CompTIA Security+ Certification
Security Operations
Enterprise Security
In this guide, we explore essential devices used in enterprise security—starting with firewalls and moving on to Intrusion Detection and Prevention Systems (IDS/IPS). This comprehensive overview will help you understand how these technologies protect your network from sophisticated cyber threats.
Firewalls
Firewalls serve as a critical first line of defense by enforcing robust security policies on network traffic. They inspect both incoming and outgoing data packets against a set of predefined rules to decide whether the traffic should proceed deeper into the network or be blocked.
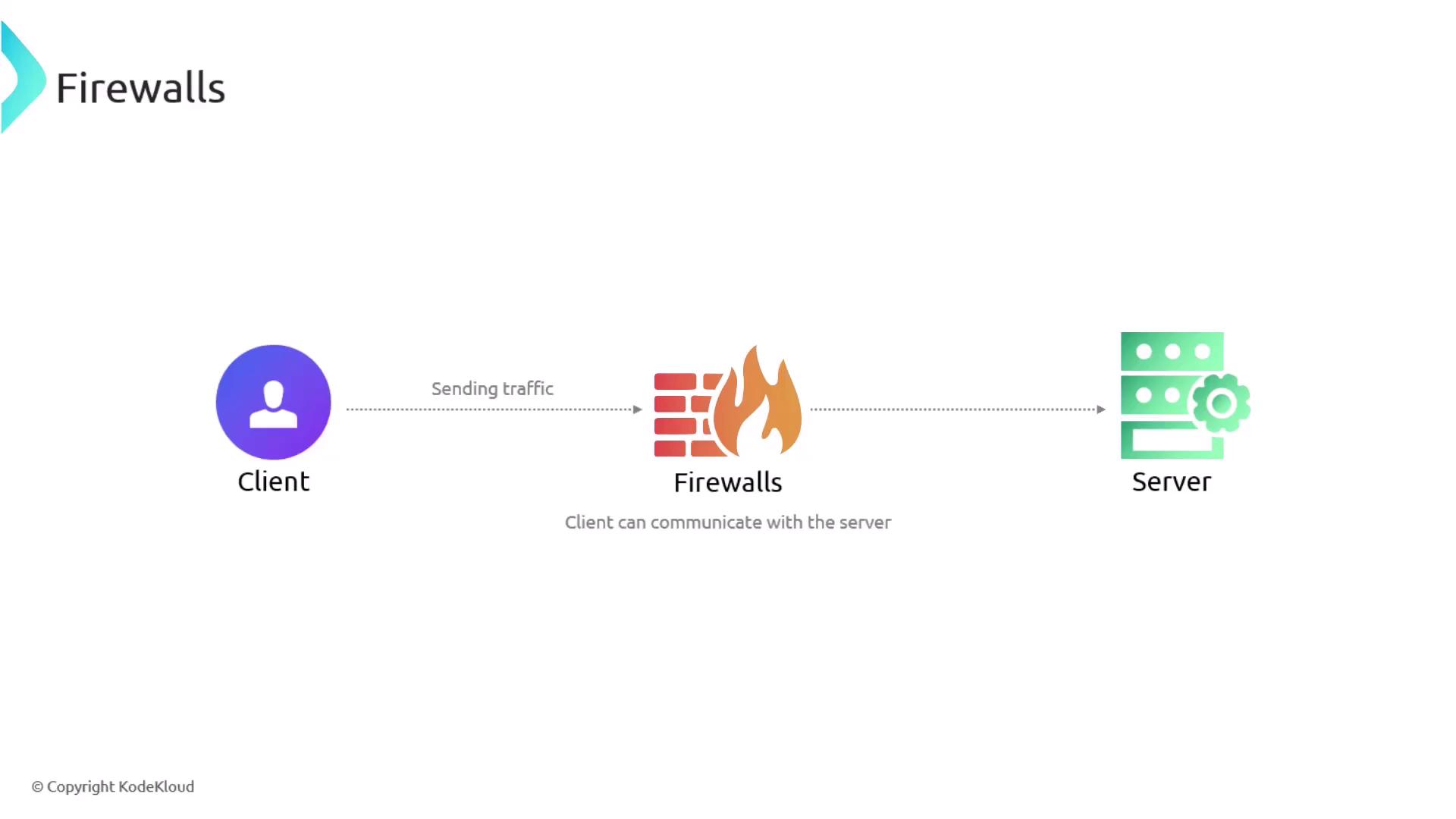
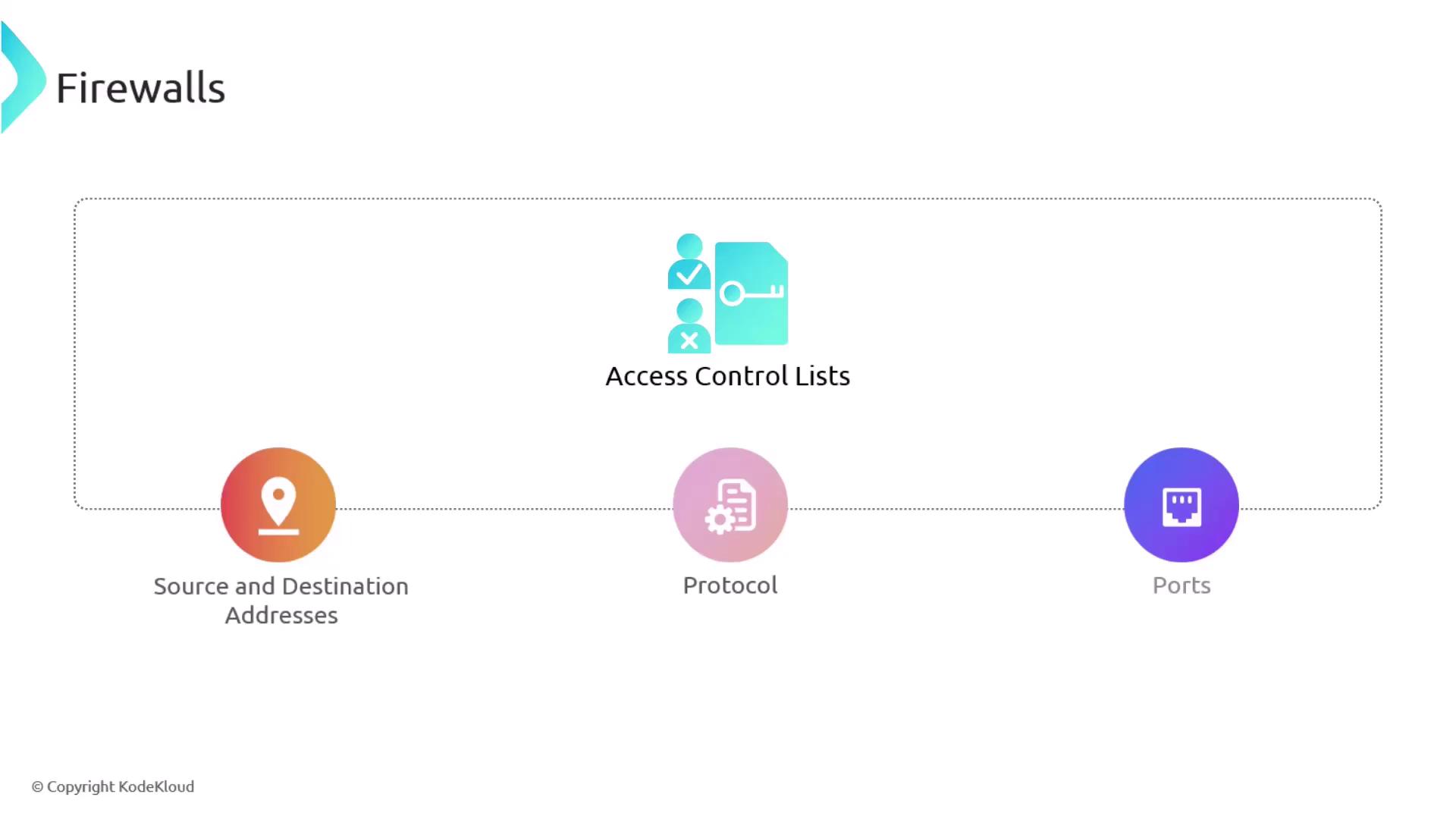
These devices operate using an Access Control List (ACL), which defines rules based on various packet attributes such as source and destination IP addresses, protocols, and ports. By filtering traffic with precision, firewalls help mitigate the risk of unauthorized access.
IDS and IPS Systems
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS) and Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS) are pivotal to a layered security strategy, continuously analyzing network traffic in real time. While both technologies monitor for anomalies and malicious activities, they differ in their response methods.
Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)
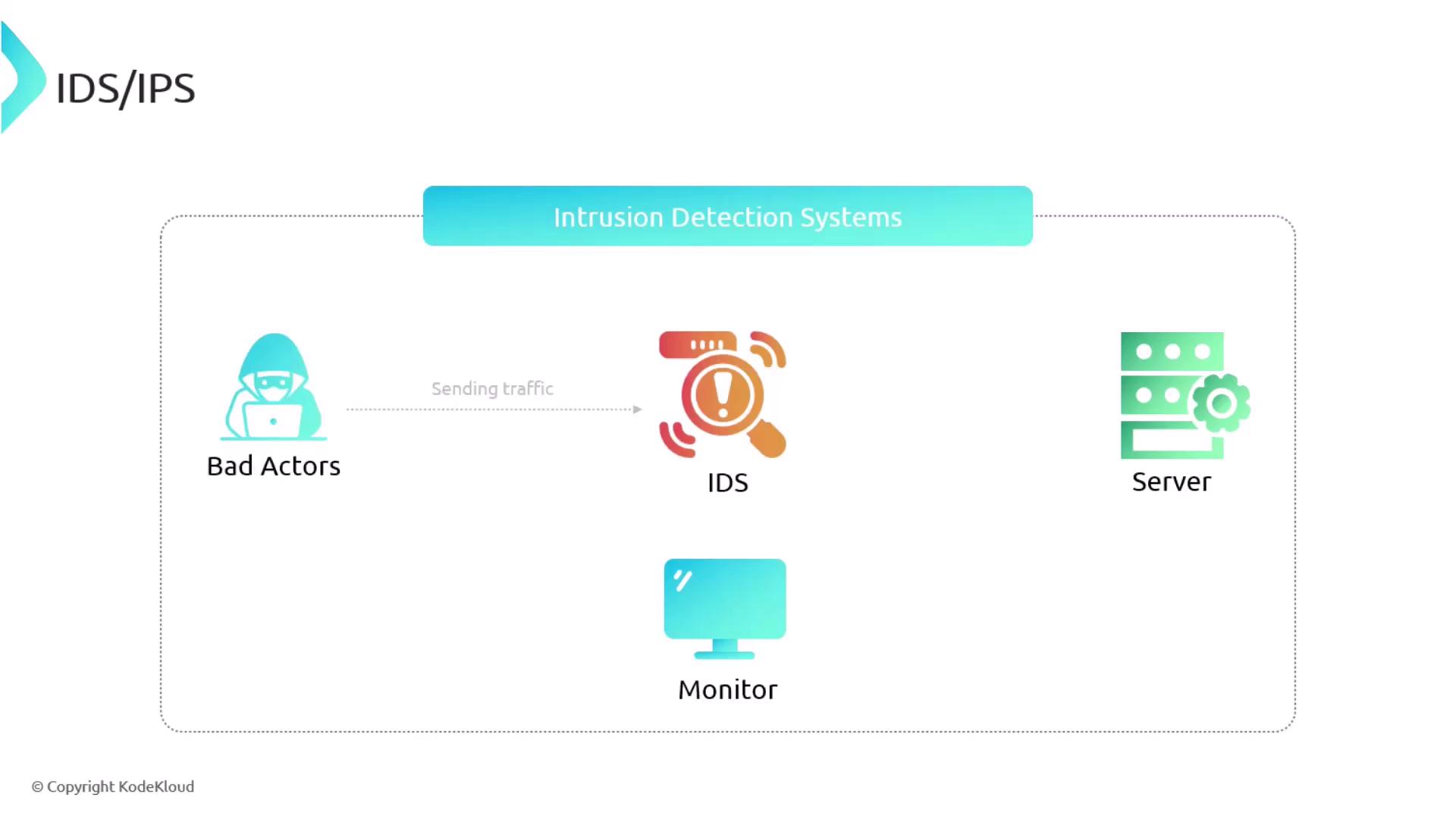
IDS solutions monitor network traffic and generate alerts when suspicious or anomalous activities are detected. They operate much like antivirus software by identifying known malicious signatures and unusual behavior patterns.
Note
IDS solutions are ideal for environments where immediate blocking of traffic is not required, but prompt alerting and monitoring are essential.
