DP-900: Microsoft Azure Data Fundamentals
Cosmos DB
Demo Create Cosmos DB Account
In this lesson, you’ll learn how to provision an Azure Cosmos DB account, configure a NoSQL database and container, enable global distribution, and insert your first document using the Data Explorer. By the end, you’ll understand Cosmos DB’s core concepts and be ready to build globally distributed applications.
1. Create an Azure Cosmos DB Account
- In the Azure portal, type Cosmos DB in the search bar and select Azure Cosmos DB.
- Click Create Azure Cosmos DB account.
- Under API, choose Azure Cosmos DB for NoSQL:
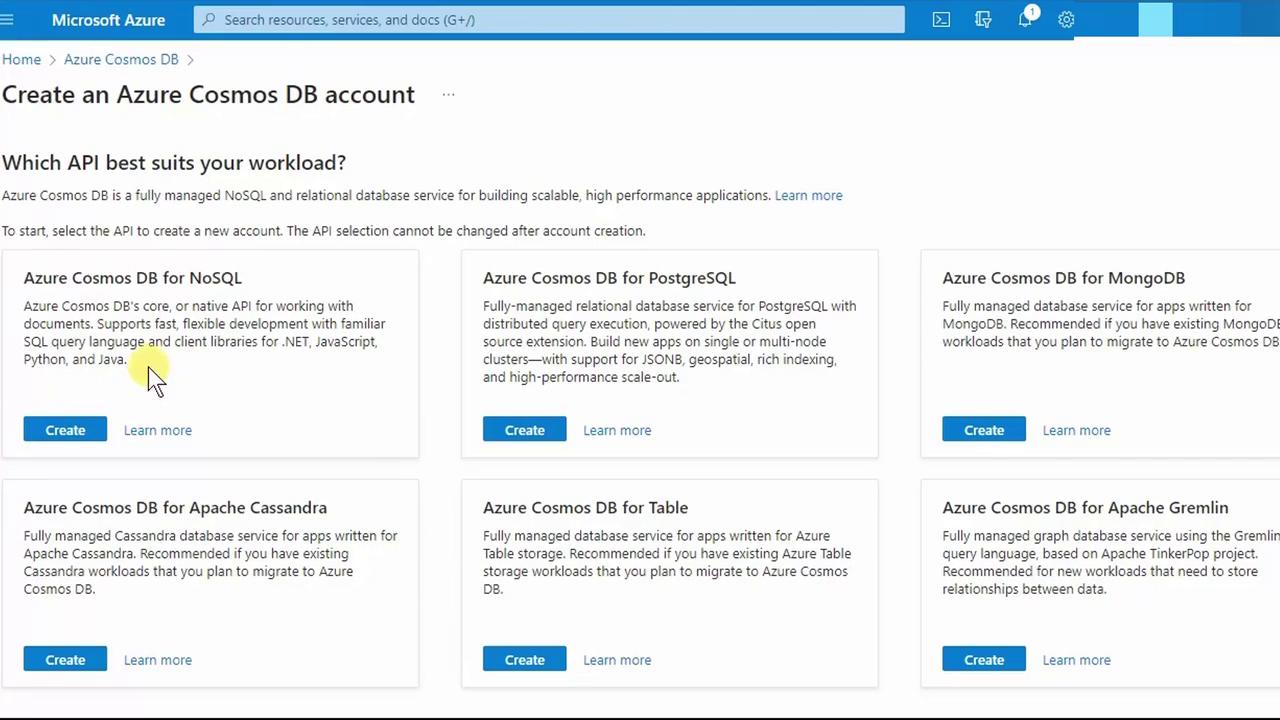
- Click Create and fill out the Basics tab:
- Subscription: Select your Azure subscription
- Resource group: Pick an existing group or create a new one, e.g., MyResourceGroup
- Account Name: Enter a unique name (e.g.,
phvcosmos) - Region: Choose the nearest region (e.g., East US)
2. Choose Capacity Mode
Cosmos DB offers two billing models. Select the mode that best fits your workload:
| Capacity Mode | Billing Model | Ideal For |
|---|---|---|
| Provisioned throughput | Request Units (RUs/sec) | Predictable performance workloads |
| Serverless | Pay per request | Infrequent or bursty traffic |
- Under Capacity mode, pick Provisioned throughput.
- Enable the free tier discount (if eligible).
- Optionally Limit total throughput to prevent unexpected RU charges.
Note
Limiting throughput helps you stay within budget by capping the maximum RUs your account can consume.
3. Configure Global Distribution
- Switch to the Global distribution tab.
- Toggle Multi-region writes (allows writes in all regions).
