication:
Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security. - Documentation and Training:
Maintain clear IAM policies and procedures, and provide regular training to ensure best practices are followed.
Conclusion
Implementing and maintaining a comprehensive IAM system is essential for protecting enterprise resources and ensuring users have access commensurate with their roles. By carefully assigning permissions, adopting the principle of least privilege and segregation of duties, and conducting regular audits, organizations can enhance security, streamline user management, and boost overall system performance.

Thank you for exploring this guide on IAM. For further details and updates, continue exploring our technical documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content