DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
Analyzing Data
Processing Modes
Welcome to the Azure Data Fundamentals course. In this article, we’ll compare three key data processing modes—batch, streaming, and hybrid—to help you architect the right solution for your analytics needs.
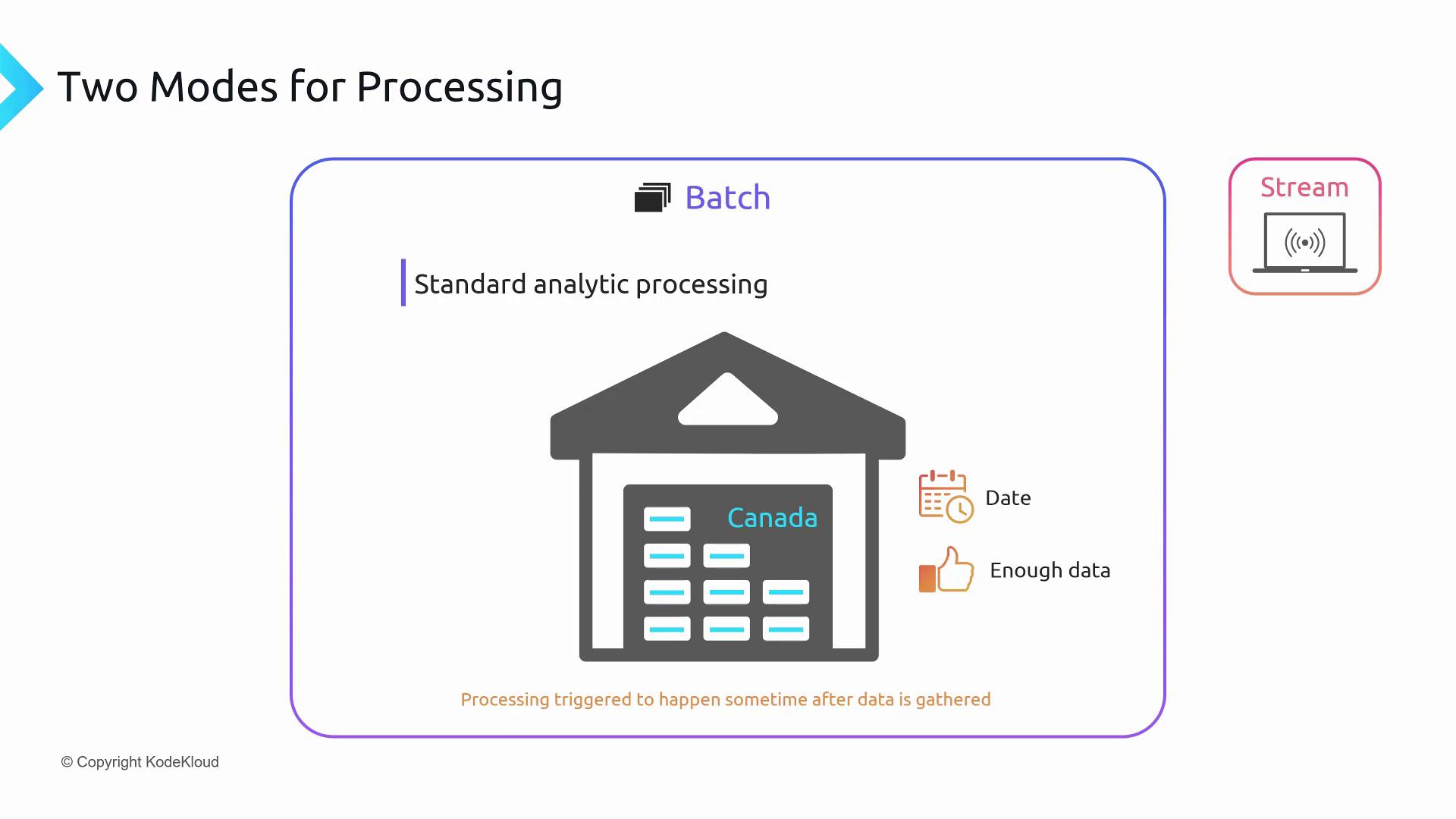
Batch Processing
Batch processing aggregates data over a period, loads it into storage, and runs analytics as a single job. It’s ideal for large-scale reporting when real-time insights aren’t required.
Key steps:
- Collect data (e.g., all sales transactions across Canada).
- Load into a central data warehouse.
- Execute analytics on a schedule (daily, weekly, monthly).
- Generate dashboards and reports.