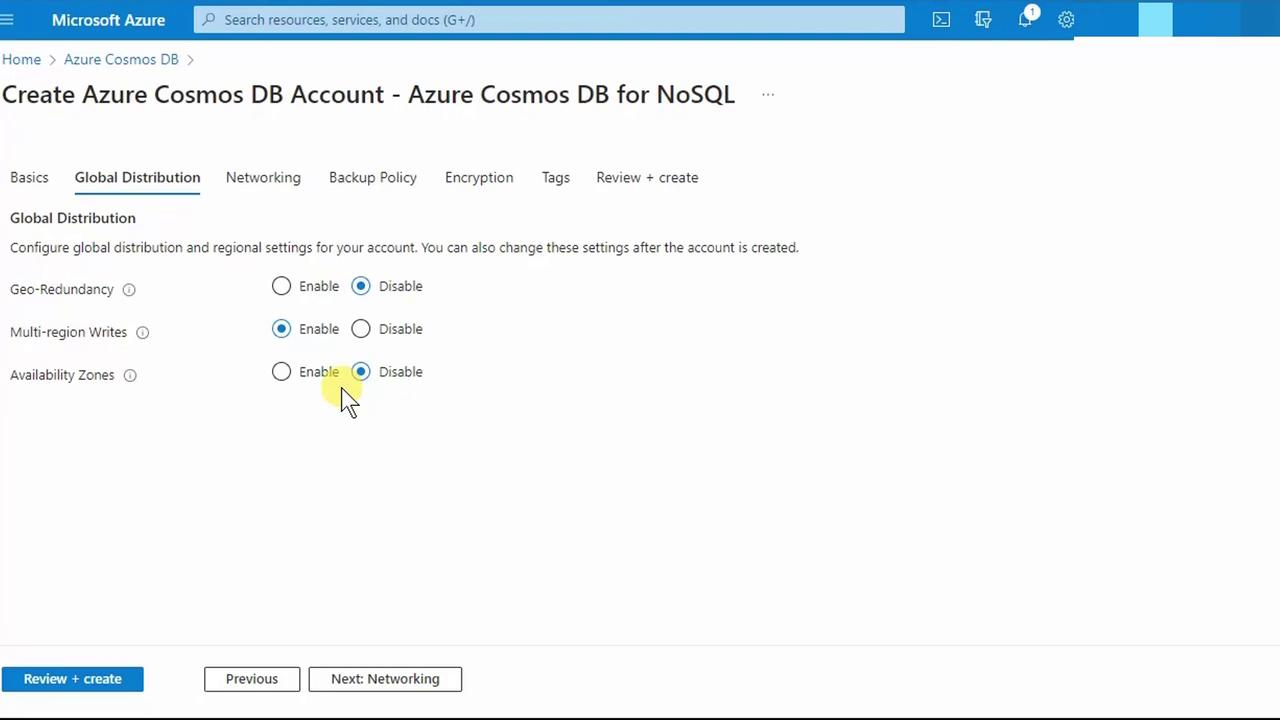
- Click Review + create.
- After validation passes, click Create. Deployment may take a few minutes.
4. Add a Container
- Go to your new account’s Overview page and click + Create Container.
- By default:
- Database ID: items
- Container ID: items