Intrusion Prevention Systems (IPS)
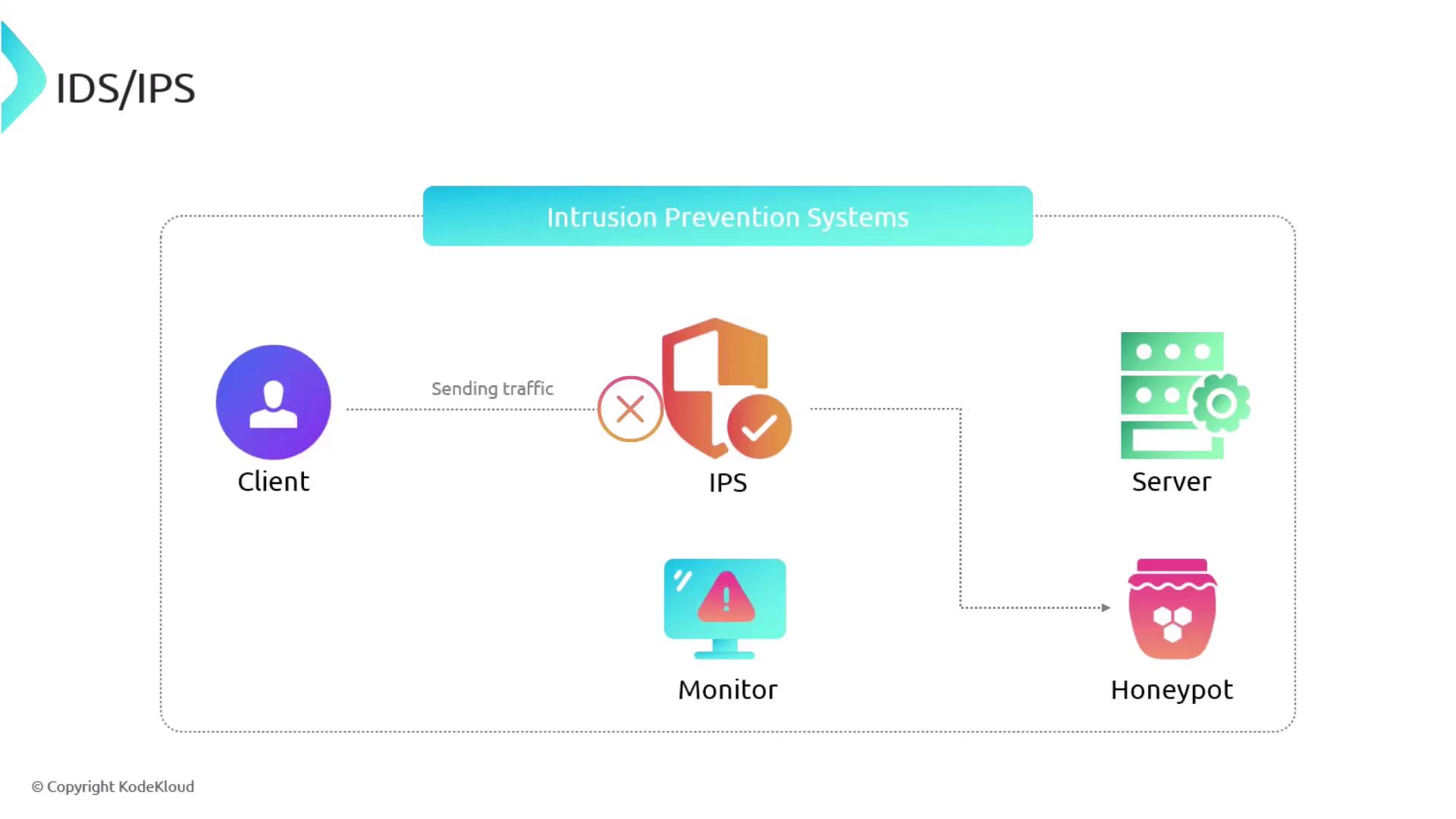
In contrast, IPS devices take actionable steps when they detect potentially harmful activity. Once an IPS identifies illicit behavior, it can reset connections, block traffic sources temporarily or permanently, or even redirect traffic to a honeypot for deeper analysis.
Note
Deploying an IPS can significantly reduce the window of opportunity for intrusions by actively mitigating detected threats in real time.
Both IDS and IPS are essential for enhancing your enterprise's security posture. While IDS focuses on detection and alerting, IPS takes immediate action to neutralize threats, offering a comprehensive defense strategy against a wide array of cyber attacks.
For further insights into network security and related technologies, check out these resources:
Watch Video
Watch video content