You can trigger batch jobs in different ways:
| Trigger Type | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Time-based | Runs at fixed calendar intervals | Daily sales report at midnight |
| Event-based | Starts when data reaches a predefined count | Forecast after 5,000 transactions |
| Conditional | Activates on custom business logic | Inventory update on low stock |
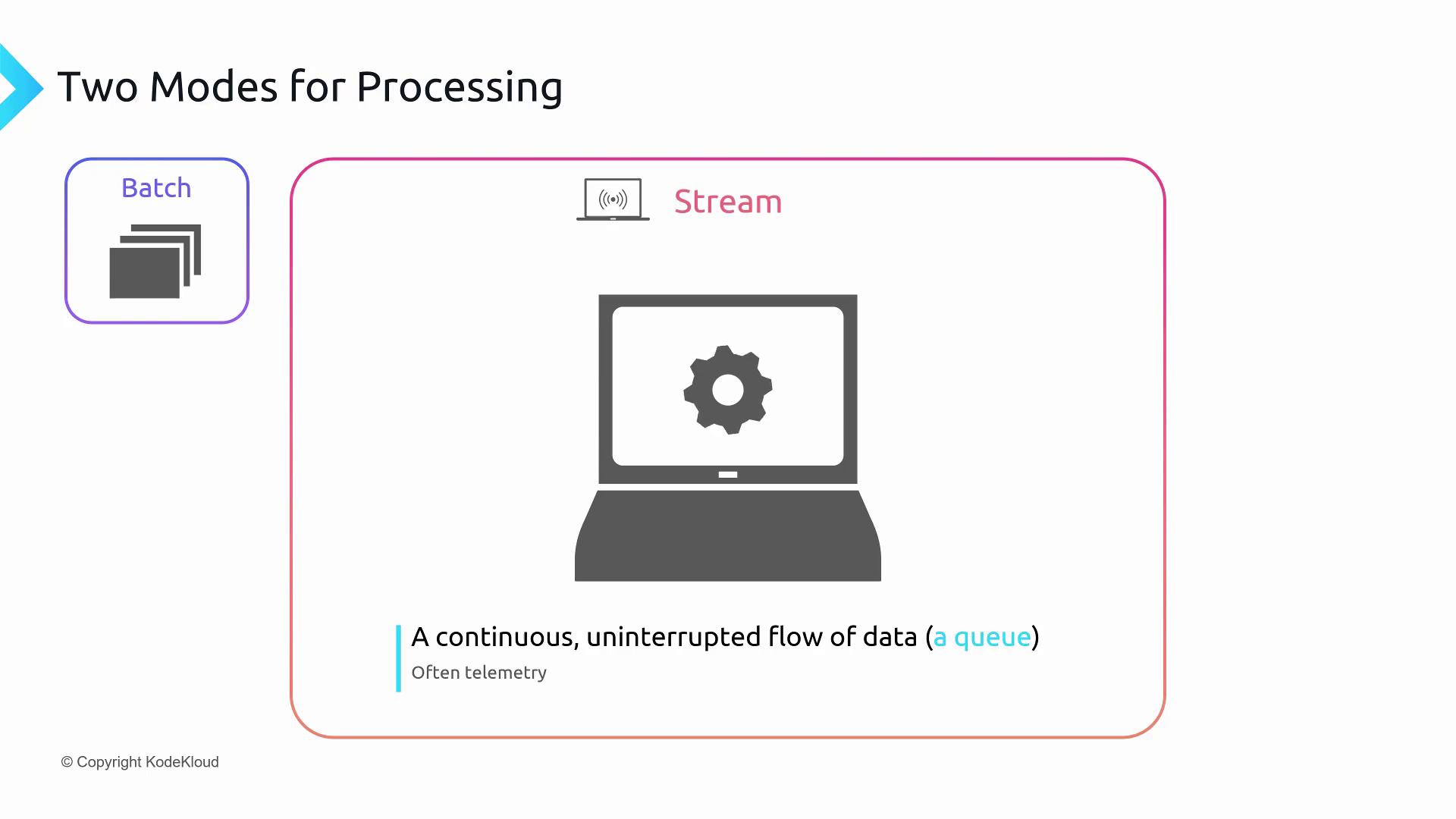
Stream Processing
Stream processing ingests and analyzes data continuously, delivering low-latency insights. It’s commonly used for IoT telemetry, clickstreams, and other real-time workloads.
Core characteristics:
- Continuous data flow (e.g., sensor readings, user events).
- Processing aimed at real time or near real time.
- Rolling time windows to group and analyze recent data slices.