- Throughput: 400 RUs/sec on the container (1,000 RUs/sec at the account level)
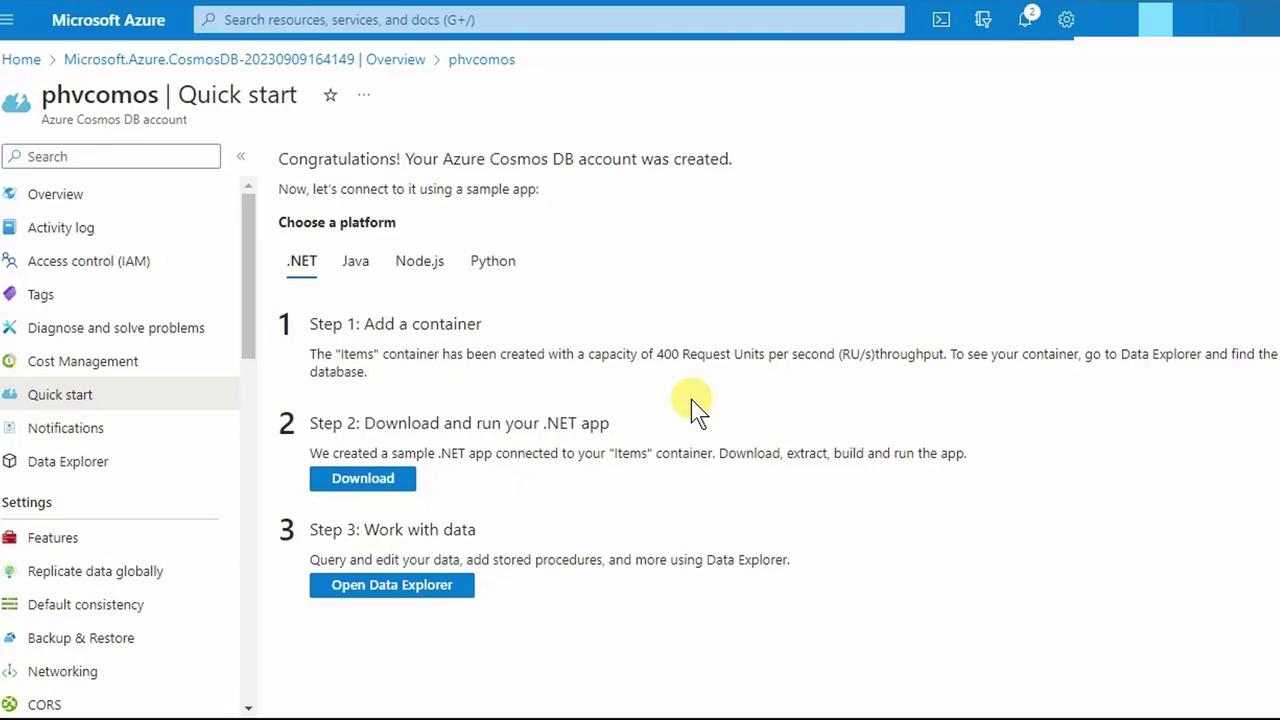
You can also download sample apps in .NET, Java, Node.js, or Python, or use Data Explorer to explore and manage data.
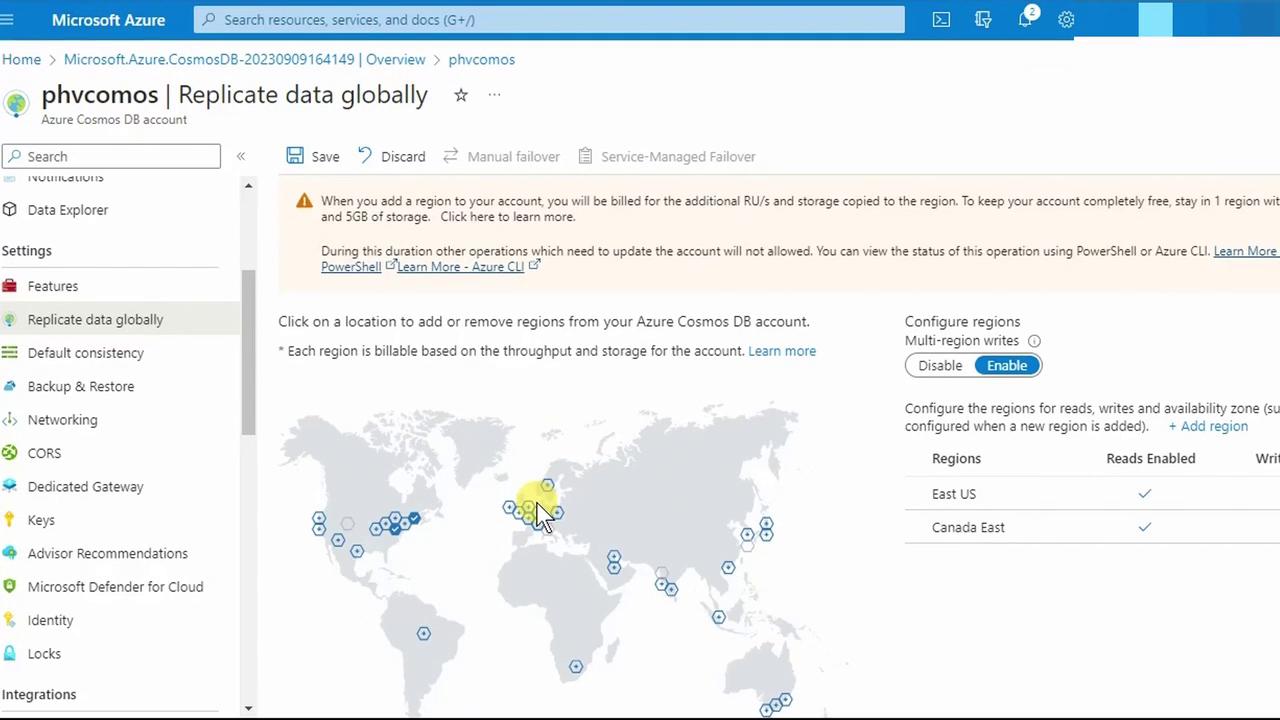
5. Configure Global Replication
- Under Settings, select Replicate data globally.