Rolling Time Windows
A rolling time window processes events within a fixed duration that shifts forward by a defined increment. For example, with a 5-minute window that advances every minute:
- 5:29 PM: process data from 5:24–5:29
- 5:30 PM: process data from 5:25–5:30
Note
Time windows longer than one second are generally considered near real-time rather than true real-time.
Hybrid Processing
Hybrid processing combines continuous ingestion with scheduled batch analytics. You ingest stream data in real time and also store it for periodic batch processing.
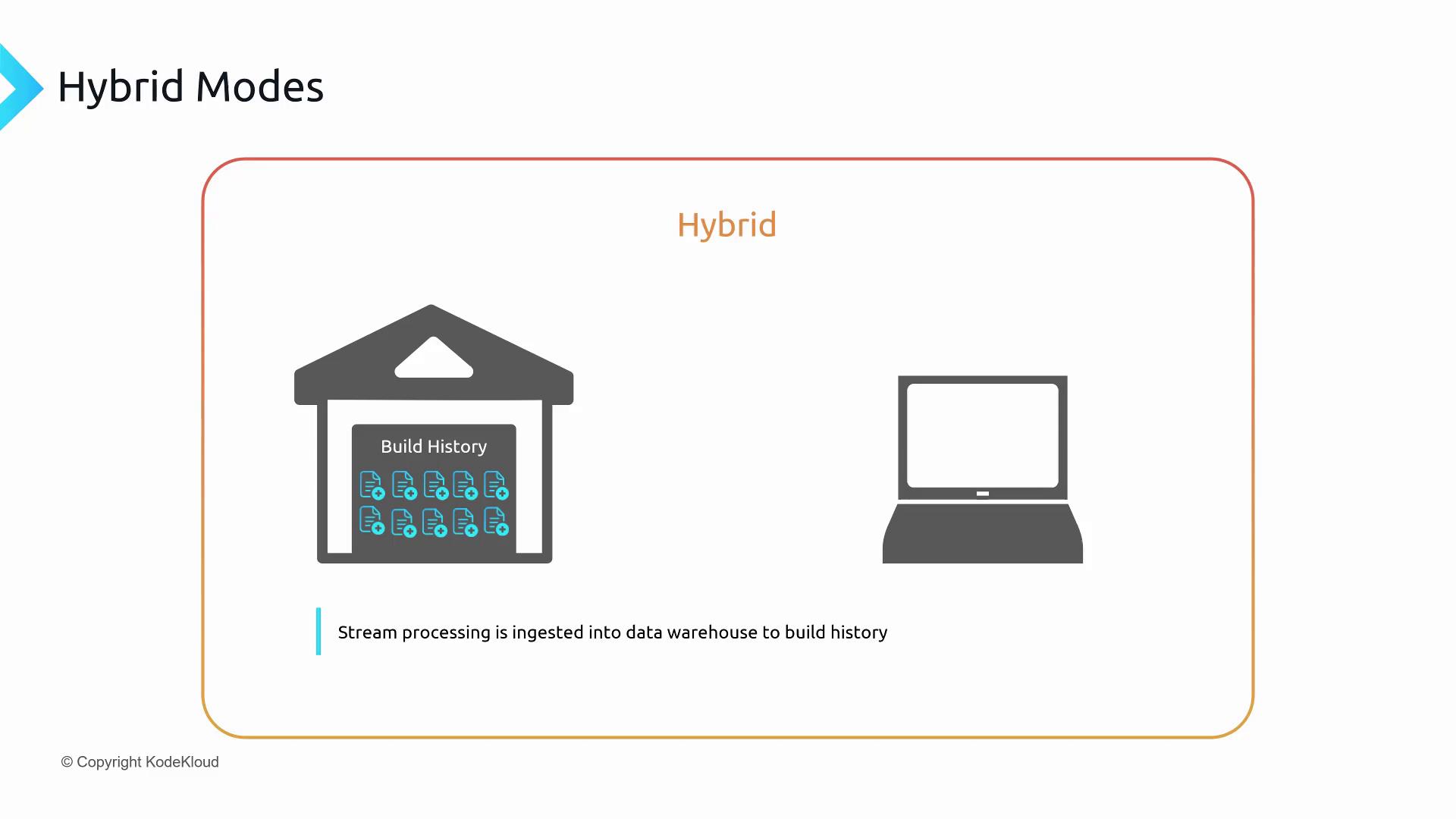
Use case: A connected refrigerator streams temperature data continuously but only needs trend analysis every few hours or daily.
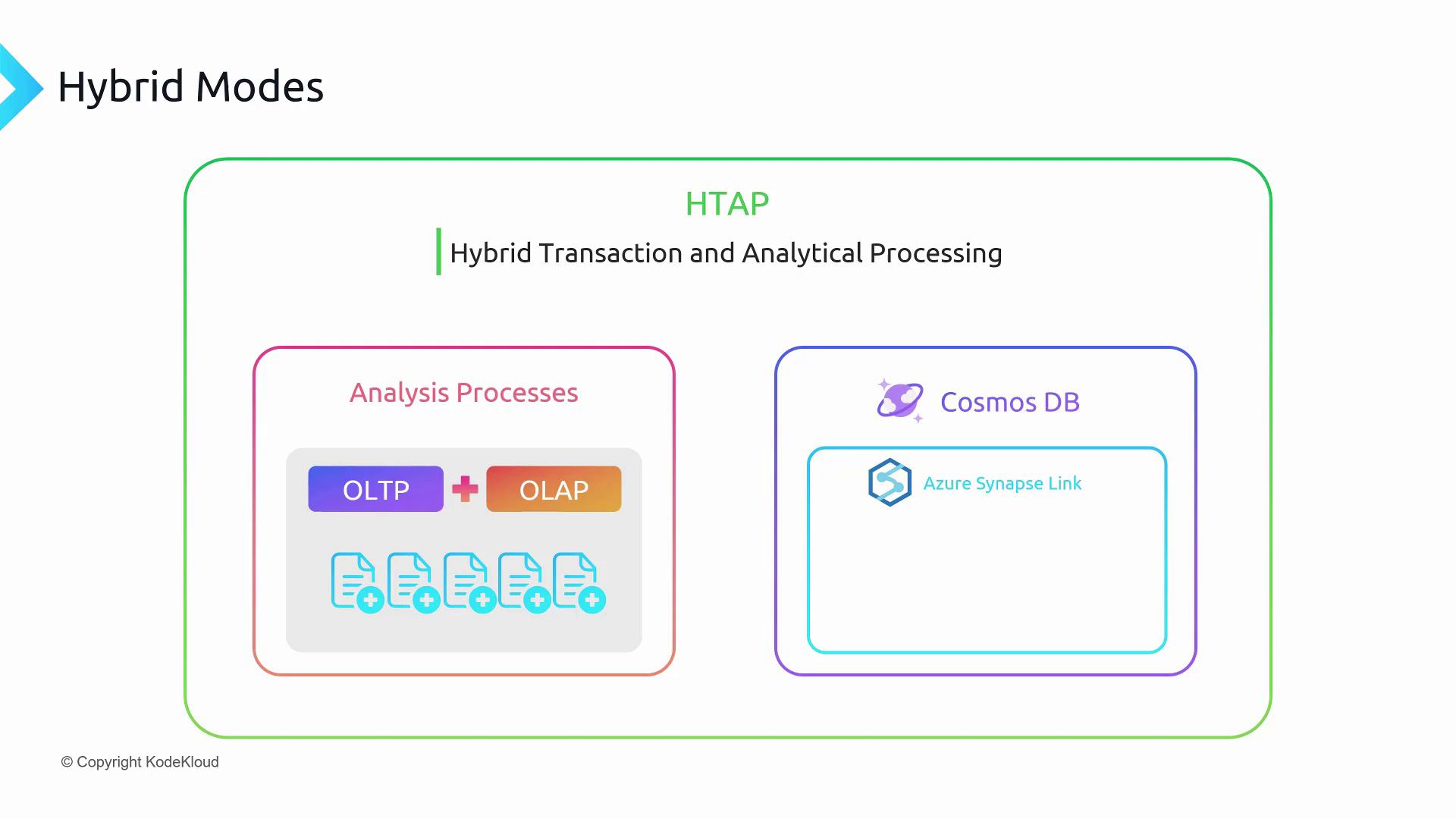
Hybrid Transactional and Analytical Processing (HTAP)
HTAP merges OLTP and OLAP in a single pipeline. With Azure Cosmos DB for high-volume transactions and Azure Synapse Link to feed data directly into Azure Synapse Analytics, you can eliminate separate ETL tasks.
Stream Processing Components
To build a robust streaming pipeline, you need:
Events
Individual messages from devices or applications (e.g., temperature readings, status updates).Ingestion Services
- Azure Event Hubs for large-scale streaming.
- Azure IoT Hub optimized for IoT scenarios.
- Apache Kafka as an open-source alternative.
Sinks
Downstream targets such as data lakes, data warehouses, or analytics platforms.Analytic Clusters
Scalable compute clusters for resource-intensive, near real-time processing when single-node compute isn’t enough.
Further Reading
- Azure Data Lake Storage overview
- Azure Synapse Analytics documentation
- Design patterns for streaming pipelines
Watch Video
Watch video content