- On the world map, click to add a secondary region (e.g., Canada Central).
Warning
Adding regions with Multi-region writes multiplies RU consumption across each region. Ensure your account-level RU quota covers all selected regions, or adjust your throughput accordingly.
Geo-redundancy vs. Multi-region Writes
- Multi-region writes: Clients can write to any configured region.
- Geo-redundancy: Maintains a passive standby region for automatic failover.
You may enable both if you require active-active writes and automatic failover.
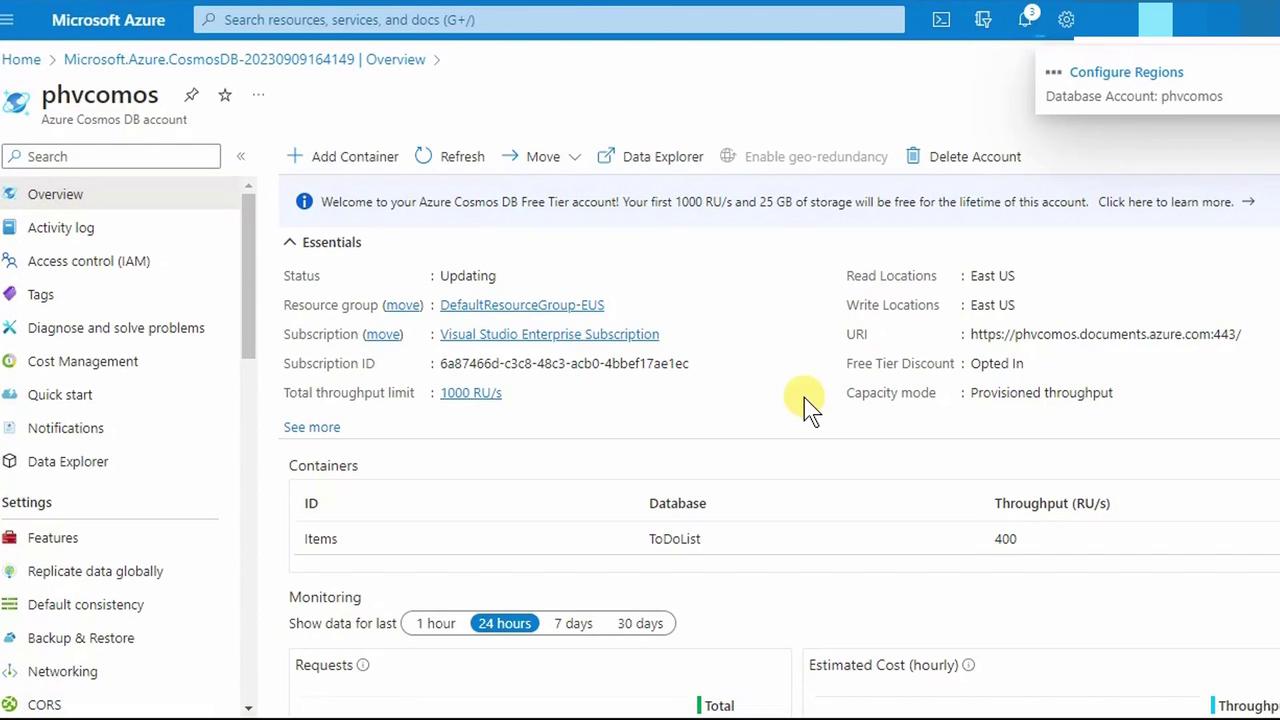
- Click Save. Back in Overview, you’ll now see all configured regions:
6. Explore Data Explorer
- In the portal menu, choose Data Explorer (or press Ctrl + F and search for it).

- Expand your items database and container.

- Click New Item. Replace the default JSON:
{
"id": "replace_with_new_document_id"
}
with:
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"FirstName": "Peter",
"LastName": "Vogel"
}
- Press Save. Cosmos DB augments your document with system properties:
{
"CustomerId": 1,
"FirstName": "Peter",
"LastName": "Vogel",
"id": "3a0585fd-1202-4855-91ef-5077ca6c263c",
"_rid": "VRJWANGK1u0BAAAAAAAAAA==",
"_self": "dbs/VRJWAA==/colls/VRJWANGK1u0=/docs/VRJWANGK1u0BAAAAAAAAAA==/",
"_etag": "\"b002c1f-0000-0100-0000-64fcd0bf0000\"",
"_attachments": "attachments/",
"_ts": 1694292751
}
Key system properties:
- _etag: Concurrency control
- _ts: Last-modified timestamp
Congratulations! You have successfully created an Azure Cosmos DB account, configured a NoSQL database and container, set up global distribution, and inserted your first document. For more details, see the Azure Cosmos DB documentation.
Watch Video
Watch video content